High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Rational numbers Irrational numbers Exponents Negative numbersSquare roots
Here is everything you need to know about square numbers and square roots. You will learn what a square number is and how to find the square roots of numbers and expressions. You will also apply this knowledge to problem solve.
Students first work with square roots in 8 th grade math and expand that knowledge as they move into high school math classes.
What is a square number?
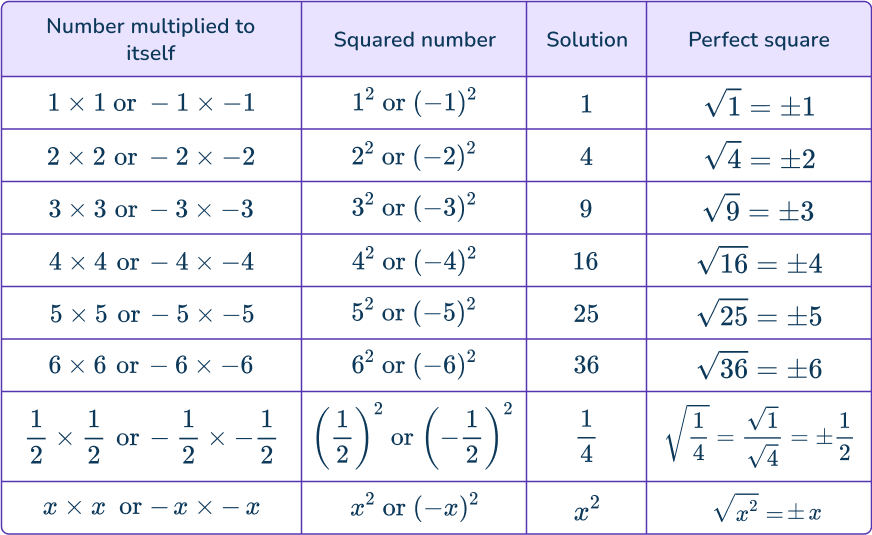
A square number is a number that is the result of multiplying that number to itself, or “squared”. In other words, a square number is found when multiplying any number by itself. The solution when a number is multiplied to itself is called a perfect square.
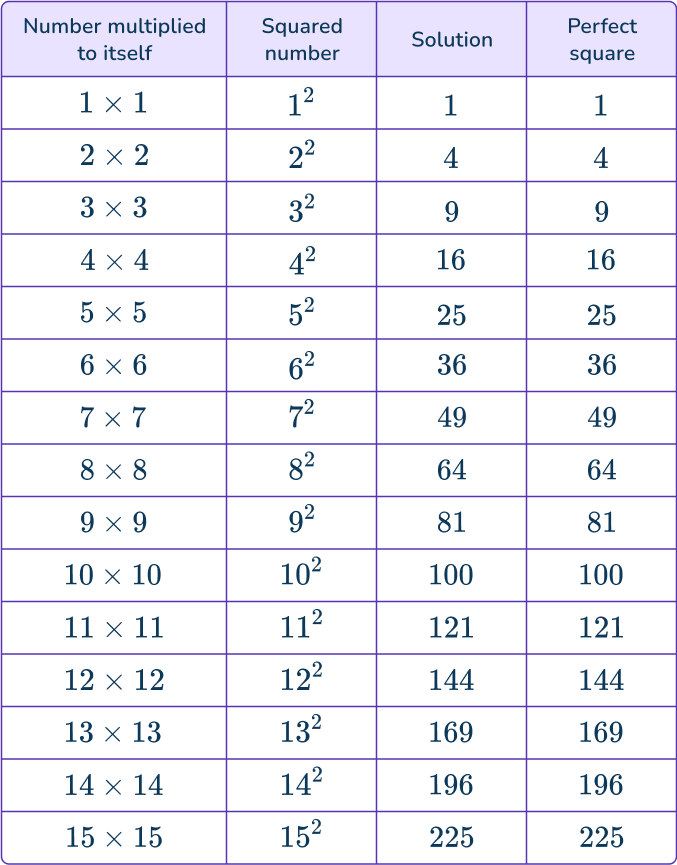
Look at this table to see the relationship.
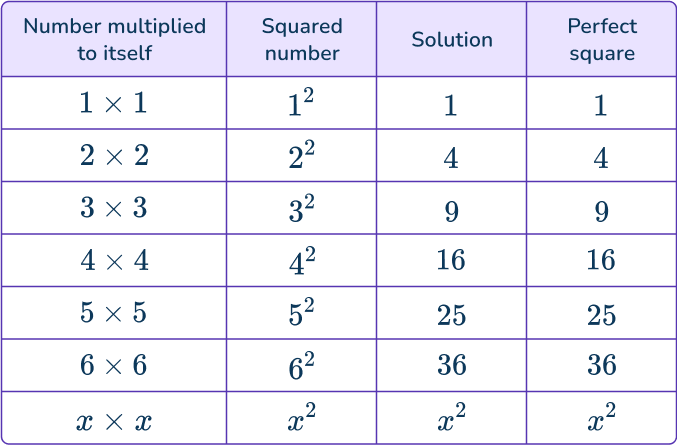
Square numbers can also be represented by an array that forms squares.
You can arrange 1^2 as a square which has side lengths 1 unit.

You can arrange 2^2 as a square which has side lengths 2 units.
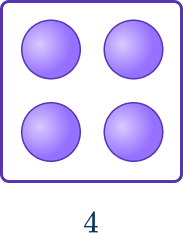
You can arrange 3^2 as a square which has side lengths 3 units.

You can arrange 4^2 as a square which has side lengths 4 units.
There are an infinite number of perfect square numbers, which makes it impossible to know all of them. However, remembering the perfect squares up to 15 \times 15 is extremely helpful for problem solving purposes.
![[FREE] Square Roots Worksheet (Grade 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Square-Roots-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Square Roots Worksheet (Grade 8)
![[FREE] Square Roots Worksheet (Grade 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Square-Roots-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your 8th grade students’ understanding of square roots. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Square Roots Worksheet (Grade 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Square-Roots-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Square Roots Worksheet (Grade 8)
![[FREE] Square Roots Worksheet (Grade 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/Square-Roots-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your 8th grade students’ understanding of square roots. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREESquaring negative numbers
Negative numbers can be squared like positive numbers.
For example:
\begin{aligned}(- \; 5)\times(- \; 5)&=25\rightarrow(- \; 5)^2=25 \\\\(- \; 7)\times(- \; 7)&=49\rightarrow(- \; 7)^2=49 \end{aligned}Notice how (- \; 5)^2=(5)^2=25
The square of any negative number is always positive as you are multiplying a negative by a negative, which gives you a positive answer.
What is a square root?
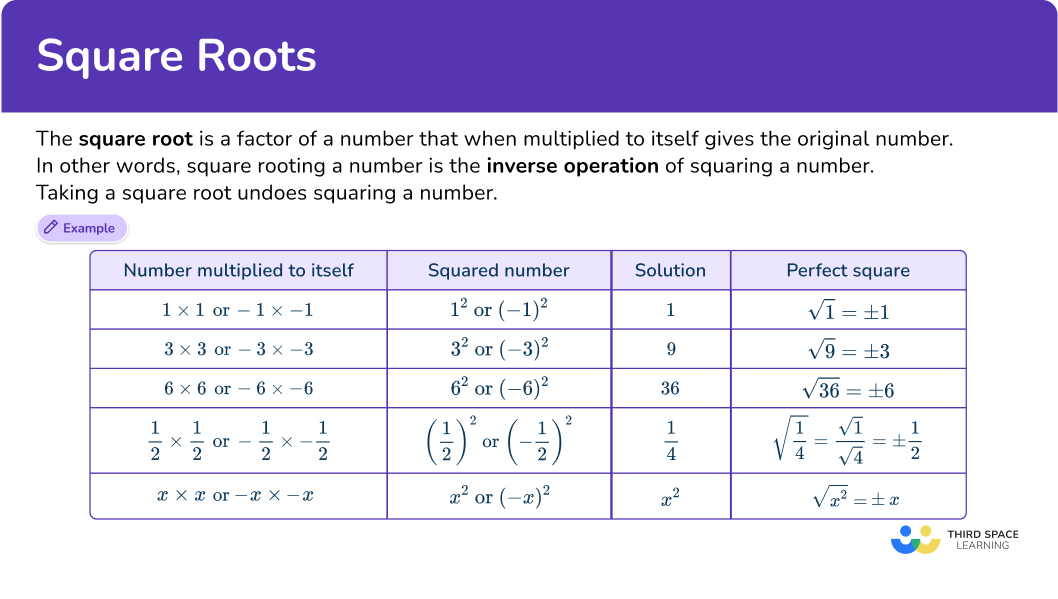
The square root is a factor of a number that, when multiplied to itself, gives the original number. In other words, square rooting a number is the inverse operation of squaring a number. Taking a square root undoes squaring a number. The square root symbol (square root function) looks like this:
\sqrt{\;}Its mathematical name is a radical or radical symbol.
The square root of a number is represented by:
\sqrt{4} where 4 is considered the radicand because it is the number under the radical symbol.
\sqrt{4}=2. In this case, 2 is the principal square root because it is the positive square root.
Since 2\times{2}=4, and (- \; 2)\times(- \; 2)=4, then \sqrt{4}=2 or - \; 2. This is sometimes written as \sqrt{4}=\pm \; {2}.
Algebraic expressions such as variables can be squared. For example, x^2 means x\times{x}. So, \sqrt{x^2}=x. Taking the square root undoes the squaring.
x^4 is also a square term because x^{2}\times{x}^{2}=x^{4} so, \sqrt{x^{4}}=x^{2}
You can simplify square root expressions by breaking the expression down into perfect square factors.
Notice how \sqrt{32} is not a perfect square. The expression can still be simplified by breaking the number into perfect square factors. Specifically, look for the largest square factor of the number under the radical.
In this case, the largest square factor of 32 is 16. So, \sqrt{32} can be rewritten as \sqrt{16\times{2}} which is \sqrt{16}\times\sqrt{2}.
Since 16 is a perfect square, you can take the square root, but \sqrt{2} is not a perfect square, so you cannot take the square root without a calculator; it’s considered to be an irrational number.
\begin{aligned}\sqrt{32}&=\sqrt{16}\times\sqrt{2} \\\\ &=4\times\sqrt{2} \\\\ &=4\sqrt{2} \end{aligned}\sqrt{32} fully simplified is 4\sqrt{2}.
See also: How to simplify radicals
What is a square number?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 8 th grade math?
- Grade 8: Expressions and Equations (8.EE.A.2)
Use square root and cube root symbols to represent solutions to equations of the form x^{2}=p and x^{3}=p, where p is a positive rational number. Evaluate square roots of small perfect squares and cube roots of small perfect cubes. Know that \sqrt{2} is irrational.
How to find square roots
In order to find square roots:
- Write an expression using the \bf{\sqrt{\;}} (radical sign).
- Find the square root, simplify if necessary.
- Write the simplified answer.
Square numbers and square roots examples
Example 1: square root of a perfect square
Find the square root of 81.
- Write an expression using the \bf{\sqrt{\;}} (radical sign).
The square root of 81 is expressed as \sqrt{81} .
2Find the square root, simplify if necessary.
\sqrt{81} is a whole number because 81 is a perfect square.
3Write the simplified answer.
\sqrt{81}=9 and \sqrt{81}=- \; 9 because 9\times{9}=81 and - \; 9\times{- \; 9}=81
Example 2: square root of a fraction
Find the square root of \cfrac{1}{16}.
Write an expression using the \bf{\sqrt{\;}} (radical sign).
The square root of \cfrac{1}{16} is represented by \sqrt{\cfrac{1}{16}} .
Find the square root, simplify if necessary.
\sqrt{\cfrac{1}{16}} is a perfect square because 1 and 16 are perfect square numbers. You can rewrite it with the radical in the numerator and the radical in the denominator.
\sqrt{\cfrac{1}{16}}=\cfrac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{16}}
\cfrac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{16}}=\cfrac{1}{4} or - \; \cfrac{1}{4}.
Write the simplified answer.
\sqrt{\cfrac{1}{16}}=\cfrac{\sqrt{1}}{\sqrt{16}}=\cfrac{1}{4} or - \; \cfrac{1}{4}.
Example 3: square root of an algebraic expression
Find the square root of 225s^{4}.
Write an expression using the \bf{\sqrt{\;}} (radical sign).
The square root of 225s^{4} is represented by \sqrt{225s^{4}}
Find the square root, simplify if necessary.
\sqrt{225s^{4}} is a perfect square expression because 225 is a perfect square number and s^4 is a perfect square expression.
15\times{15}=225
s^{2}\times{s}^{2}=s^{4}
Write the simplified answer.
How to find square roots of algebraic expressions with non-perfect squares
In order to find square roots of algebraic expressions with non-perfect squares:
- Find the largest square factor(s) of the term under the root.
- Rewrite the radical as a product of the square factor(s) and the other factors.
- Simplify the radical expression.
Example 4: square root of an algebraic expression
Simplify \sqrt{8x^{3}}.
Find the largest square factor(s) of the term under the root.
Square numbers are 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, …
The largest square factor of 8 is 4 because 4\times{2}=8
The largest square factor of x^3 is x^2 because x^{2}\times{x}=x^{3}
Rewrite the radical as a product of the square factor(s) and the other factors.
Simplify the radical expression.
Take the square root of 4 and x^2 because both are perfect squares.
How to solve problems involving square numbers and square roots
In order to problem solve with square numbers and square roots:
- Identify whether you need to square or square root the number/variable.
- Perform the operation.
- Clearly state the answer within the context of the question.
Example 5: word problems with square numbers
The area of a square is 36\mathrm{~in}^{2}. Using the formula to find area of a square, \text{Area}=s^{2}, find the side length of the square.
Identify whether you need to square or square root the number/ variable.
The question is to find the side length, so using the formula you are taking the square root.
Perform the operation.
\text{Area}=s^{2} where the area is 36\mathrm{~in}^{2}.
Clearly state the answer within the context of the question.
Since the question is asking for side length, the positive value is the solution not the negative value.
The side length of the square is 6 inches.
Example 6: word problems with square roots
Two times a number squared is 32. Calculate the possible value(s) of the number.
Identify whether you need to square or square root the number/variable.
In this case, you will have to take the square root to find the solution.
Perform the operation.
Two times a number squared is 32 can be written as the equation 2\times{x}^{2}=32.
Clearly state the answer within the context of the question.
For this problem, both + \; 4 and - \; 4 are the solutions.
Check both values in the original equation to validate your answer.
2\times(4)^{2}=32
2\times(- \; 4)^{2}=32
Teaching tips for square numbers and square roots
- Incorporate discovery based learning activities so that students can be like mathematicians and explore perfect square numbers and square roots on their own.
- If students struggle with multiplication tables, have them use a digital, online square root calculator.
Easy mistakes to make
- Squaring numbers incorrectly
For example, thinking that squaring a number means to double it.
3^{2}≠ {6}
3^{2}=3\times{3}=9
- Forgetting about the negative root when taking a square root
For example, only recognizing positive values of square roots of integers.
\sqrt{100}=10 (only thinking the answer is 10 )
\sqrt{100}=\pm \; {10}
Related laws of exponents lessons
Practice square numbers and square roots questions
1. What is the square root of the number, 169?




Taking the square root of 169 means \sqrt{169}. 169 is a perfect square number because 13\times13=169 and – \; 13\times{- \; 13}=169
So, \sqrt{169}=\pm \; {13}
2. What is the square root of a^{6}?




The square root of a^6 is represented by \sqrt{a^6}. a^6 is a perfect square term because a^{3}\times{a^{3}}=a^{6} so, \sqrt{a^{6}}=a^{3}
3. What are the values of \sqrt{144}?
1 and 12

12 and – \; 12

72 and – \; 72

12 and – \; 11

\sqrt{\;} means square root, so, \sqrt{144} means to take the square root of 144. In other words, what number multiplied to itself is 144?
12\times{12}=144 and – \; 12\times{- \; 12}=144.
\sqrt{144}=\pm \; {12}
4. Simplify the square root expression, \sqrt{36 y^{3}}.




Look for the perfect square factors of 36y^3 in order to simplify it.
36 is a perfect square and y^{3}=y^{2}\times{y} where y^{2} is a perfect square term.
\sqrt{36y^{3}}=\sqrt{36}\times\sqrt{y^2}\times\sqrt{y}
Take the square root of the perfect square terms
\begin{aligned}\sqrt{36y^{3}}&=6\times{y}\times\sqrt{y} \\\\ &=6y\sqrt{y} \end{aligned}
\sqrt{36y^{3}} simplified is 6y\sqrt{y}
5. Find the side length of a square with an area of 81\mathrm{~cm}^{2}.




A square has four equal sides and to find the area of a square you take the side length and square it. So, if you have the area and need to find the side length, take the square root.
\begin{aligned}\text{Area}&=s^{2} \\\\ 81&=s^{2} \\\\ \sqrt{81}&=\sqrt{s^{2}} \\\\ \pm \; {9}&=s \end{aligned}
Since this is the length of the side of a square only the positive value works. So the side length of the square is 9 \, cm.
6. 3 times a number squared is 363. Find the number(s).




3 times a number squared is 363 translates to be:
\begin{aligned}3 \times x^{2}&=363 \\\\ 3x^{2}&=363 \\\\ \cfrac{3x^{2}}{3}&=\cfrac{363}{3} \\\\ x^{2}&=121 \\\\ \sqrt{x^{2}}&=\sqrt{121} \\\\ x&=\pm \; {11}\end{aligned}
In this case, both + \; 11 and – \; 11 work. Check both solutions to verify.
\begin{aligned}3\times(11)^{2}&=363 \\\\ 3\times{121}&=363 \\\\ 3\times(- \; 11)^{2}&=363 \\\\ 3\times{121}&=363 \end{aligned}
Square numbers and square roots FAQs
If you take the square root of a negative number on a calculator, you will get “error.” The reason being that the square root of a negative number is not a real number, it is an imaginary number which is part of the complex number system.
Typically in 8 th grade math, you will be asked to find the square root of natural numbers, positive whole numbers, positive integers, and positive real numbers (decimals and fractions).
In algebra 1 and algebra 2 classes you will learn how to find the square root of polynomials. There are polynomials that are considered to be perfect square expressions such as perfect square trinomials.
To solve for the missing side of right triangles you will use the Pythagorean Theorem (Pythagoras’ Theorem), a^2+b^2=c^2. Since the theorem has square terms, you will have to use square root to find missing side lengths.
See also: Pythagorean Theorem
Quadratic equations have a squared term and square root undoes squaring. So, you will need to sometimes use square root to solve quadratic equations.
Yes, you can take the square root of prime numbers but they will be considered irrational numbers. So, either leave them under the radial symbol such as \sqrt{5} or use a square root calculator to find the answer.
Remember the answer in a calculator will have many decimal places because irrational numbers are non-repeating, non-terminating numbers, so you will have to round the answer.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!