High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
Math nets
Here you will learn about nets of 3D shapes and how they are used to calculate surface area.
Students will first learn about nets in the 6 th grade with their work with 3D solids and finding surface area. They will expand this knowledge as they progress through middle school and high school.
Every week, we teach lessons on math nets to students in schools and districts across the US as part of our online one-on-one math tutoring programs. On this page we’ve broken down everything we’ve learnt about teaching this topic effectively.
What are math nets?
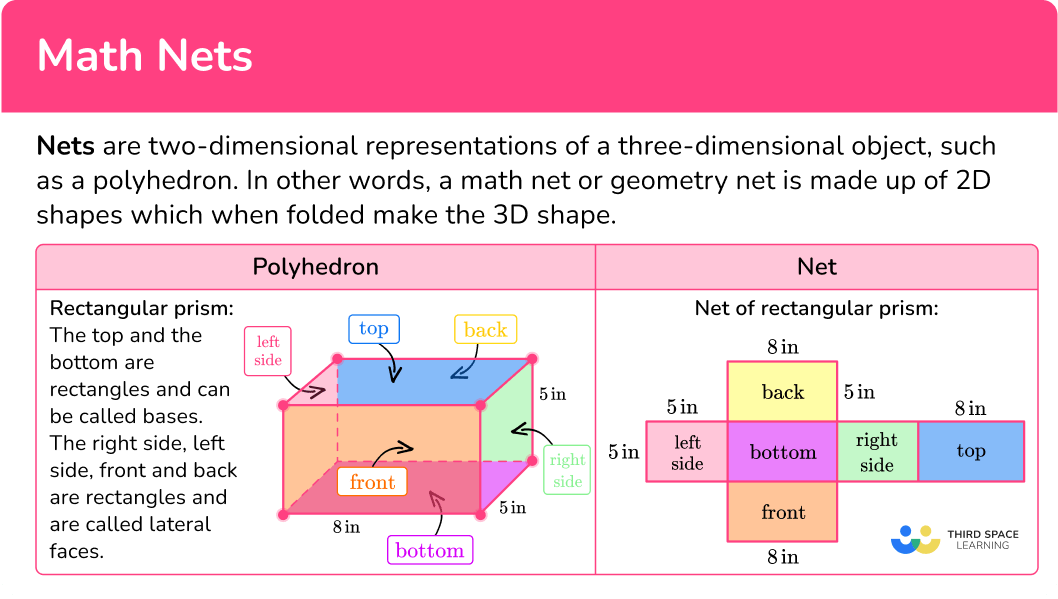
Nets are two-dimensional representations of a three-dimensional object, such as a polyhedron. In other words, a math net or geometry net is made up of 2D shapes which when folded make the 3D shape.
Let’s take a look at nets of the polyhedrons that are common.
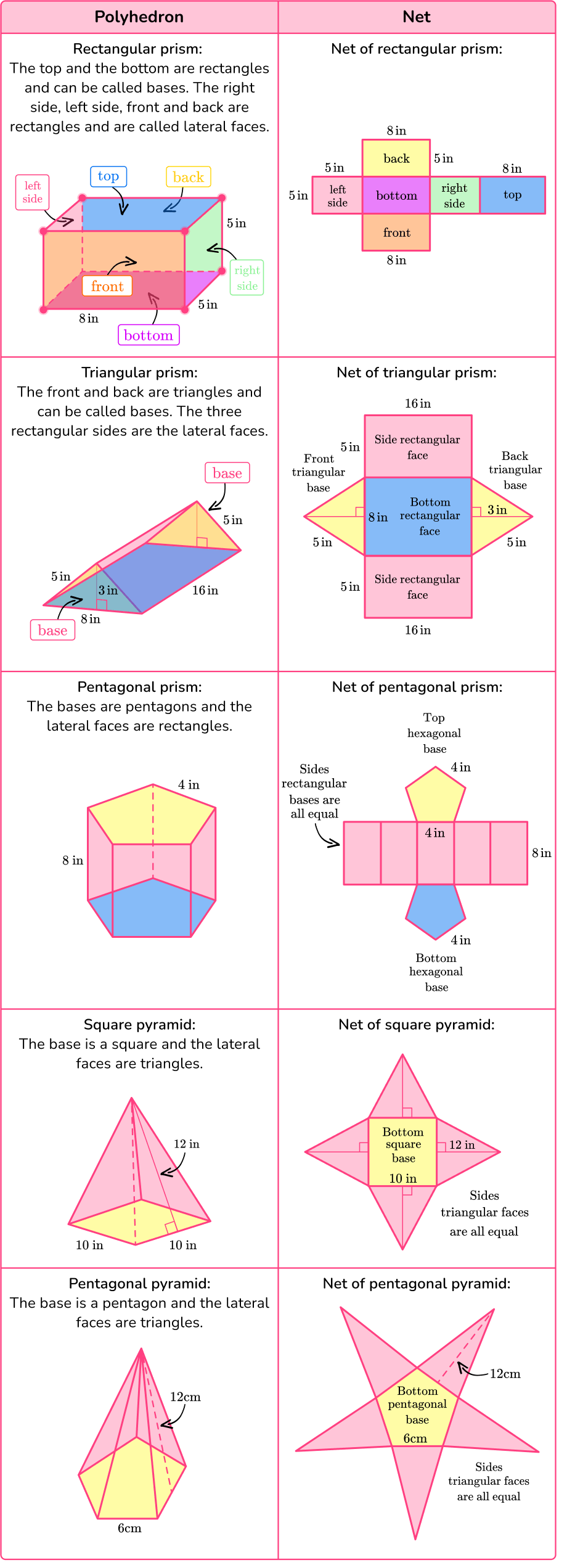
Nets can be used to calculate the surface area of three-dimensional shapes.
For example,
Here is a rectangular prism and its net.
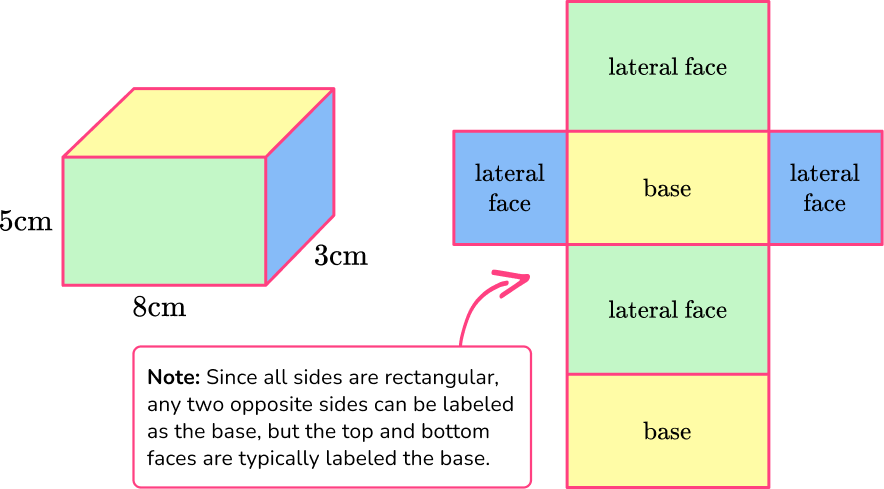
It has 3 pairs of congruent faces since the opposite faces are the same.
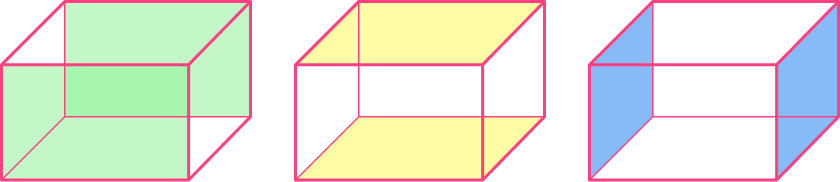
To calculate the surface area of the rectangular prism, calculate the area of each face and then add them together.
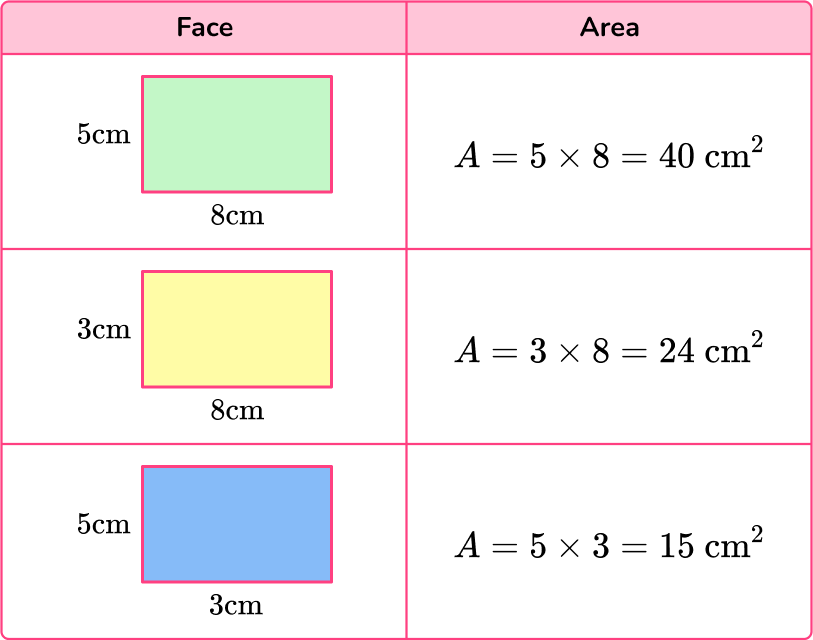
The surface area of the prism is the sum of the areas. You can multiply each area by 2 and then add them together, or you can add each area twice since each rectangle appears twice in the prism:
\begin{aligned} & 2 \times 40+2 \times 24+2 \times 15= \\\\ & 80+48+30=158 \mathrm{~cm}^2 \end{aligned}
OR
40+40+24+24+15+15=158\mathrm{~cm}^2
The surface area of the rectangular prism is equal to 158 \mathrm{~cm}^2.
Note: Surface area is measured in square units. For example, \mathrm{mm}^2, \mathrm{~cm}^2, \mathrm{~m}^2 etc.
What are math nets?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6 th grade math?
- Grade 6 – Geometry (6.G.A.4)
Represent three-dimensional figures using nets made up of rectangles and triangles, and use the nets to find the surface area of these figures. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems.
![[FREE] Math Nets Worksheet (Grade 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Math-Nets-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Math Nets Worksheet (Grade 6)
![[FREE] Math Nets Worksheet (Grade 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Math-Nets-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your 6th grade students’ understanding of math nets. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Math Nets Worksheet (Grade 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Math-Nets-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Math Nets Worksheet (Grade 6)
![[FREE] Math Nets Worksheet (Grade 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Math-Nets-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your 6th grade students’ understanding of math nets. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEHow to draw the net of a 3D solid
In order to draw the net of a 3D solid:
- Identify all the sides of the 3D solid.
- Draw the base.
- Draw the lateral sides and have them connect to the base.
- If the 3D figure is a prism, draw the second base so that it is connected to one of the lateral sides.
Math nets examples
Example 1: draw a net from a rectangular prism
Draw the net representing this rectangular prism.
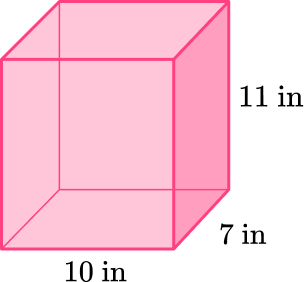
- Identify all the sides of the 3D solid.
There are 6 sides of this rectangular prism.
The bottom (base) is a rectangle with dimensions of 10 inches \times \, 7 inches.
The top (base) is equal to the bottom.
The right side is a rectangle that is 7 inches by 11 inches.
The left side is equal to the right side.
The front is a rectangle with dimensions of 10 inches \times \, 11 inches.
The back is equal to the front.
2Draw the base.
3Draw the lateral sides and have them connect to the base.
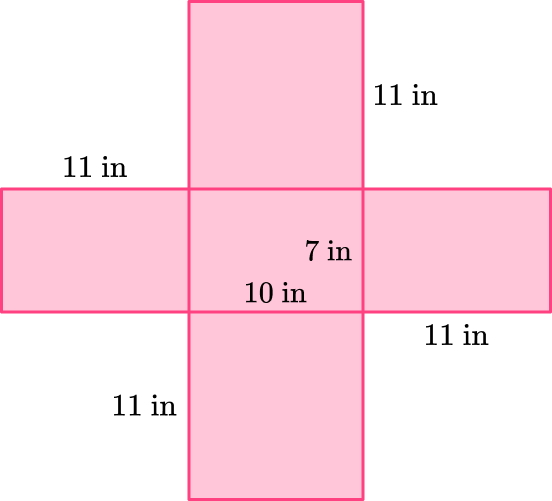
4If the 3D figure is a prism, draw the second base so that it is connected to one of the lateral sides.
This is a rectangular prism so it has a second base that has dimensions 10~{in} \times 7~{in}.
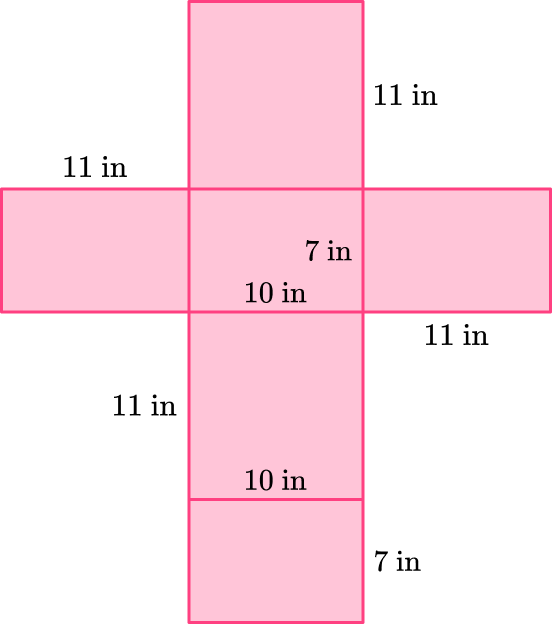
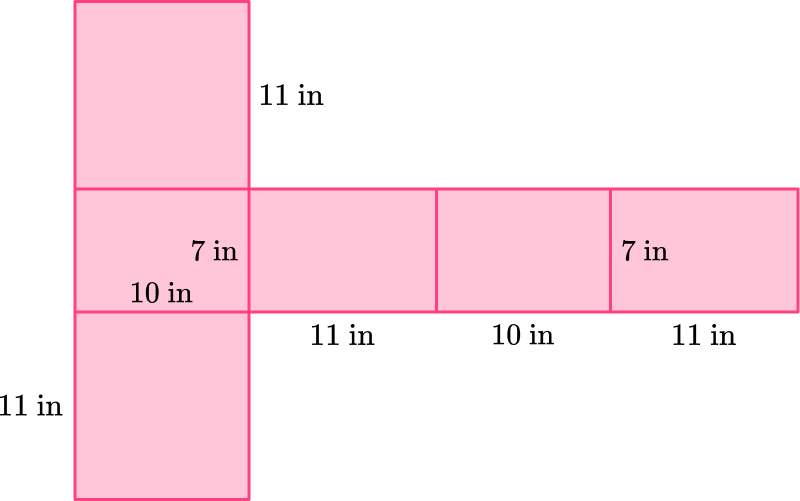
Note: The rectangular prism can be unfolded different ways. For example,
Example 2: draw a net from a hexagonal prism
Draw a net representing this hexagonal prism.
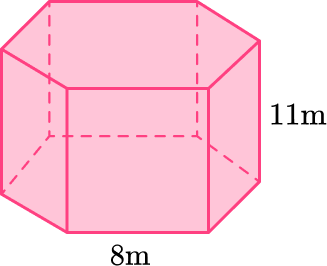
The bases are regular hexagons which means the hexagons have equal measure sides and angles.
There are six lateral sides that are rectangles. Since the base is a regular hexagon, the dimensions of each of the rectangular lateral faces is 8~{m} \times 11~{m}.
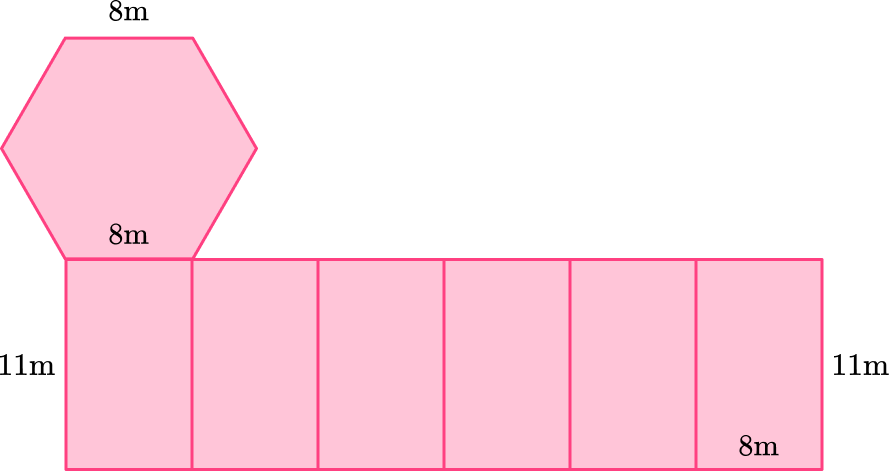
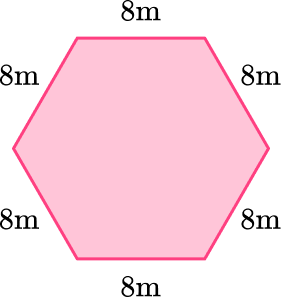

The side of the hexagon base matches up with the shorter side of the rectangular face so they can be connected. You can connect the hexagon base to any of the rectangles.
This is a hexagonal prism so there are two hexagon bases that are equal.
The second hexagon base can be connected to the rectangular as long as it’s on the other side. It can be drawn like this:
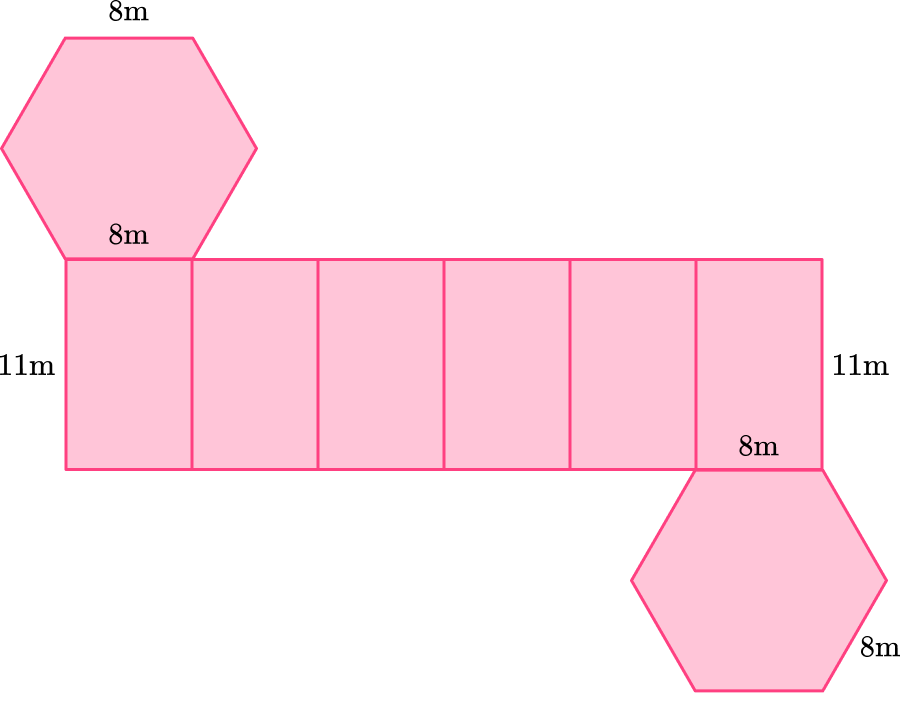
You can also draw it like this:
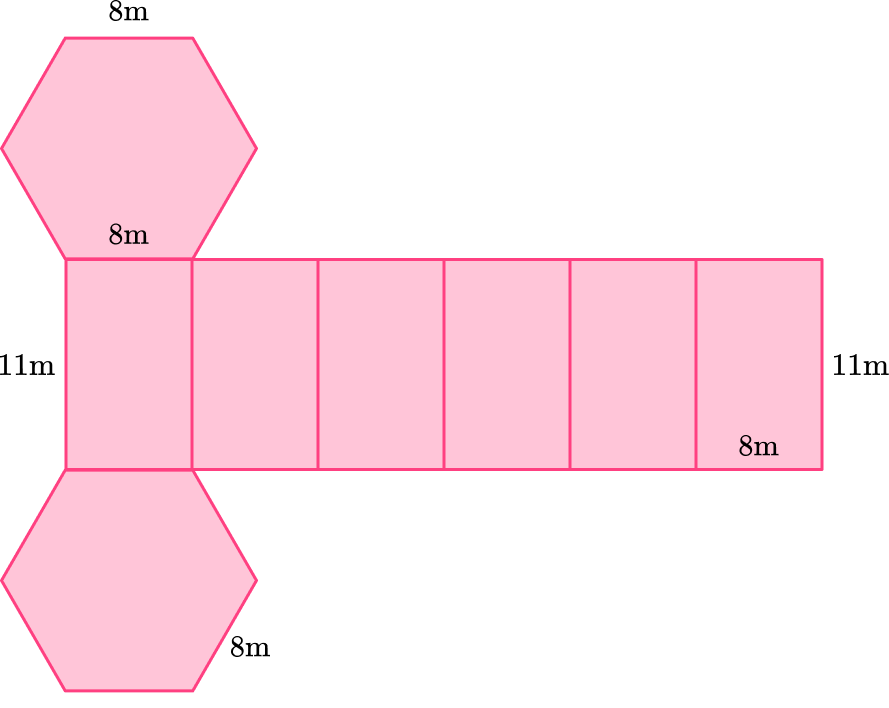
Or even like this:
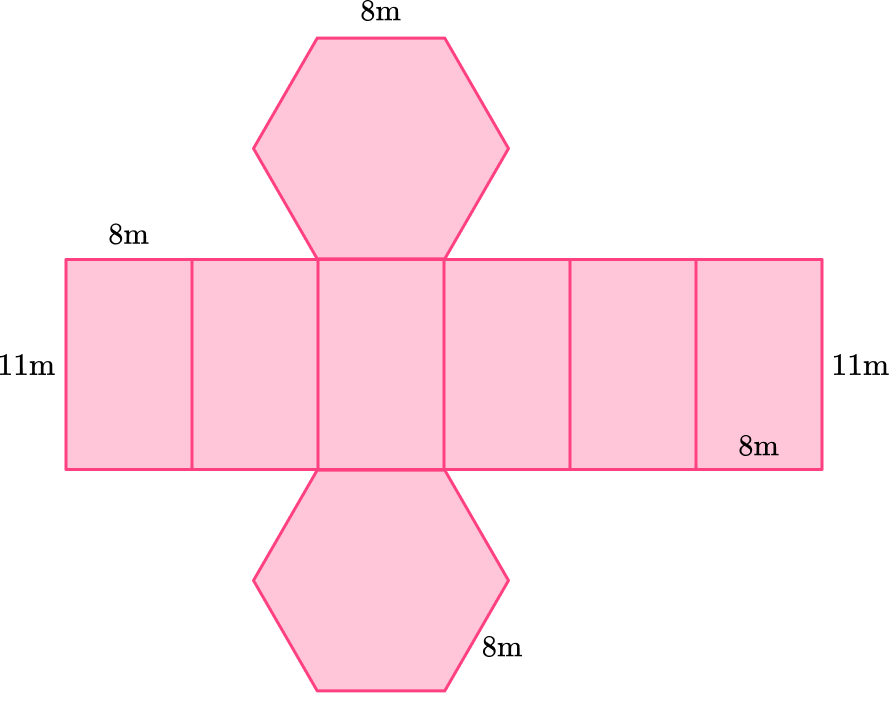
Example 3: draw a net from a square pyramid
Draw a net representing the pyramid below.
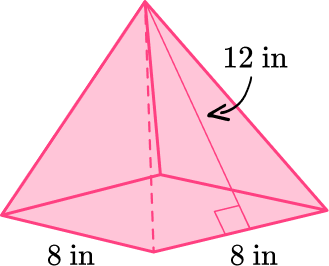
The base is a square that has dimensions 8~{in} \times 8~{in}.
There are four lateral sides that are triangles.
The triangles are all equal and have a base length of 8~{in} and a height of 12~{in}.
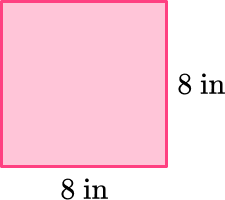
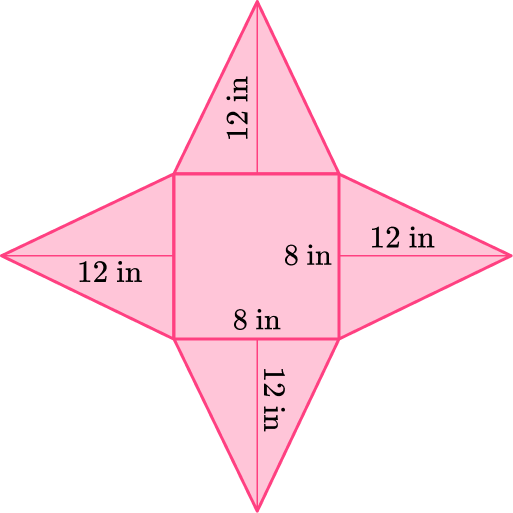
The solid is a pyramid, so it only has one base.
How to calculate the surface area from a net
In order to calculate the surface area of 3-D solids using nets:
- Identify the dimensions of each of the faces.
- Calculate the area of each face.
- Add the areas of the faces together.
- Include the units.
Example 4: find surface area of the prism using nets
The net of a rectangular prism is given. Find the surface area of the prism.
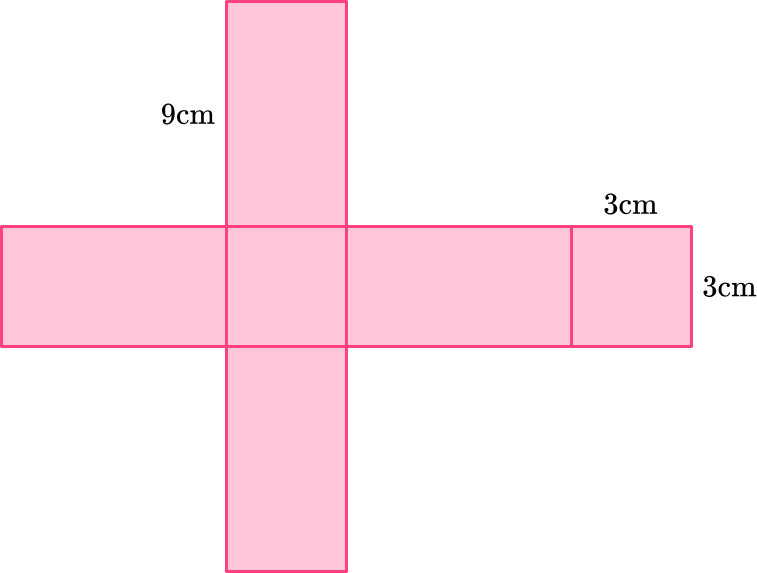
Two bases are squares with dimensions 3~{cm} \times 3~{cm}.
The four lateral faces are rectangles with dimensions 9~{cm} \times 3~{cm}.
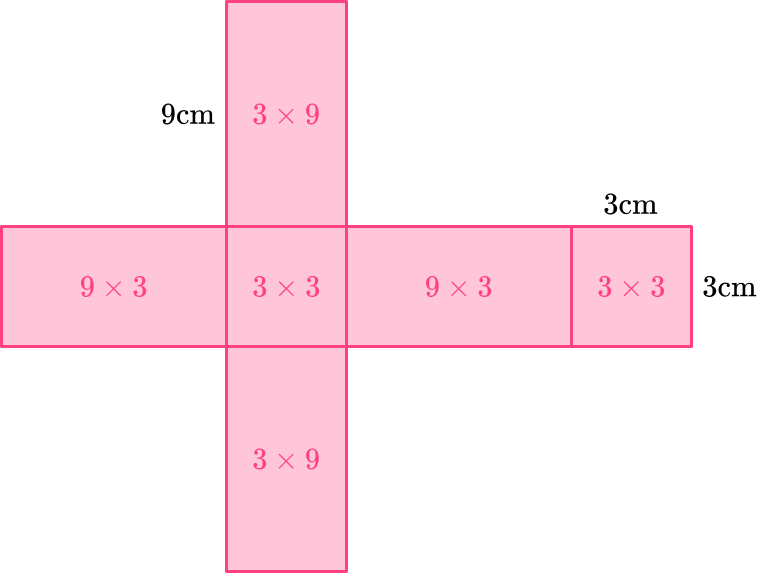
Each of the four lateral faces are rectangles with dimensions 3 \times 9.
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Area of rectangle }=b \times h \\\\
& \text { Area of rectangle }=3 \times 9 \\\\
& \text { Area of rectangle }=27
\end{aligned}
Since all four of the lateral faces are equal, multiply the area by 4.
27 \times 4=108
The bases are squares with dimensions 3 \times 3. Since the bases are equal, find the area of one of them and multiply it by 2.
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Area of square }=b \times h \\\\
& \text { Area of square }=3 \times 3 \\\\
& \text { Area of square }=9
\end{aligned}
2 \times 9=18
108+18=126
Note:
You can also just add up all the areas of each of the sides instead of multiplying the area of the lateral face by 4 and the bases by 2.
27+27+27+27+9+9=126
The surface area of this rectangular prism is 126 \mathrm{~cm}^2
Example 5: find the surface area of the prism using nets
The net of a triangular prism is given. Find the surface area (the triangular bases are equilateral triangles).
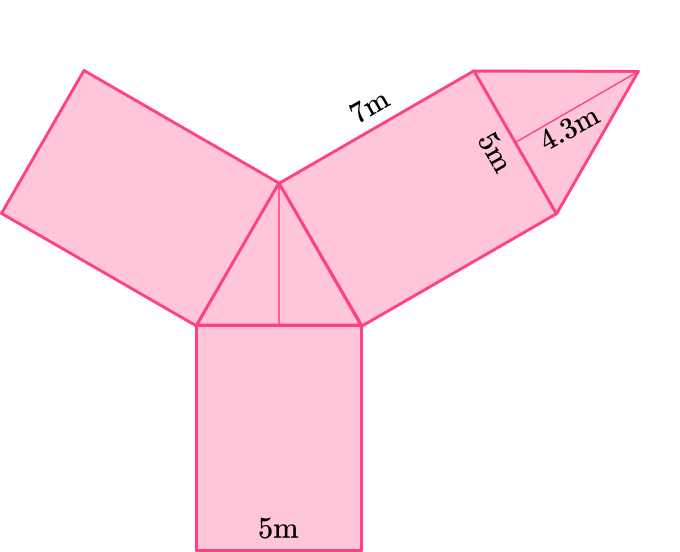
There are two triangular bases that are equal. The base length is 5~{m} and the height is 4.3~{m}.
There are three rectangular lateral faces that are equal. The base of the rectangles is 5~{m} and the height of the rectangle is 7~{m}.
Since the bases are triangles that are equal. Find the area of one and multiply it by two.
\begin{aligned} & \text { Area of triangle }=\cfrac{1}{2} \times b \times h \\\\ & \text { Area of triangle }=\cfrac{1}{2} \times 5 \times 4.3 \\\\ & \text { Area of triangle }=10.75 \end{aligned}
2 \times 10.75=21.5
Since all three lateral faces are equal, find the area of one and then multiply it by 3.
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Area of rectangle }= b \times h \\\\
& \text { Area of rectangle }= 5 \times 7 \\\\
& \text { Area of rectangle }=35
\end{aligned}
3 \times 35=105
21.5+105=126.5
The surface area of this triangular prism is 126.5~{m}^2
Example 6: find the surface area of the pyramid using nets
The net of a pyramid is given. Find its surface area.
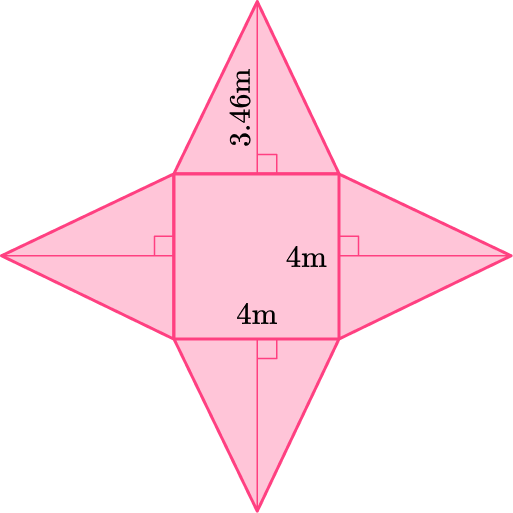
There is one square base with dimensions 4~{m} \times 4~{m}.
There are four equal triangular lateral faces. The height is 3.46~{m} and the base is 4~{m}.
There is only one base which is a square.
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Area of square }=b \times h \\\\
& \text { Area of square }=4 \times 4 \\\\
& \text { Area of square }=16
\end{aligned}
The lateral faces are triangles and they are all equal. Find the area of one lateral face and multiply it by 4.
\begin{aligned}
& \text { Area of triangle }=\frac{1}{2} \times b \times h \\\\
& \text { Area of triangle }=\frac{1}{2} \times 4 \times 3.46 \\\\
& \text { Area or triangle }=6.92 \\\\
& 4 \times 6.92=27.68
\end{aligned}
16+27.68=43.68
The surface area of the pyramid is 43.68 \mathrm{~m}^2
Teaching tips for the math net
- Make sure that students have had time to work with physical 3 D models and nets before asking them to solve with surface area.
- Have learners create their own net from a 3 D solid using paper or cardboard, and then have them fold the net to see if it matches the 3 D solid.
- Although printable worksheets and interactive digital platforms have their place in the classroom for extra practice, infusing activities where students have the opportunity to create different types of nets will help them to formulate a deep understanding of the topic.
Easy mistakes to make
- Having difficulty visualizing the 2D net from a 3D solid
The two dimensional net of a three dimensional solid can sometimes be difficult for students to visualize. Using strategies such as taking steps to first identify the bases and then identify the lateral faces can be helpful.
- Interpreting surface area as volume and using a cubed dimension
Surface area is the total area of all the faces of a geometric solid. In other words, it is the sum of the areas of each of the sides or faces. Since surface area is total area, it will always have a square dimension not a cubic dimension like volume. Using nets helps to reinforce the concept of surface area because it allows for students to see the 2 D shapes as flat surfaces which helps them to understand surface area.
- Confusing lateral area with total surface area
Lateral area is the area of each of the sides and total surface area is the area of the bases plus the area of the sides. When asked to find lateral area, be sure to only add up the area of the sides – which are always rectangles in a prism and triangles in a pyramid.
Practice math net questions
1) Which solid represents the net?
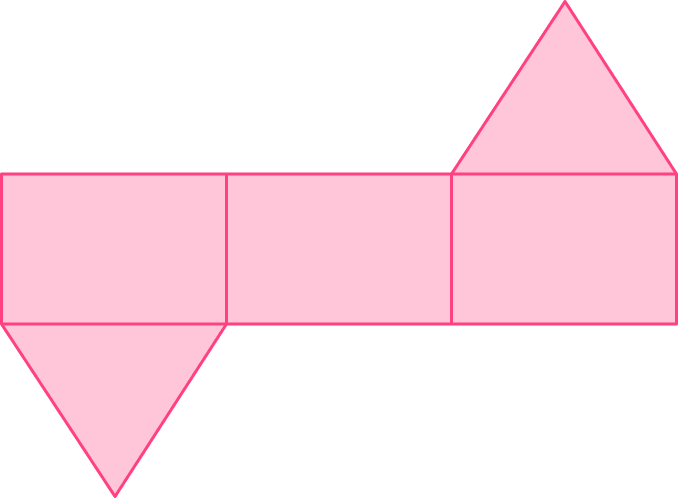



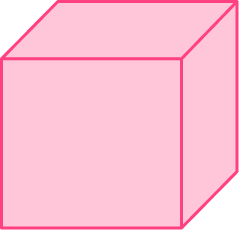

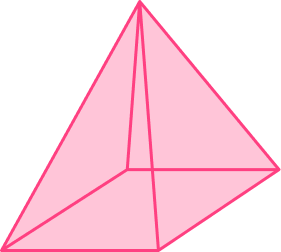

The net has three rectangular lateral faces and two triangular bases.
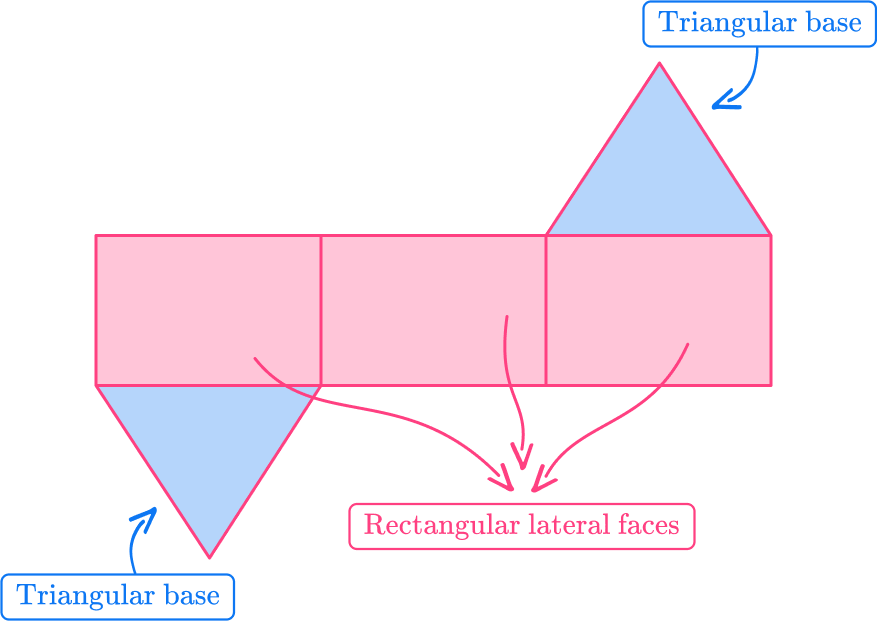
Prisms have bases that are equal and rectangular lateral faces.
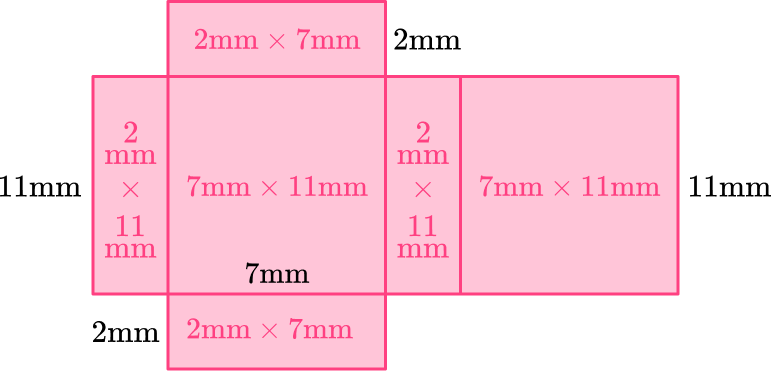
2) Which net represents this rectangular prism?
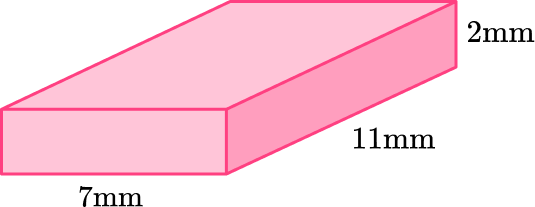
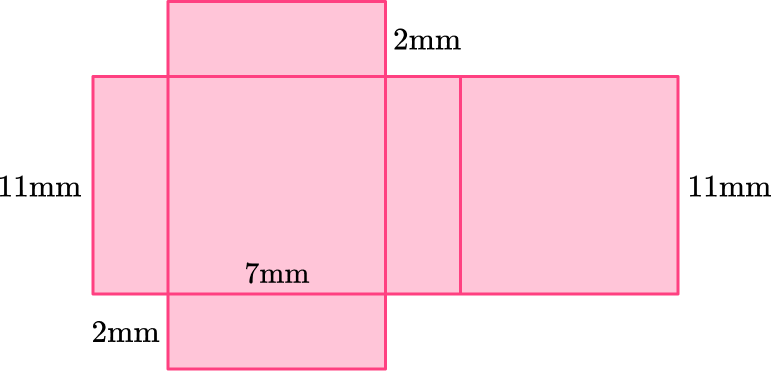

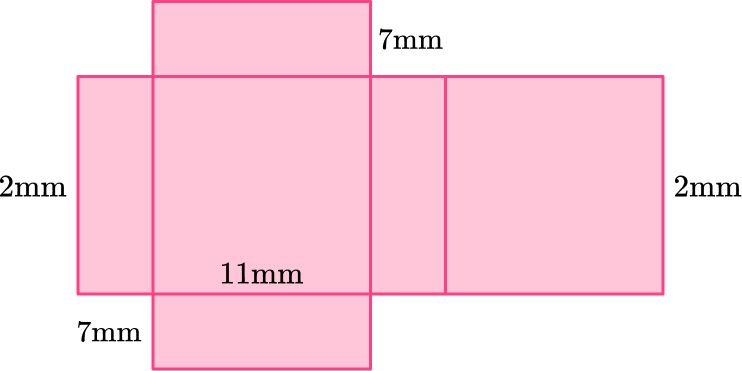

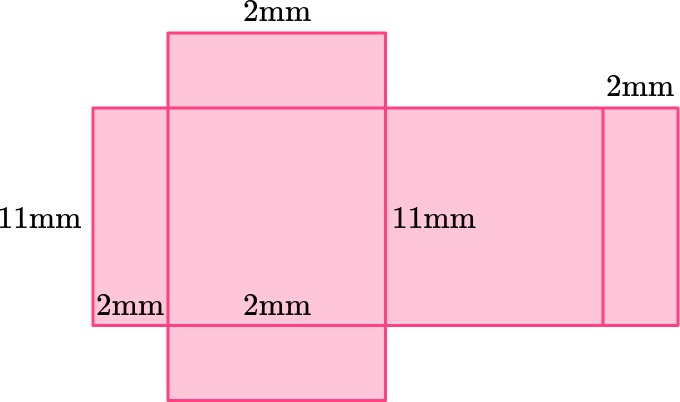

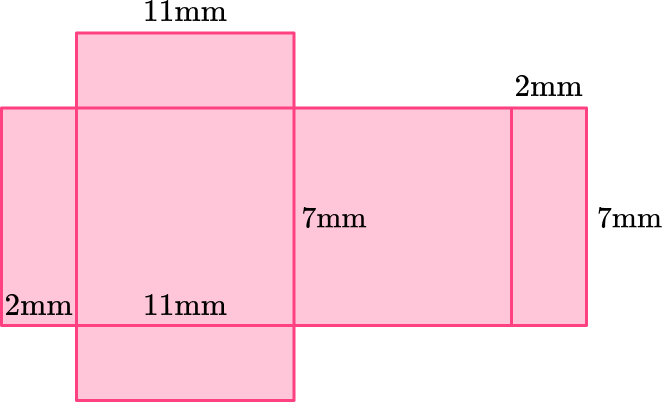

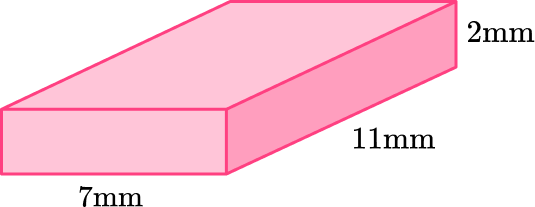
This rectangular prism has two bases that are 7~{mm} \times 11~{mm}, 2 lateral faces that are 2~{mm} \times 11~{mm}, and two lateral bases that are 7~{mm} \times 2~{mm}.
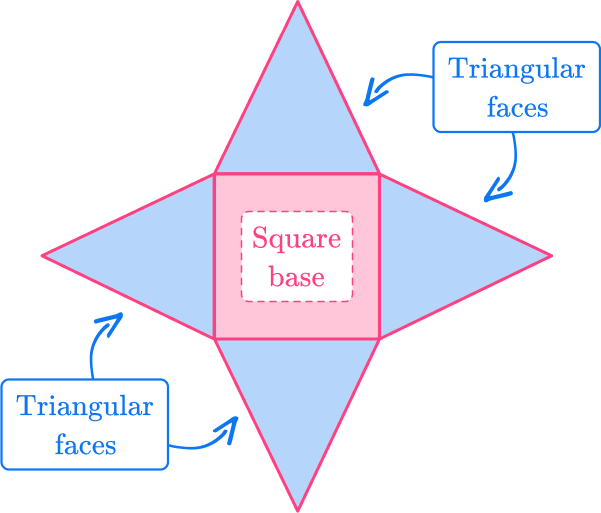
3) Which solid figure would the net make if it was folded together?

triangular prism

rectangular prism

cube

pyramid

Pyramids have one base that can be any polygon and triangular faces.
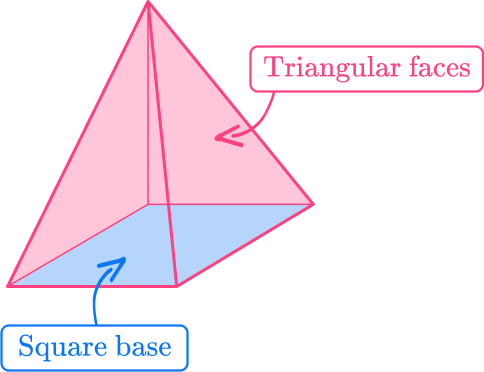
4) Which solid figure would the net make if it was folded together?
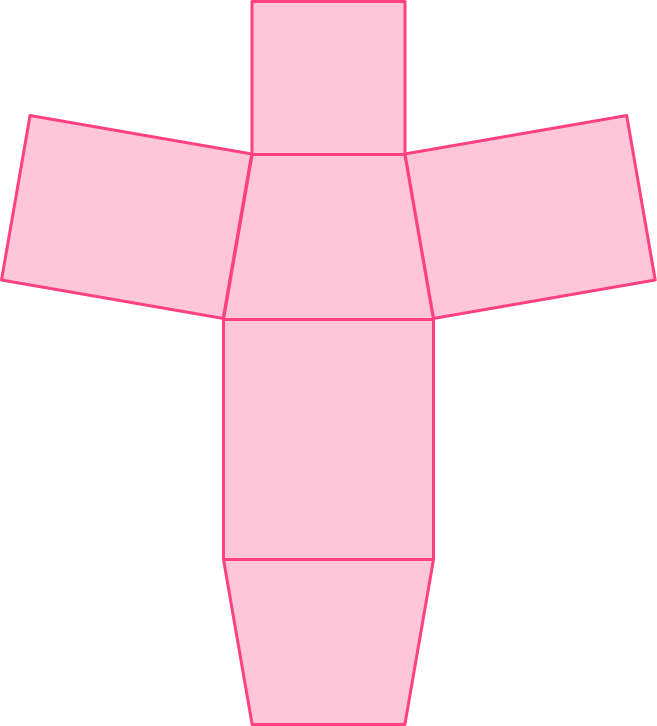

rectangular prism

triangular prism

trapezoidal prism

square pyramid

The net is made up of two trapezoid bases and 4 rectangular lateral faces. When the net is folded, it would be a prism with trapezoid bases – a trapezoidal prism.
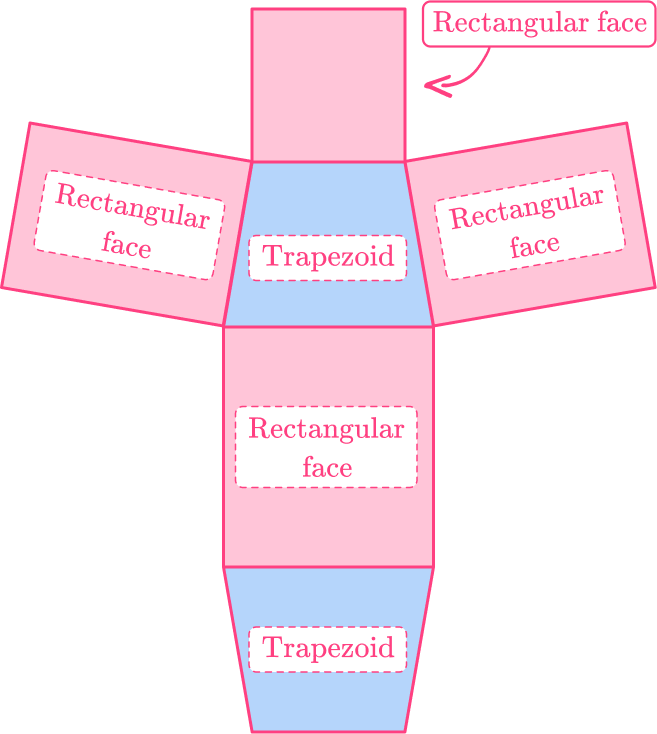
5) Calculate the surface area of this prism, using the net.
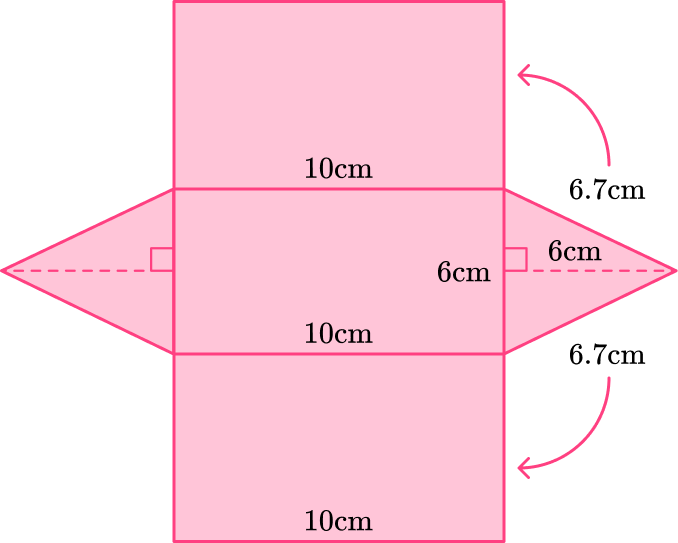




Surface area is the total area of the surface of a 3 D solid shape or if given a net, it is the total area of each of the faces. The number of faces on this prism is 6.
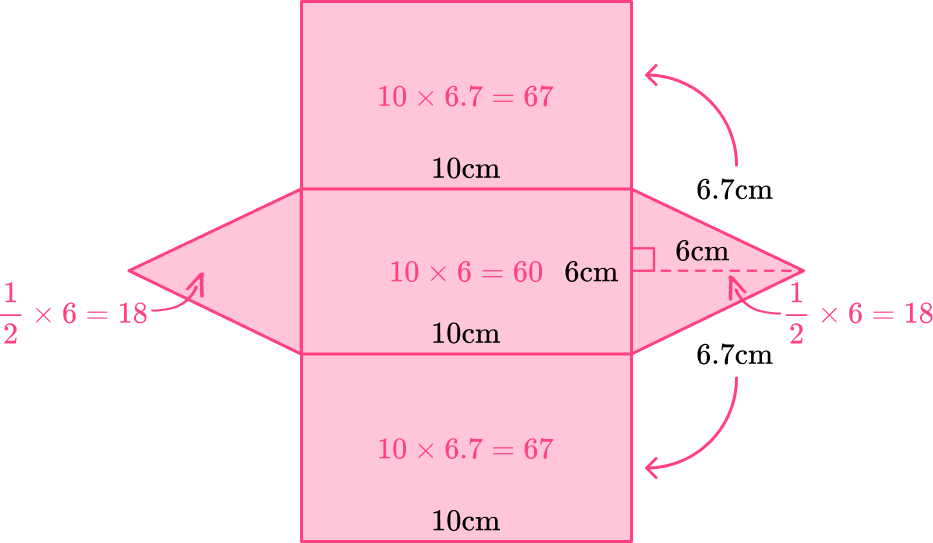
\begin{aligned} & \text { Area of lateral face }=6.7 \times 10 \\\\ & \text { Area of lateral face }=67 \end{aligned}
There are two lateral faces with the dimensions 6.7~{cm} by 10~{cm} so you can multiply 67 by 2.
67 \times 2=134
\begin{aligned} & \text { Area of lateral face }=6 \times 10 \\\\ & \text { Area of lateral face }=60 \end{aligned}
There is only one lateral face with dimensions 6~{cm} by 10~{cm}.
\begin{aligned} & \text { Area of triangular base }= \cfrac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 6 \\\\ & \text { Area of triangular base }=18 \end{aligned}
There are two triangular bases that are equal so you can multiply 18 by 2.
18 \times 2=36
Add up all the areas to find the total surface area.
\text { Surface area }=134+60+36=230
230 \mathrm{~cm}^2 is the total surface area of the triangular prism.
6) The net can be folded into a cube. If the side length of one of the squares is 3 inches, what is the total surface area of the cube?
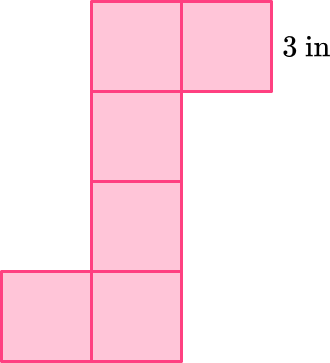




The total surface area is the sum of all the areas of all the faces. A cube or cuboid has 6 faces that are equal squares so the nets of a cube are made up of 6 squares. The area of one of those squares is 9 \, \mathrm{in}^2.
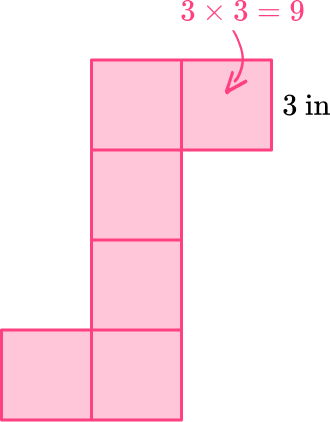
Multiply that area by 6 to find the total surface area.
6 \times 9=54
The total surface area is 54 ~{in}^2
Math nets FAQs
A dodecahedron is a 3 -dimensional shape that is made up of 12 faces. The most familiar type of dodecahedron is one that has 12 faces that are regular pentagons.
A tetrahedron, also known as a triangular pyramid, is a 3 -dimensional shape that has 4 faces that are triangles.
An octahedron is a 3 -dimensional shape that has 8 faces. It is often comprised of two pyramids joined together. The faces of an octahedron are triangles.
The next lessons are
- Pythagorean theorem
- Trigonometry
- Circle math
- Frequency table
- Types of data
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!