GCSE Tutoring Programme
Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring.
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
2D shapes Angles in polygons Types of angles Angles in a triangle Angles in a quadrilateral Angle rules SubstitutionThis topic is relevant for:

Angles In A Hexagon
Here we will learn about angles in a hexagon, including finding the sum of the interior angles and solving problems involving interior angles and exterior angles.
There are also angles in a hexagon worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are angles in a hexagon?
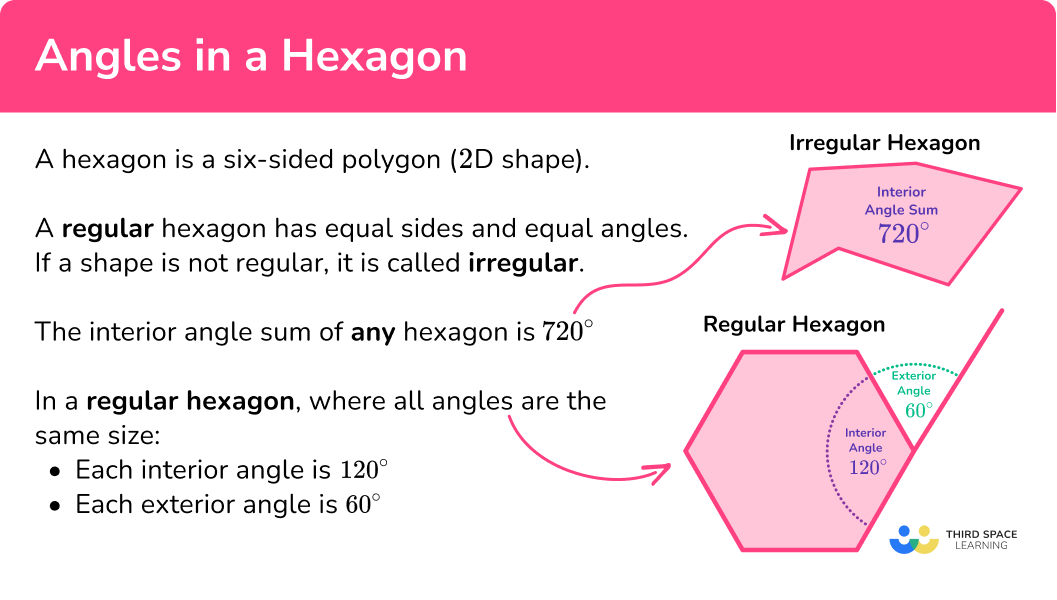
Angles in a hexagon are the angles in a six-sided polygon (2D shape).
- A regular hexagon has six equal side lengths, six vertices and six equal interior angles.

- An irregular hexagon has 6 sides which are not all equal, and 6 interior angles which are not all equal.

Sum of interior angles of a hexagon add to \bf{720^{⚬}}.
Sum of exterior angles of a hexagon add to \bf{360^{⚬}}.
What are angles in a hexagon?
Interior and exterior angles of a hexagon
We need to be able to solve problems involving angles in a hexagon.
To do this we need to work with the interior and exterior angles of a hexagon.
A pair of interior and exterior angles of all polygons add to 180^{\circ} because they form a straight line. They are supplementary angles.
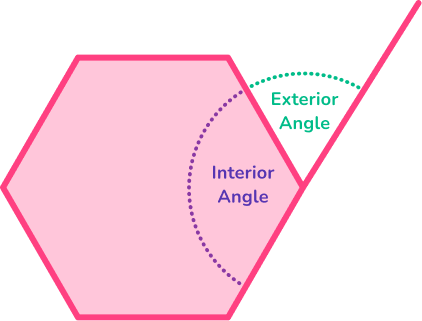
- Interior angles of a hexagon are the angles inside the 2D shape, formed when two sides of the shape meet.
We can find the sum of the interior angles of a hexagon by using the formula,
\text{Sum of interior angles}=(n-2) \times 180, where n is the number of sides.
A hexagon has 6 sides, so n=6.
\begin{aligned} \text{Sum of interior angles of a hexagon} & =(6-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =4 \times 180 \\\\ & =720^{\circ} \end{aligned}
The formula above uses the relationship between the angles in a triangle and the number of triangles a polygon can be split into.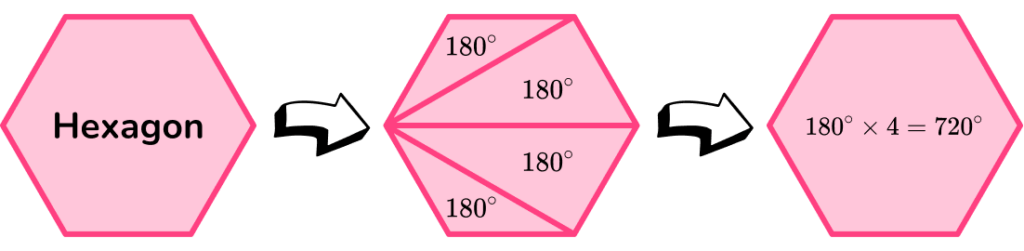
To find an interior angle of a regular hexagon we can divide the sum of the interior angles by the number of sides, in this case, 6.
Step-by-step guide: Interior angles of a polygon
- Exterior angles of a hexagon are the angles between the hexagon and the extended line from the next side.
The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is always 360^{\circ}.
To find each of the exterior angles of a regular hexagon we can use the formula,
\text{Exterior angle of a regular polygon}=\frac{360}{n}, where n is the number of sides.
Alternatively, if we know the size of the exterior angle of a polygon, we can use a rearrangement of the above formula to identify the number of sides the polygon has.
\text{Number of sides}=\frac{360}{\text { exterior angle }}
Step-by-step guide: Exterior angles of a polygon
How to solve problems involving angles in a hexagon
In order to solve problems involving angles in a hexagon:
- Identify if the hexagon is regular or irregular.
- Identify what the question is asking for.
- Solve the problem using the information you have gathered.
How to solve problems involving angles in a hexagon

Angles in polygons worksheet (includes angles in a hexagon)

Get your free angles in a hexagon worksheet of 20+ angles in polygons questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Angles in polygons worksheet (includes angles in a hexagon)

Get your free angles in a hexagon worksheet of 20+ angles in polygons questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on angles in polygons
Angles in a quadrilateral is part of our series of lessons to support revision on angles in polygons. You may find it helpful to start with the main angles in polygons lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Angles in a hexagon examples
Example 1: finding the exterior angle of a regular hexagon
Below is a regular hexagon. Find the angle marked x.
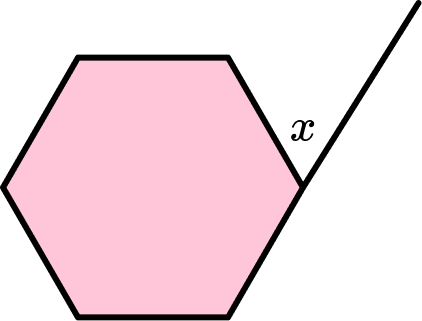
- Identify if the hexagon is regular or irregular.
The question tells us that this is a regular hexagon. This means the sides of the hexagon are equal and the interior angles are equal.
2Identify what the question is asking for.
The question wants us to find the angle x, which is one of the six exterior angles of this hexagon.
3Solve the problem using the information you have gathered.
To find the size of the exterior angles of a regular hexagon we can use the formula,
\text{Exterior angle of a regular polygon}=\frac{360}{n}, where n is the number of sides.
So, the missing angle can be calculated as
x=\frac{360}{6}=60^{\circ}.So, the exterior angle of a hexagon equals 60^{\circ}.
Example 2: finding the sum of the interior angles of a hexagon
What is the sum of the interior angles of a hexagon?
The question does not clarify whether the hexagon is regular or irregular, however, this doesn’t matter in the context of the question. The sum of the interior angles of a hexagon will be the same whether it is regular or irregular.
The question asks us to calculate the sum of the internal angles of a hexagon.
To calculate the sum of the interior angles of a hexagon, octagon or any polygon we can use the formula,
\text{Sum of interior angles}=(n-2) \times 180, where n is the number of sides.
So, the interior angle of a hexagon can be calculate as,
\begin{aligned}
& =(n-2) \times 180 \\\\
& =(6-2) \times 180 \\\\
& =4 \times 180 \\\\
& =720^{\circ}
\end{aligned}
Example 3: finding an interior angle of a regular hexagon
Below is a regular hexagon shape. Find the angle marked x.
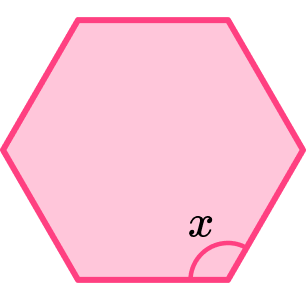
The question tells us that this is a regular hexagon.
The question wants us to find the angle x, which is one of the six interior angles of this hexagon.
To find the size of an interior angle of any hexagon we need to first calculate the sum of the interior angles.
To calculate the sum of the interior angles of any polygon we can use the formula,
\text{Sum of interior angles}=(n-2) \times 180, where n is the number of sides.
So, the interior angle of a hexagon can be calculated as,
\begin{aligned} & =(n-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =(6-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =4 \times 180 \\\\ & =720^{\circ} \end{aligned}
Now that we know the angles inside a hexagon sum to 720^{\circ}, we can divide this by the number of sides, in this case 6, to find the size of one interior angle.
So, the missing angle can be calculated as
x=\frac{720}{6}=120^{\circ}.
Hence, the missing angle measures 120^{\circ}.
Example 4: finding an interior angle of an irregular hexagon
Below is a polygon. Find the size of the missing angle x.
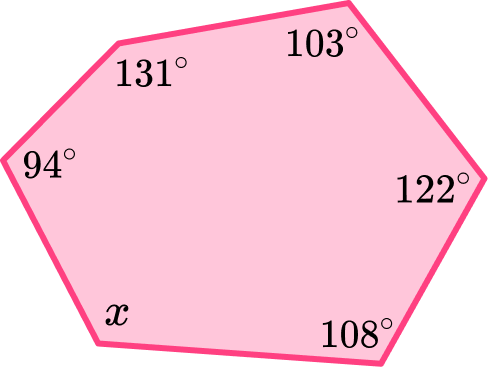
The question does not state whether the polygon is regular or irregular, however, the interior angles of the hexagon are not equal, so it must be irregular.
The question asks us to calculate the sum of the internal angles of a hexagon.
To find the size of an interior angle of any hexagon we need to first calculate the sum of the interior angles.
To calculate the sum of the interior angles of any polygon we can use the formula,
\text{Sum of interior angles}=(n-2) \times 180, where n is the number of sides.
So, the interior angle of a hexagon can be calculated as,
\begin{aligned} & =(n-2)\times 180 \\\\ & =(6-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =4 \times 180 \\\\ & =720^{\circ} \end{aligned}
Now that we know the angles inside a hexagon sum to 720^{\circ}, we can subtract the interior angles we know, to find the missing value.
x=720-(94+131+103+122+108)=162^{\circ}
Example 5: finding an exterior angle of an irregular hexagon
Below is an irregular polygon. Find the size of the missing angle x.
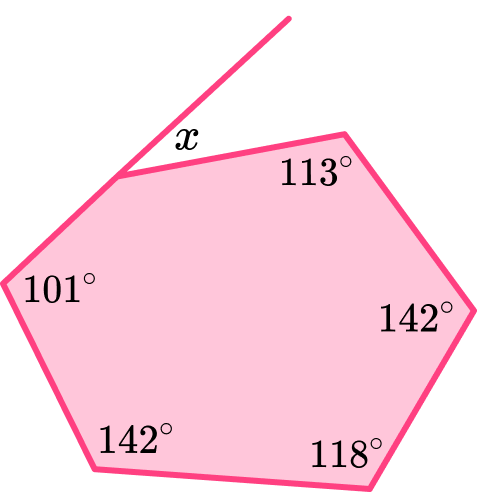
The question states that the polygon is irregular.
The question asks us to find the missing exterior angle.
To find the size of the exterior angle, x, we need to find the missing interior angle that corresponds to it, labelled y on the diagram below.
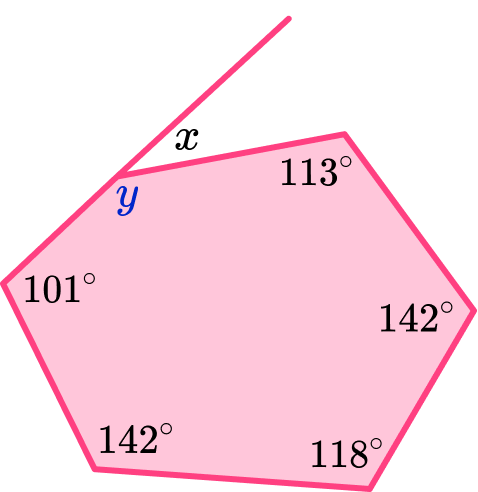
To find the size of an interior angle of any hexagon we need to first calculate the sum of the interior angles.
To calculate the sum of the interior angles of any polygon we can use the formula,
\text{Sum of interior angles}=(n-2) \times 180, where n is the number of sides.
So, the interior angle of a hexagon can be calculated as,
\begin{aligned} & =(n-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =(6-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =4 \times 180 \\\\ & =720^{\circ} \end{aligned}
Now that we know the angles inside a hexagon sum to 720^{\circ}, we can subtract the interior angles we know, to find the missing value.
y=720-(101+142+118+142+113)=104^{\circ}
Now that we know the value of the interior angle corresponding to x, we can use the fact that the interior and exterior angles of all polygons add to 180^{\circ} because they form a straight line, to calculate the exterior angle.
So, x=180-104=76^{\circ}.
Example 6: solving angle problems involving hexagons
The diagram shows a tessellation from a section of floor tiles.
The shape is formed by two regular polygons.
Find the size of the angle labelled x.
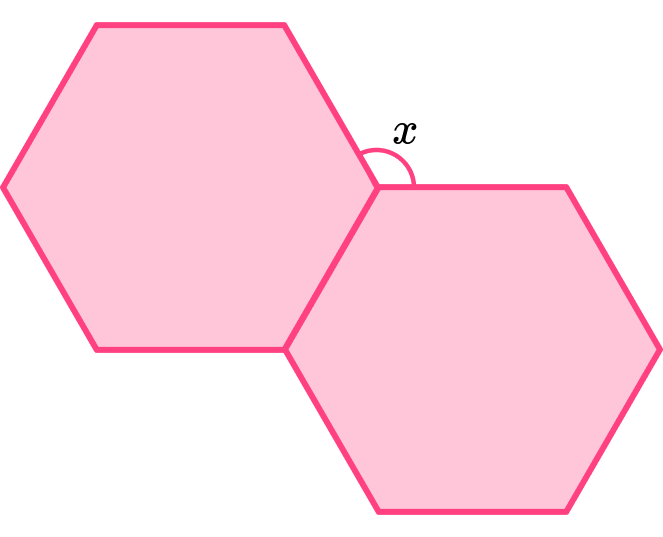
The question states that both polygons in the diagram are regular polygons.
The questions asks us to find the size of the angle x, which is formed on the exterior of the two regular hexagons.
To find the size of the angle, x, we need to find the missing interior angles that meet it at the point.
To find the size of an interior angle of any hexagon we need to first calculate the sum of the interior angles.
To calculate the sum of the interior angles of any polygon we can use the formula,
\text{Sum of interior angles}=(n-2) \times 180, where n is the number of sides.
So, the interior angle of a hexagon can be calculated as,
\begin{aligned} & =(n-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =(6-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =4 \times 180 \\\\ & =720^{\circ} \end{aligned}
Now that we know the angles inside a hexagon sum to 720^{\circ}, we can divide this by the number of sides, in this case 6, to find the size of one of the interior angles.
So, the interior angles are
\frac{720}{6}=120^{\circ}.
Now that we know that the two interior angles are 120^{\circ} each, we can use the angle fact ‘angles around a point sum to 360^{\circ} ’ to find the angle x.
So, x=360-(120+120)=120^{\circ}.
Common misconceptions
- Regular and irregular polygons
It is important to correctly identify whether a polygon is regular or irregular, using the information given in the question or on the diagram. Do not assume one or the other.
- Using the formulae incorrectly
Whether a polygon is regular or irregular will determine how the formulae for working with interior and exterior angles can be used. For example, the formula,
\text{Exterior angle of a regular polygon}=\frac{360}{n}, where n is the number of sides.
It can only be used to find the size of exterior angles of regular polygons, where all exterior angles are equal.
Practice angles in a hexagon questions
1. Calculate the exterior angle of a regular hexagon.




We can find the size of an exterior angle of any regular polygon using the formula,
\text{Exterior angle of a regular polygon}=\frac{360}{n}, where n is the number of sides.
So, the size of exterior angles of a regular hexagon can be calculated as \frac{360}{6}=60^{\circ}.
2. Calculate the sum of the interior angles of a 6 sided polygon.




We can find the sum of the interior angles of any polygon using the formula,
\text{Sum of interior angles}=(n-2) \times 180, where n is the number of sides.
So, the sum of the interior angles of a hexagon can be calculated as,
\begin{aligned} & =(n-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =(6-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =4 \times 180 \\\\ & =720^{\circ} \end{aligned}
3. The diagram shows a hexagon. Calculate the missing angle x.





To find the value of one interior angle of an irregular polygon, we first need to calculate the sum of the interior angles of the polygon.
We can find the sum of the interior angles of any polygon using the formula,
\text{Sum of interior angles}=(n-2) \times 180, where n is the number of sides.
So, the sum of the interior angles of a hexagon can be calculated as,
\begin{aligned} & =(n-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =(6-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =4 \times 180 \\\\ & =720^{\circ} \end{aligned}
Now that we know the angles inside the hexagon sum to 720^{\circ}, we can subtract the interior angles we know, to find the missing value.
x=720-(142+130+71+152+148)=77^{\circ}
4. The diagram shows a hexagon. Calculate the missing angle x.
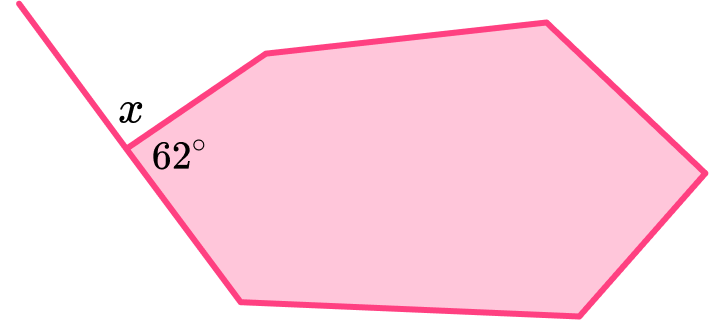




The interior and exterior angles of any polygon sum to 180, so,
x=180-62=118^{\circ}.
5. The diagram shows a hexagon. Calculate the missing angle x.
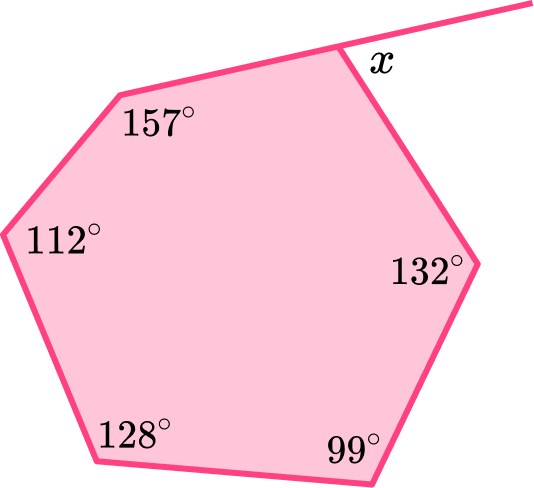




To find the size of the exterior angle, x, we need to find the missing interior angle that corresponds to it. To find the size of an interior angle of any hexagon we need to first calculate the sum of the interior angles.
To calculate the sum of the interior angles of any polygon we can use the formula,
\text{Sum of interior angles}=(n-2) \times 180, where n is the number of sides.
So, the interior angle of a hexagon can be calculated as,
\begin{aligned} & =(n-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =(6-2) \times 180 \\\\ & =4 \times 180 \\\\ & =720^{\circ} \end{aligned}
Now that we know the angles inside a hexagon sum to 720^{\circ}, we can subtract the interior angles we know to find the missing value.
y=720-(157+112+128+99+132)=92^{\circ}
Now that we know the value of the interior angle corresponding to x, we can use the fact that the interior and exterior angles of all polygons add to 180 because they form a straight line, to calculate the exterior angle.
So, x=180-92=88^{\circ}.
6. Two regular polygons meet at a vertex forming two triangles between them. Find the size of the missing angle x.
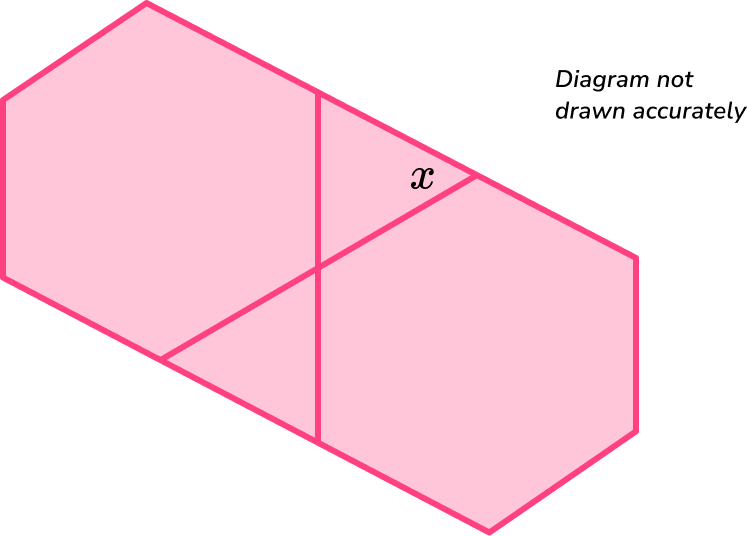




To find the size of the angle, x, we need to recognise that it is an exterior angle to the regular hexagon.
Now that we know the exterior angles of a hexagon sum to 360^{\circ}, we can divide this by the number of sides, in this case 6, to find the size of one of the exterior angles.
So, the exterior angles are
\frac{360}{6}=60^{\circ}.
Angles in a hexagon GCSE questions
1. Here is a regular polygon with 6 sides. Calculate the size of the interior angle of this shape x.
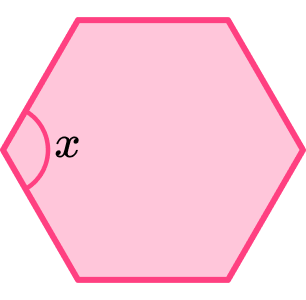
(2 marks)
(1)
120^{\circ}(1)
2. The diagram shows a hexagon. Find the missing angle x.
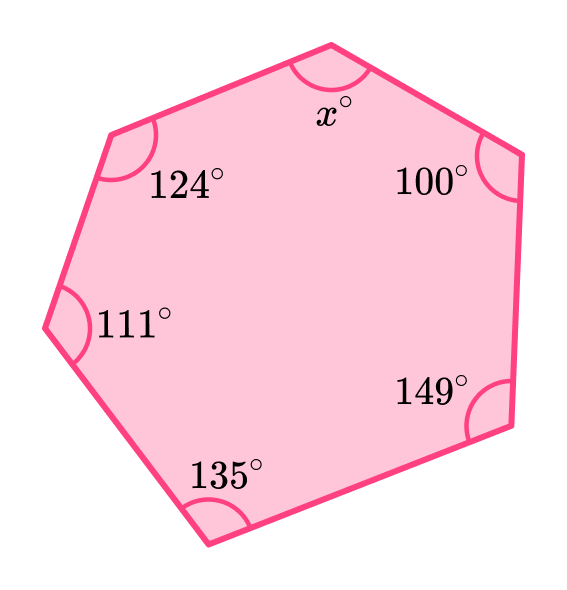
(3 marks)
(1)
720-(124+111+135+149+100)(1)
101^{\circ}(1)
3. The exterior angle of a regular polygon is 60^{\circ}. Find the number of sides the polygon has, hence, name the shape.
(2 marks)
(1)
Hexagon
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.