One to one maths interventions built for KS4 success
Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons now available
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Coordinates maths Translation Reflection Function notation (basic) Composite functions Types of graphs Sin graph Cos graph Tan graphThis topic is relevant for:

Graph Transformations
Here we will learn about graph transformations, including translating vertically, translating horizontally and reflecting in the coordinate axes.
There are also graph transformation worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are graph transformations?
Graph transformations involve performing transformations such as translations and reflections on the graph of a function.
In GCSE mathematics you may be asked to sketch a graph after a given transformation, or asked to write down the position of a coordinate after a transformation has been applied.
To do this we need to understand what each of the graph transformations look like and how they relate to the original function.
What are graph transformations?
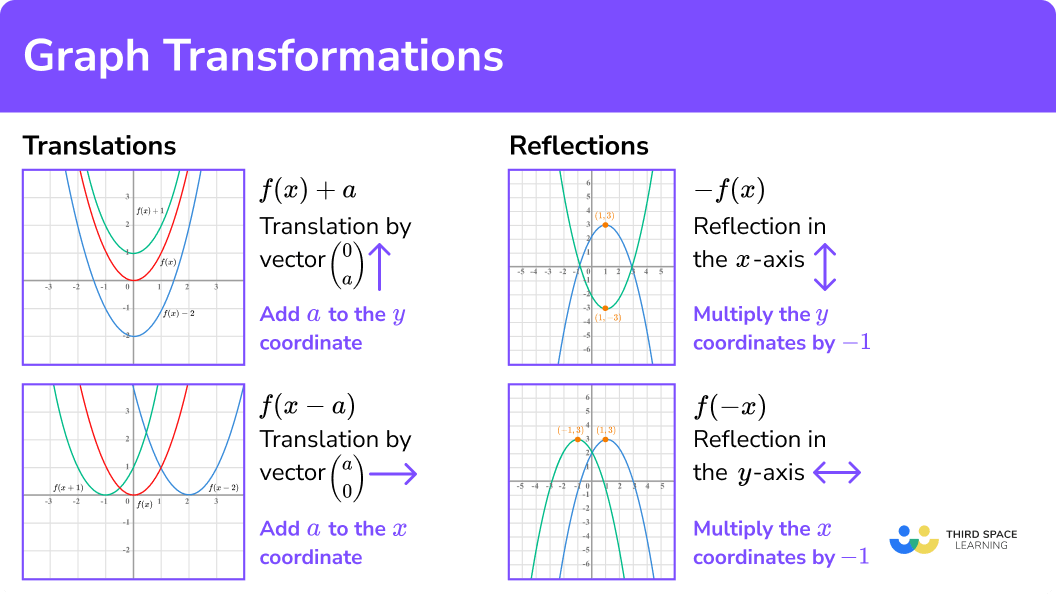
Transformations of functions
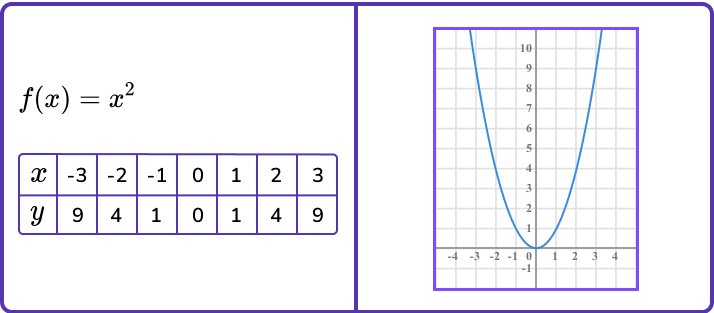
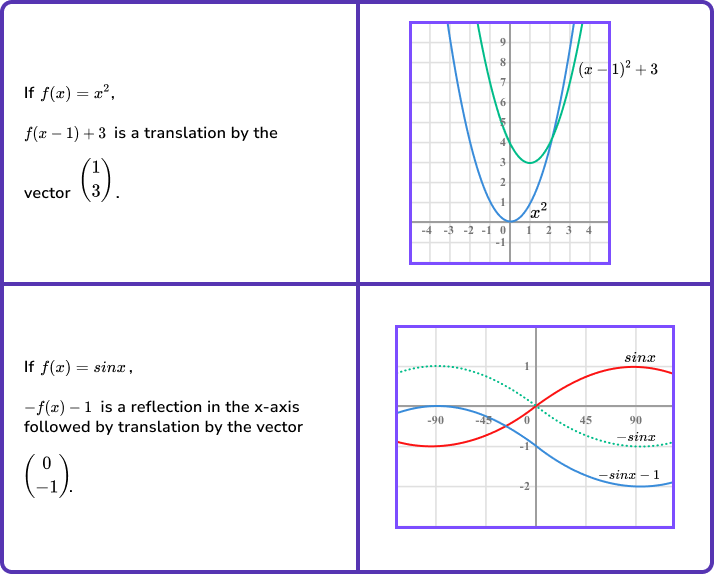
Let’s use a simple function such as y=x^2 to illustrate translations.
First you can write it using function notation and draw the graph using a table of values to help.
- Translating the graph in a vertical direction.
This can be done by adding or subtracting a constant from the y -coordinate. The transformed graph is green.
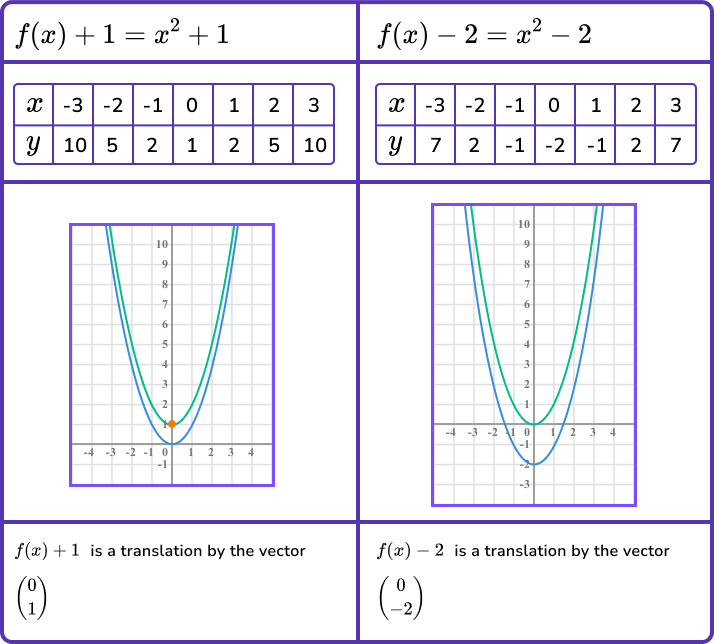
So translating vertically by the vector \left( \begin{matrix} 0 \\ a \\ \end{matrix} \right) can be done using the transformation f(x)+a.
- Translating the graph in a horizontal direction.
This can be done by adding or subtracting a constant from the x -coordinate.
The transformed graph is blue.
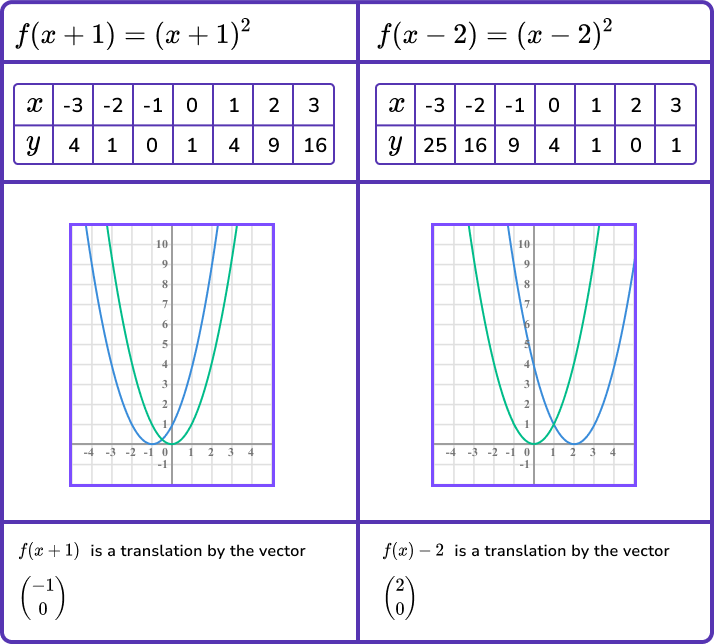
So translating vertically by the vector \left( \begin{matrix} a \\ 0 \\ \end{matrix} \right) can be done using the transformation f(x-a).
Notice how the transformation f(x+1) translated the graph to the left and not the right.
- Reflecting a graph of a function.
The function y=f(x) has a point (1,3) as shown.
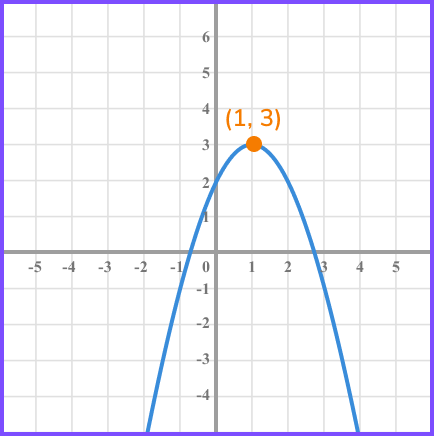
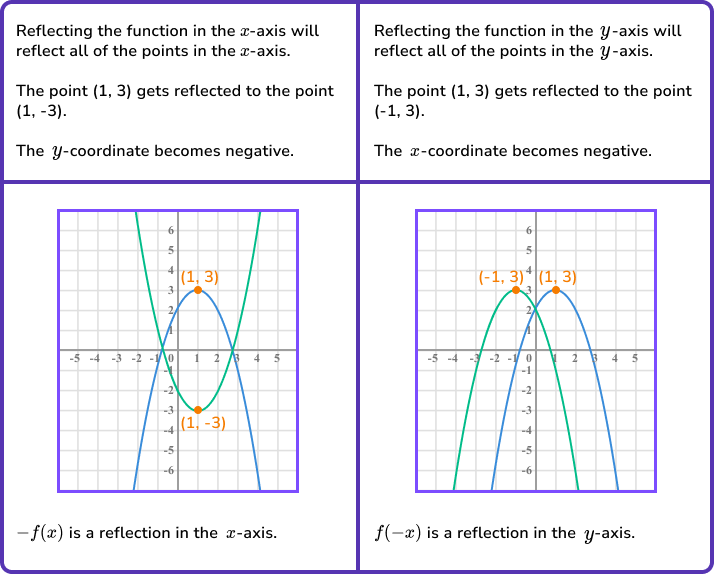
You will need to be able to apply all of these transformations to coordinates marked on unknown functions as well as sketch transformations of known functions such as the graphs of sin (x), cos (x) and tan (x).
Combinations of transformations
The different translations and reflections can be combined.
For example,
Further study
In A Level Mathematics these transformations of functions are looked at in more depth to include a horizontal stretch f(ax) and a vertical stretch af(x). These, and more complicated transformations, are applied to functions such as polynomials, exponentials, inverse functions and more complicated trigonometric functions.
In A Level Further Mathematics other transformations such as rotations, enlargements and shears are applied using matrices.
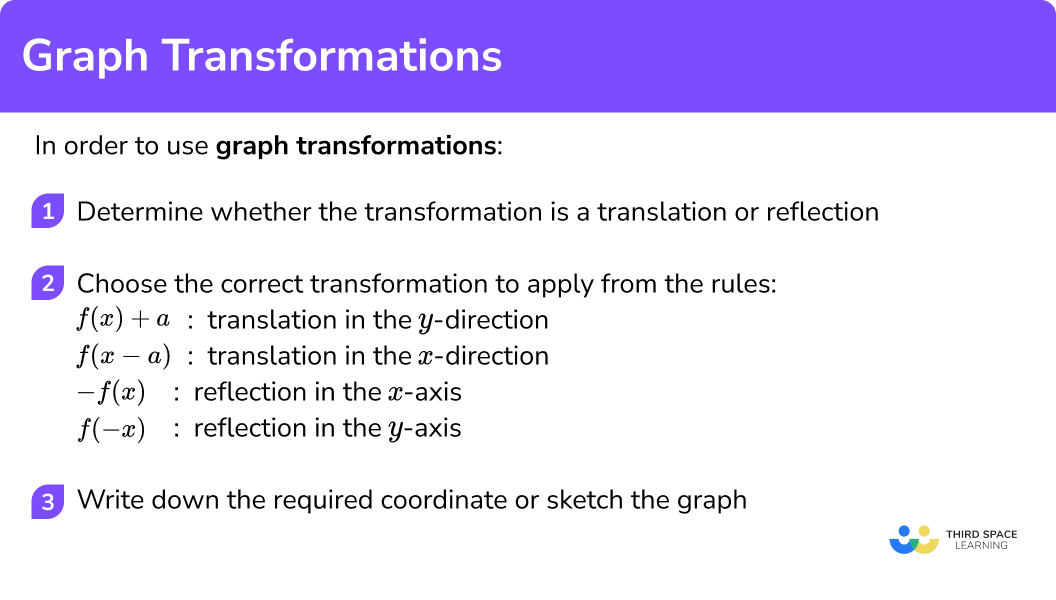
How to use graph transformations
In order to use graph transformations:
- Determine whether the transformation is a translation or reflection.
- Choose the correct transformation to apply from the rules.
\quad \;\; f(x)+a is a translation in the \bf{y-} direction.
\quad \;\; f(x-a) is a translation in the \bf{x-} direction.
\quad \;\; -f(x) is a reflection in the \bf{x-} axis.
\quad \;\; f(-x) is a reflection in the \bf{y-} axis. - Write down the required coordinate or sketch the graph.
Explain how to use graph transformations
Graph transformations worksheet

Get your free graph transformations worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Graph transformations worksheet

Get your free graph transformations worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on interpreting graphs
Graph transformations is part of our series of lessons to support revision on interpreting graphs. You may find it helpful to start with the main interpreting graphs lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Graph transformations examples
Example 1: applying a translation in the y- direction
The diagram shows the graph of y=f(x) and a point on the graph P(2,5).
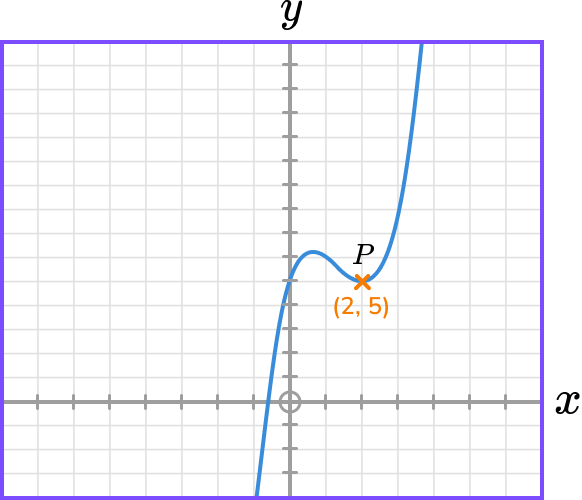
State the coordinate of the image of point P on the graph y=f(x)-4.
- Determine whether the transformation is a translation or reflection.
The function has been translated.
2Choose the correct transformation to apply from the rules.
\quad \;\; f(x)+a is a translation in the \bf{y-} direction.
\quad \;\; \color{#C5C5C5} f(x-a) is a translation in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{x-} direction.
\quad \;\; \color{#C5C5C5} -f(x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{x-} axis.
\quad \;\; \color{#C5C5C5} f(-x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{y-} axis.
f(x)-4 is a translation by the vector \left( \begin{matrix} 0 \\ -4 \\ \end{matrix} \right). We need to subtract 4 from the y- coordinate.
3Write down the required coordinate or sketch the graph.
5-4 = 1Therefore, the image of coordinate P will be (2,1).
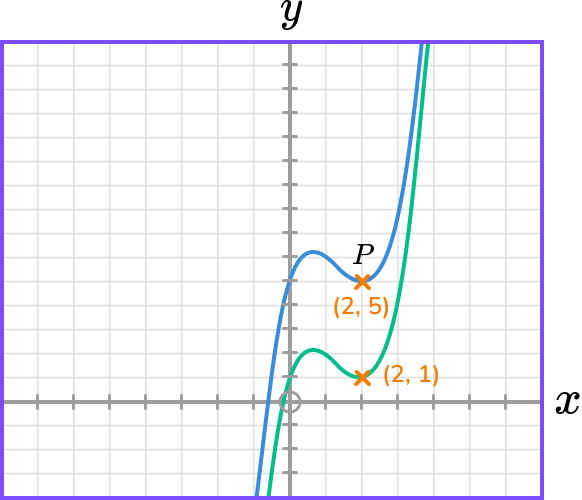
Example 2: applying a translation in the x- direction
The diagram shows the graph of y=f(x) and a point on the graph P(2,5).
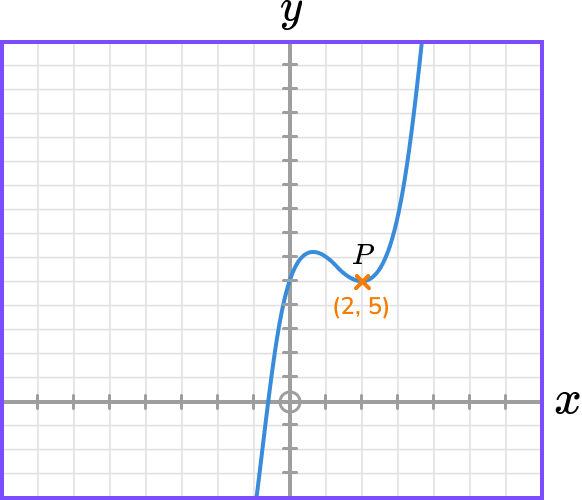
State the coordinate of the image of point P on the graph y=f(x+5).
Determine whether the transformation is a translation or reflection.
The function has been translated.
Choose the correct transformation to apply from the rules.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(x)+a is a translation in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{y-} direction.
f(x-a) is a translation in the \bf{x-} direction.
\color{#C5C5C5} -f(x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{x-} axis.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(-x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{y-} axis.
f(x+5) is a translation by the vector \left( \begin{matrix} -5 \\ 0 \\ \end{matrix} \right). We need to subtract 5 from the x -coordinate.
Write down the required coordinate or sketch the graph.
Therefore, the image of coordinate P will be (-3,5).
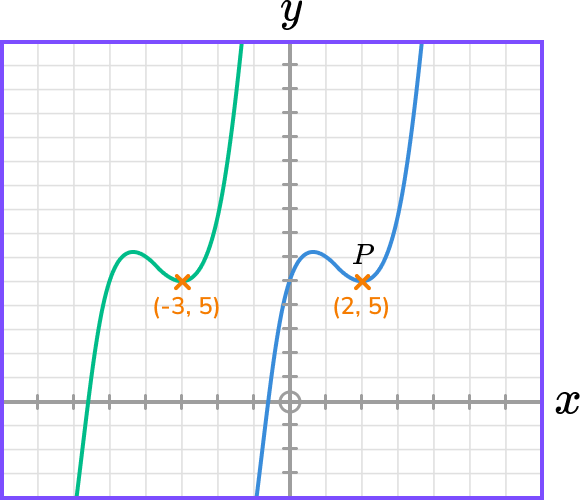
Example 3: applying a reflection in the x- axis
The diagram shows the graph of y=f(x) and a point on the graph P(2,5).
Sketch the graph and state the coordinate of the image of point P on the graph y=-f(x).
Determine whether the transformation is a translation or reflection.
The function has been reflected.
Choose the correct transformation to apply from the rules.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(x)+a is a translation in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{y-} direction.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(x-a) is a translation in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{x-} direction.
-f(x) is a reflection in the \bf{x-} axis.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(-x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{y-} axis.
We need to multiply the y- coordinates by -1.
Write down the required coordinate or sketch the graph.
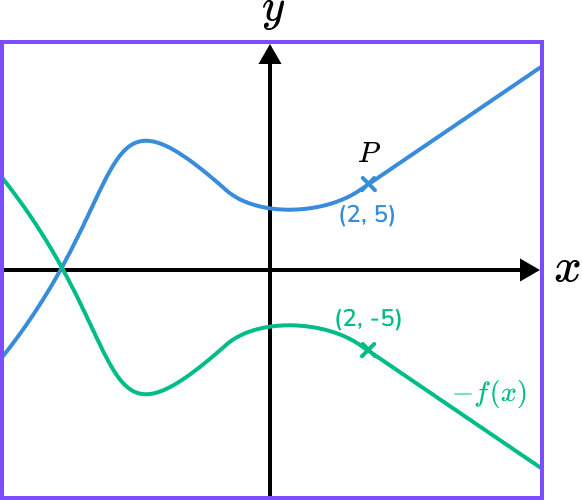
The image of the coordinate of P will be (2,-5).
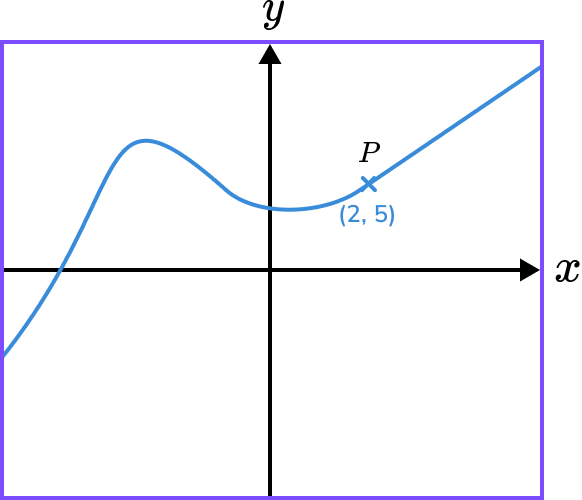
Example 4: applying a reflection in the y- axis
The diagram shows the graph of y=f(x) and a point on the graph P(2,5).
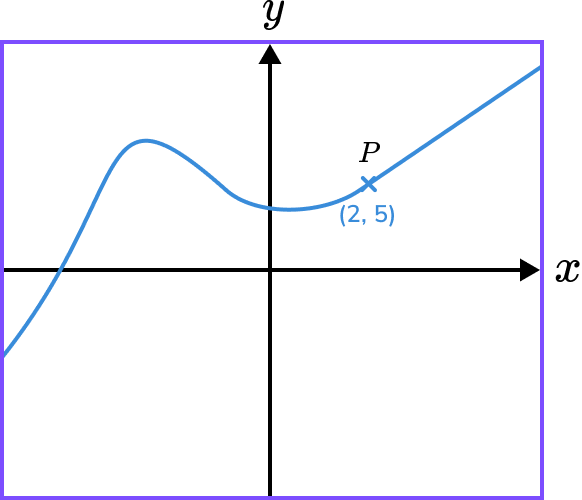
Sketch the graph and state the coordinate of the image of point P on the graph y=f(-x).
Determine whether the transformation is a translation or reflection.
The function has been reflected.
Choose the correct transformation to apply from the rules.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(x)+a is a translation in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{y-} direction.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(x-a) is a translation in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{x-} direction.
\color{#C5C5C5} -f(x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{x-} axis.
f(-x) is a reflection in the \bf{y-} axis.
We need to multiply the x- coordinates by -1.
Write down the required coordinate or sketch the graph.
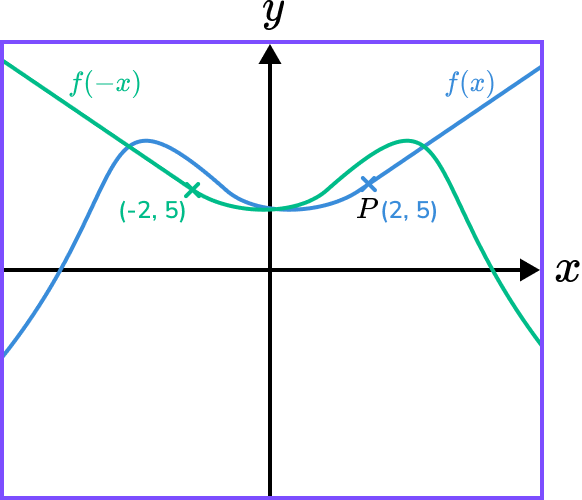
The image of coordinate P will be (-2,5).
Example 5: applying a combination of translations
The image shows the graph of the quadratic function f(x) which has a turning point at (-3,-2).
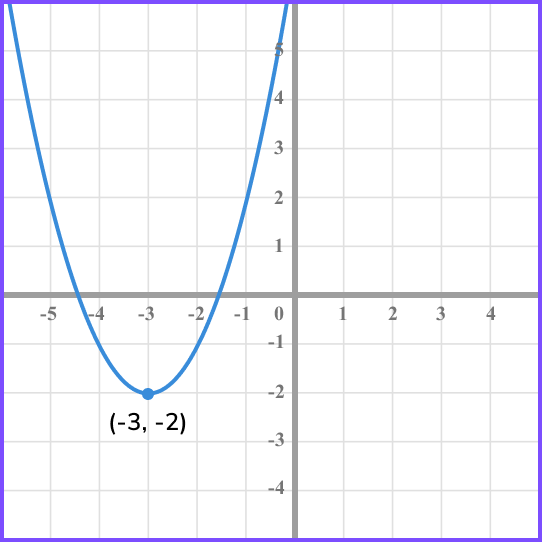
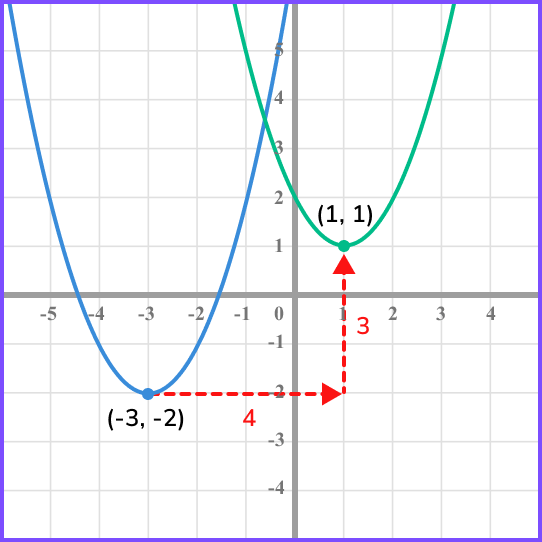
Sketch the graph of the function f(x-4)+3, labelling the coordinate of the turning point.
Determine whether the transformation is a translation or reflection.
The function has been translated twice.
Choose the correct transformation to apply from the rules.
f(x)+a is a translation in the \bf{y-} direction.
f(x-a) is a translation in the \bf{x-} direction.
\color{#C5C5C5} -f(x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{x-} axis.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(-x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{y-} axis.
f(x-4)+3 is a translation by the vector \left( \begin{matrix} 4 \\ 3 \\ \end{matrix} \right). We need to add 4 to the x- coordinate and add 3 to the y- coordinate.
Write down the required coordinate or sketch the graph.
Therefore, the turning point will be (1,1).
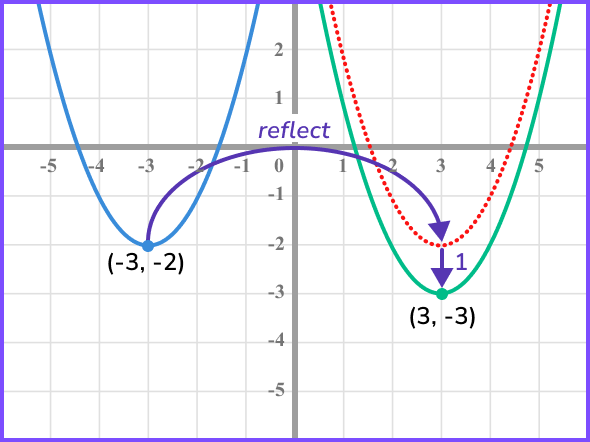
Example 6: applying a combination of reflections and translations
The image shows the graph of the quadratic function f(x) which has a turning point at (-3,-2).
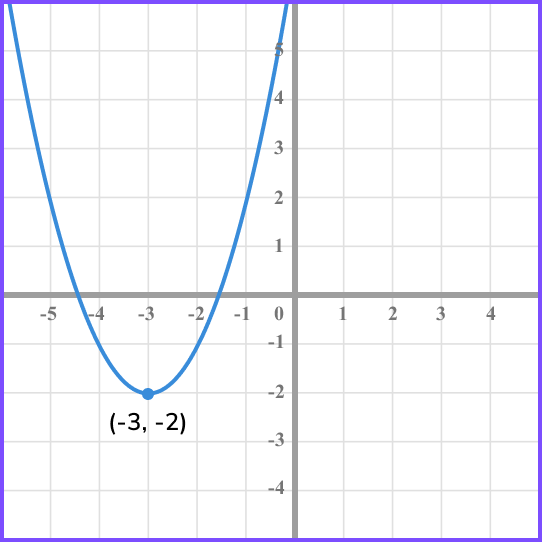
Sketch the graph of the function f(-x)-1, labelling the coordinate of the turning point.
Determine whether the transformation is a translation or reflection.
The function has been reflected and translated.
Choose the correct transformation to apply from the rules.
f(x)+a is a translation in the \bf{y-} direction.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(x-a) is a translation in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{x-} direction.
\color{#C5C5C5} -f(x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{x-} axis.
f(-x) is a reflection in the \bf{y-} axis.
f(-x)-1 is a reflection in the y- axis followed by a translation by the vector \left( \begin{matrix} 0 \\ -1 \\ \end{matrix} \right).
We need to multiply the x- coordinate by -1 and then subtract 1 from the y- coordinate.
Write down the required coordinate or sketch the graph.
Therefore, the turning point will be (3,-3).
Example 7: identifying a transformation
The curve with equation y=f(x) is translated so that the minimum point at (-1, 0) is translated to (5,0). Find the equation of the new curve.
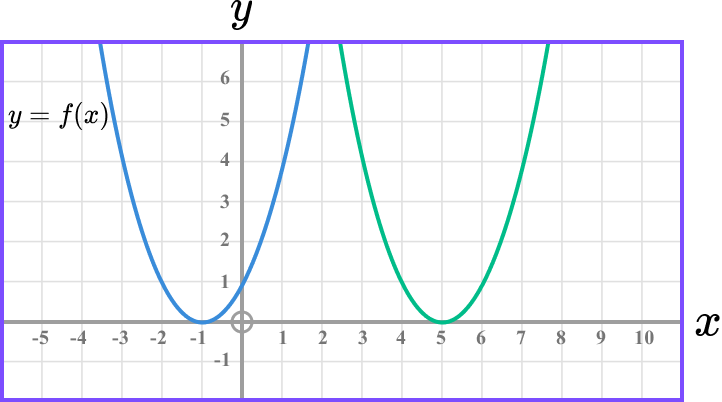
Determine whether the transformation is a translation or reflection.
The function has been translated.
Choose the correct transformation to apply from the rules.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(x)+a is a translation in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{y-} direction.
f(x-a) is a translation in the \bf{x-} direction.
\color{#C5C5C5} -f(x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{x-} axis.
\color{#C5C5C5} f(-x) is a reflection in the \color{#C5C5C5} \bf{y-} axis.
Write down the required coordinate or sketch the graph.
In this case we need to write the equation of the new graph.
The graph has been translated by the vector \left( \begin{matrix}
6 \\ 0 \\ \end{matrix} \right).
The equation of the new graph is y=f(x-6).
Common misconceptions
- Performing the wrong horizontal translation
A common mistake is thinking the transformation of f(x+2) will mean the function translates to the right by 2. We can see that if we apply the transformation to the function, find a table of values and then plot the points, the function actually translates to the left.
This is because, when we use the transformation f(x+2), the y -values we obtain are for values of x that would normally be two places to the right, so we are shifting those points to the left. f(x+2) moves the graph to the left by 2, \ f(x-2) moves the graph to the right by 2.
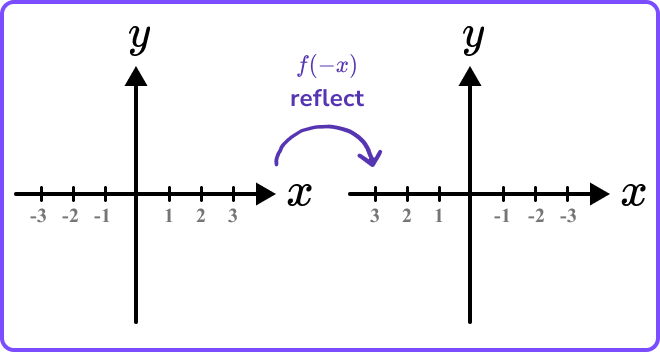
- Reflecting in the wrong axes
A common mistake is to confuse the reflections of -f(x) and f(-x).
If y=f(x), \ -f(x)=-y. This means the y -values are being multiplied by -1.
Applying f(-x) is changing the sign of the x -value before applying the function.
It’s the same as taking the coordinate axes and switching the signs on the numbers on the x- axis.
Practice graph transformations questions
1. (3,1) is a point on the graph of y=f(x).
Find the coordinate of the image of the point (3,1) on the graph of y=f(x-4).




f(x-4) is a translation by \left( \begin{matrix} 4 \\ 0 \\ \end{matrix} \right). Add 4 to the x- coordinate.
2. (-2,3) is a point on the graph of y=f(x).
Find the coordinate of the image of the point (-2,3) on the graph of y=f(x)+2.




f(x)+2 is a translation by \left( \begin{matrix} 0 \\ 2 \\ \end{matrix} \right). Add 2 to the y- coordinate.
3. (5,-1) is a point on the graph of y=f(x).
Find the coordinate of the image of the point (5,-1) on the graph of y=f(-x).




f(-x) is a reflection in the y- axis. Multiply the x- coordinate by -1.
4. (-4,-2) is a point on the graph of y=f(x).
Find the coordinate of the image of the point (-4,-2) on the graph of y=-f(x).




-f(x) is a reflection in the x- axis. Multiply the y- coordinate by -1.
5. (2,1) is a point on the graph of y=f(x).
Find the coordinate of the image of the point (2,1) on the graph of y=f(x+3)+5.




f(x+3)+5 is a translation by \left( \begin{matrix} -3 \\ 5 \\ \end{matrix} \right). Subtract 3 from the x- coordinate and add 5 to the y- coordinate.
6. (-5,2) is a point on the graph of y=f(x).
Find the coordinate of the image of the point (-5,2) on the graph of y=-f(x)-3.




-f(x)-3 is a reflection in the x- axis followed by a translation by \left( \begin{matrix} 0 \\ -3 \\ \end{matrix} \right). Multiply the y- coordinate by -1, then subtract 3.
Graph transformation GCSE questions
1. The diagram shows the function f(x) and the point P(-1,2).
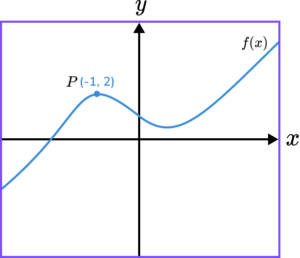
Write down the coordinates of the image of P after the following transformations.
(a) f(x-2)
(b) f(x)-2
(c) f(-x)
(d) -f(x+3)
(5 marks)
(a) (1,2)
(1)
(b) (-1,0)
(1)
(c) (1,2)
(1)
(d)
Correct x -value of -4
(1)
Correct y -value of -2
(1)
2. The diagram shows the graph of the function f(x).
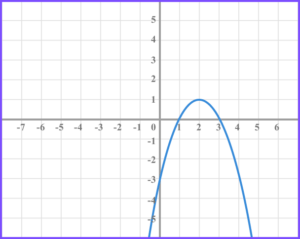
(a) On the grid below draw the function f(x+5) .
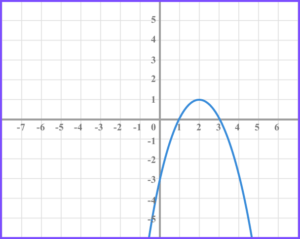
(b) On the grid below draw the function f(-x)-2 .
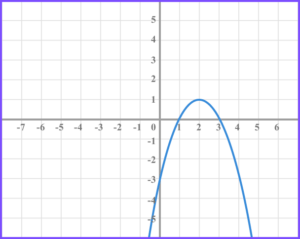
(3 marks)
(a)
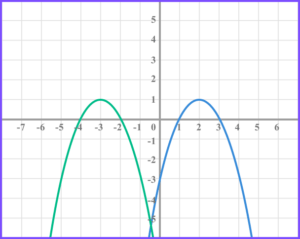
(1)
(b)
Reflection shown with correct x -value of turning point.
(1)
Reflection shown with correct y -value of turning point.
(1)
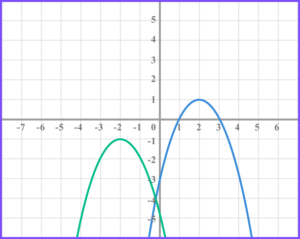
3. The graphs of f(x) = sin \ x and g(x) =cos \ x are shown below.
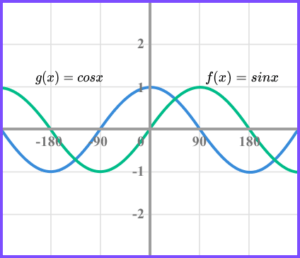
Complete the following table, giving each transformation of g(x) in terms of a transformation of f(x). The first one has been done for you.
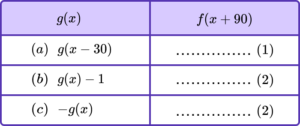
(5 marks)
(a) f(x+60)
(1)
(b)
+90 in brackets
(1)
-1 outside brackets
(1)
f(x+90)-1
(c)
-90 in brackets, f(x-90)
(2)
or
-1 in front of f
(1)
+90 in brackets
(1)
-f(x+90)Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Sketch translations and reflections of the graph of a given function
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.