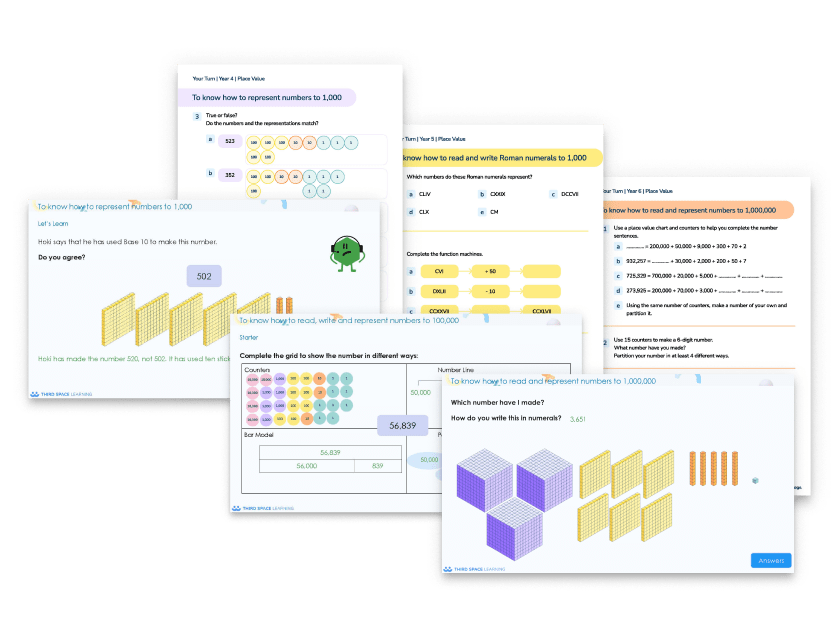
What Is Place Value? Primary School Explanation With Free Resources
Place value is the value of each digit in a number depending on its position. It helps us to understand and compare numbers, and make calculations.
What is place value?
Place value helps you to understand the value of each digit within a number. The same digit can have different values depending on its position in a number.
For example in 362, the 6 represents 6 tens. But, in 326, the 6 represents 6 ones.
How place value works
Each place value is ten times greater than the place value to its right.
Children must understand that while a digit can be the same, its value depends on where it is in the number.
- A digit in the tens place has a value ten times greater than the same digit in the ones place.
- A digit in the hundreds place has a value ten times greater than the same digit in the tens place.
The right to left pattern means that values of the places increase as you move from right to left.
In the simplest the column place value grid:
- The furthest right digit is in the ones place.
- The next digit to the left is in the tens place.
- The next is the hundreds place, then thousands, ten thousands, and so on.
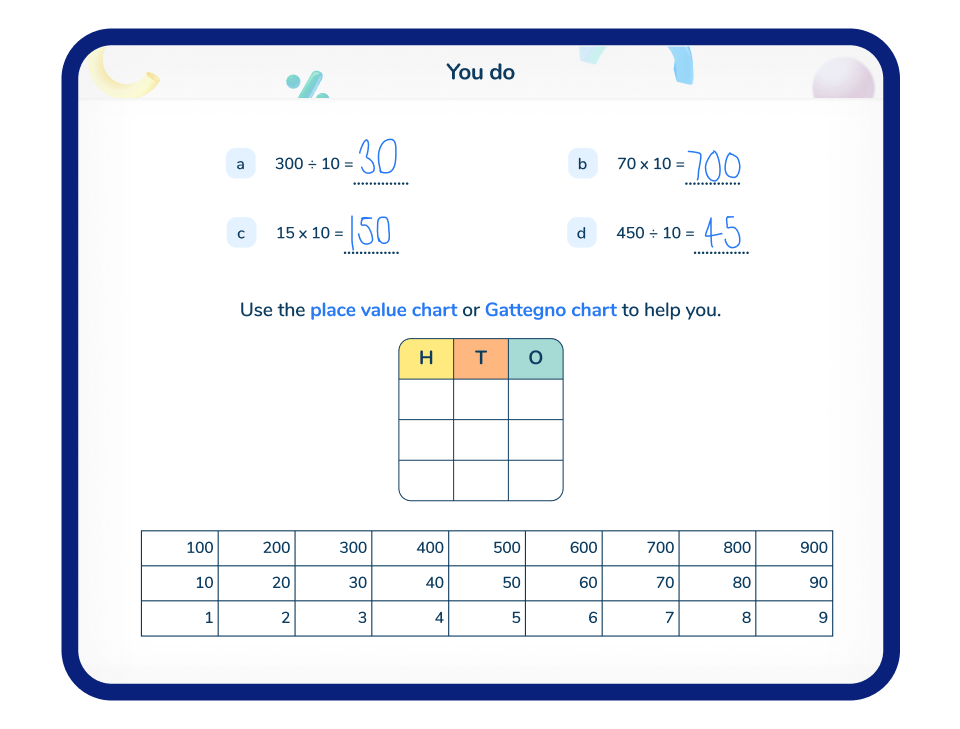
Place value charts
Often, the best way to teach children the order of place value is with a place value chart or place value grid like the one below. This is the expanded place value chart that pupils start to encounter as they learn about larger numbers in primary school.
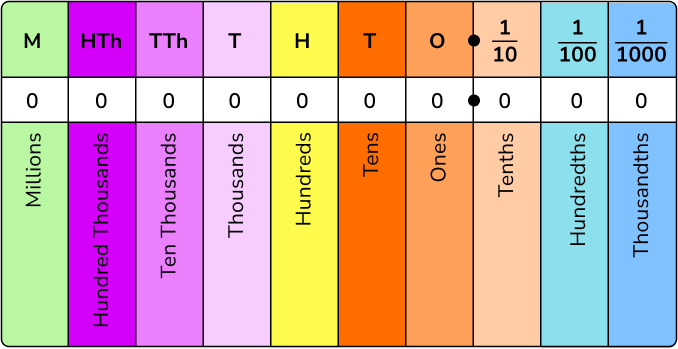
Place value charts have letters on them to represent each position Millions, Hundred Thousands, Ten Thousands, Thousands, Hundreds, Tens, Ones, tenths, hundredths, and so on.
You can download your own place value grid and activity here! It takes no time at all to make and then you can physically manipulate the numbers to show their place value. This makes a real difference when working with children.
Free Place Value Worksheets and Lessons For Year 1 to Year 6
Download this free resource pack of place value worksheets, questions and teaching aids. All resources support a maths mastery approach and are matched to White Rose maths and align with NCETM.
Download Free Now!Understanding place value’s right to left pattern
Place value is key to understanding how we ‘read’ numbers differently from words. When looking at place value you
When do children learn about place value in school?
Place value is arguably one of the most important areas of the primary maths curriculum.
Every year group has a set of objectives specifically focused on number and place value. All teachers start the term in September with lessons recapping previous place value work and building on it with larger (or smaller in the case of decimals) numbers as the confidence of the class increases.

taken from Third Space Learning’s online maths lessons.
Examples of these objectives are below.
Place value in Year 1
In Year 1, pupils should:
- Count to and across 100;
- Count, read and write numbers to 100 in numerals.
Pupils may also begin to recognise place value in numbers beyond 20 by reading, writing, counting and comparing numbers up to 100, supported by objects and pictorial representations.

Unlimited primary maths tutoring with Skye, the voice-based AI maths tutor.
Built on the same principles, pedagogy and curriculum as our traditional tutoring, but with more flexibility, reach and lower cost.
Join the schools already helping hundreds of primary pupils nationwide with Skye’s one to one maths tutoring.
Watch Skye in actionPlace value in Year 2
In Year 2, pupils should:
- Recognise the place value of each digit in a two-digit number (tens, ones);
- Read and write numbers to at least 100 in numerals and in words;
- Use place value and number facts to solve problems.
By the end of Year 2, pupils should know the number bonds to 20 and be precise in using and understanding place value.
Place value in Year 3
In Year 3, pupils should:
- Recognise the place value of each digit in a three-digit number (hundreds, tens, ones);
- Read and write numbers up to 1000 in numerals and in words;
- Use larger numbers to at least 1000, applying partitioning related to place value using varied and increasingly complex problems;
- Use a variety of representations, including those related to measure;
- Continue to count in ones, tens and hundreds, so that they become fluent in the order and place value of numbers to 1000.
Place value in Year 4
In Year 4, pupils should:
- Recognise the place value of each digit in a four-digit number (thousands, hundreds, tens, and ones);
- Know that over time, the numeral system changed to include the concept of zero and place value.
Place value in Year 5
In Year 5, pupils should:
- Read, write, order and compare numbers to at least 1 000 000 and determine the value of each digit.
Place value in Year 6
In Year 6, pupils should:
- Read, write, order and compare numbers up to 10 000 000 and determine the value of each digit.
Place value usually makes an appearance in KS2 SATs too, whether it’s the placement of digit in a number, converting units and money or working with decimals. Download free sample SATs place value questions for year 6.
How will children be taught place value at primary school?
Throughout primary school, two concrete maths resources are used to help make place value easy to understand for children. Both of the following aids do this by representing place value in a visual manner.
Dienes blocks for place value
Dienes blocks are cubes that are used to represent units/ones, tens, hundreds and thousands.
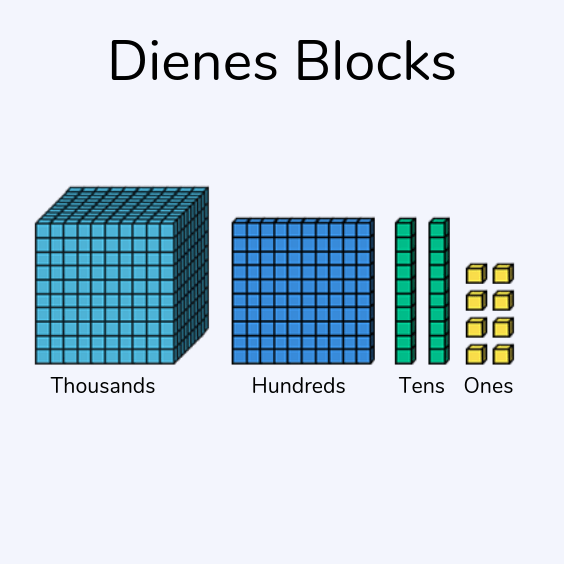
These cubes are a simple way for children to make different numbers. To make the number 174, they would need to gather one set of 100, 7 sets of 10 and four single cubes.
Arrow cards for place value
Arrow cards are simple visual representations of hundreds, tens and units that children can manipulate to create different numbers and learn about place value.
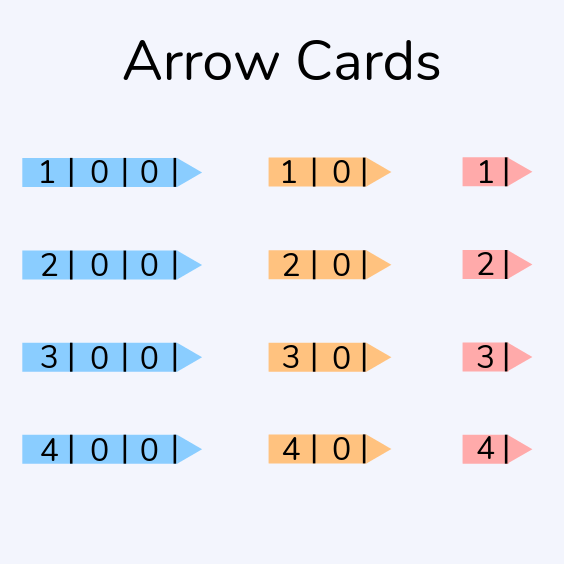
Children may be asked to make up numbers to show that they have a firm grasp of place value. For example, if a child was asked to make the number 241, they would place the 40 card over the last two digits on the 200 one, and the 1 card over the last digit on the 40 card.
Understanding place value is crucial for children before they can move on to adding and subtracting two-digit numbers.
If you’re interested in digging deeper into this topic, then we recommend reading this detailed guide to teaching place value at KS2 and trying out some of these place value games and place value worksheets.
How does place value relate to other areas of maths?
Place value is intrinsically linked to many other areas of maths. A solid understanding of place value is vital to allow children to competently work through calculations using the four operations in order to add, subtract, multiply and divide.
Place value provides a quick mental method to compare numbers and determine which is larger or smaller.
At KS3 and KS4 students then progress to become more confident with decimal place value and confident manipulation of the decimal point.
Place value and other areas of maths: year-by-year breakdown for teachers
In Year 2, recording addition and subtraction in columns supports place value and prepares for formal written methods with larger numbers. Year 2 also connects the 10 multiplication table to place value.
In Year 3, pupils solve problems, including missing number problems, using number facts, place value, and more complex addition and subtraction.
Year 3s use their understanding of place value and partitioning, and practice using columnar addition and subtraction with increasingly large numbers up to three digits to become fluent.
They will also connect tenths (1/10) to place value.
In Year 4, place value is used in multiplication and division, where known and derived facts are used to multiply and divide mentally.
Year 4 pupils should connect hundredths to tenths and place value. Their understanding of the number system and decimal place value is extended at this stage to include the tenths and then hundredths place value columns. In measurement, Year 4 pupils build on their understanding of place value and decimal notation to record metric measures, including money.
In Year 5, pupils use their knowledge of place value and multiplication and division to convert between standard units, such as metres and kilometres.
Place value practice questions for primary school pupils
Try these to get an idea of how comfortable your pupil is with place value.
1) In the following numbers, what is the digit 7 worth?
a) 405.7
b) 30,070
Answers:
a) 7 tenths
b) 7 tens – 70
2) Jack has four number cards: 2, 3, 4 and 7. He uses each card once to make a four-digit number. He places 4 in the tens column; 2 so that it has a higher value that any of the other digits; the remaining two digits so that 7 has the higher value. What number did Jack make?
Answer: 2743
3) Look at this number: 23,451.96. Write the digit that is in the
a) hundreds place
b) hundredths place
Answers:
a) 4
b) 6
4) Write the number 402,037 in words.
Answer: Four hundred and two thousand and thirty seven
Place value CPD and teaching resources
Visit the Third Space Learning YouTube channel for detailed guides to teaching place value. Aimed at all experience levels including teaching assistants as well as Heads of maths, the videos are presented by experts breaking down fundamentals of place value into bite size steps.
Place value essentials video playlist
See also:
- Tens frame
- What is a Square Number?
- What is BODMAS or BIDMAS?
- Maths Word Problems Explained for Parents and Teachers
- What is Part Whole Model?
Place value is the value of each digit in a number.
For example, the 6 in 863 represents 6 tens, or 60; however, the 6 in 6,003 represents 6 thousands, or 6,000.
Every digit in a number has a place value. It depends on its position in the number. It is important that children understand that while a digit can be the same, its value depends on where it is in the number. A place value grid can support children to identify a number’s place value.
A place value grid is a useful resource to teach children place value. Maths manipulatives, such as dienes blocks, are also useful tools to develop children’s understanding of place value. Dienes blocks are cubes that are used to represent units/ones, tens, hundreds and thousands.
A solid understanding of place value is vital as it links to the four operations in maths, addition, subtraction, multiplication and division, among other key skills in maths.
If you want to know what other maths terminology primary school pupils will need to learn by the end of KS2, our free primary maths dictionary for kids has child friendly definitions of all key maths vocabulary.
DO YOU HAVE STUDENTS WHO NEED MORE SUPPORT IN MATHS?
Skye – our AI maths tutor built by teachers – gives students personalised one-to-one lessons that address learning gaps and build confidence.
Since 2013 we’ve taught over 2 million hours of maths lessons to more than 170,000 students to help them become fluent, able mathematicians.
Explore our AI maths tutoring or find out about a primary school maths tutor for your school.