GCSE Tutoring Programme
Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring.
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Types of angles Angles in a triangle Angle rulesThis topic is relevant for:

Vertically Opposite Angles
Here we will learn about vertically opposite angles including how to find missing angles which are vertically opposite each other at the same vertex.
There are also angles in polygons worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR GCSE exam style questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are vertically opposite angles?
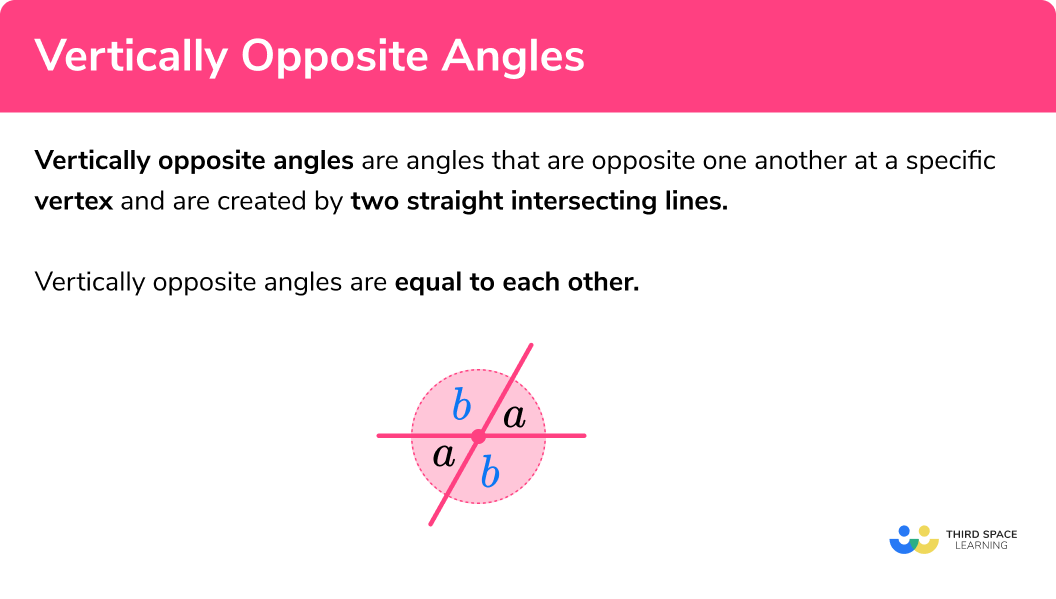
Vertically opposite angles are angles that are opposite one another at a specific vertex and are created by two straight intersecting lines.
Vertically opposite angles are equal to each other.
These are sometimes called vertical angles.
Here the two angles labelled
You can try out the above rule by drawing two crossing lines and measuring the angles opposite to one another.
You will also notice that angle
Note because the sum of angles
Before we start looking at specific examples it is important we are familiar with some key words, terminology and symbols required for this topic.
What are vertically opposite angles?
Keywords
- Angle: defined as the amount of turn around a common vertex.
- Vertex: the point created by two line segments meeting (plural is vertices)
- How to label an angle:
We normally label angles in two main ways:
1By giving the angle a ‘name’ which is normally a lower case letter such as
2By referring to the angle as the three letters that define the angle. The middle letter refers to the vertex at which the angle is e.g. see the diagram for the angle we call ABC:
- Angles on a straight line equal
180º :
Angles on one part of a straight line always add up to
However see the next diagram for an example of where
Note – you can try out the above rule by drawing out the above diagrams and measuring the angles using a protractor.
- Angles around a point equal
360º :
Angles around a point will always equal
- Supplementary and Complementary Angles:
Two angles are supplementary when they add up to
Two angles are complementary when they add up to
How to solve vertically opposite angles problems
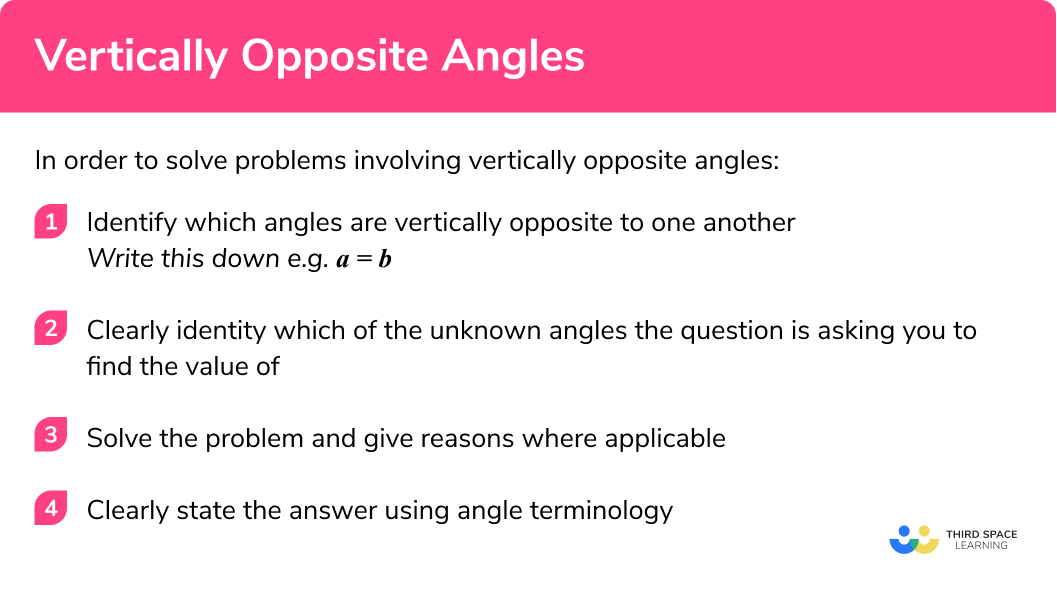
In order to solve problems involving angles you should follow these steps:
- Identify which angles are vertically opposite to one another.
Write this down e.g.a = b . - Clearly identity which of the unknown angles the question is asking you to find the value of.
- Solve the problem and give reasons where applicable.
- Clearly state the answer using angle terminology.
How to solve vertically opposite angles problems.
Vertically opposite angles worksheet

Get your free vertically opposite angles worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Vertically opposite angles worksheet

Get your free vertically opposite angles worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREEVertically opposite angles examples
Example 1: two angles that are vertically opposite
Find the value of angle
- Identify which angles are vertically opposite to one another.
The angle labelled
2 Clearly identify which of the unknown angles the question is asking you to find the value of.
The angle labelled
3 Solve the problem and give reasons where applicable.
4 Clearly state the answer using angle terminology.
Example 2: two angles that are vertically opposite
Find the values of angles
The angle labelled
The angles labelled
You will notice that
Example 3: finding all the angles around a point with vertically opposite angles
Find the values of the angles labelled
The angle labelled
The angle labelled
The angles labelled
Example 4: vertically opposite angles with algebra
Using vertically opposite angles find the value of
The angle labelled
The angle labelled
We are not being asked to find an angle we are being asked to find the value of
The four angles total
Example 5: problem solving
In the diagram below
Find the value of angle
The angle of size
Find angle
Angle
Angle
Example 6: worded problem
Two angles with values of
Prove the two angles are both
The angles labelled
You are being asked to prove the size of each angle is
Therefore the size of the two angles can be found by substitution
Angle 1:
Angle 2:
Therefore both angles are
Common misconceptions
- Incorrectly labelling angles which are vertically opposite one another
- Misuse of the ‘straight line’ rule where angles do not share a vertex
- Finding the incorrect angle due to misunderstanding the terminology
Related lessons
Vertically opposite angles is part of our series of lessons to support revision on angle rules. You may find it helpful to start with the main angle rules lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Practice vertically opposite angles questions
1. Find the value of the angle labelled x :




Angle x is vertically opposite the given angle of 67^{\circ} so it is the same.
2. Find the value of the angle labelled x :




Angle x is vertically opposite the given angle of 146^{\circ} so it is the same.
3. Find the value of the angle labelled x :




Angle x is vertically opposite the given angle of 98^{\circ} so it is the same.
4. Find the value of the angle labelled x and y :




Angle x is vertically opposite the given angle of 112^{\circ} so it is the same.
Angle x and angle y lie on a straight line so they must add up to 180 .
5. Two angles with values of 2x and 50^{\circ} are vertically opposite one another. Find the value of x .




Angle 2x is vertically opposite the given angle of 50^{\circ} so it is the same.
To solve for x , we divide 50 by 2 .
6. Two angles with values of 6x+10 and 10x-70 are vertically opposite one another. Find the value of x




Angle 6x + 10 is vertically opposite angle of 10x − 70 so they are the same.
Solving the equation, 6x + 10 = 10x − 70 , leads to the correct value for x .
Vertically opposite angles GCSE exam questions
1. Find the size of angles a and b .
(2 marks)
a = 142^{\circ} (because vertically opposite angles are equal)
(1)
b: 180 − 142 = 38^{\circ} (because angles on a straight line add to 180)
(1)
a = 142^{\circ}, b = 38^{\circ}
2.
(a) Write an equation involving x.
(b) Use your equation to find the size of the angles.
(4 marks)
(a)
2x + 14 = 3x − 5
(1)
(b)
14 = x − 5
(1)
x = 19
(1)
Angles:
2 \times 19 + 14 = 52
= 52^{\circ}
(1)
3. Prove that triangle ABC is a right angle triangle
(3 marks)
Angle ACB = 24^{\circ} since they are vertically opposite
(1)
66 + 24 = 90
(1)
180 − 90 = 90 (angles in a triangle add up to 180 ),
so angle BAC is 90^{\circ} and this is a right angle triangle.
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.