One to one maths interventions built for KS4 success
Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons now available
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Decimal place value Decimals Fractions ArithmeticThis topic is relevant for:

Decimal Number Line
Here we will learn about decimal number lines, including what decimal number lines are and how to use them.
There are also decimal number line worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is a decimal number line?
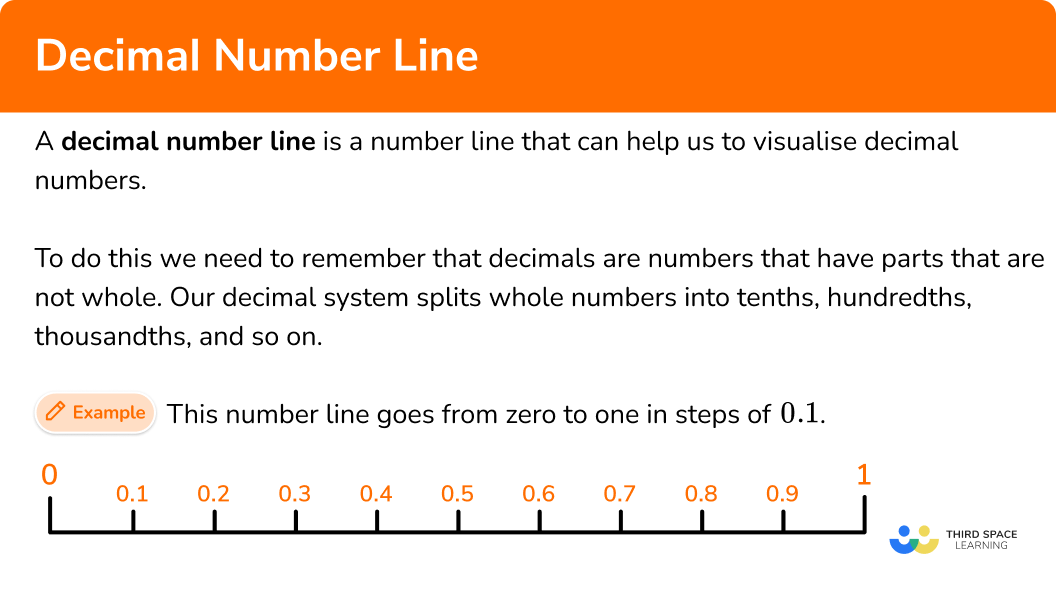
A decimal number line is a number line that can help us to visualise decimal numbers. Decimal numbers are parts of whole numbers and have digits after a decimal point.
Decimals are numbers that have parts that are not whole. Our number system splits whole numbers into tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on.
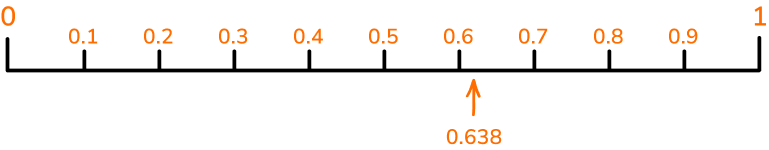
For example, this number line goes from zero to one in steps of 0.1.

Below, the number \bf{0.638} has been marked on a decimal number line. Its position has been estimated between 0.6 and 0.7, but closer to 0.6.
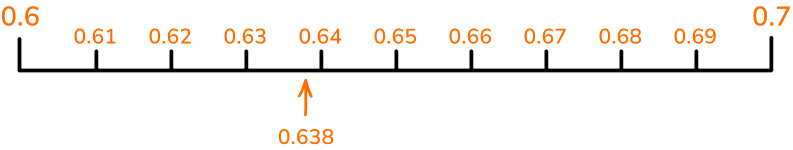
If we zoom in and consider a number line between 0.6 and 0.7 that goes up in steps of 0.01 then we can position the decimal \bf{0.638} more accurately. This time the position has been estimated between 0.63 and 0.64, but closer to 0.64.
If we zoom in once more and consider a number line between 0.63 and 0.64 that goes up in steps of 0.001 then we can mark the decimal \bf{0.638} in its exact position.
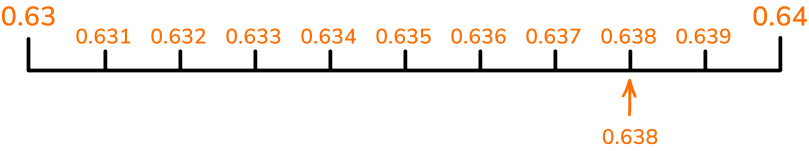
Decimal number lines can use hundredths or thousandths. The scale can be split up into different equal parts (or increments).
For example, this decimal number line has been split up into fifths that go up in steps of 0.2.

This decimal number line has been split up into halves that go up in steps of 0.5.

This decimal number line has been split up into quarters that go up in steps of 0.25.

Decimal number lines can also be used to represent negative numbers.
For example,
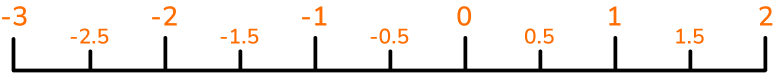
What is a decimal number line?
How to fill in values on a decimal number line
In order to fill in values on a decimal number line:
- Consider the top and bottom of the scale and the number of intervals.
- Calculate the length of each interval step by finding the difference in the top and bottom of the scale and dividing by the number of intervals.
- Fill in the missing values.
Explain how to fill in values on a decimal number line

Decimals worksheet (includes decimal number line)

Get your free decimal number line worksheet of 20+ decimals questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Decimals worksheet (includes decimal number line)

Get your free decimal number line worksheet of 20+ decimals questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on decimals
Decimal number line is part of our series of lessons to support revision on decimals. You may find it helpful to start with the main decimals lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Decimal number line examples
Example 1: fill in the scale
Fill in the scale.

- Consider the bottom and top of the scale and the number of intervals.
The bottom of the scale is 7, the top of the scale is 8 and there are 5 intervals.
2Calculate the length of each interval step by finding the difference in the top and bottom of the scale and dividing by the number of intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale} - \text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.This gives,
(8-7)\div 5=0.2.So the scale goes up in steps of 0.2.
3Fill in the missing values.
Start from the bottom of the scale, 7, and go up the scale, adding on 0.2 each time.

Example 2: fill in the scale
Fill in the scale.

Consider the bottom and top of the scale and the number of intervals.
The bottom of the scale is 5, the top of the scale is 9 and there are 8 intervals.
Calculate the length of each interval step by finding the difference in the top and bottom of the scale and dividing by the number of intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale} - \text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(9-5) \div 8=0.5.
So the scale goes up in steps of 0.5.
Fill in the missing values.
Start from the bottom of the scale, 5 and go up the scale, adding on 0.5 each time.

Example 3: fill in the scale
Fill in the scale.

Consider the bottom and top of the scale and the number of intervals.
The bottom of the scale is 12, the top of the scale is 14 and there are 5 intervals.
Calculate the length of each interval step by finding the difference in the top and bottom of the scale and dividing by the number of intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale} - \text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(14-12)\div 5=0.4.
So the scale goes up in steps of 0.4.
Fill in the missing values.
Start from the bottom of the scale, 12 and go up the scale, adding on 0.4 each time.

Example 4: finding a missing value
Find the missing value.

Consider the bottom and top of the scale and the number of intervals.
The bottom of the scale is 5.2, the top of the scale is 6.0 and there are 8 intervals.
Calculate the length of each interval step by finding the difference in the top and bottom of the scale and dividing by the number of intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale} - \text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(6.0-5.2)\div 8=0.1.
So the scale goes up in steps of 0.1.
Fill in the missing values.
We need the 4th value. So we can multiply the interval step by 5 and add it to the bottom of the scale,
5.2+(4\times 0.1)=5.6.

You can always fill in other values on the scale to double check.
Example 5: finding a missing value
Find the missing value.

Consider the bottom and top of the scale and the number of intervals.
The bottom of the scale is 14, the top of the scale is 17 and there are 6 intervals.
Calculate the length of each interval step by finding the difference in the top and bottom of the scale and dividing by the number of intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale} - \text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(17-14)\div 6=0.5.
So the scale goes up in steps of 0.5.
Fill in the missing values.
We need the 5th value. So we can multiply the interval step by 5 and add it to the bottom of the scale,
14+(5\times 0.5)=16.5.

You can always fill in other values on the scale to double check.
Example 6: finding a missing value
Find the missing value.

Consider the bottom and top of the scale and the number of intervals.
The bottom of the scale is 7.1, the top of the scale is 7.5 and there are 8 intervals.
Calculate the length of each interval step by finding the difference in the top and bottom of the scale and dividing by the number of intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale} - \text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(7.5-7.1)\div 8=0.05.
So the scale goes up in steps of 0.05.
Fill in the missing values.
We need the 7th value. So we can multiply the interval step by 7 and add it to the bottom of the scale,
7.1+(7\times 0.05)=7.45.

You can always fill in other values on the scale to double check.
Common misconceptions
- Assuming a decimal number line goes up in tenths
It is worth double checking what the intervals in a number line are. It is easy to assume it will be tenths, but often steps of 0.2 are used. This is a useful tip when reading scales on graphs.
Practice decimal number line questions
1. Find the missing value.
![]()




The bottom of the scale is 6, the top of the scale is 7 and there are 5 intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale}-\text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(7-6)\div 5=0.2.
We need the 2nd value, so we can multiply the interval step by 2 and add it to the bottom number.
6+(2\times 0.2)=6.4
The missing value is 6.4.
2. Find the missing value.
![]()




The bottom of the scale is 2.1, top of the scale is 2.7 and there are 6 intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale}-\text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(2.7-2.1)\div 6=0.1.
We need the 2nd value, so we can multiply the interval step by 2 and add it to the bottom number.
2.1+(2\times 0.1)=2.3
So the missing value is 2.3.
3. Find the missing value.
![]()




The bottom of the scale is 5.2, the top of the scale is 5.3 and there are 10 intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale}-\text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(5.3-5.2)\div 10=0.01.
We need the 5th value, so we can multiply the interval step by 5 and add it to the bottom number.
5.2+(5\times 0.01)=5.25
The missing value is 5.25.
4. Find the missing value.
![]()




The bottom of the scale is 16.2, the top of the scale is 18.2 and there are 5 intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale}-\text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(18.2-16.2)\div 5=0.4.
We need the 4th value, so we can multiply the interval step by 4 and add it to the bottom number.
16.2+(4\times 0.4)=17.8
The missing value is 17.8.
5. Find the missing value.
![]()




The bottom of the scale is 6.5, the top of the scale is 9.0 and there are 10 intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale}-\text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(9.0-6.5)\div 10=0.25.
We need the 3rd value, so we can multiply the interval step by 3 and add it to the bottom number.
6.5+(3\times 0.25)=7.25
The missing value is 7.25.
6. Find the missing value.
![]()




The bottom of the scale is 5.5, the top of the scale is 7.3 and there are 6 intervals.
To calculate the length of an interval step we can use the formula
(\text{Top of the scale}-\text{bottom of the scale}) \div \text{number of intervals}.
This gives,
(7.3-5.5)\div 6=0.3.
We need the 3rd value, so we can multiply the interval step by 3 and add it to the bottom number.
5.5+(3\times 0.3)=6.4
The missing value is 6.4.
Decimal number line GCSE questions
1.
![]()
(a) Find the number 1.7 on the number line.
Mark it with a cross (X).
![]()
(b) Find the number 0.13 on the number line.
Mark it with a cross (X).
(2 marks)
(a)
![]()
(1)
(b)
![]()
(1)
2.

(a) Write down the number marked by the arrow.

(b) Write down the number marked by the arrow.

(c) Write down the number marked by the arrow.
(3 marks)
(a) 3.8
(1)
(b) 5.74
(1)
(c) 2.366
(1)
3.
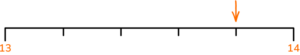
(a) Write down the number marked by the arrow
(b) Write down the number marked by the arrow.
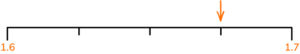
(c) Write down the number marked by the arrow.
(3 marks)
(a) 13.8
(1)
(b) 0.55
(1)
(c) 1.675
(1)
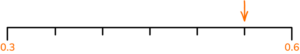
4. Amir says that the number the arrow is pointing to is 0.34.
Liam says that the number the arrow is pointing to is 0.38.
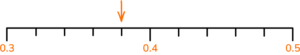
Who is correct? Explain your answer.
(2 marks)
Liam
(1)
Correct explanation
(1)
For example, Amir thinks the scale goes up in steps of 0.01.
The scale goes up in steps of 0.02, so the correct answer is 0.38.
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Understand and use decimal number lines
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.