GCSE Tutoring Programme
Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring.
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Coordinates maths How to find the midpoint Parts of a circle Equations Quadratic equations Expanding brackets Solving equations Surds SubstitutionThis topic is relevant for:

Equation Of A Circle
Here we will learn about the equation of a circle including how to recognise the equation of a circle, form an equation of a circle given its radius and centre, use the equation of a circle to find its centre and radius, and solve problems.
There are also equation of a circle worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is the equation of a circle?
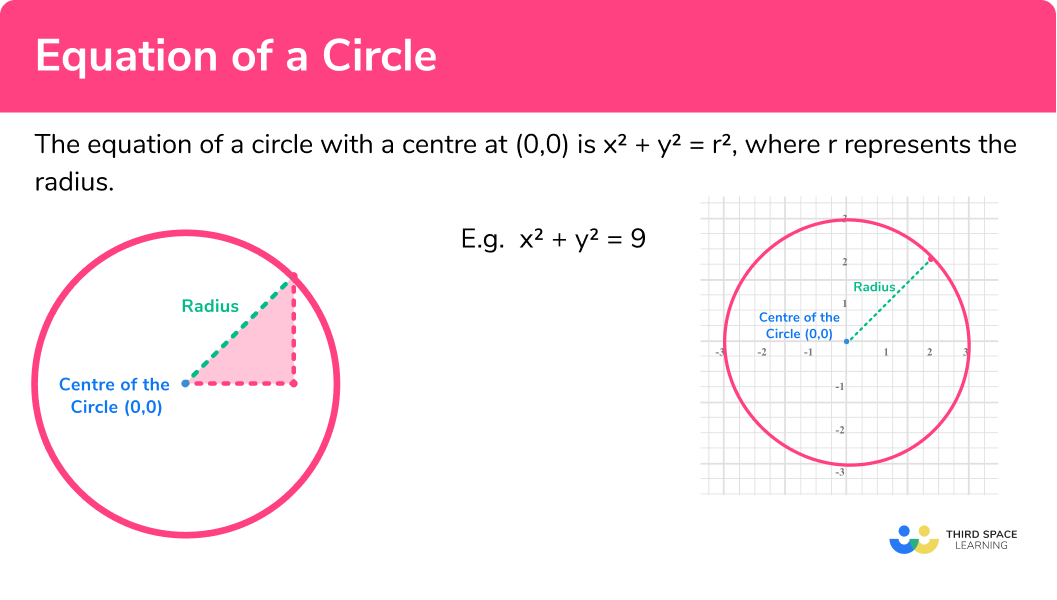
The equation of a circle is x^2 + y^2 = r^2 , where r represents the radius (with a centre at 0,0 ).
The definition of a circle is a set of all points on a plane that are a fixed distance from a centre. That distance is called the radius.
For GCSE, you need to be able to recognise and use the equation of a circle with centre at the origin so consider the drawing below of a circle on a set of axes:
Now consider a right angled triangle created when the radius of the circle is the hypotenuse of the triangle (see the below figures):
- The horizontal line is the distance to the x coordinate.
- The vertical line is the distance to the y coordinate.
- The hypotenuse is the distance of the radius.
You can now apply Pythagoras’ theorem to the above:
a^2+b^2=c^2
a = x coordinate
b = y coordinate
c = radius
Therefore the general form of the equation of a circle centred at (0,0) is:
x^2+y^2=r^2
E.g.
Draw circle with equation x^2+y^2=9
The circle has a centre at (0,0) .
9 represents r^2 , so the radius r is given by 3 .
What is the equation of a circle?
How to use the equation of a circle
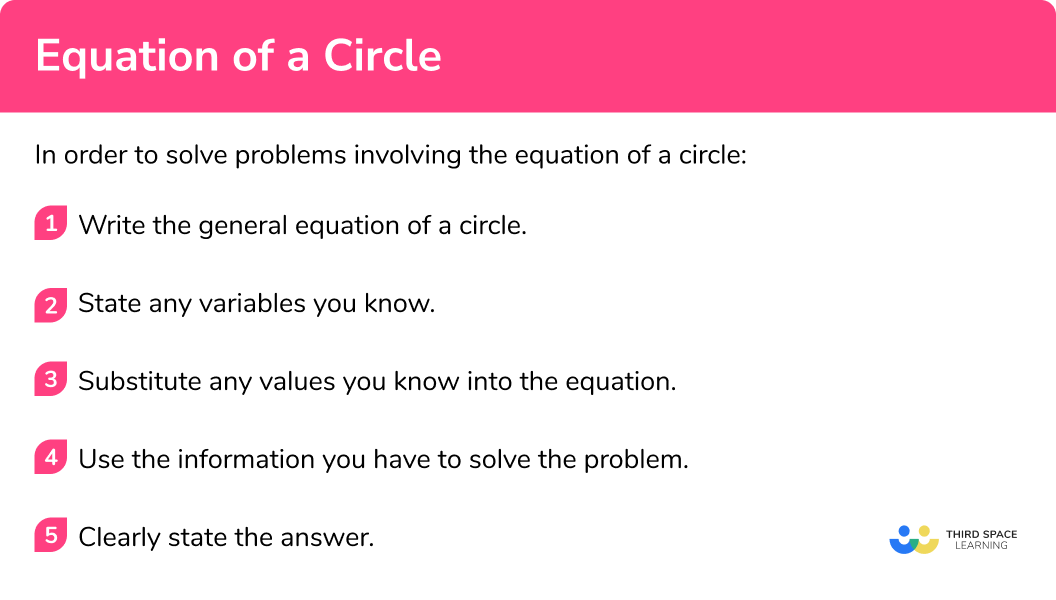
In order to solve problems involving the equation of a circle:
- Write the general equation of a circle.
- State any variables you know.
- Substitute any values you know into the equation.
- Use the information you have to solve the problem.
- Clearly state the answer.
How to use the equation of a circle
Equation of a circle worksheet

Get your free equation of a circle worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD NOW
Equation of a circle worksheet

Get your free equation of a circle worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD NOWRelated lessons on circles, sectors and arcs
Equation of a circle is part of our series of lessons to support revision on circles, sectors and arcs. You may find it helpful to start with the main circles, sectors and arcs lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Equation of a circle examples
Example 1: writing the equation of a circle with a centre at the origin
What is the equation of a circle with a radius of 3 and a centre at the origin
- Write the general equation of a circle.
2State any variables you know.
Radius = 3
3Substitute any values you know into the equation.
x^2+y^2=3^24Use the information you have to solve the problem.
5Clearly state the answer.
Equation of the circle is :
x^2+y^2=9Example 2: writing the equation of a circle with a centre at the origin
What is the equation of a circle with a radius of 1.5 and a centre at the origin.
x^2+y^2=r^2Radius = 1.5
x^2+y^2=1.5^2Equation of the circle is:
x^2+y^2=2.25Example 3: writing the equation of a circle with a centre at the origin
What is the equation of a circle with a radius of \sqrt5 and a centre at the origin.
x^2+y^2=r^2Radius = \sqrt5
x^2+y^2=\sqrt5^2Equation of the circle is:
x^2+y^2=5Example 4: finding the radius of a circle given its equation
What is the radius of the circle with the equation
x^2+y^2=4 x^2+y^2=r^2Radius is unknown
Equation of the circle is given as x^2+y^2=4
We do not know any variables so we are unable to substitute here.
We that the radius squared is equal to 4 , so
The radius is 2.
Example 5: finding the radius of a circle given its equation
What is the radius of the circle with the equation
x^2+y^2=15Give you answer to 2 decimal places.
x^2+y^2=r^2Radius is unknown. Equation of the circle is given as x^2+y^2=15
We do not know any variables so we are unable to substitute here.
We know the equation of the circle is given in the question, therefore, we can create an equation for the radius:
The question asks for the answer to be given to 2 decimal places, therefore: r = 3.87
Example 6: finding the radius of a circle given its equation
What is the radius of the following circle?
2x^2+2y^2=100Give your answer to 1 decimal place.
x^2+y^2=r^2Radius is unknown. Equation of the circle is given as 2x^2+2y^2=100
We do not know any variables so we are unable to substitute here.
We need to rearrange the equation so it is in the form:
x^2+y^2=r^2Therefore,
And so:
The question asks for the answer to be given to 1 decimal places, therefore: r=7.1
Common misconceptions
- The radius squared
Remember in the equation the radius is shown as a squared value. To find the radius you need to square root this value.
- The radius and negatives
The radius cannot be negative because as the radius is a length it must always be a positive value.
- Equation in correct form
Remember in order to apply the equation of a circle to a question it must be in the form: x^2+y^2=r^2
Practice equation of a circle questions
1. What is the equation of a circle with a radius of 4 and a centre at the origin?




2. What is the equation of a circle with a radius of 6 and a centre at the origin?




3. What is the equation of a circle with a radius of \sqrt3 and a centre at the origin?




4. What is the radius of the circle with the equation x^2+y^2=100




5. What is the radius of the circle with the equation (to two decimal places):
x^2+y^2=20




6. What is the radius of the circle with the equation (to two decimal places):
4x^2+4y^2=64




Therefore,
\begin{aligned} r^{2}=16 \\ r=\sqrt{16} \\ r=4 \end{aligned}
Equation of a circle GCSE questions
1. What is the equation of the circle with centre (0, 0) and radius of 2\sqrt3 units?
(2 marks)
2\sqrt3 being squared at any point, or 12 seen
(1)
x^2+y^2=12
(1)
2. What is the equation of the circle with centre (0, 0) and radius of \frac{2}{3} units?
(2 marks)
\frac{2}{3} being squared at any point, or \frac{4}{9} oe seen
(1)
x^2+y^2=\frac{4}{9} oe
(1)
3. Find the radius of the circle with the following equation.
Give your answer in the form a\sqrt b
(3 marks)
Divide equation by 5 or x^2+y^2=40 seen
(1)
\sqrt40
(1)
2\sqrt10
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.