One to one maths interventions built for KS4 success
Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons now available
This topic is relevant for:

Cubes And Cube Roots
Here we will learn about cube numbers and cube roots including what a cube number is, what a cube root is, as well as how to cube a number and how to find the cube root of an integer. You’ll also learn how to solve problems by applying knowledge of cube numbers.
There are also cube numbers and cube roots worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is a cube number?
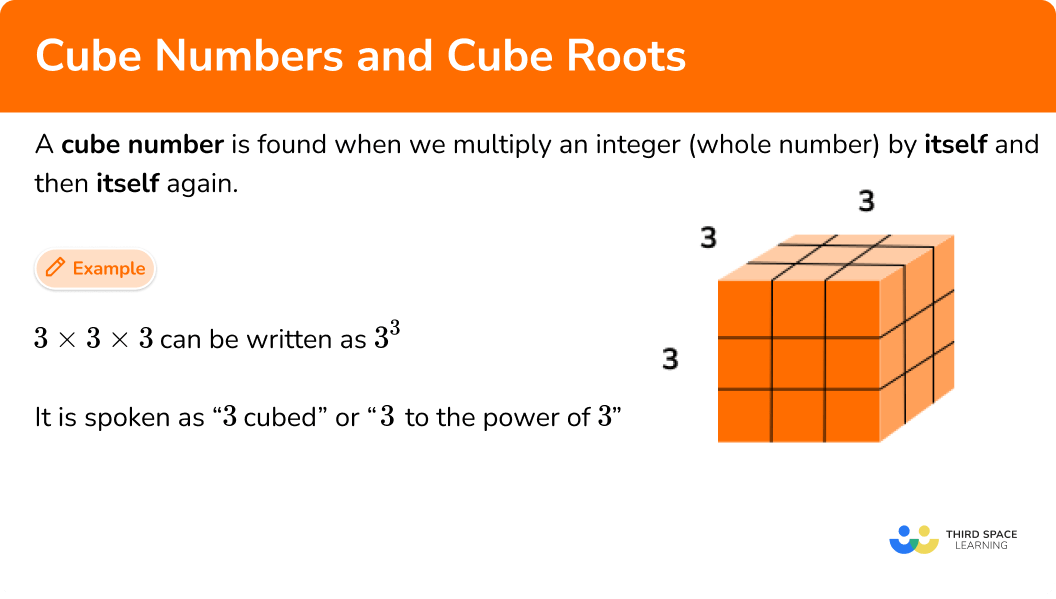
A cube number is the product of three identical factors. To find a cube number, multiply an integer (whole number) by itself and then itself again, for example, 3 x 3 x 3 = 27. These are sometimes called ‘perfect cubes’.
We can cube numbers with decimals but we do not refer to these as cube numbers.
A given number / variable that is ‘cubed’ is multiplied by itself three times.
E.g.
A cube number is found when we multiply an integer (whole number) by itself,
Here are the first
A cube number can be represented as an array which forms the shape of a cube that has a length 3 units, width 3 units and depth 3 units.
E.g.
If we look at
Any cube number will form the shape of a cube.
What is a cube number?
Perfect cubes
The cube number of an integer is also called a perfect cube.
We can cube numbers with decimal places but we do not refer to these as cube numbers or perfect cubes.
A given number or variable that is ‘cubed’ is multiplied by itself and this applies to decimals as to integers.
It’s relatively straightforward to work out the cube root of a perfect cube but it is a much harder process to work out decimal cube roots. You quickly end up working with surds and irrational numbers.
Cubing negative numbers
We can also cube negative numbers.
E.g.
You will notice that when we cube a negative number we get a negative number.
This is because a negative number multiplied by a negative number multiplied by a negative number gives us a negative result.
Learn more by reviewing our lesson on negative numbers.
When we cube negative
This is true for all numbers (and variables) and means:
What is a cube root?
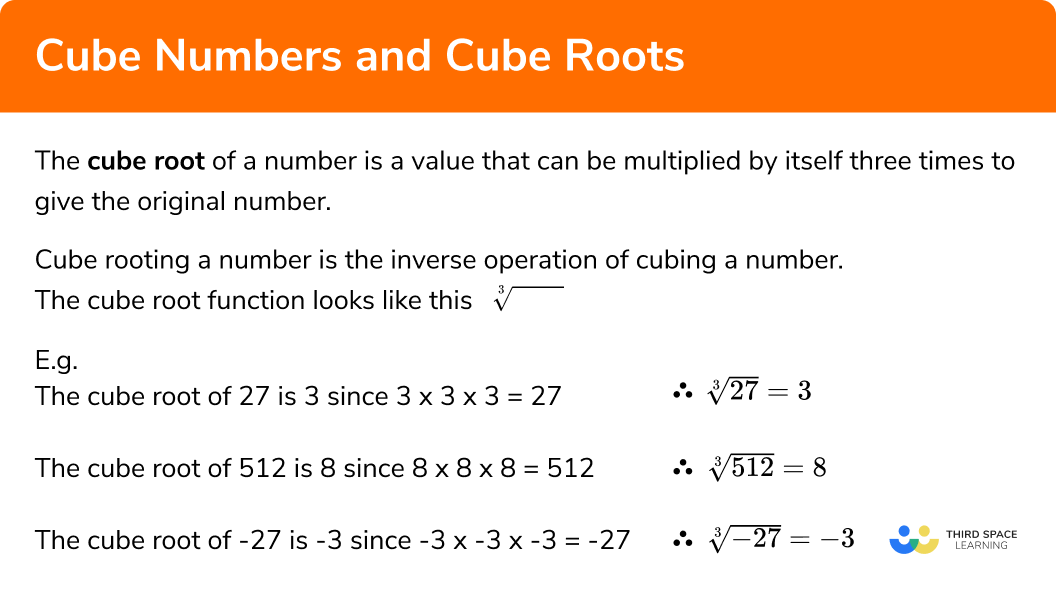
The cube root of a number is a value that can be multiplied by itself three times to give the original number.
A cube root is the inverse operation of cubing a number.
The cube root symbol looks like this
When we cube a positive number we get a positive result and when we cube a negative number we get a negative result.
So the cube root of a positive number is also a positive number, and the cube root of a negative number is also a negative number.
E.g.
What is a cube root?
Cube numbers worksheet

Get your free cube numbers worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Cube numbers worksheet

Get your free cube numbers worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on powers and roots
Cube numbers and cube roots is part of our series of lessons to support revision on powers and roots. You may find it helpful to start with the main powers and roots lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Key words
Term
A single number (constant) or variable
E.g.
in the expression
Coefficient
The number which the variable is being multiplied by
E.g.
in
Integer
A whole number
E.g.
Index (also called exponent or powers)
The index number is the amount of times you multiply a number/variable by itself.
E.g.
the index number in
Note: the plural of index is indices
Note: you will see index number as a superscript
Base number
The number/unknown that is being multiplied by itself an amount of times
E.g.
the base number in
Advanced vocabulary – only for Additional Maths, A-Level
Real numbers
Any positive or negative number is called a real number. Numbers that are not ‘real’ are called imaginary numbers. Integers, decimals, fractions are all examples of real numbers
E.g.
Imaginary numbers
Numbers that are not real are called imaginary numbers, for example you will notice we cannot find the square root of a negative number (try it on a calculator), this because it is an imaginary number.. Numbers that contain an imaginary part and real part are called complex numbers.
Cube numbers and cube roots examples
Example 1
What is
So
Example 2
What is
So
Example 3
What is the cube root of
The cube root of
So
How to use cube numbers and cube roots
- Identify whether you need to cube or cube root the number/variable
- Perform the operation
- Clearly state the answer within the context of the question e.g. including units
Now you will focus on solving problems using your knowledge of cube numbers and cube roots.
Explain how to solve problems involving cube numbers and cube roots in 3 steps

Cubes and cube roots problem examples
Example 4: knowledge of cube numbers
Danny says
- Identify whether you need to cube or cube root the number/variable
The question focus is on cubing
2 Perform the operation
3 Clearly state the answer within the context of the question
Danny is wrong because
The mistake Danny made was he did
Example 5: problem solving with cube roots
Ava says the cube root of an integer is always smaller than the original number. Prove Ava is incorrect.
Identify whether you need to cube or cube root the number/variable
You are looking for a relationship between the cube root of an integer and the original number. It will help to write down your cube numbers and their cube roots.
Perform the operation
Clearly state the answer within the context of the question
Ava is incorrect because
The answer here is not smaller than the original number.
Example 6: solving problems involving cube numbers
The sum of two cube numbers is
Identify whether you need to cube or cube root the number/variable
Remember sum means add. Therefore you are looking for two cube numbers that add together to make
It will help here to list the cube numbers up to
Perform the operation
The Cube Numbers:
You now need to pick two of these numbers that when added together make
Clearly state the answer within the context of the question
The two cube numbers are
Example 7: cube numbers within a 3D polygon
A cube has a volume of
Identify whether you need to cube or cube root the number/variable
The volume of a cube is found by multiplying the length, width and height together. For a cube the length, width and height are the same length.
Therefore you are looking for a number that when multiplied by itself three times (or cubed) is equal to
Therefore you need to find the cube root of
Perform the operation
Clearly state the answer within the context of the question
Therefore the length of the cube is
Example 8: cube numbers within a 3D polygon
Length of one side of a cube is
Identify whether you need to cube or cube root the number/variable
The volume of a cube is found by multiplying the length, width and height together. For a cube the length, width and height are the same length.
Therefore you are are going to multiply the side length by itself three or ‘cube’ the length.
Therefore you need to cube
Perform the operation
Clearly state the answer within the context of the question
Therefore the volume of the cube is
Example 9
Lexi says “when you add three consecutive cube numbers, the answer is always odd.”
Is Lexi right? Explain your answer.
Identify whether you need to cube or cube root the number/variable
To prove Lexi wrong we only need to find one example where she is incorrect, this is sometimes known as proof by contradiction.
Therefore we are looking for
Perform the operation
The cube numbers:
You are now looking for one example where three of these numbers when added together make an even number.
For example:
Clearly state the answer within the context of the question
Lexi is wrong because
Common misconceptions
- Cube numbers
Incorrect understanding of cubing a number
E.g.
- Cube roots
Not recognising that a negative number cube rooted is negative
E.g.
\sqrt[3]-8 = -2
Practice cube numbers and cube roots questions
1. What is 10 cubed?




2. What is the value of the cube root of 216?




3. What is (-7)^3?




4. What is the value of \sqrt[3]{-1}?




5. The sum of two cube numbers is 65 . Find the two cube numbers.
8 and 27

8 and 57

1 and 64

27 and 38

The cube numbers up to 65 are 1, 8, 27, 64.
The two that add up to 65 are 1 and 64.
6. A cube has a volume of 512 cm^3. What is the length of one side?
170.7cm

8cm

256cm

5.12cm

We find the volume of a cube by multiplying the length, the width and the height together.
These are all equal for a cube so we need to find a number that, when multiplied by itself three times, gives us 512.
Therefore we need to find the cube root of 512.
\sqrt[3]{512}=8
Cube numbers and cube roots GCSE questions
1. Work out the value of:
(a) 3^{3}
(b) 5 \times 2^{3}
(c) 6^{3} − 3^{3}
(3 Marks)
(a) 3 \times 3 \times 3
27
(1)
(b) 5 \times 8
40
(1)
(c) 216 – 27
189
(1)
2. Here is a list of numbers:
1000 \quad \quad 18 \quad \quad 8 \quad \quad 64 \quad \quad 7 \quad \quad 144 \quad \quad 1 \quad \quad 19
(a) List the cube numbers
(b) Which number is a square and cube number?
(2 Marks)
(a) 1000, 8 , 64 and 1
(1)
(b) 64
(1)
3. Find the value of:
(a) \sqrt[3]{729}
(b) \sqrt[3]{-1}
(c) \sqrt[3]{-8}
(3 Marks)
(a) 9
(1)
(b) -1
(1)
(c) -2
(1)
4. Simplify the following expression
5^{3} \times \sqrt[3]{x^{3}}
(2 Marks)
Correct coefficient
(1)
Correct x (or x^{1} )
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Calculate cube numbers up to 10 × 10 × 10
- Use positive integer powers and their associated real roots
- Recognise and use the cube numbers
- Apply properties of cubes to a context
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.