What is BODMAS: Explained For Primary School (With Practice Questions)
BODMAS crops up throughout primary school maths so here we cover what BODMAS means, and provide you with some BODMAS questions and exercises you can use to help any KS2 child practise accurately carrying out BODMAS calculations.
What is BODMAS?
BODMAS is an acronym to help children remember the order of mathematical operations – the correct order in which to solve maths problems.
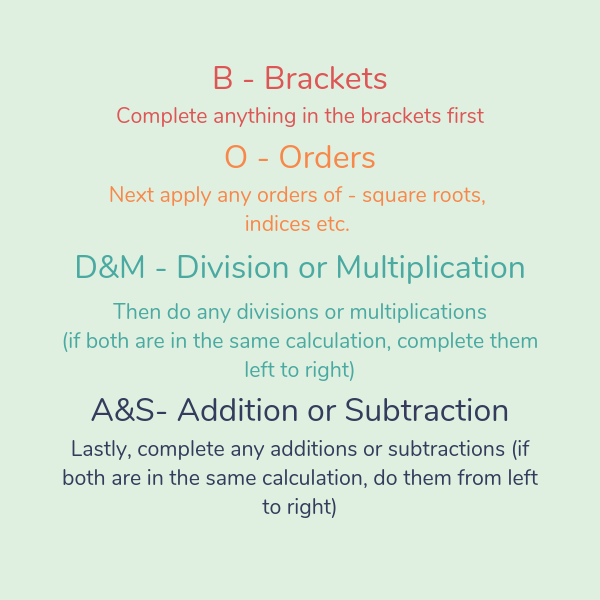
Bodmas stands for B-Brackets, O-Orders (powers/indices or roots), D-Division, M-Multiplication, A-Addition, S-Subtraction.
What is the BODMAS rule
The BODMAS rule states that division and multiplication must be done before addition and subtraction in any mathematical example. And if there are brackets (or parentheses) and orders (of powers or roots), these must be done first of all.
For example in the question 47 + 54 ÷ 9 the answer is 53 not 11.2r.
The BODMAS rule follows the order of the BODMAS acronym ie B – Brackets, O – Order of powers or roots, D – Division, M – Multiplication A – Addition, and S – Subtraction.
Mathematical expressions with multiple operators need to be solved from left to right in the order of BODMAS. Division and Multiplication are considered as interchangeable and depend on which comes first in the expression, as are Addition and Subtraction.
Some children use the Bodmas rule as a mnemonic (like Richard Of York Gave Battle In Vain is used to remember the colours Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo, Violet).
“Orders” means square roots and indices (which you may know as square numbers, powers or exponents).
Remember when you’re dealing with negative numbers that the BODMAS rule still applies. The negative sign doesn’t make a difference to the order of the mathematical operation.
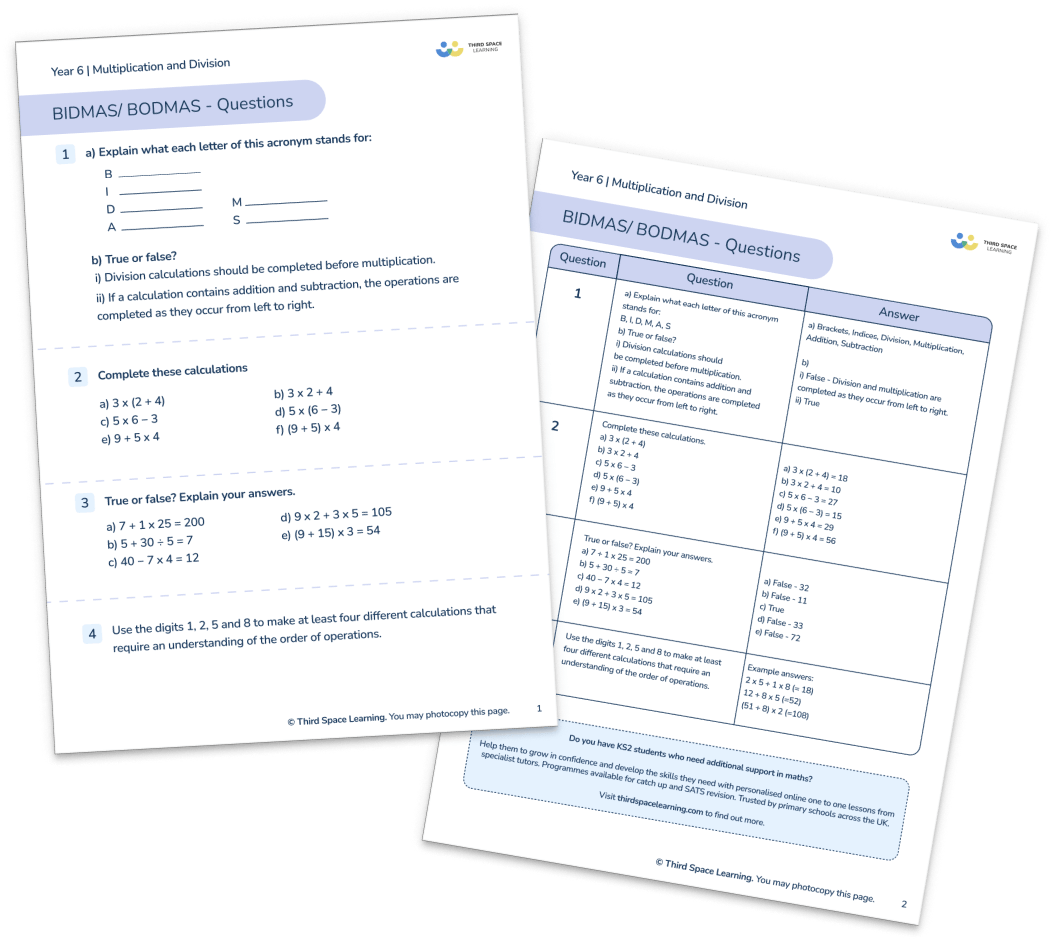
Year 6 BIDMAS or BODMAS Worksheet
Download this FREE worksheet, that includes 14 questions to practise working with BIDMAS and BODMAS.
Download Free Now!BODMAS meaning
When presented with a number sentence containing more than one operation (such as 3 + 4 x 2) the operations cannot be completed from left to right, but instead in their order of importance according to the BODMAS rule.
What is BIDMAS?
BIDMAS is an alternative acronym to BODMAS to help remember the order of operations. The only difference is that there’s an I for Indices instead of O for Order of powers. The meaning is the same. The BIDMAS rules is the one more commonly used in primary schools today.
BIDMAS stands for Brackets, Indices, Division/Multiplication, Addition/Subtraction.
BODMAS and BIDMAS can also be referred to as PEMDAS.
Mathematical operations
Mathematical operations are what you do to the numbers given. The four main operations are:
- addition (+);
- subtraction (-);
- multiplication (x);
- and division (÷).

Unlimited primary maths tutoring with Skye, the voice-based AI maths tutor.
Built on the same principles, pedagogy and curriculum as our traditional tutoring, but with more flexibility, reach and lower cost.
Join the schools already helping hundreds of primary pupils nationwide with Skye’s one to one maths tutoring.
Watch Skye in actionWhat does order of operations mean?
This is the order in which certain operations must be completed, from brackets (also known as parentheses) first to addition and subtraction last.
It is important that division and multiplication are represented alongside each other as they are of equal importance (so must be completed from left to right, whichever appears first) – this is the same for addition and subtraction.
BODMAS examples
Below are some examples of BODMAS questions and answers children might see in real life in schools. We’ve given you the right answer and at least one different answer to show you where children might make a mistake or work through BODMAS in the wrong order.
BODMAS Questions and Answers
Question 1: 6 + 2 x 7
The correct answer is 20.
The multiplication must be completed first (2 x 7 = 14) and then the addition (6 + 14 = 20).
This may be commonly miscalculated as 56 by working from left to right (6 + 2 = 8, 8 x 7 = 56).
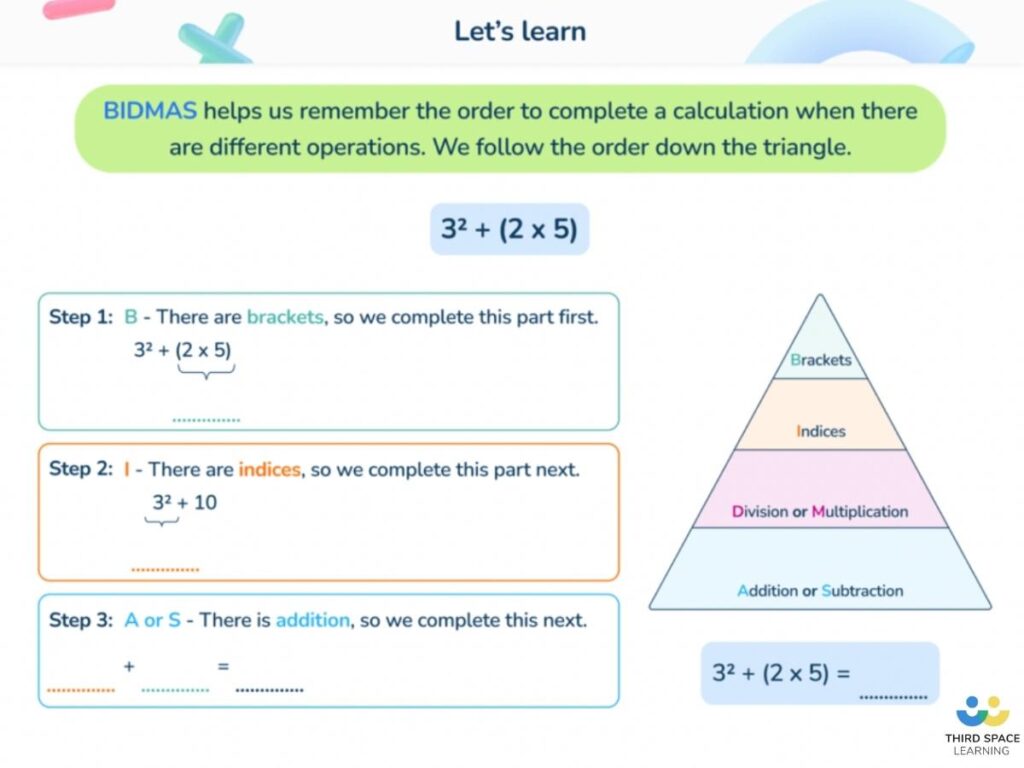
Question 2: 3 x (2 + 4) + 52
The correct answer is 43.
The BODMAS rule states we should calculate the Brackets first (2 + 4 = 6), then the Orders (52 = 25), then any Division or Multiplication (3 x 6 (the answer to the brackets) = 18), and finally any Addition or Subtraction (18 + 25 = 43).
Children can get the wrong answer of 35 by working from left to right.
Question 3: 5 – 2 + 6 ÷ 3
The correct answer is 5.
The division must be completed first (6 ÷ 3 = 2) which then leaves addition and subtraction; as both are of the same importance, we can then work from left to right. 5 – 2 + 2 (the answer to 6 ÷ 3) = 5.
This may be commonly miscalculated as either 3 by working from left to right, or as 1 by wrongly assuming that addition should be completed before subtraction.
When do children learn about BODMAS in primary school?
BODMAS is taught in upper KS2 and often primary school children won’t come across the order of operations until Year 6.
The national curriculum states that Year 6 pupils should be taught to use their knowledge of the order of operations to carry out calculations involving the four operations.
The non-statutory guidance advises that pupils explore the order of operations using brackets; for example, 2 + 1 x 3 = 5 and (2 + 1) x 3 = 9.
BODMAS calculator
For children who need some extra support to understand BODMAS, the order of operations, or the other trickier aspects of the primary maths curriculum, Third Space Learning’s AI tutor, Skye, engages with pupils spoken two-way conversation to build confidence in maths.
Learn more about primary AI maths tutoring here.
Most calculators and computers nowadays are sophisticated enough to complete calculations according to BODMAS. However it’s worth testing any calculator out just to be sure. There are also plenty of BODMAS calculators available online.
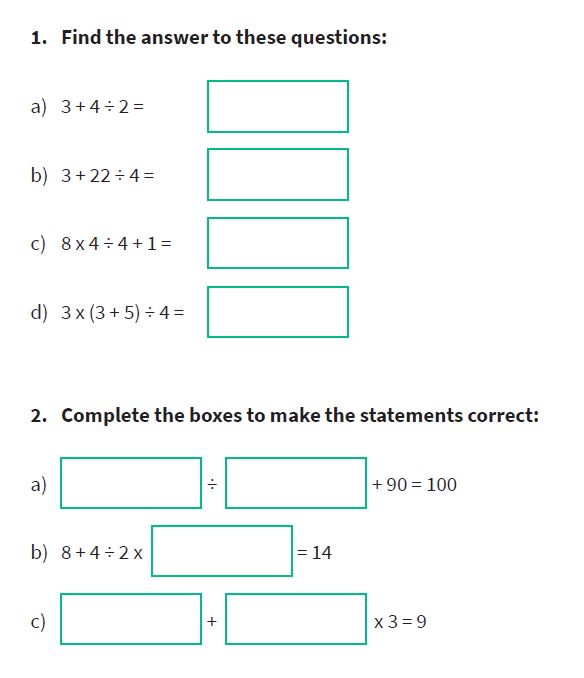
Practice KS2 BODMAS questions
1) 29 – 4 x 6 + 5 =
Answer: 10
2) Write what the two missing numbers could be. (4 + ?) x ? = 100
Answer: 6 and 10 (4 + 6) x 10 = 100
3) Write the missing numbers to make these calculations correct.
a) 200 x ? – 200 = 200
b) (100 – ?) x 100 = 100
Answers: a) 2 b) 99
4) Write the correct sign >, < or = in each of the following
a) (10 + 5) – 9 [ ] (10 + 9) – 5
b) 3 x (4+5) [ ] (3 x 4) + 5
c) (10 x 4) / 2 [ ] 10 x (4 / 2)
Answers :
a) (10 + 5) – 9 < (10 + 9) – 5
b) 3 x (4+5) > (3 x 4) + 5
c) (10 x 4) / 2 = 10 x (4 / 2)
Practice Year 6 BODMAS questions
Other primary maths curriculum topics you may need help on:
- What is a unit fraction?
- What is a number sentence?
- What is place value?
- What are number bonds?
- Properties of shapes
- What are 2D shapes?
- What are 3D shapes?
- What is long multiplication?
Or just go straight to this maths dictionary for kids for a more comprehensive overview.
DO YOU HAVE STUDENTS WHO NEED MORE SUPPORT IN MATHS?
Skye – our AI maths tutor built by teachers – gives students personalised one-to-one lessons that address learning gaps and build confidence.
Since 2013 we’ve taught over 2 million hours of maths lessons to more than 170,000 students to help them become fluent, able mathematicians.
Explore our AI maths tutoring or find out about online maths tuition for your school.