What Is Long Multiplication: Explained For Primary School Parents And Kids
Long multiplication is multiplying a number with two or more digits by a two-digit number, e.g. 34 x 27,851 x 82 or 4,274 x 93. This article explains the process for doing long multiplication following the column multiplication method used in primary schools at KS2.
What is long multiplication?
Long multiplication is a method of multiplying larger numbers together. In the primary curriculum long multiplication is taught for multiplying two, three and four digit numbers by two digit numbers.
Long multiplication methods
The mathematics appendix in the national curriculum demonstrates the formal method of long multiplication:
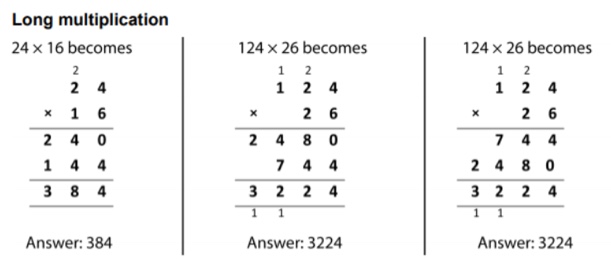
The first and third multiplication questions demonstrate the most common long multiplication methods and are explained in more detail below.
Long multiplication example: 24 x 16
16 is partitioned to become 10 and 6. 24 is multiplied by 6 first, which equals 144; 24 is then multiplied by 10 to become 240; 144 and 240 are added together to make 384.
In order to succeed at long multiplication, it is essential that children are fluent in their multiplication facts and times tables. If you have pupils in your class struggling to learn them, then we recommend trying out these times tables games as a great next step.
FREE KS2 Long Multiplication Worksheets
A series of ready-to-use worksheets to help pupils practice their long multiplication skills.
Download Free Now!Long multiplication example: 124 x 26

Here is a step by step guide to long multiplication for the second example:
- Set the question in the formal method, taking care of place value so that the ones and tens column of each line up. We’ve written 124 as the top number (multiplier) and 26 as the bottom number (multiplicand).
- Remember to start the process of multiplication with the ones place
- Multiply 6 by 4 ones
- Write the answer down correctly – including any regrouping
- Multiply 6 by 2 tens
- Add anything that you have regrouped from the previous multiplication
- Multiply 6 by 1 hundred
- Write the answer down correctly
- As we are now multiplying by 10, we show this by putting a zero as the ones column
- Multiply 2 (tens) by 4 ones
- Write the answer correctly
- Multiply 2 (tens) by 2 tens
- Write the answer down
- Multiply 2 (tens) by 1 hundred
- Write the answer correctly
- Add the two answers (sometimes known as partial products) together correctly to find the final answer
The correct answer is 3,224.
Now, all you need to do is follow these steps for any other similar long multiplication question.

Unlimited primary maths tutoring with Skye, the voice-based AI maths tutor.
Built on the same principles, pedagogy and curriculum as our traditional tutoring, but with more flexibility, reach and lower cost.
Join the schools already helping hundreds of primary pupils nationwide with Skye’s one to one maths tutoring.
Watch Skye in actionWhen will my child learn about long multiplication in primary school?
Children first learn about the long multiplication method in Year 5, where they are expected to multiply numbers up to 4 digits by one- or two-digit numbers using a formal written method, including long multiplication for two-digit numbers. This is continued in Year 6.
- In Year 5 the national curriculum objectives for multiplication and division include ‘pupils should be taught to multiply numbers up to 4 digits by a one- or two-digit number using a formal written method, including long multiplication for two-digit numbers.’
- In Year 6 the national curriculum objectives for multiplication and division include ‘pupils should be multiply multi-digit numbers up to 4 digits by a two-digit whole number using the formal written method of long multiplication.’
As children become more confident, they will need to use their multiplication knowledge to multi-step long multiplication problems.
Third Space Learning’s online one-to-one tutoring is personalised to the needs of each individual student, helping to fill in learning gaps, bringing them up to Year group level, as well as giving students more confidence in maths.
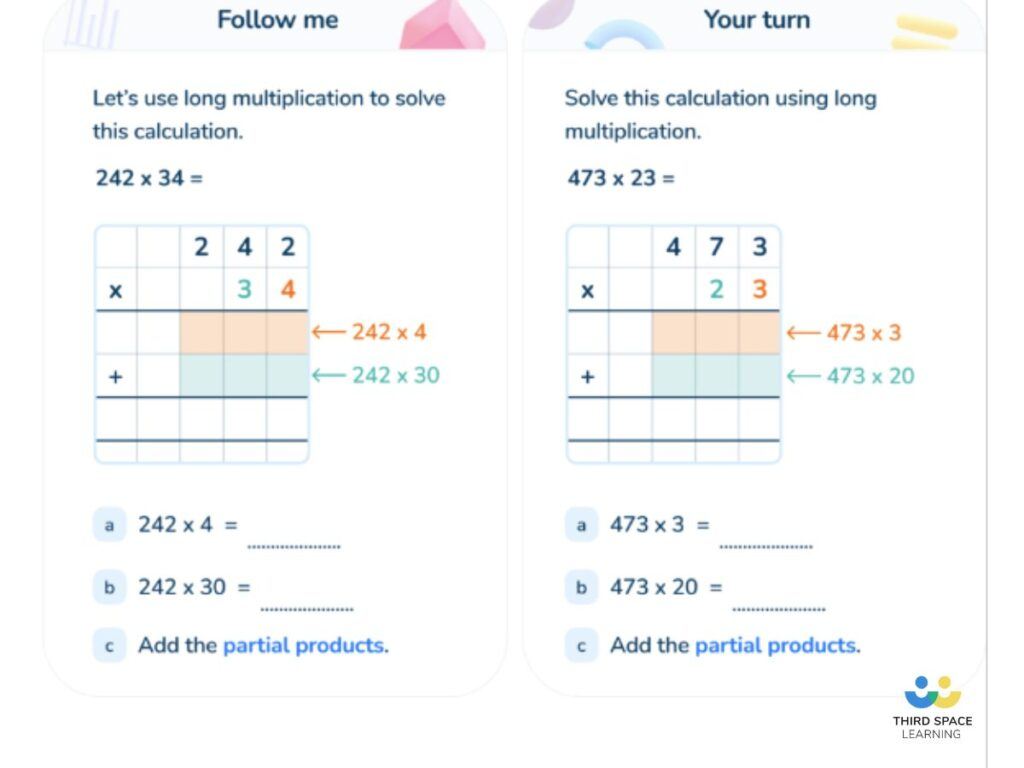
Long multiplication questions
1. 746 x 23 =
(Answer: 17,158)
2. A box contains trays of melons. There are 15 melons in a tray. There are 3 trays in a box. A supermarket sells 40 boxes of melons. How many melons does the supermarket sell?
(Answer: 15 x 3 x 40 = 1,800)
3. Write the two missing digits to make this long multiplication correct.
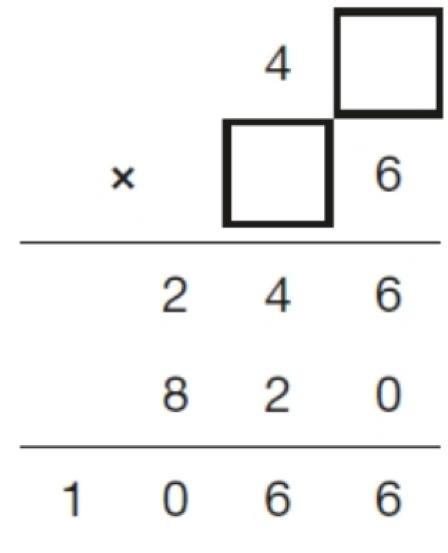
(Answer: 41 x 26)
4. A toy shop orders 11 boxes of marbles. Each box contains 6 bags of marbles. Each bag contains 45 marbles. How many marbles does the shop order in total?
(Answer: 11 x 6 x 45 = 2,970)
5. A shop sells sheets of sticky labels. On each sheet there are 36 rows and 18 columns of labels. How many labels are there altogether on 45 sheets?
(Answer: 36 x 18 x 45 = 29,160)
Long multiplication, also called column multiplication, is a method of multiplication, usually used for 3-digit and larger numbers.
Short multiplication is the method recommended when multiplying a 3-digit or larger number with a 1-digit number. Long multiplication is more often used when multiplying numbers that are both at least 2-digit.
Long multiplication is most often introduced in Year 5.
If you do need to track back to establish a more solid base in multiplication then, there is a bootcamp for multiplication or a more comprehensive guide to teaching multiplication to each year group throughout KS2. Keeping your pupils engaged whilst helping them develop their multiplication skills is also important, so we created a blog on the best multiplication games to play at KS1 and KS2.
Looking for more information on teaching multiplication?
DO YOU HAVE STUDENTS WHO NEED MORE SUPPORT IN MATHS?
Skye – our AI maths tutor built by teachers – gives students personalised one-to-one lessons that address learning gaps and build confidence.
Since 2013 we’ve taught over 2 million hours of maths lessons to more than 170,000 students to help them become fluent, able mathematicians.
Explore our AI maths tutoring or find out about online maths tuition for your school.