GCSE Tutoring Programme
Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring.
This topic is relevant for:

Types Of Angles
Here we will learn about the different types of angles including how to identify angle types and estimate them.
There are also types of angles worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are the different types of angles?
An angle is formed between two lines (rays) meeting around a common point (vertex).
They are measured in degrees and have the degree sign °.
An angle is indicated by the symbol (∠) followed by three capital letter with the middle letter as the vertex of the angle.
The name of the angle on the left is
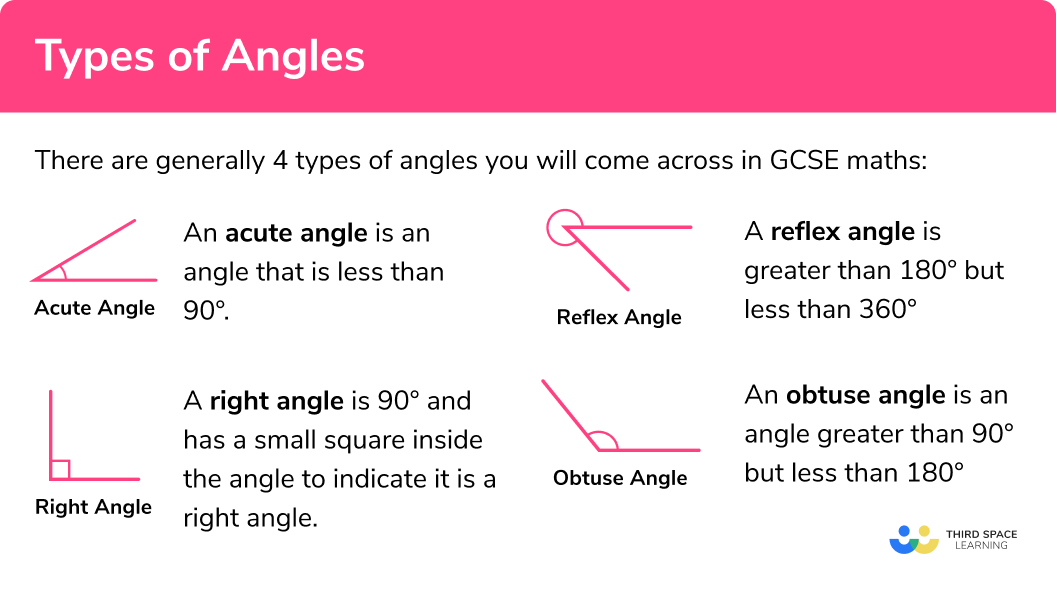
There are generally
Acute Angles – An acute angle is an angle that is less than
Obtuse Angles – An obtuse angle is an angle greater than
Reflex Angles – A reflex angle is greater than
Right Angles – A right angle is
It is also important to note:
Straight Angle – A straight angle is one-half a whole turn and is
Complete turn – A full rotation is
Did you know the word angle comes from the Latin word angulus, which means a corner?
See also: Angles in a triangle
What are the different types of angles?
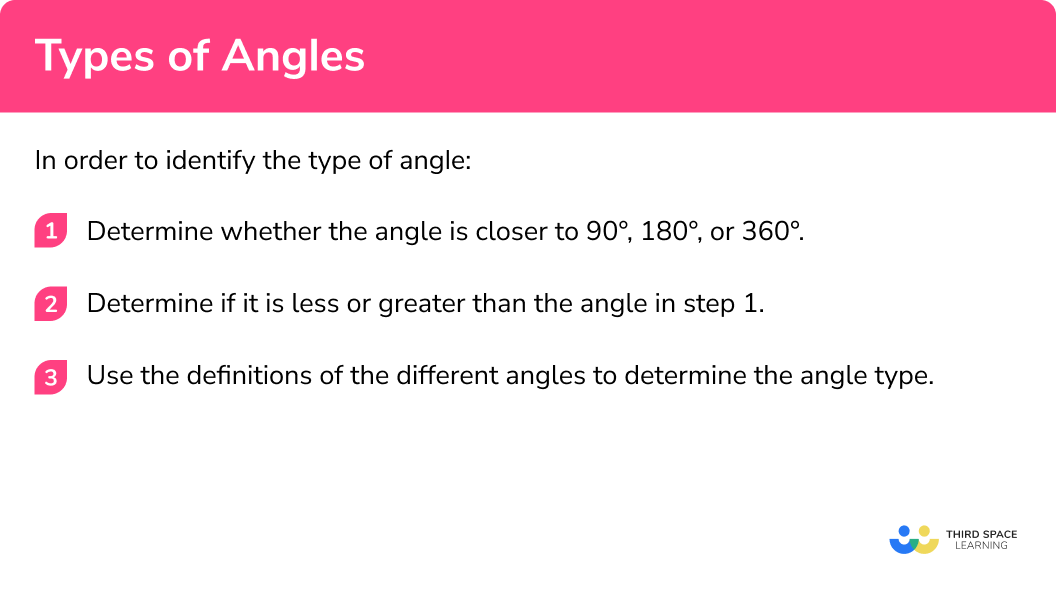
How to identify the type of angle
In order to find the angle type:
- Determine whether the angle is closer to
90° ,180° , or360° . - Determine if it is less or greater than the angle in step
1 . - Use the definitions of the different angles to determine the angle type.
How to identify the type of angle
Types of angles worksheet

Get your free types of angles worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Types of angles worksheet

Get your free types of angles worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREETypes of angles examples
Example 1: classify angle given a diagram
What type of angle is seen below?
- Determine whether the angle is closer to
90° ,180° , or360° .
On examination the above angle is closest to
2Determine if it is less or greater than the angle in step
Less than
3Use the definitions of the different angles to determine the angle type.
Since the angle is less than
Example 2: classify angle given a measure
An angle is
The angle is closest to
Since the angle is less than
Example 3: estimating the size of an angle
Estimate the size of the missing angle.
In the above example, the given angle is closer to the
Common misconceptions
- Looking at the incorrect angle in the question
Particularly when it comes to reflex angles make sure to look at the angle indicated by the arc and not the acute angle.
- Forgetting the degree sign
When measuring or estimating angles your answer must always be given in degrees.
Practice types of angles questions
1. State the name of the angle in the diagram below:

Acute angle

Right angle

Obtuse angle

Reflex angle

The mark in the corner tells us that this is 90° , so it is a right angle.
2. State the the name of the angle in the diagram below.

Acute angle

Right angle

Obtuse angle

Reflex angle

This angle is greater than 90° , and less than 180° , so it is an obtuse angle.
3. An angle is 87.8° . What type of angle is it?
Acute angle

Right angle

Obtuse angle

Reflex angle

This angle is less than 90° , so it is an acute angle.
4) An angle is 298° . What type of angle is it?
Acute angle

Right angle

Obtuse angle

Reflex angle

This angle is greater than 180° and less than 360° , so it is a reflex angle.
5. Which estimate best describes the size of the angle below:

Approximately 30°

Approximately 150°

Approximately 220°

Approximately 290°

The angle is between 270° and 360° , so 290° is a reasonable estimate.
6. Which estimate best describes the size of the angle below:

Approximately 120°

Approximately 240°

Approximately 60°

Approximately 280°

The angle is between 180° and 270° , so 240° is a reasonable estimate.
Types of angles GCSE questions
1. (a) What is the special name for the angle below:

(b) Estimate the size of the angle above.
(2 marks)
Acute angle
(1)
Accept any answer between 0° and 90°
(1)
2. Below is a trapezium.
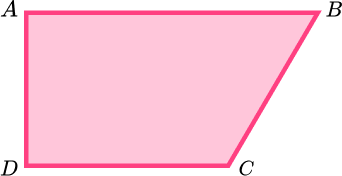
(a) Mark the acute angle with an X.
(b) Mark the obtuse angle with an O.
(c) Mark the right angle with an R.
(3 marks)
Marks ∠ABC with an X.
(1)
Marks ∠DCB with an O.
(1)
Marks either ∠BAD or ∠CDA with an R.
(1)
3.
a) What is the mathematical name of the shape below?
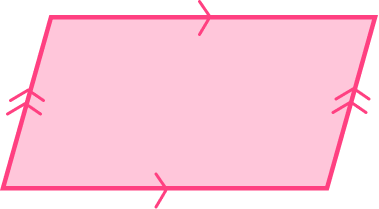
b) Estimate the size of the obtuse angles in the shape above.
(2 marks)
Parallelogram
(1)
Accept any answer between 90° and 180°.
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.