GCSE Tutoring Programme
"Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring."
This topic is relevant for:

Factors And Multiples
Here we will learn about factors and multiples, including their definitions, listing factors and multiples, and problem solving with factors and multiples.
There are also factors and multiples worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are factors and multiples?
Factors and multiples are two different types of numbers.
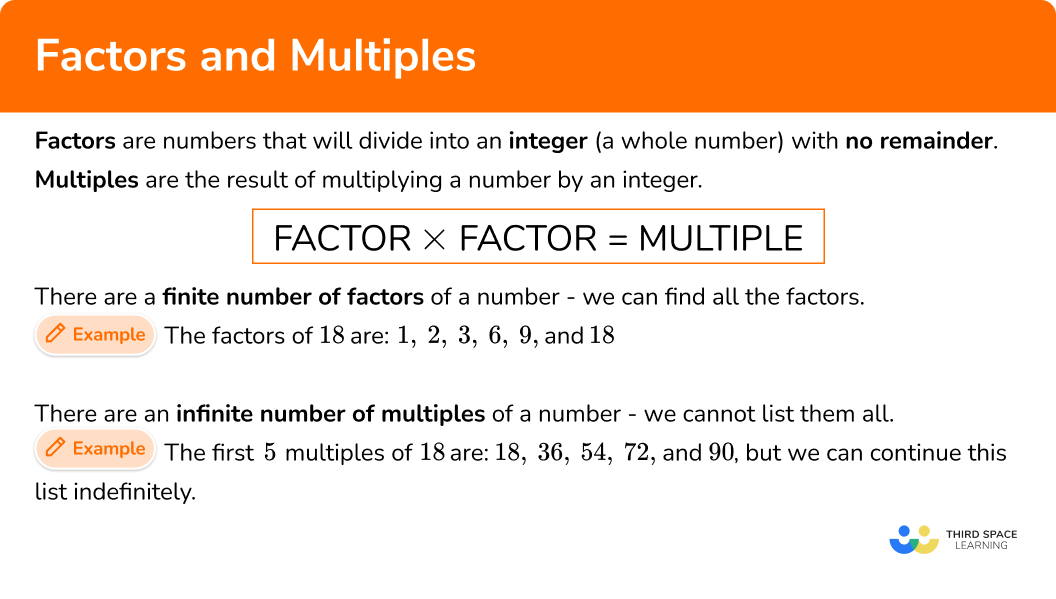
Factors are numbers that will divide into an integer (a whole number) with no remainder. Another name for a factor is a divisor.
Multiples are the result of multiplying a number by an integer.

What are factors and multiples?
Factors
There are a finite number of factors of a number.
For example, the factors of 18 are 1,2,3,6,9, and 18.
To find all of the factors of any integer, we write out all of the factor pairs in order.
Step-by-step guide: Factors
The highest common factor (HCF), or greatest common factor, is the largest number that is a factor of two or more numbers.
For example, the highest common factor of the numbers 6,8 and 10 is 2.
Step-by-step guide: Highest common factor
Prime numbers have only two factors, themselves and 1.
Any positive integer that is not a prime number is a composite number. Composite numbers have at least 2 factor pairs.
Step-by-step guide: Prime numbers
Multiples
There are an infinite number of multiples of a number.
For example, the first 5 multiples of 18 are 18,36,54,72, and 90, but we can continue this list indefinitely.
To calculate a multiple of a number n, we have to multiply it by an integer.
Step-by-step guide: Multiples
The lowest common multiple (LCM), or least common multiple, is the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more numbers.
For example, the lowest common multiple of the numbers 8 and 10 is 40.
Step-by-step guide: Lowest common multiple
We can use factors and multiples to solve problems involving probability, area, substitution, solving quadratics, and equivalent fractions.
How to list factors
In order to list all of the factor pairs of a number n:
- State the pair \bf{1 \times n} .
- Write the next smallest factor of \bf{n} and calculate its factor pair.
- Repeat until the next factor pair is the same as the previous pair.
- Write out the list of factors for \bf{n} .
Explain how to list factors

Factors and multiples worksheet

Get your free factors and multiples worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Factors and multiples worksheet

Get your free factors and multiples worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on factors, multiples and primes
Factors and multiples is part of our series of lessons to support revision on factors, multiples and primes. You may find it helpful to start with the main factors, multiples and primes lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Factors examples
Example 1: listing factors (odd number)
List the factors of 15.
- State the pair \bf{1 \times n} .
As n=15, you have the first factor pair 1\times{15}.
2Write the next smallest factor of \bf{n} and calculate its factor pair.
As 15 is an odd number, 15\div{2} is not an integer and so 2 is not a factor of 15.
15\div{3}=5 and so the next factor pair is 3\times{5}.
3Repeat until the next factor pair is the same as the previous pair.
So far you have,
\begin{aligned} &1\times{15}\\\\ &3\times{5} \end{aligned}As 15 is odd, you cannot divide 15 by any even number and get an integer and so 4 is not a factor of 15.
The next factor to try is 5.
As factors are commutative, 3\times{5}=5\times{3} which is the same as the previous factor pair.
We have now found all of the factor pairs,
\begin{aligned} &1\times{15}\\\\ &3\times{5} \end{aligned}4Write out the list of factors for \bf{n} .
Reading down the first column of factors, and up the second column, the factors of 15 are 1, 3, 5, and 15.
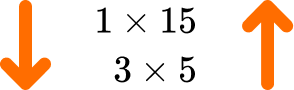
Example 2: listing factors (square number)
List the factors of 16.
As n=16, you have the first factor pair 1\times{16}.
As 16 is an even number, 2 is a factor of 16.
16 \div 2=8 and so the next factor pair is 2 \times 8.
So far we have,
\begin{aligned} &1\times{16}\\\\ &2\times{8} \end{aligned}
16 is not a multiple of 3.
16 is a multiple of 4,
16 \div 4=4 and so the next factor pair is 4 \times 4.
You have reached a repeated factor and so you have found all of the factor pairs for 16,
\begin{aligned} &1\times{16}\\\\ &2\times{8}\\\\ &4\times{4} \end{aligned}
Reading down the first column of factors, and up the second column, the factors of 16 are 1,2,4,8 and 16.
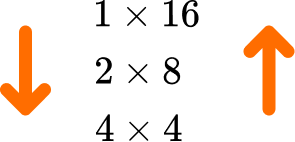
Notice that as you have a repeated factor, you have an odd number of factors in the list above. This can help to determine that 16 is a square number.
Example 3: listing factors (common factors)
The factors of 21 are 1,3,7, and 21. By finding the factors of 6, determine the common factors of 6 and 21.
As you want to list the common factors of 6 and 21, you need to find the factors of each of them, and then highlight common factors (the numbers that appear in both lists).
You already have the factors of 21, so you just need to find the factor pairs for 6.
The first factor pair is 1\times{6}.
As 6 is an even number, you can divide 6 by 2 and get an integer.
6\div{2}=3 and so the next factor pair is 2\times{3}.
The next factor to try is 3 and you have already used this in the previous factor pair (2\times{3}=3\times{2}).
Therefore we have found all of the factor pairs,
\begin{aligned} &1\times{6}\\\\ &2\times{3} \end{aligned}
The factors of 6 are 1,2,3, and 6.
The factors of 21 are 1,3,7, and 21.
The common factors of 6 and 21 are 1 and 3.
Although you are not asked for it here, you can see that the highest common factor of 6 and 21 is 3.
How to calculate multiples
In order to calculate multiples of a number n:
- State the first multiple of \bf{n} .
- Calculate the second multiple of \bf{n} .
- Continue until you have calculated the number of multiples needed.
- Write the solution.
Explain how to calculate multiples

Multiples examples
Example 4: listing multiples (two digit number)
List the first 5 multiples of 12.
The first multiple of 12 is 12\times{1}=12.
The second multiple of 12 is 12\times{2}=24.
\begin{aligned} &12\times{3}=36 \\\\ &12\times{4}=48 \\\\ &12\times{5}=60 \end{aligned}The first 5 multiples of 12 are 12,24,36,48, and 60.
Example 5: calculate a specific multiple
What is the 13th multiple of 6?
You only need to calculate the 13th multiple of 6 so you can move on to step 2.
It is worth noting here that we are looking at the multiples of 6.
Move on to step 3.
The 13th multiple of 6 is 6\times{13}=78.
The 13th multiple of 6 is 78.
Example 6: common multiples
Given that the first 5 multiples of 12 are 12,24,36,48, and 60, find a common multiple of 8 and 12.
You have the first 5 multiples of 12 and so you need to find the multiples of 8.
The first multiple of 8 is 8\times{1}=8.
You are looking for a number that is also a multiple of 12.
\ 8 is not a multiple of 12 so you need to continue.
The second multiple of 8 is 8\times{2}=16.
16 is not a multiple of 12 so you need to continue.
24 is a multiple of 12. You have found a common multiple of 8 and 12 so you do not need to continue.
The first common multiple of 8 and 12 is 24.
If you continued to list the multiples of 8 and 12 you would find other common multiples. 24 is the lowest common multiple of 8 and 12.
Common misconceptions
- Factors and multiples
Factors and multiples are easily mixed up. Remember multiples are the multiplication table, whereas factors are the numbers that go into another number without a remainder.
- Remember \bf{1} and the number itself for factors
All numbers are a factor of themselves and 1 is a factor of every number.
For example, the factors of 6 are 1,2,3,6 and so 6 is a factor of itself.
- Remember the number itself for multiples
All numbers are a multiple of themselves.
For example, the multiples of 6 are 6,12,18,24 and so on and so 6 is a multiple of itself.
Practice factors and multiples questions
1. List the factors of 24.
2 and 12, 3 and 8, 4 and 6

24, 48, 72, 96, and 120


1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12 and 24

The factor pairs of 24 are,
\begin{aligned} &1\times{24}\\\\ &2\times{12}\\\\ &3\times{8}\\\\ &4\times{6} \end{aligned}
So the factors of 24 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12 and 24.
2. List the factors of 49.
1 and 49


1, 7, and 49


The factor pairs of 49 are,
\begin{aligned} &1\times{49}\\\\ &7\times{7} \end{aligned}
So the factors of 49 are 1, 7, and 49.
3. The factors of 8 are 1,2,4 and 8. By finding the factors of 30, determine the common factors of 8 and 30.


1 and 2


The factor pairs of 30 are,
\begin{aligned} &1\times{30}\\\\ &2\times{15}\\\\ &3\times{10}\\\\ &5\times{6} \end{aligned}
So the factors of 30 are \colorbox{yellow}{1}, \colorbox{yellow}{2}, \ 3, \ 5, \ 6, \ 10, \ 15, and 30.
The factors of 8 are \colorbox{yellow}{1}, \colorbox{yellow}{2}, \ 4, and 8.
The common factors of 8 and 30 are 1 and 2.
4. List the first 5 multiples of 30.




So, the first 5 multiples of 30 are 30, 60, 90, 120, and 150.
5. What is the 4th multiple of 15?




6. Determine the first 2 common multiples of 3 and 4.




The first 8 multiples of 3 are 3, \ 6, \ 9, \colorbox{yellow}{12}, \ 15, \ 18, \ 21 and \colorbox{yellow}{24}.
The first 8 multiples of 4 are 4, \ 8, \colorbox{yellow}{12}, \ 16, \ 20, \colorbox{yellow}{24}, \ 28 and 32.
The first common factor of 4 and 3 is 12 and the second is 24.
Factors and multiples GCSE questions
1. Here is a list of numbers,
1, \ 2, \ 3, \ 4, \ 6, \ 10, \ 12, \ 16, \ 24, \ 25 .
(a) Write down the multiples of 4.
(b) Which numbers have a factor of 3?
(c) A common multiple of two numbers is 18. The numbers also have a common factor of 3. Write down the two numbers.
(d) Which number has exactly 5 factors?
(5 marks)
(a) 4, 12, 16, 24
(1)
(b) 3, 6,12, 24
(1)
(c) 3 and 6
(2)
(d) 16
(1)
2. Bus A and Bus B leave the depot at 7:40am.
It takes 40 minutes for Bus A to return to the depot.
It takes 30 minutes for Bus B to return to the depot.
What time will both buses be back at the depot?
(3 marks)
Multiples of 30 and 40 listed.
(1)
120 minutes = 2 hours
(1)
9:40am
(1)
3. (a) The length and width of a rectangle are both integers. How many possible rectangles can be drawn with an area of 24cm^{2}?
(b) An isosceles triangle also has side lengths that are integers. How many triangles can be drawn with a perimeter of 8cm?
(4 marks)
(a)
Factor pairs of 24 are 1 and 24, 2 and 12, 3 and 8, 4 and 6 .
(1)
4 rectangles
(1)
(b)
\cfrac{8-[2, 4, 6]}{2}
(1)
1 \ (2cm, \ 3cm, \ 3cm only)
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.