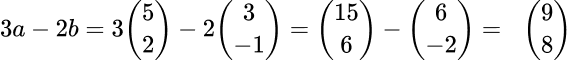GCSE Tutoring Programme
Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring.
This topic is relevant for:

Geometry – Maths GCSE
Here we will learn about geometry, including 2D shapes, angles, 3D shapes, Pythagoras theorem, trigonometry, circle theorems, vectors, loci and construction, and transformations.
There are also geometry worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is geometry?
Geometry is an area of mathematics which deals with properties of shape and measurements. The word geometry comes from Ancient Greek – “geo” meaning earth and “metron” meaning measurement.
In this page we will link to lots of other pages that will help with a variety of geometry topics.
Here are the different areas of geometry that may be examined in GCSE mathematics.
What is geometry?

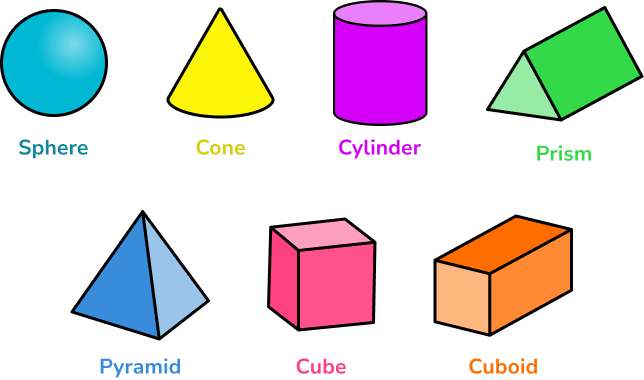
2D shapes
2D shapes are flat shapes which only have two dimensions, e.g. a length and a width.
Examples of 2D shapes are triangles, rectangles, hexagons and circles.

Step-by-step guide: 2D shapes (coming soon)
There are many different tasks you may be asked to perform involving 2D shapes.
- Symmetry
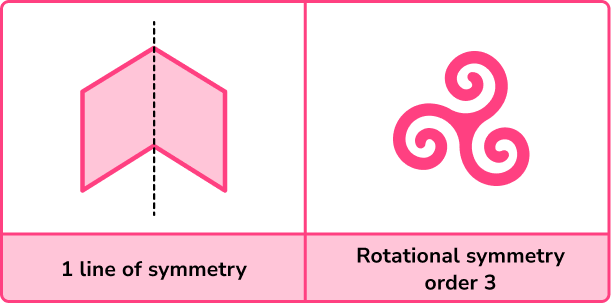
Symmetry is when a line is drawn through a shape to make one side of the line a reflection of the other. It is a property of a 2D polygon or 3D polyhedron.
There are two different types of symmetry that you need to be aware of, lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry.
Step-by-step guide: Symmetry
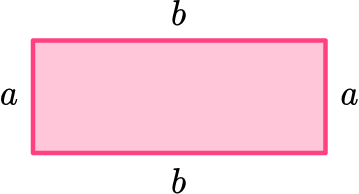
- Perimeter
The perimeter is the total distance around the outside of a 2D shape.
Step-by-step guide: How to work out perimeter
- Area
Area is a measure of how much space there is inside of a 2 dimensional shape.
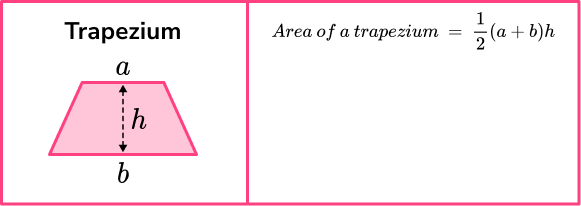
Step-by-step guide: Area
See also: How to work out area
- Circles, sectors and arcs
Circles are round plane figures whose boundaries consist of points equidistant from a fixed point.
The parts of a circle have specific names and properties which you need to know for all circle related questions.
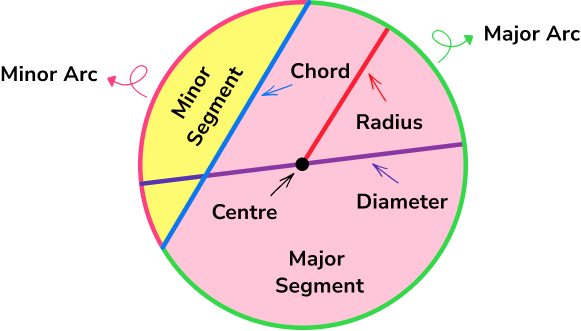
As well as the area and circumference of a circle, we can also find the area of a sector, the arc length, the perimeter of the sector, the perimeter and area of a segment and the equation of a circle.
Step-by-step guide: Circles, sectors and arcs
- Polygons
Polygons are 2D shapes made from straight lines.
You will deal with two different types of polygons.
Regular polygons
Regular polygons have specific properties, they have equal side lengths and equal internal angles.
Irregular polygons
Irregular polygons do not have equal sides and do not have equal angles.
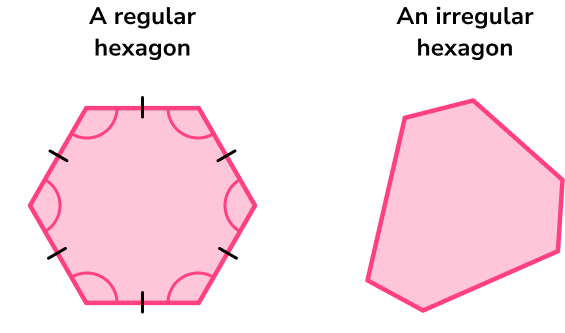
You will also need to be able to solve problems involving angles in polygons.
Step-by-step guide: Polygons (coming soon)
Geometry worksheets

Over 90 geometry worksheets ready to download and give to your GCSE students. Each with functional and applied reasoning questions and exam style questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Geometry worksheets

Over 90 geometry worksheets ready to download and give to your GCSE students. Each with functional and applied reasoning questions and exam style questions.
DOWNLOAD FREEAngles
Angles are measures of turn.
GCSE mathematics uses angles measured in degrees (^{\circ}). A full turn is 360^{\circ}.
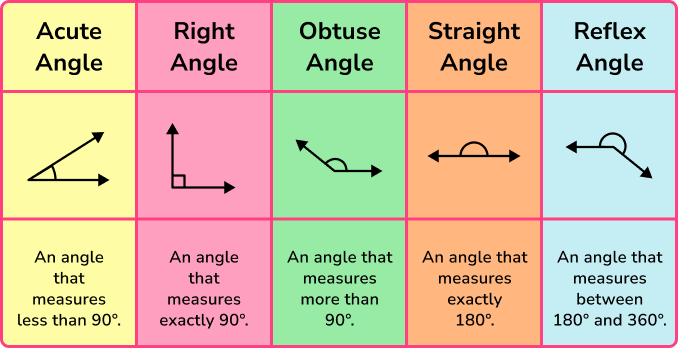
Step-by-step guide: Angles
There are many different questions in GCSE mathematics that will involve using or finding angles.
- Angle rules
Angle rules enable us to calculate unknown angles. Here are some of the important rules.
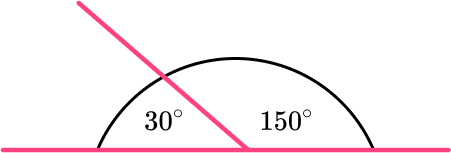
Angles on a straight line equal \bf{\underline{180^{\circ}}}
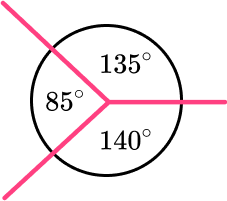
Angles around a point equal \bf{\underline{360^{\circ}}}
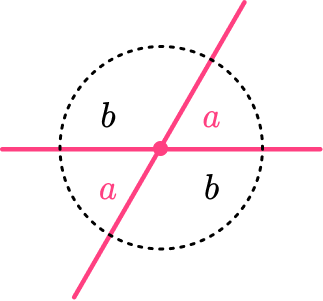
Vertically opposite angles are equal
Step-by-step guide: Angle rules
- Angles in parallel lines
Angles in parallel lines are angles that are created when two parallel lines are intersected by another line called a transversal.
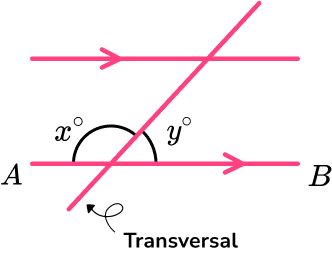
To do this we use three facts about angles in parallel lines.
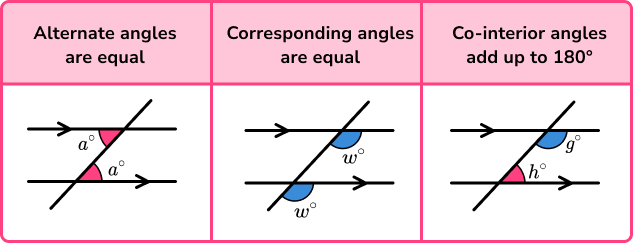
Step-by-step guide: Angles in parallel lines
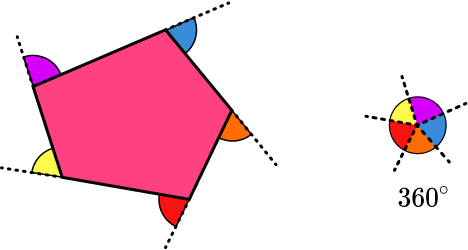
- Angles in polygons
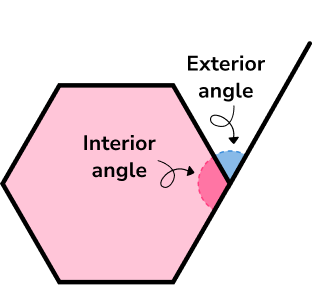
Angles in polygons relate to the interior and exterior angles of regular and irregular polygons.
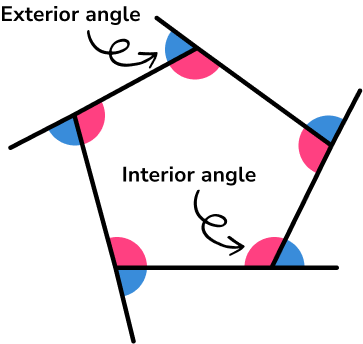
The sum of the exterior angles of a polygon is always equal to 360^{\circ} .
Interior and exterior angles add up to 180^{\circ} .
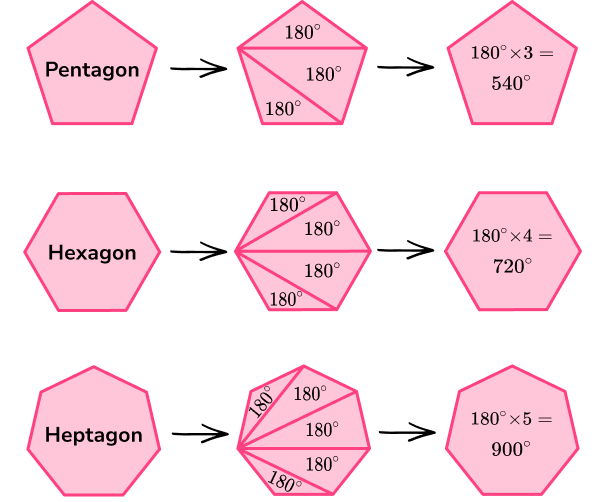
The sum of interior angles can be calculated using the formula,
Sum of interior angles = (n-2) \times 180
where n represents the number of sides.
Step-by-step guide: Angles in polygons
3D shapes
3D shapes (three-dimensional shapes) are solid shapes that have 3 dimensions, height, width and depth.
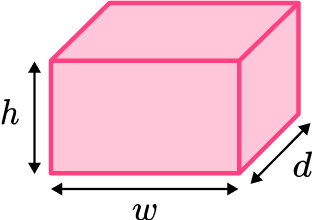
3D shapes is a broad topic which covers many different facts and skills. Here we are going to look at several sub-topics that will help us when we are working with 3D shapes.
Step-by-step guide: 3D shapes (coming soon)
- Properties of 3D shapes
The properties of 3D shapes can help to describe and classify them.
Three key properties are faces, edges and vertices which are illustrated below.
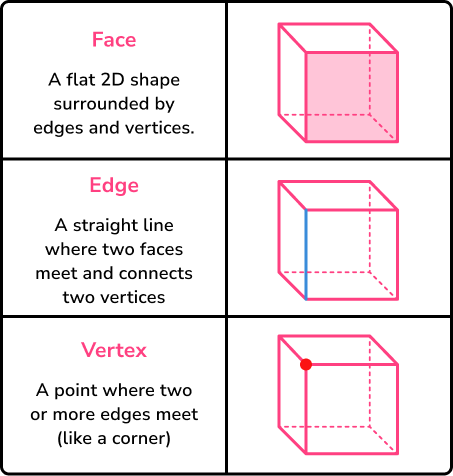
Step-by-step guide: Faces, edges and vertices
- Prisms
A prism is a 3D shape that has congruent cross sections. It is a 3D shape that can be sliced like a loaf of bread, and each slice will look like the same flat shape.
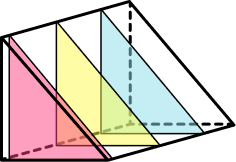
Step-by-step guide: Prism shape
- Surface area
Surface area is the total area occupied by the surface of a 3D shape.
To find the surface area of a prism or pyramid it is often helpful to draw the net of the 3D shape, calculate the area of each face, and then add them together.
Step-by-step guide: How to calculate surface area
- Volume
Volume can be understood as the amount of water that could fill a hollow version of a 3D shape. Volume is measured in cubic units. One cubic unit is the volume of water that would fill a cube with sides 1 unit in length.
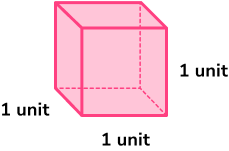
Volume = 1 \ unit^{3}
For the GCSE syllabus you will use formulas to find the volume of prisms, pyramids and spheres (higher GCSE only).
Volume of a prism = \text{area of the cross section} \times \text{depth}
Volume of a pyramid = \frac{1}{3} \times \text{base area} \times \text{height}
Volume of a sphere = \frac{4}{3} \times \pi \times radius^{3}
Step-by-step guide: How to calculate volume
- Plans and elevations
This topic is about visualising 3D shapes from different perspectives. There are three perspectives and these have been illustrated in this diagram.
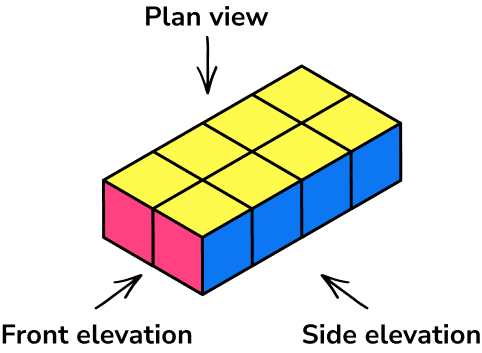
Step-by-step guide: Plans and elevations
Pythagoras theorem
Pythagoras’ theorem states that the square of the longest side of a right angled triangle (called the hypotenuse) is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Pythagoras’ theorem is a^2+b^2=c^2 .
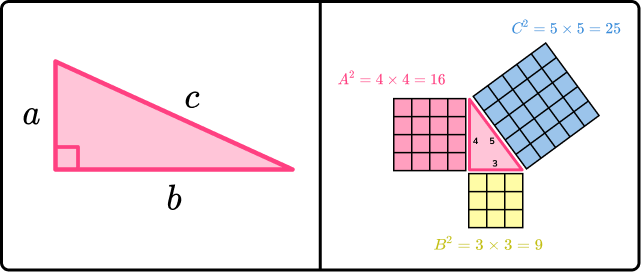
Side c is known as the hypotenuse. The hypotenuse is the longest side of a right-angled triangle. Sides a and b are known as the adjacent sides. They are adjacent, or next to, the right angle.
We can only use Pythagoras’ theorem with right-angled triangles.
Step-by-step guide: Pythagoras theorem
Trigonometry
Trigonometry is the relationship between angles and side lengths within triangles; it is derived from the Greek words “trigōnon” meaning triangle and “metron” meaning measure.
We can use trigonometry to solve problems involving right angled triangles.
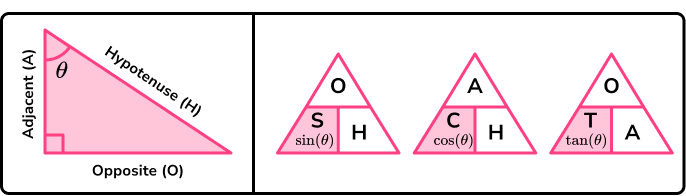
We can also use trigonometry to solve problems involving non-right angled triangles and other shapes.
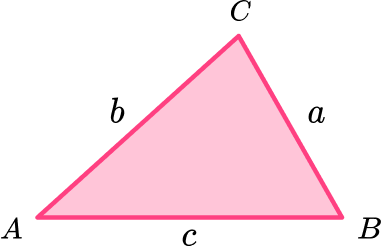
| The sine rule | The cosine rule | Area of any triangle |
|---|---|---|
| \frac{a}{\sin (A)}=\frac{b}{\sin (B)}=\frac{c}{\sin (C)} | a^{2}=b^{2}+c^{2}-2bc\cos(A) | A=\frac{1}{2}ab\sin(C) |
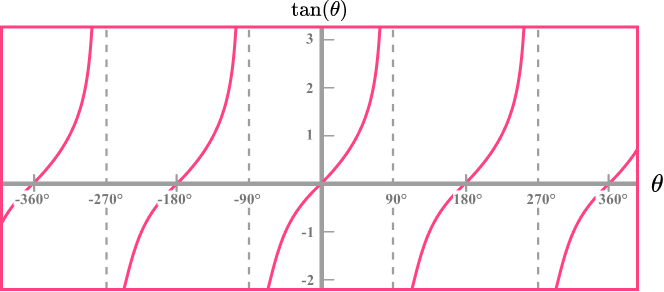
You will also need to know the graphs of the trigonometric functions.
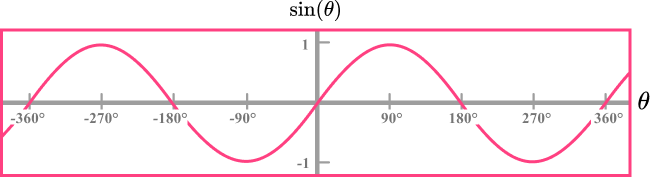
The graph of \bf{y = sin(θ)}
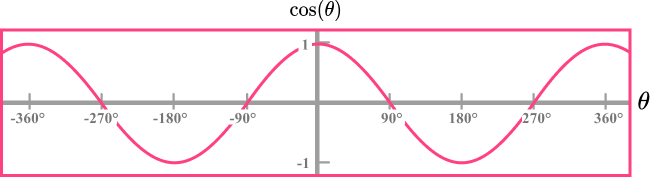
The graph of \bf{y = cos(θ)}
The graph of \bf{y = tan(θ)}
Step-by-step guide: Trigonometry
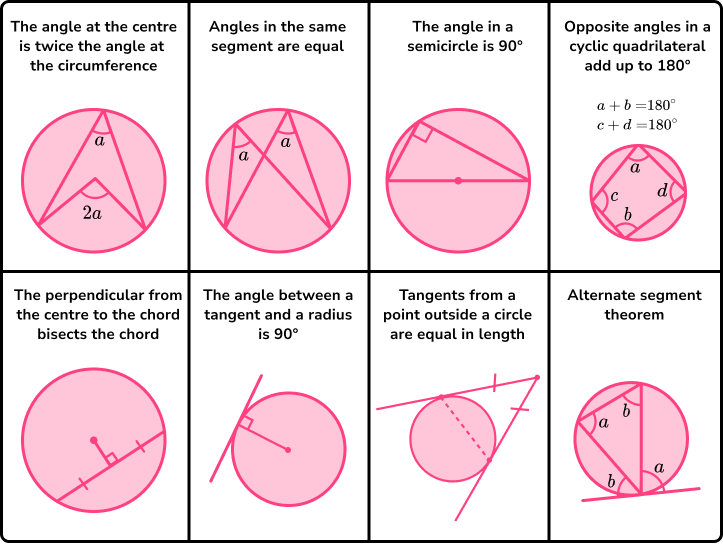
Circle theorems
Circle theorems are properties that show relationships between angles within the geometry of a circle. We can use these theorems along with prior knowledge of circles and other angle properties to calculate missing angles, without the use of a protractor.
Step-by-step guide: Circle theorems
Vectors
A vector is a quantity which has both magnitude and direction. It can be used to show a movement. A quantity which has just magnitude (size) is called a scalar.
There are many different questions in GCSE mathematics that will involve using or finding vectors.
Step-by-step guide: Vectors
- Vector notation
This diagram shows a vector representing the move from point \mathrm{A} to point \mathrm{B}.
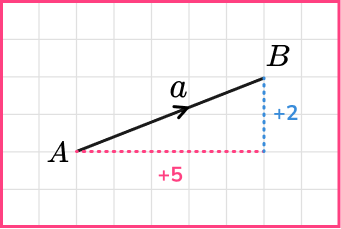
In maths we use special notation to write the vector \mathrm{A} to \mathrm{B}. Boldface is often used in textbooks.
\overrightarrow{AB} =\textbf{a}=\underline{a}Step-by-step guide: Vector notation
- Vector geometry
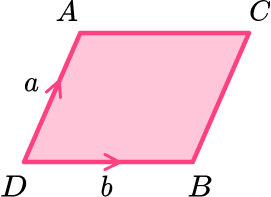
Write the vector \overrightarrow{CD} in terms of \textbf{a} and \textbf{b}.
\overrightarrow{CD}= -\textbf{a}-\textbf{b}Loci and construction
Constructions between points and lines are accurate drawings where a perpendicular line is drawn from a point to a line.
To do this we need to use a pencil, a straight-edge (a ruler) and compasses.
For example,
Loci are the set of points or regions that satisfy a property or rule.
To draw loci we will need to use constructions such as perpendicular bisectors and angle bisectors.
There are some standard loci that we will be required to be able to draw.
Step-by-step guide: Loci and construction (coming soon)
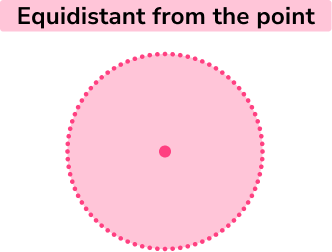
- Equidistant from a fixed point (an arc or circle)
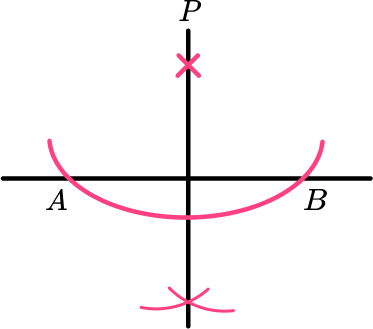
- Equidistant from two fixed points (perpendicular bisector)
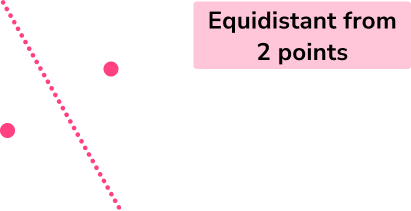
Step-by-step guide: Perpendicular bisector
- Equidistant from a straight line

- Equidistant from two intersecting straight lines (an angle bisector)
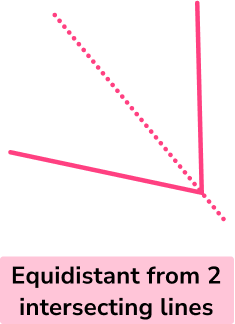
In GCSE mathematics, you may be asked to construct shapes or loci in different contexts. You may also need to combine this with knowledge of angles, bearings, scale drawings and ratio.
Step-by-step guide: Angle bisector
Transformations
Transformations change the size and/or the position of a shape.
To do this we need a 2D shape (such as a polygon) and to follow the instructions given. These instructions are sometimes known as a mapping.
There are four geometric types of transformations.
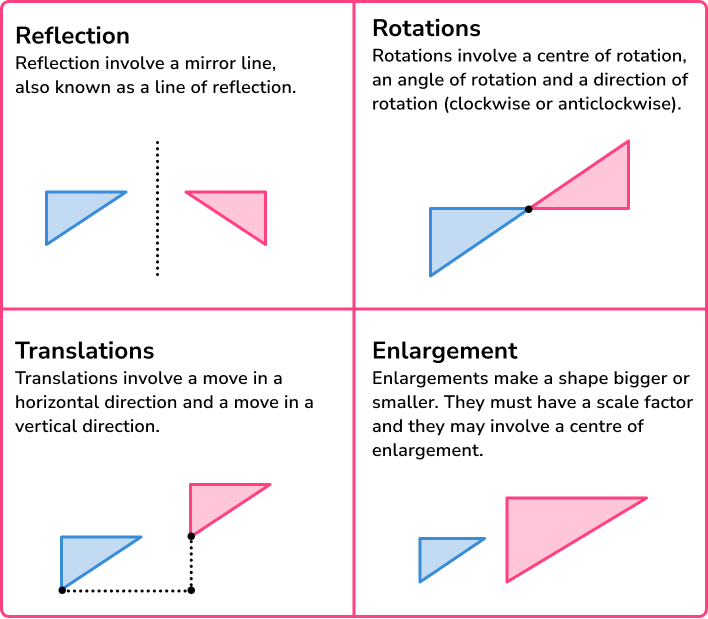
In GCSE mathematics, you may be asked to transform a shape on a coordinate axes. You may also need to describe a transformation using knowledge of column vectors, equations of straight line graphs, angles of turn or scale factors of similar shapes.
Step-by-step guide: Transformations
Common misconceptions
- Rotational symmetry/lines of symmetry
Lines of symmetry are mixed up with rotational symmetry. A line of symmetry divides the shape equally into two symmetrical pieces. A rotational symmetry is the number of times a shape fits into itself when rotated a full-turn around its centre.
- Confusing perimeter with area
Remember, perimeter is distance around the outside whilst area is the space inside the shape.
- Angles properties
Make sure you know your angle properties. Getting these confused can cause quite a few misconceptions.
– Angles in a triangle total 180^{\circ} .
– Angles in a quadrilateral total 360^{\circ} .
– Angles on a straight line total 180^{\circ} .
- Using the wrong formula
There are several formulas that are given on the formula sheet for surface area and volume. Make sure you select the right one by correctly identifying the 3D shape in the question and what it is asking you to calculate.
- Missing or incorrect units
You should always include units in your answer.
Volume is measured in units cubed (e.g. mm^{3}, \ cm^{3}, \ m^{3} etc).
Surface area is measured in units squared (e.g. mm^{2}, \ cm^{2}, \ m^{2} etc).
- Make sure you identify the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle
It is very important to make sure that the hypotenuse is correctly identified and labelled when solving problems involving Pythagoras’ theorem or trigonometry.
Practice geometry maths questions
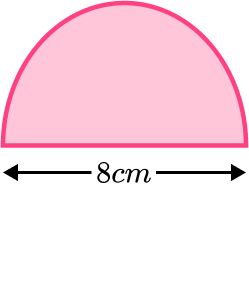
1. Find the area of the semicircle.




2. A polygon has an interior angle sum of 2520^{\circ}. Find the number of sides.




Divide 2520 by 180 and add 2.
2520\div 180 +2=14+2=16
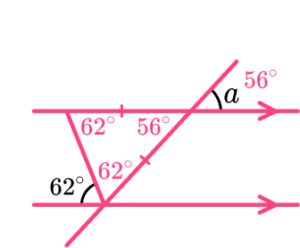
3. Find the angle a.
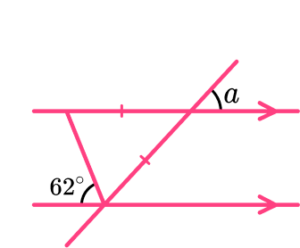




Use alternate angles, angles in an isosceles triangle and vertically opposite angles.
4. Find the volume of the prism.
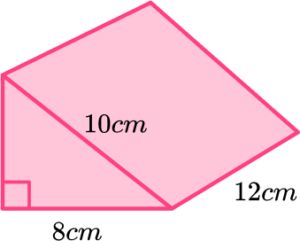




Use Pythagoras’ theorem to find the missing side of the right angled triangle (6 \ cm). Then find the area of the triangle and multiply it by 12.
\begin{aligned} &h=\sqrt{10^2-8^2}=\sqrt{36}=6 \\\\ &\text{Area}=\frac{1}{2}bh=\frac{1}{2}\times 8\times 6=24 \\\\ &\text{Volume}=24\times 12=288 \end{aligned}
5. If \bf{a}=\left( \begin{matrix} 4 \\ -3 \end{matrix} \right) and \bf{b}=\left( \begin{matrix} -2 \\ 5 \\ \end{matrix} \right) . Find 2\bf{a} -3 \bf{b} .




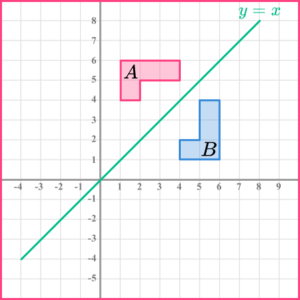
6. What is the equation of the line used to reflect \mathrm{A} onto \mathrm{B}?
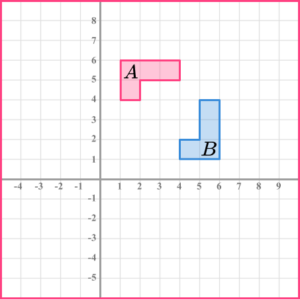




The reflection line is a diagonal line passing through the origin between both shapes. It goes through coordinates (1, 1), (2, 2), (3, 3),…. Therefore is the line y=x.
Geometry maths GCSE questions
1. The hemisphere and cone have the same volume. Find the height of the cone. Give your answer to 3 significant figures.
[The volume of a sphere = \frac{4}{3}\pi {{r}^{3}}, the volume of a cone = \frac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h ]

(3 marks)
Correct values substituted into formulas,
\frac{4}{3}\times \pi \times 5^3 \div 2 ,
or correct volume of hemisphere shown,
\frac{250}{3} \pi or 261.7993… .
(1)
A correct equation formed for h ,
\frac{250}{3}\pi=\frac{1}{3}\times \pi \times 6^2 \times h .
(1)
6.9444… = 6.94 \ cm \ (to \ 3 \ sf)(1)
2. The diagram shows triangles labelled \mathrm{P} and \mathrm{Q}.
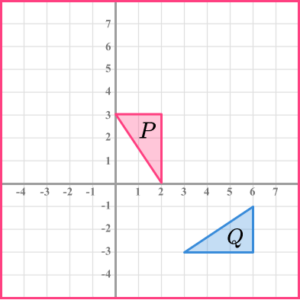
Describe the single transformation that maps \mathrm{Q} onto \mathrm{P}.
(3 marks)
Rotation
(1)
90^{\circ} anticlockwise
(1)
Centre of rotation (1, -2)
(1)
3. The diagram shows a circle centre \mathrm{O}.
\mathrm{A, B} and \mathrm{C} are points on the circumference.
\mathrm{AE} and \mathrm{CE} are tangents to the circle.
The acute angle \mathrm{AEC} = 30^{\circ}.
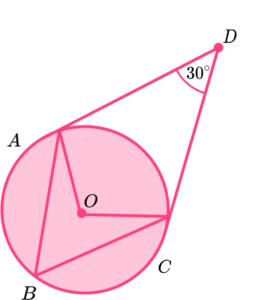
(a) State the size of angle \mathrm{OCE}, give a reason for your answer.
(b) Find the size of angle \mathrm{ABC}, give reasons for your answer.
(6 marks)
(a)
90^{\circ}
(1)
A tangent is perpendicular to the radius.
(1)
(b)
Obtuse angle AOC seen as 150^{\circ} .
(1)
Angles in a quadrilateral add up to 360^{\circ} .
(1)
Angle \mathrm{ABC} =75^{\circ}
(1)
Angle at the centre is twice the angle at the circumference.
(1)
Alternate method:
Isosceles triangle formed and angle \mathrm{ACE} given as 75^{\circ} .
(1)
Base angles in an isosceles triangle are equal.
(1)
Angle \mathrm{ABC} =75^{\circ}
(1)
Alternate segment theorem.
(1)
The most popular lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.