Math Dictionary For Kids: The Essential Guide To Math Terms For Parents And Teachers
Bet you never thought you’d need a math dictionary for kids when your child started school or when you started teaching! But as parents and teachers, the math words that children have to contend with in school may be quite different from those you learned and used in your education- even the basic math.
Throughout their time studying math in school, in elementary school, middle school and beyond, children will be introduced to a huge amount of math vocabulary, much of which may seem baffling – both to them and to you.
This online math dictionary for kids, teachers and parents is, we hope, the solution to questions and confusion and can serve as a quick reference guide. It’s an A to Z math glossary of meanings in simple language for all those words and phrases you’re not sure about, from acute angles through to word problems.
It is by no means a comprehensive list of every mathematical term that could come up throughout a child’s school life (as that would be too overwhelming), but it includes the key ones they will need to form solid foundations in elementary school and middle school math so they are ready to move onto high school math.
This blog is part of our series of blogs designed for teachers, schools and parents supporting home learning.
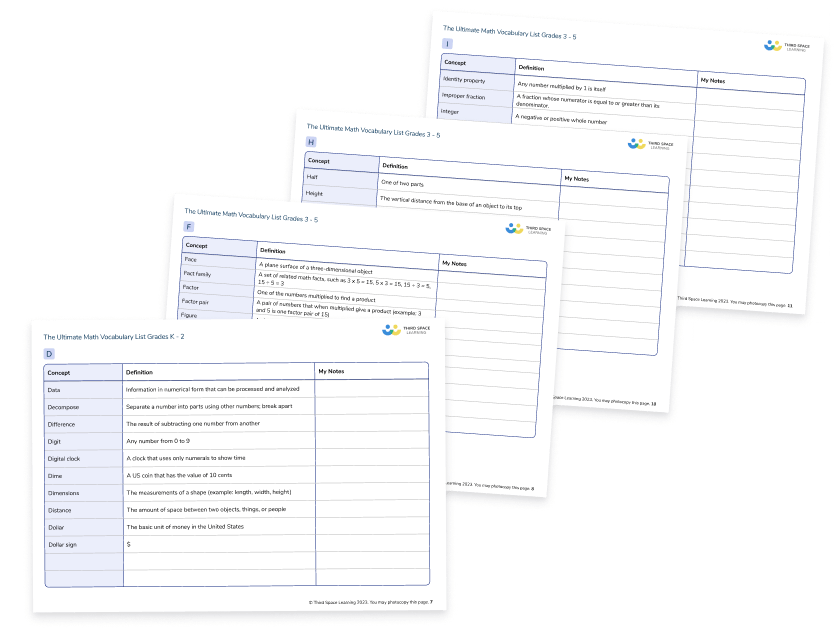
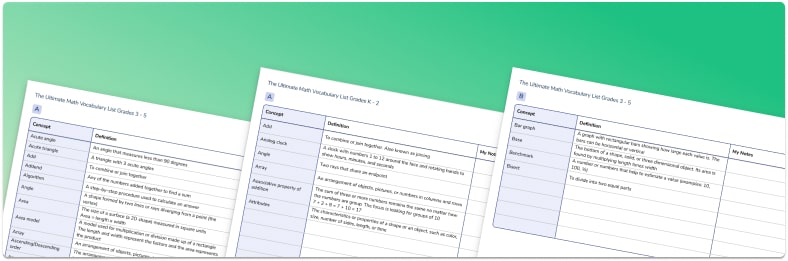
Ultimate Math Vocabulary Lists
An essential guide for students to develop their knowledge of key words and terminology in math.
Download Free Now!The importance of spoken mathematical language
When children struggle to articulate their thoughts, it is usually a sign that they do not understand the topic they are discussing in great depth and this can often be the case in math.
This quote taken from What Works Clearinghouse (WWC) reflects the importance of mathematical language amongst children:
“If children hear math vocabulary in context and then practice using it, they may be better able to understand the underlying math concepts. The panel believes there is evidence of a positive relationship between math-related talk and children’s math knowledge.”
What Works Clearinghouse, 2013
When children use spoken language in math in a productive manner, it allows them to evaluate their learning, support their peers, challenge the status quo, justify their own answers and most importantly ask questions!
Using a wide range of math vocabulary can help children to make links across not only different areas of math, but also throughout real life situations. One example of this could be in the supermarket when they would realize, thanks to their range of vocabulary, that a 50% off sticker means the same as half price. These connections in turn support students’ problem solving skills for reasoning questions in math.
Mathematical vocabulary appears in more places than you would think, and that is why it is very important that children are confident in their ability to articulate about all things mathematical!

Meet Skye, the voice-based AI tutor making math success possible for every student.
Built by teachers and math experts, Skye uses the same pedagogy, curriculum and lesson structure as our traditional tutoring.
But, with more flexibility and a low cost, schools can scale online math tutoring to support every student who needs it.
Find out moreHow you can encourage a wider range of mathematical language in your students
There are a number of ways you can encourage your students to enhance their mathematical vocabulary and they include:
- Getting them to read and test themselves with our math dictionary;
- Asking them open ended questions. No more “Do you know the answer to this question?” and more “What do you think the answer to this question is?”;
- Playing some word based math games;
- Reading outside the world of math as many children’s books will incorporate elements of math in a fun and engaging way. ‘One is a Snail, Ten is a Crab’ is a great example of this.
#
#
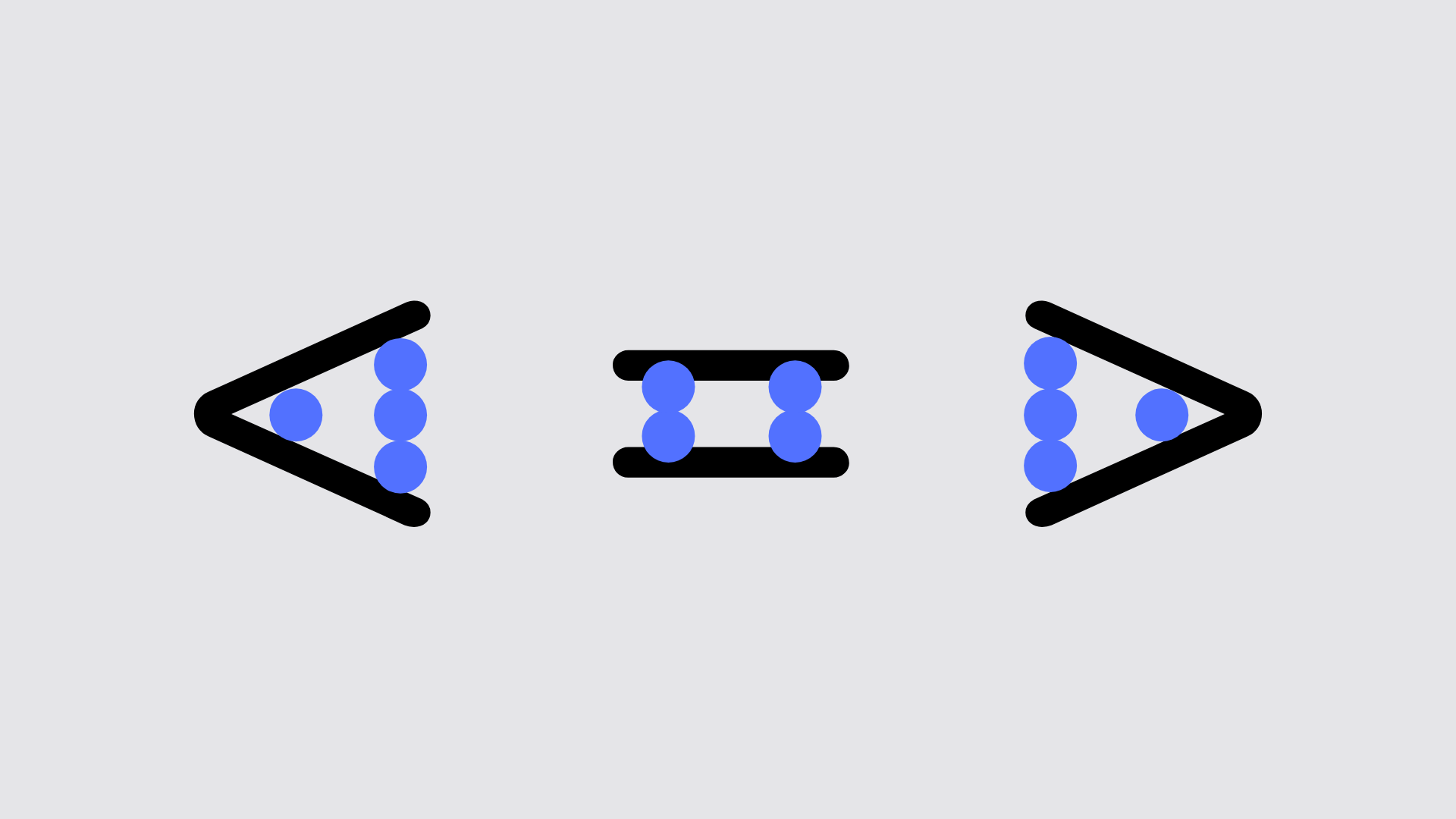
< and >
< and > are symbols representing one number being ‘greater than’ or ‘less than’ another.
For example 16 > 8 or 8 < 16 says that 16 is greater than 8 and 8 is less than 16.
12-hour and 24-hour clock
The 12-hour clock goes from 1 am in the morning to 12 noon and from 1 pm in the afternoon to 12 midnight. This is known as ‘analog’ time.
The 24-hour clock goes from 00:00 (midnight) to 23:59 (one minute to midnight). This is known as ‘digital’ time.
Read more: What is the 12 hour and 24 hour clock
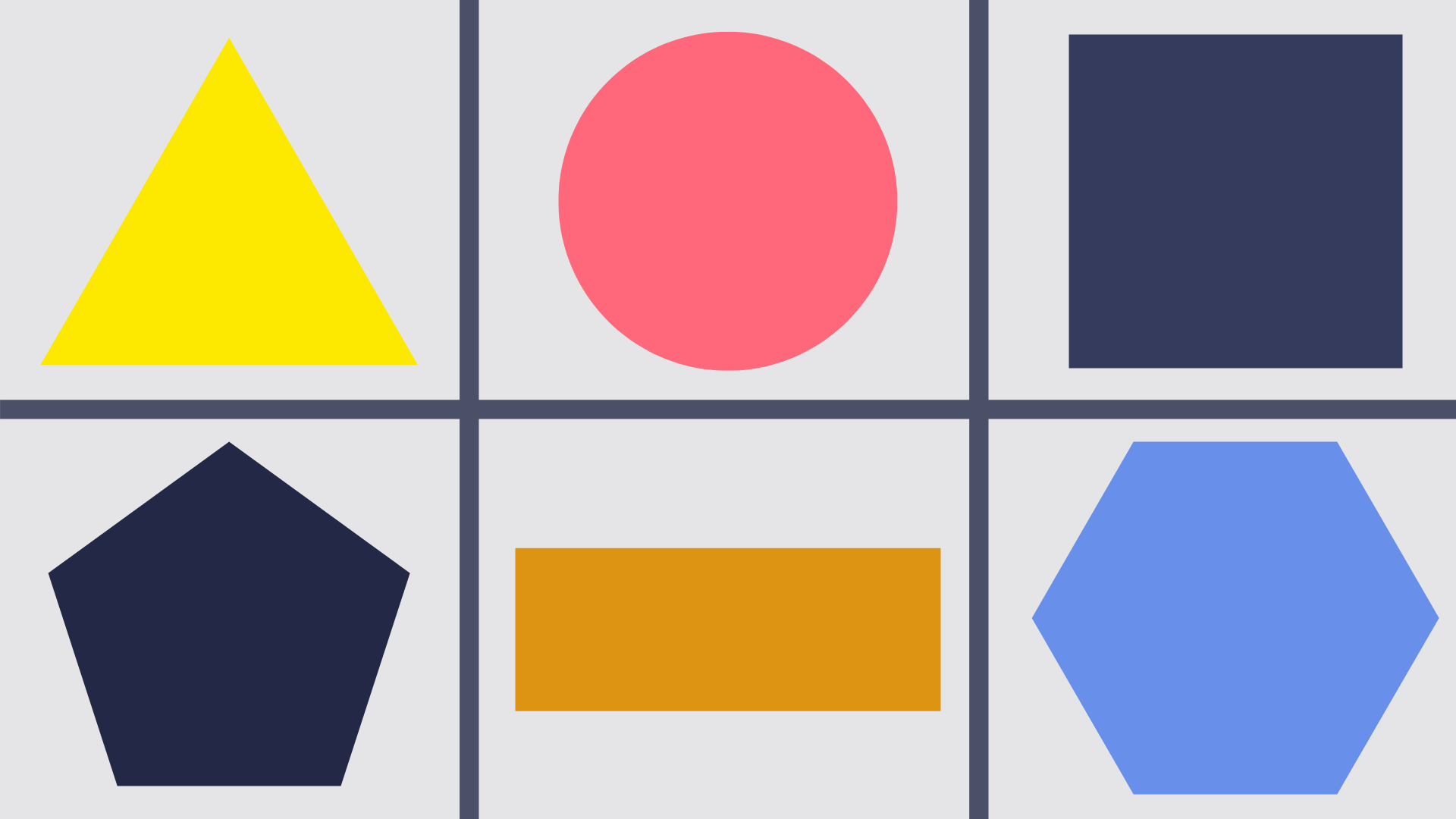
2D shapes
A 2D shape is any flat or ‘two-dimensional’ shape, such as a square, circle or triangle.
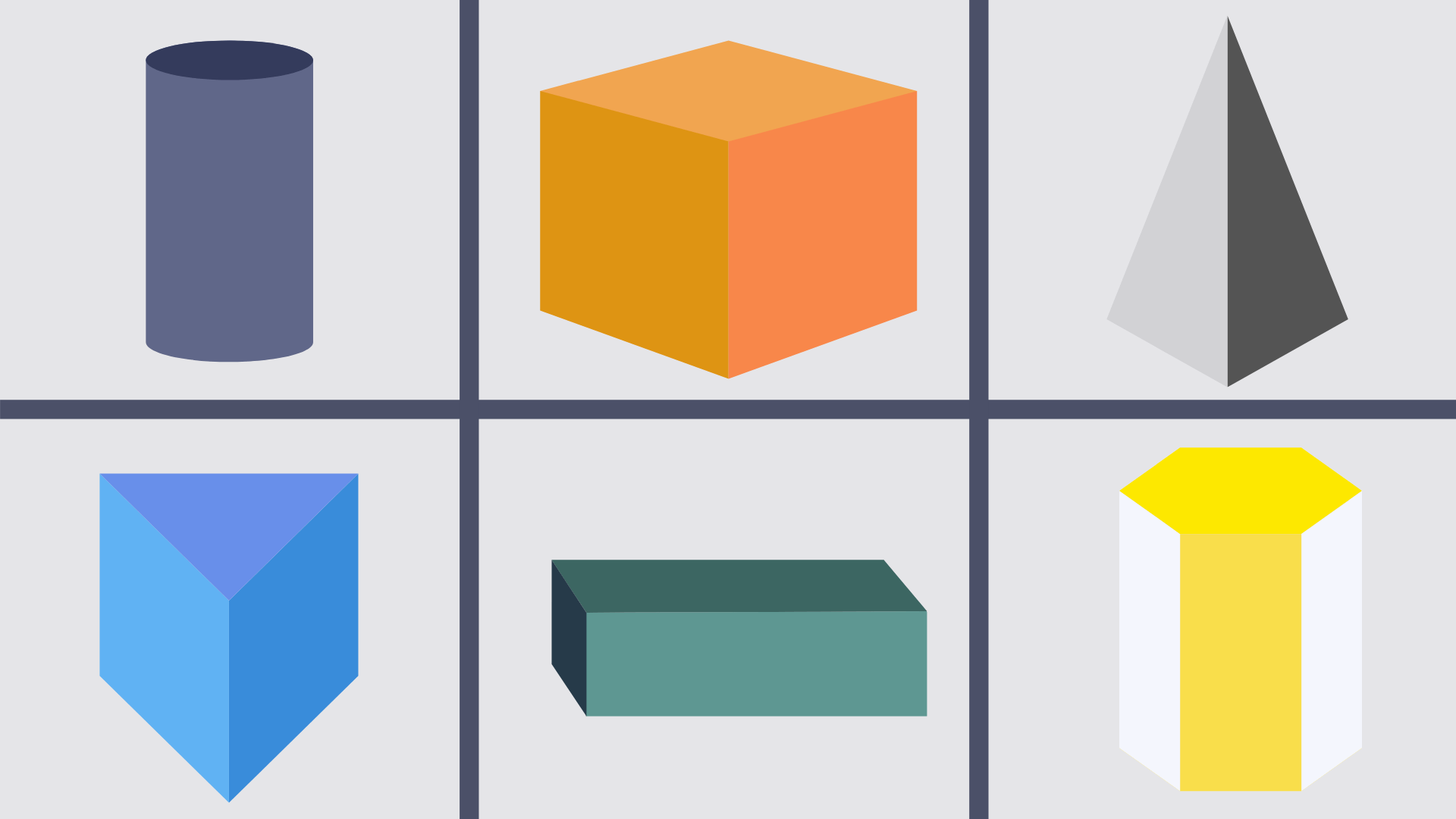
3D shapes
A 3D shape is ‘three-dimensional’ and has volume, for an example a cube (cardboard box), pyramid or cylinder (tube).
Read more: 2D shapes, 3D shapes and properties of shapes
A
A
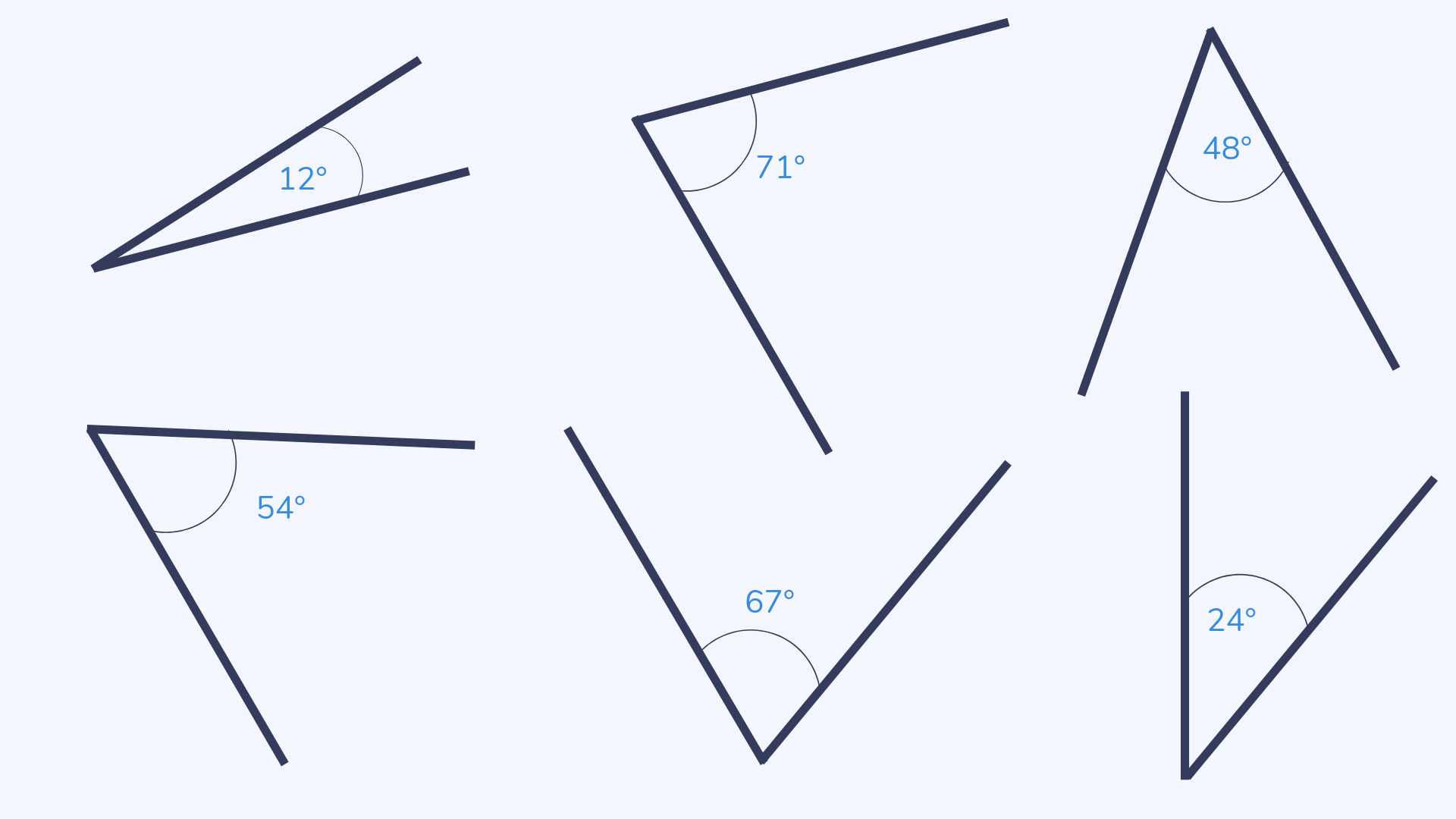
Acute angle
An acute angle is any angle less than 90°.
Addend
An addend is a number that is added to another number. For example, in the equation 7 + 5 = 12, 7 and 5 are addends.
Algebra
In algebra, letters and symbols are used to represent numbers in equations or formulae.
For example, if w = 3, what is 6w + 7?
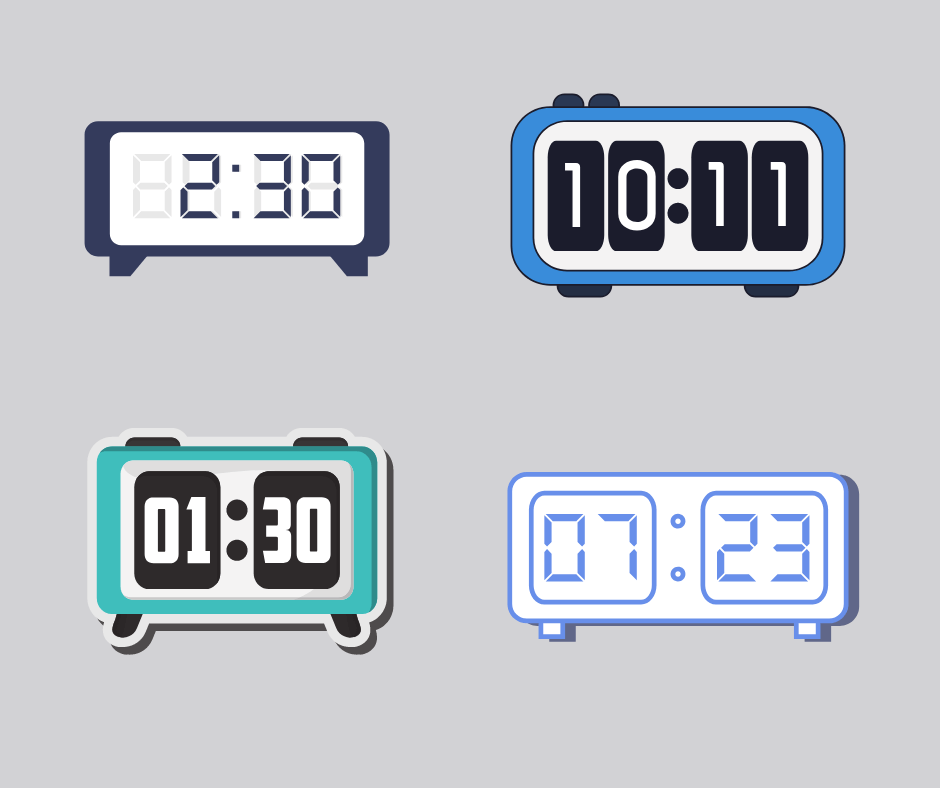
Analog and digital clocks
An analogue clock is a clock with the numbers 1 to 12 around the outside and two hands, one short hand that represents hours and one long hand that represents minutes.
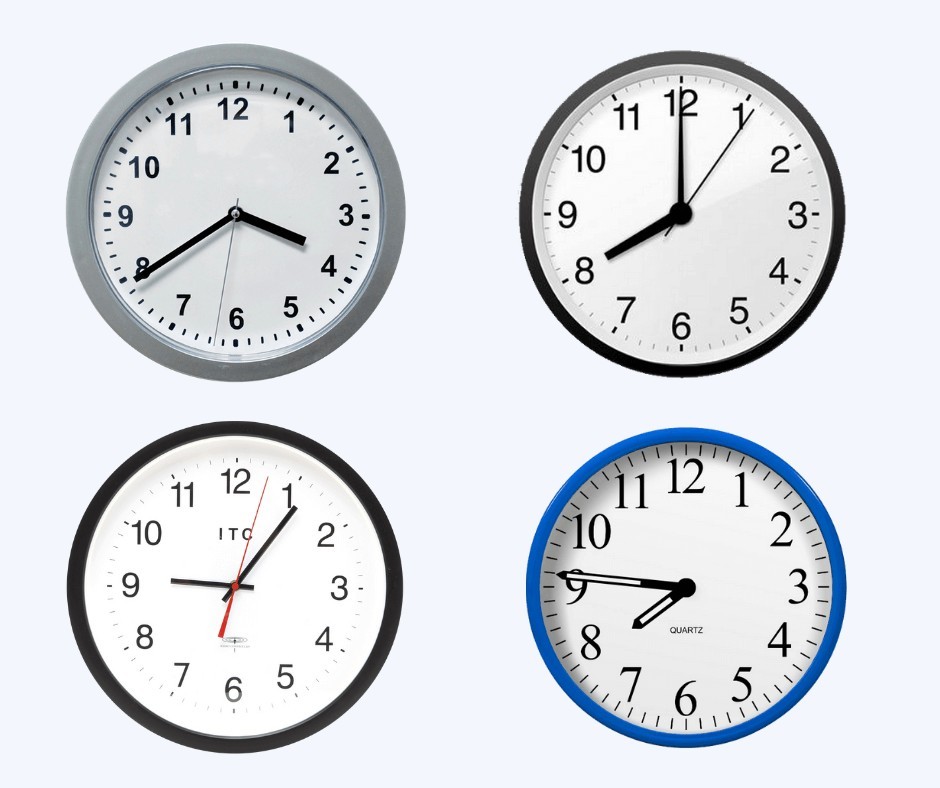
A digital clock can use 24-hour or 12-hour time and always has four digits.
For example, 15:30 is half-past three in the afternoon on a digital clock.
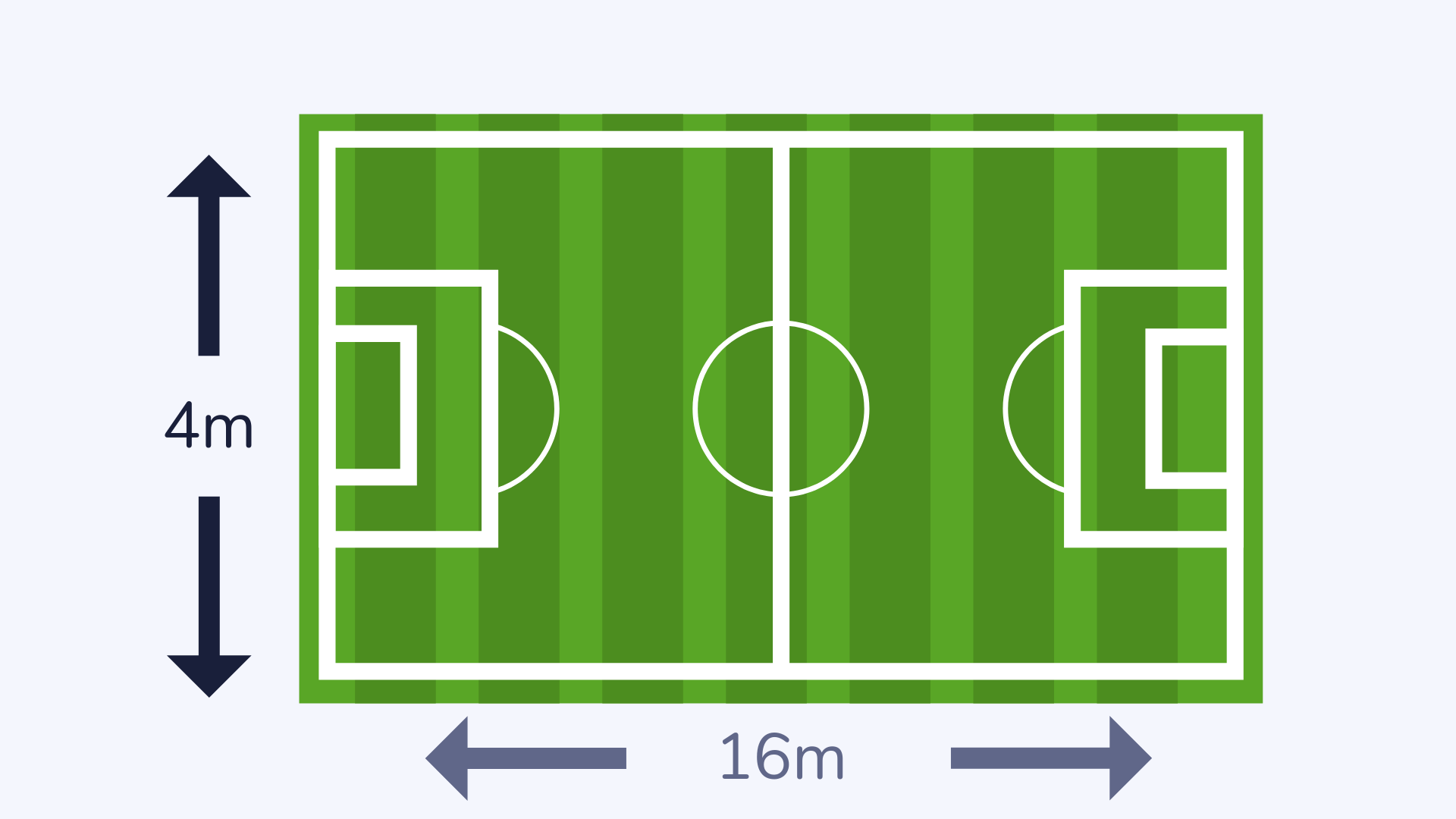
Area
The area of a shape, surface, piece of land etc. means the amount of space it takes up.
For example, a rectangular soccer field has an area of 64m² or 64 squared meters.
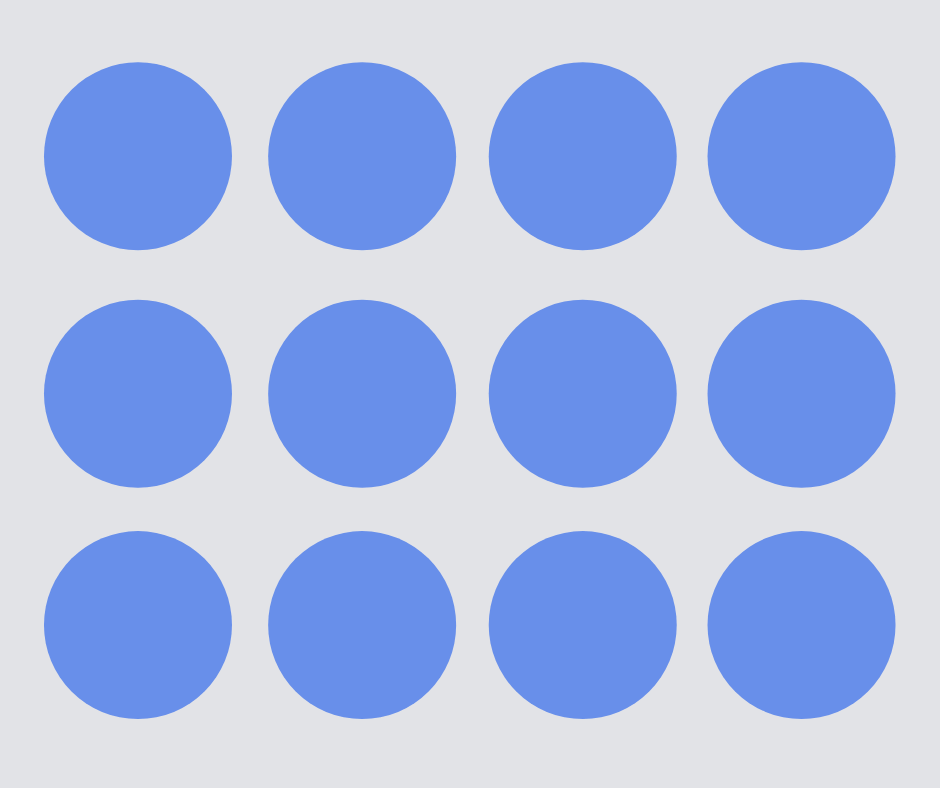
Array
An array is a visual representation of a calculation, using rows of dots, to help children understand multiplication and times tables.
An array can also help show repeated addition. For example, the array shown below can represent 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 or 4 + 4 + 4.
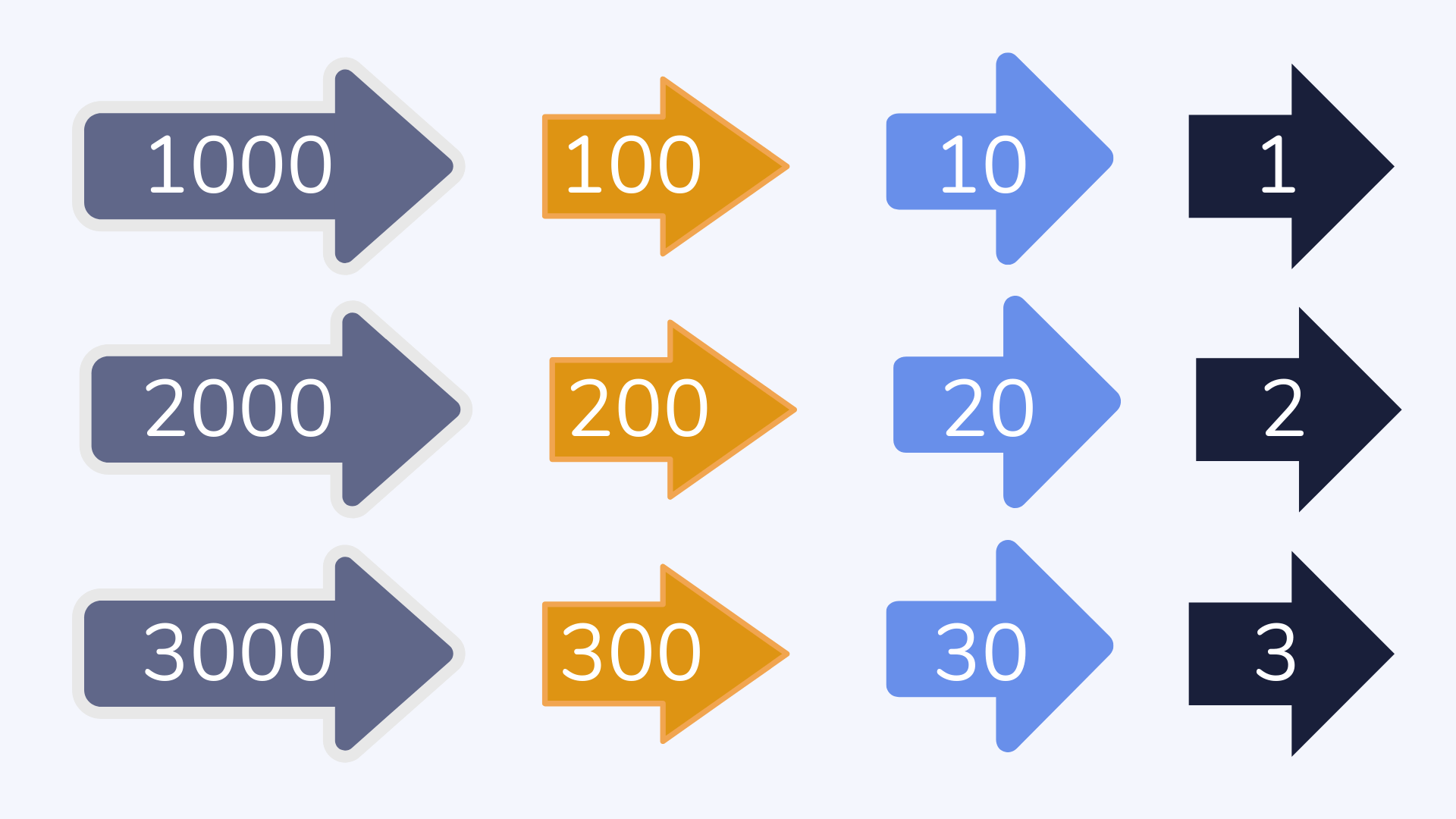
Arrow cards
Arrow cards are a math tool useful for explaining place value and how to partition numbers (separate them into ones, tens, hundreds etc).
Ascending order
To ascend means to go up, so numbers given in ascending order are going from smallest to largest or least to greatest.
For example, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 are numbers in ascending order.
Associative property
The associative property says that when we add or multiply numbers, it doesn’t matter how we group them (which we calculate first).
For example, (7 + 5) + 3 = 7 + (5 + 3) or (4 x 5) x 2 = 4 x (5 x 2)
Average
The average of a set of numbers is found by adding all the numbers together and dividing by how many numbers there are.
For example, the average of 12, 10, 8 and 6 is 9 because (12 + 10 + 8 + 6 = 36 ÷ 4).
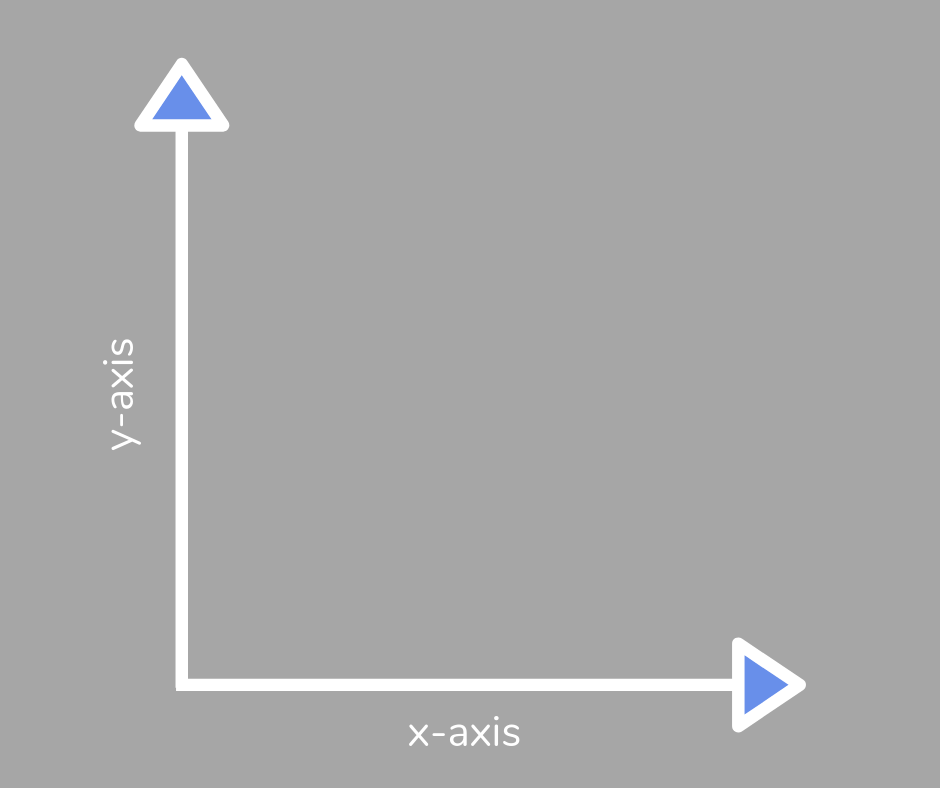
Axes
The axes of a graph or chart are the horizontal and vertical lines that create it, often known as the x-axis and y-axis.
B
B
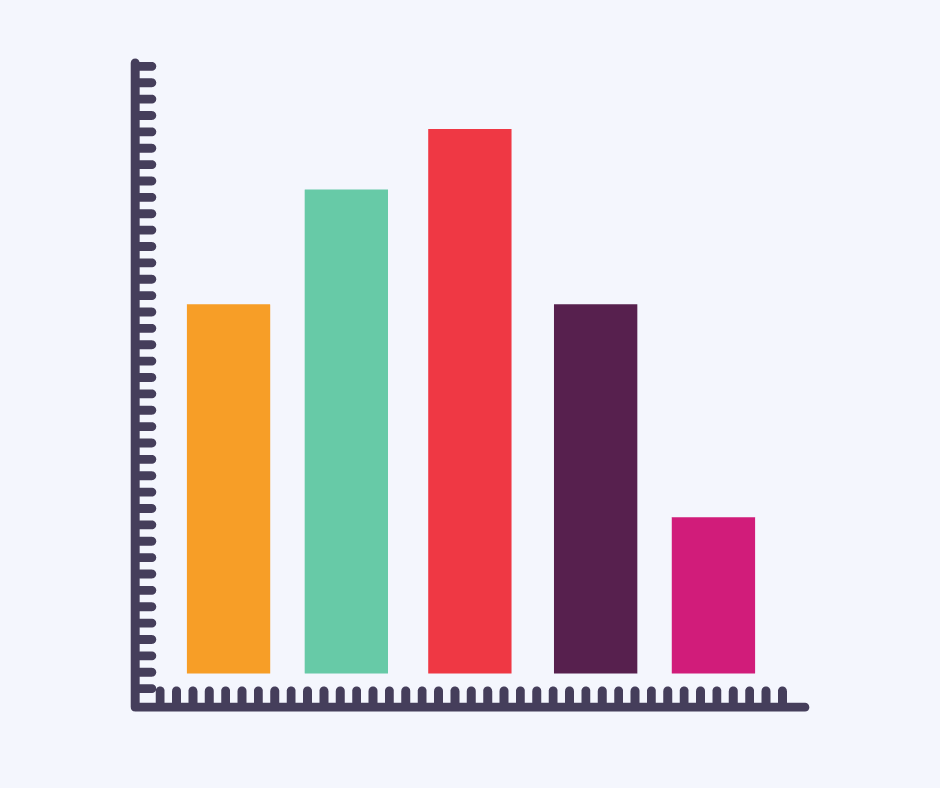
Bar graph
A bar graph is a form of graph that displays information using rectangular bars of different heights, according to their numerical value.
Bar model
A bar model is a method that uses diagrams of rectangular bars to represent math problems in a visual way, making it easier for children to see which operation to use to work out a calculation. Younger children may use cubes to physically represent this.
Read more: What is a bar model
Block graph
A block graph is a simpler version of a bar graph, but using blocks to represent the data, with each block worth 1 unit.
BODMAS
BODMAS is a rule for the order to work out calculations with mixed operations. It stands for Brackets, Orders, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction and is sometimes seen as BIDMAS (Brackets, Indices, Division, Multiplication, Addition, Subtraction). In the US, it is more commonly referred to as PEMDAS (Parentheses, Exponents, Multiplication, Division, Addition, Subtraction)
Read more: What is BODMAS?
Bridging through 10
Bridging through 10 is a way of adding numbers greater than 10 in your head.
For example, to add 8 + 7, you add 2 (from the 7) to get 10, then add the remaining 5 to get 15.
Bus stop method
The ‘bus stop’ method or short division is a way of dividing numbers with two or more digits by one or two digit numbers.
Read more: What is bus stop method
C
C
Capacity
The capacity of a container is how much that container can hold, measured using units such as litres, millilitres, pints etc.

Cardinal numbers
A cardinal number tells you how many of something there are; they refer to a set of objects. For example, there are three marbles in my hand. This is in contrast to an ordinal number which tells you the position of something in a list, for example, first, second, third.
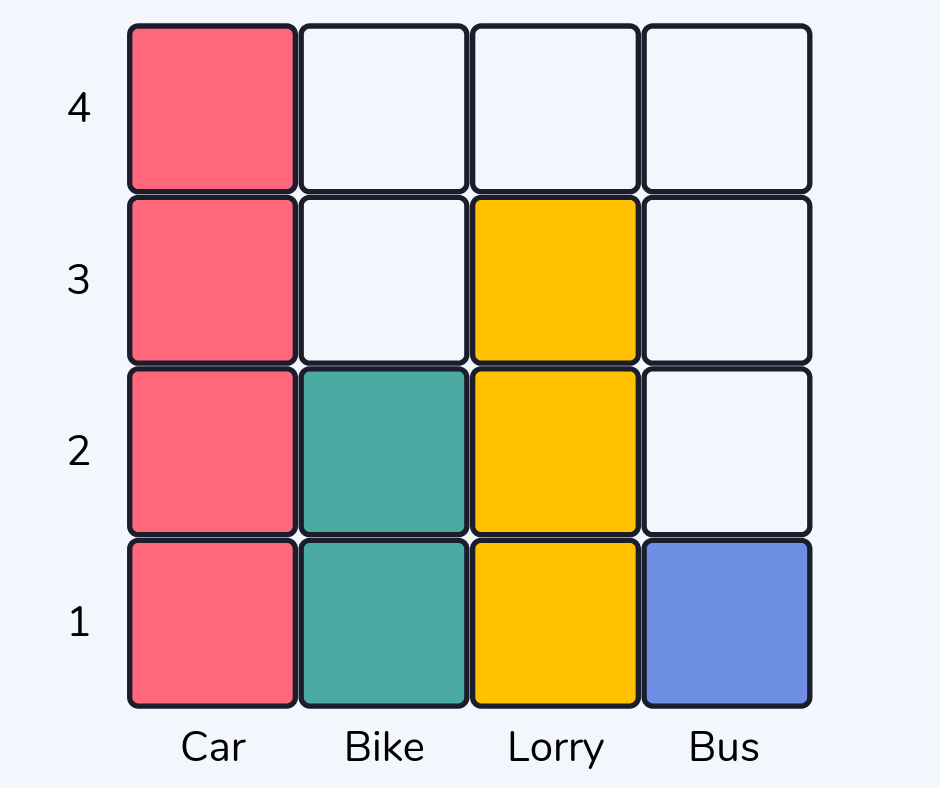
Carroll diagram
More often referred to as a simple table, a Carroll diagram is more than this and is a way of organizing information and grouping according to what criteria it fits into.
For example, which shape has 6 sides and 1 line of symmetry?
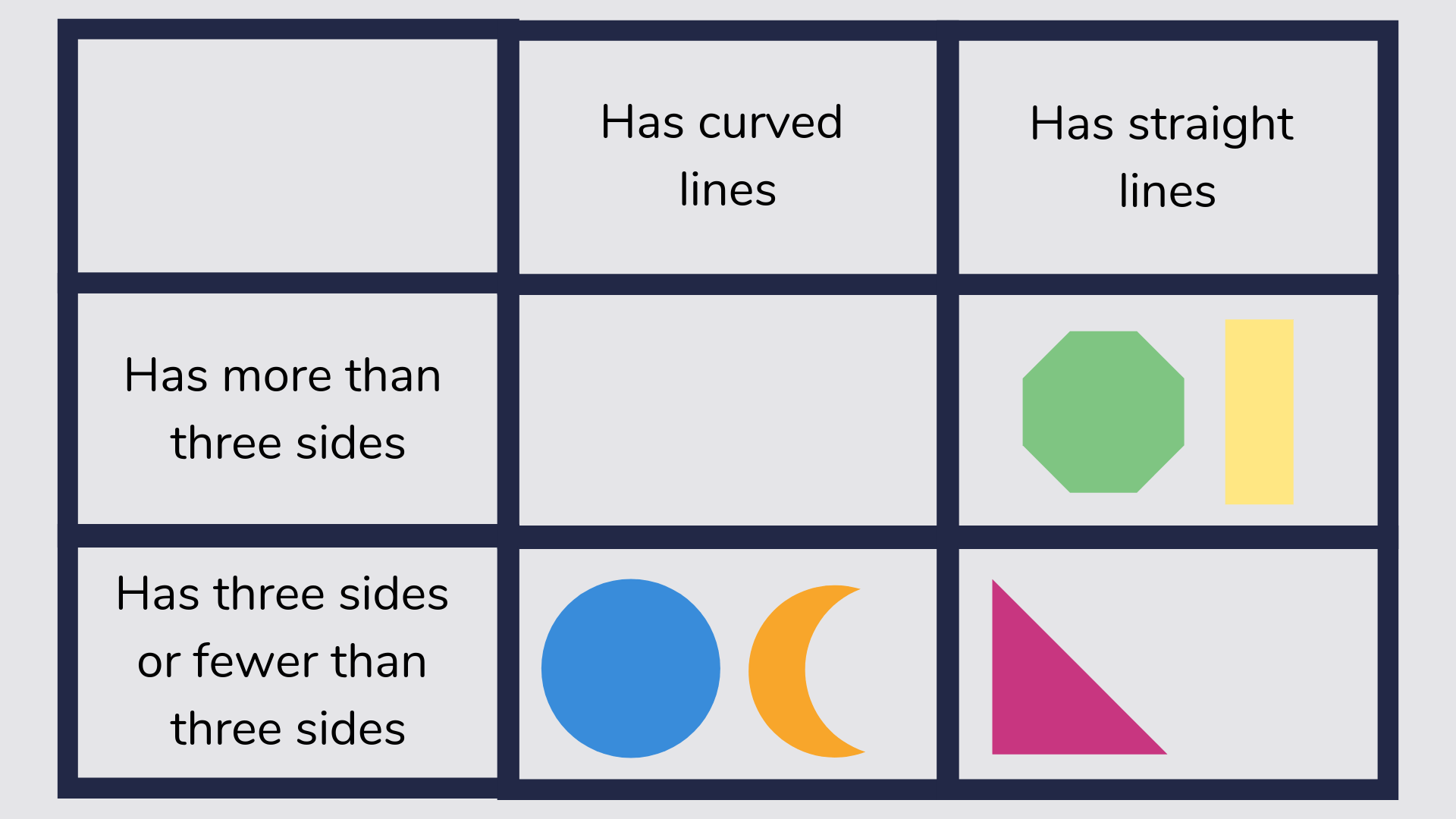
Read more: What Is A Carroll Diagram
Circle
A circle is a simple curved 2D shape, with 1 edge, no corners and infinite lines of symmetry.
Circumference
The circumference is the length around the edge of a circle.
Clockwise and anti-clockwise
To move in a clockwise direction means moving in the same direction as the hands on a clock. If something moves in the opposite direction to the hands of a clock, it is moving in a counterclockwise direction.
Coordinates
The coordinates of a shape or object refer to where on a map or graph they are, by looking at the two axes and recording the numbers they are at. These can be taught with the phrase “along the corridor and up/down the stairs” to refer to looking at the x-axis first then looking at the y-axis.
Read more: What are coordinates?
Column method
The column method is a way to solve addition and subtraction calculations that sometimes involve ‘exchanging’ or ‘regrouping’ amounts from one column to the next (which in the past has been called ‘carrying’ and ‘borrowing’).
The numbers are written on top of each other, with the correct digits in each column (e.g. hundreds, tens, ones). This is also known as standard algorithm subtraction and standard algorithm addition.
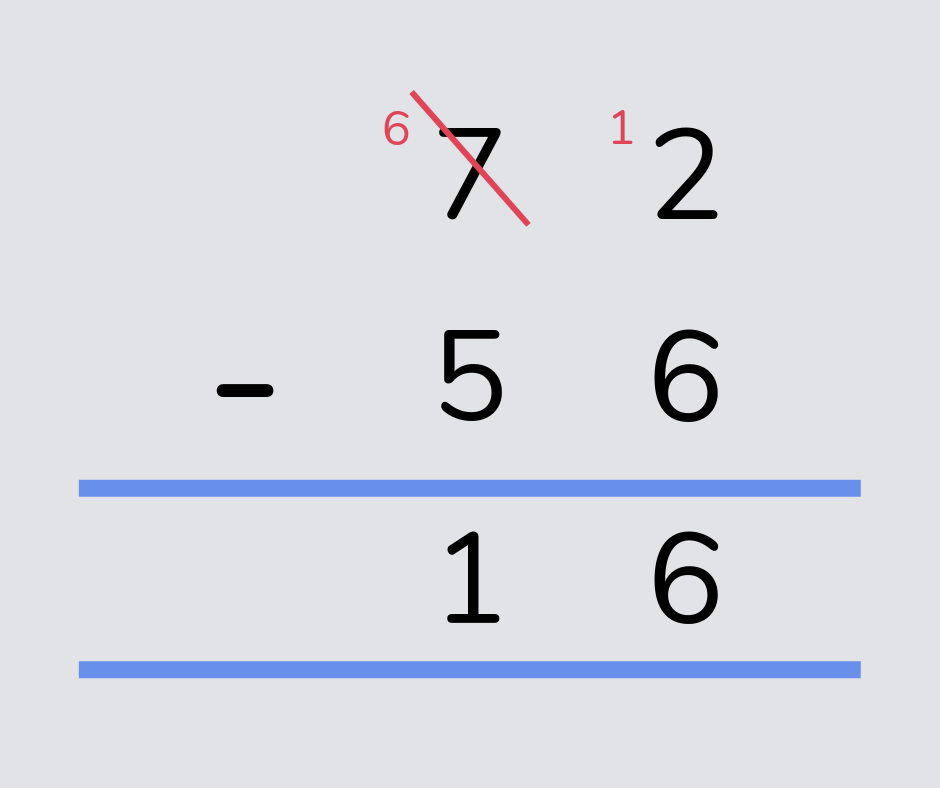
Read more:
Commutative property
The commutative property states that addition and multiplication calculations can be carried out with the numbers in any order, whereas for subtraction and division, the numbers must be in a particular order.
For example, 8 x 9 = 72 or 9 x 8 = 72
Complementary addition (subtraction on a number line or the jump strategy)
Complementary addition is a method for subtraction that involves using a number line to jump from the smaller number to the bigger number and counting the number of jumps. This method is useful in kindergarten and first grade for teaching children to ‘find the difference’ between two numbers.
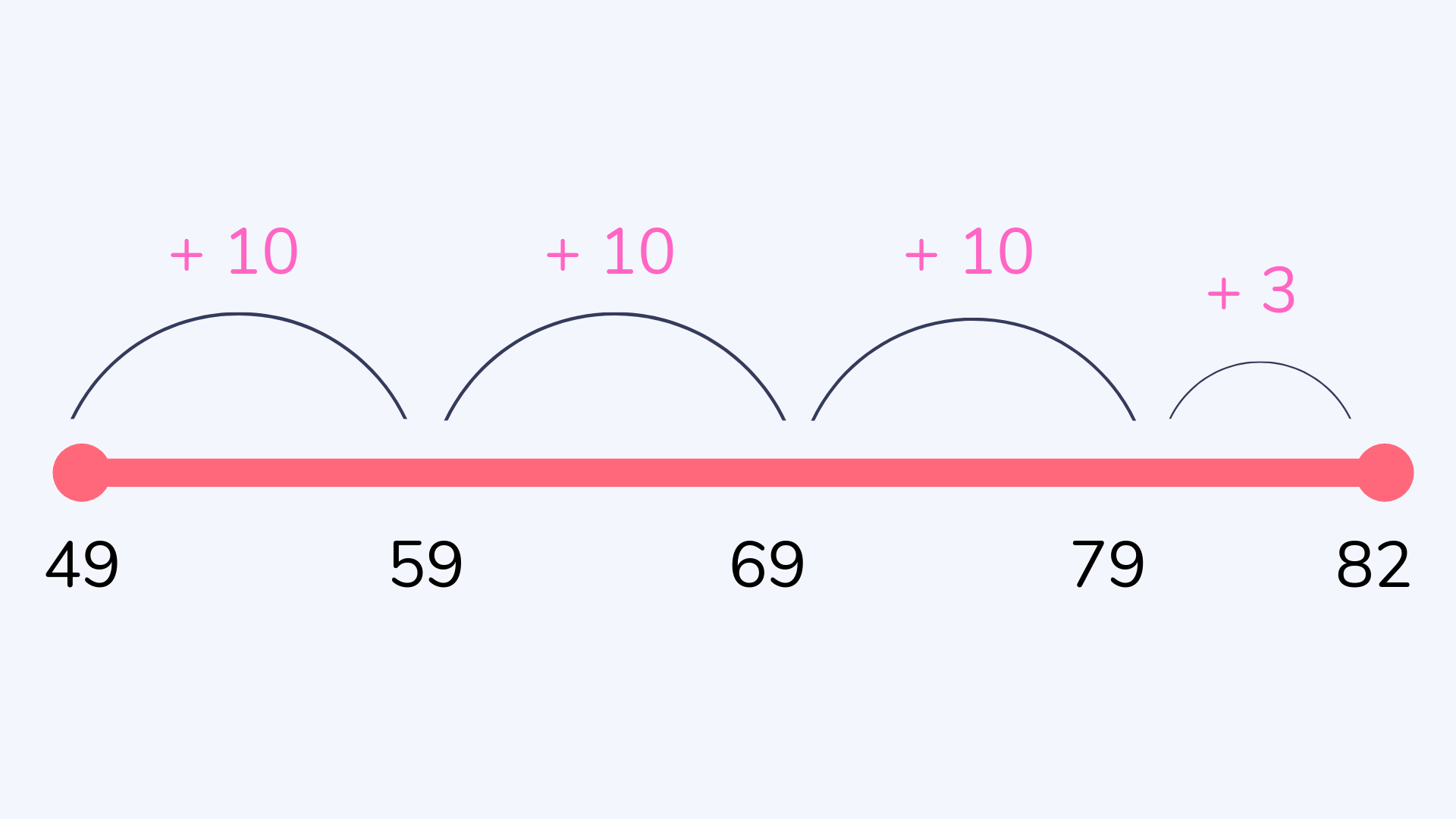
Concrete Representational Abstract approach (CRA)
The concrete, representational, abstract approach is a way of teaching mathematical concepts and theories in various stages, in order to help children fully understand and master what they are learning.
The concrete stage involves using items, models and objects, giving children a chance to be ‘hands-on.’
For example, children may solve a problem by adding groups of toys together using real toys, or they may manipulate buttons, Legos, etc when working out fractions of amounts. At school, there are a variety of concrete resources specially designed for math, such as place value counters, base ten blocks, and ten frames.
The representational stage uses visual representations of concrete objects to model problems, encouraging children to make connections between the physical object and the picture that represents the object.
For example, children may use drawings of toys to solve a problem adding toys.
The abstract stage uses symbols, such as numbers or mathematical symbols (+, -, x, =) to model problems. Children will need to master the concrete and representational stages before moving onto the abstract stage.
Converting into same units
When you convert measurements into the same units, you understand that the same length, weight or capacity can be shown in different units of measurement.
For example, a bottle of water can be measured in cups or pints and there are 2 cups in 1 pint.
Cube numbers
A cube number is the result when a number is multiplied by itself three times. When writing cube numbers, we write a small three above the number, e.g. 3 x 3 x 3 or 3³ = 27. We would read this as ‘3 cubed.’
Read more: What are cube numbers?
D
D
Data handling
Data handling is another term for statistics, meaning how we collect, display and interpret data or information, such as the most popular flavor of ice cream in a class, using tables, tally charts, pictograms, block diagrams, bar graphs, line graphs and pie charts.
Decimal
A decimal is a number that contains tenths, hundredths, thousandths etc, with a decimal point between the ones and tenths. Money is often used to teach decimals.
For example, 3.4, 2.18, $56.99If you are interested in other ways to teach your child about money, take a look at our blog.
Degrees
We use degrees as the unit of measurement for measuring angles, usually symbolized with a small circle above the number. For example, a right angle is 90° (90 degrees).
Denominator
A denominator is the name for the bottom number in a fraction. For example, in the fraction 4/10, 10 is the denominator.
Descending order
Descending order means to go from the largest number to the smallest, or greatest to least, and is the opposite of ascending order.
For example, 90, 80, 70, 60, 50 are numbers in descending order.
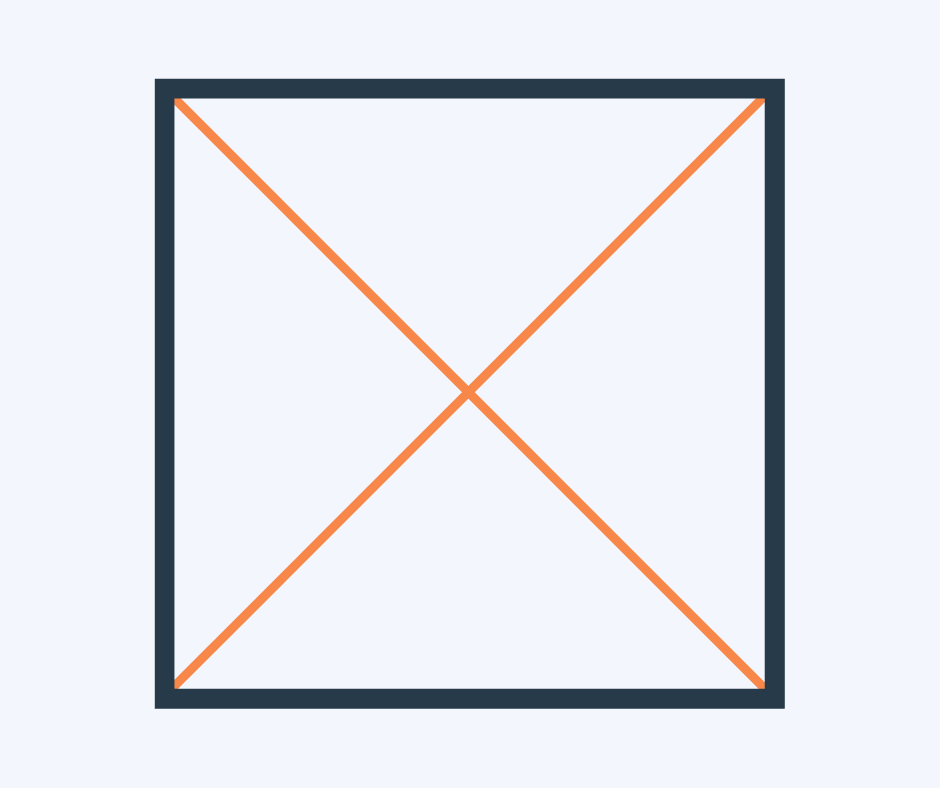
Diagonal
A diagonal is a line joining two opposite corners of a square, rectangle or other shape.
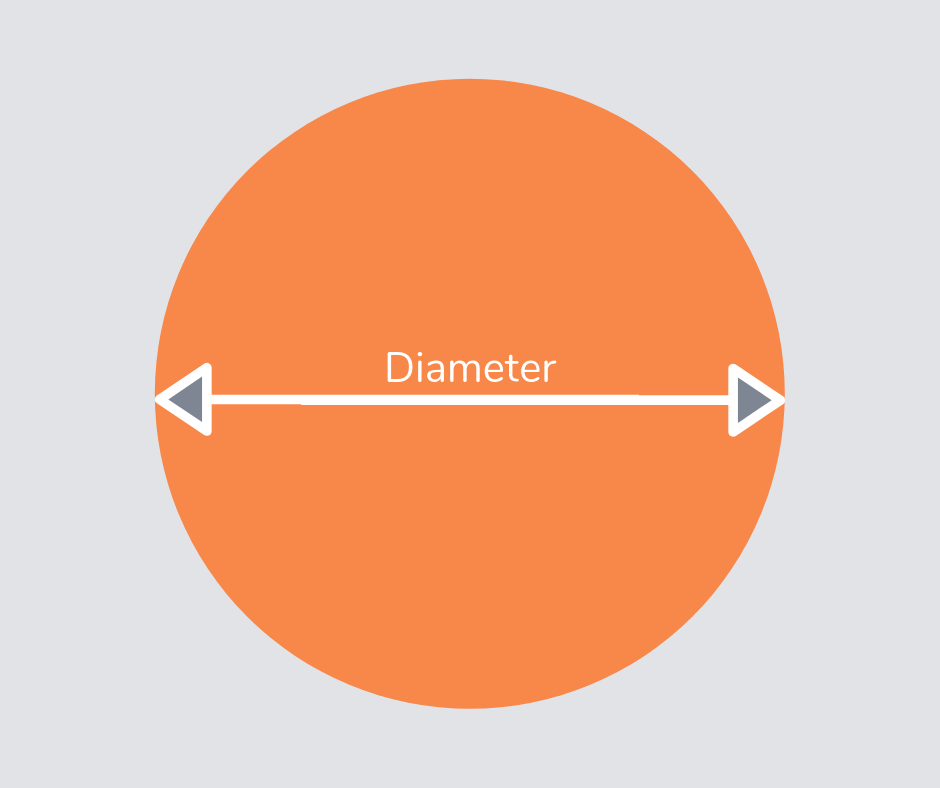
Diameter
The diameter is a straight line going from one side of a circle to another, through the center.
Distributive property
The distributive property states that multiplying a number by a group of numbers added together is the same as doing each multiplication separately.
For example, 5 x (2 + 6) = 5 x 2 + 5 x 6
Dividend
The dividend is the number that you are about to share out, or divide.
Divisor
The divisor is the number of times you need to share out, or divide, your dividend.
Division facts
Division facts are the division equations related to times tables.
For example, 50 ÷ 5 = 10 and 25 ÷ 5 = 5 are division facts related to the 5 times table.
Read more: Division For Kids: Short and Long Division Explained
E
E
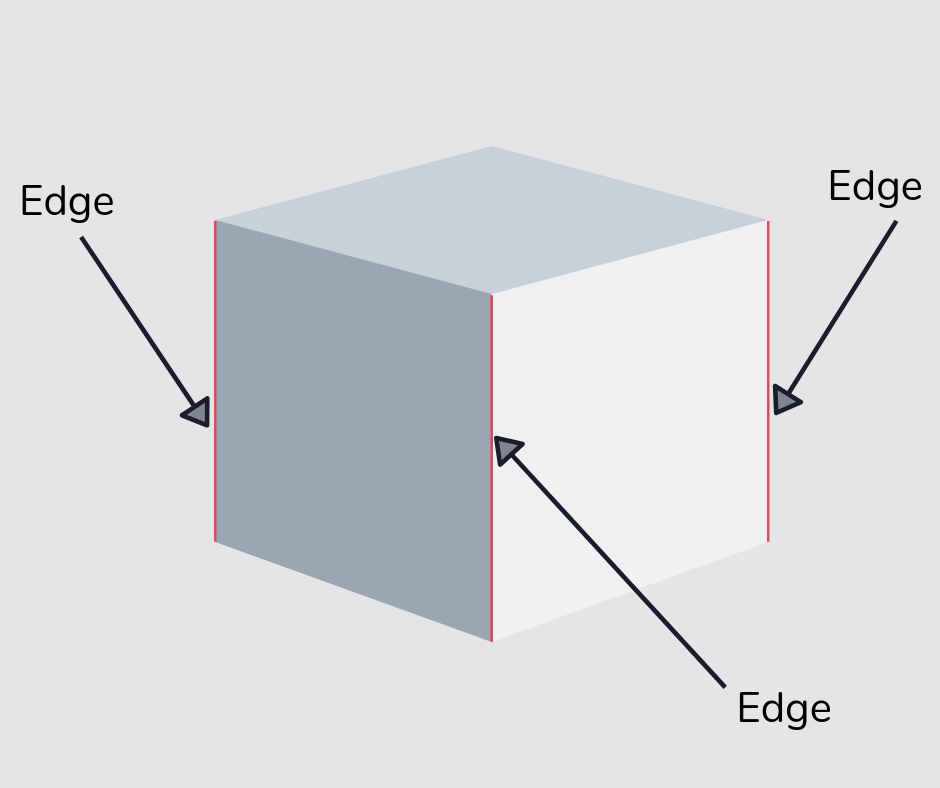
Edge
An edge is the name for lines created when two faces in a 3D shape meet.
Equation
An equation is another name for a number sentence where both sides equal the other.
For example, 12 – 5 = 3 + 4
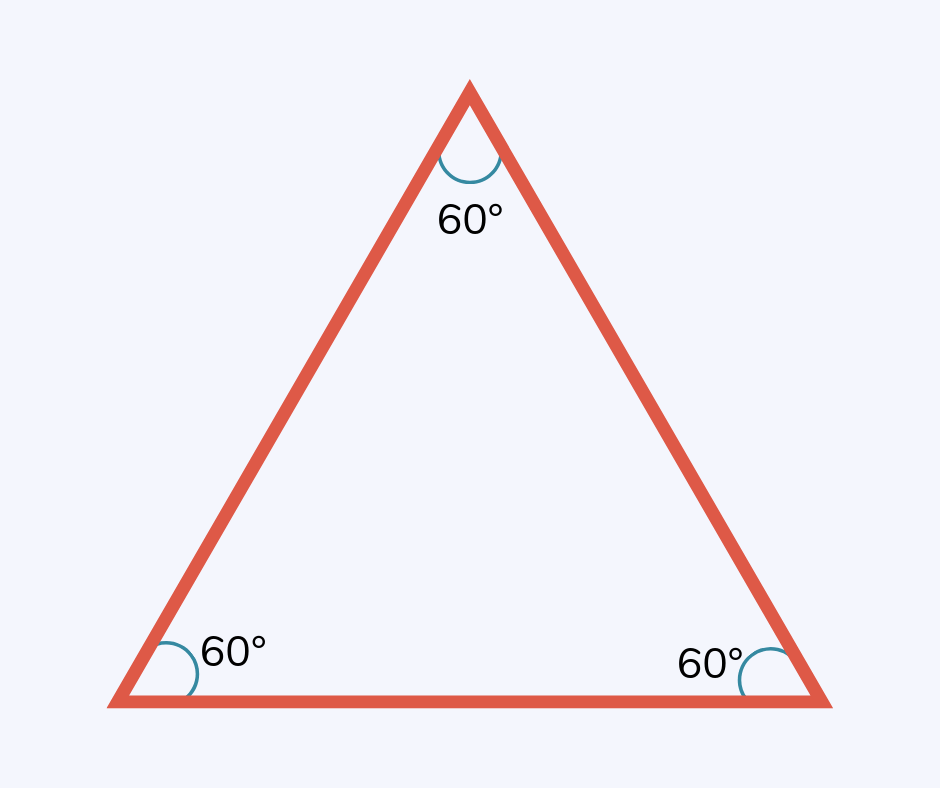
Equilateral Triangle
An equilateral triangle is a triangle with three equal sides and three equal angles.
Equivalent fractions
An equivalent fraction is one that is equal in terms of size to another, but written using different numbers. For example, \frac{1}{2} is equivalent to \frac{4}{8} and \frac{7}{14}.
Read more: What are equivalent fractions?
Estimate
To estimate is to make a clever guess to the answer of a question, by roughly calculating the value. For example, children estimated the length of the playground to be 100 yards.
Expanded notation
Expanded notation means to write a number showing the value of each digit, with each digit being multiplied by its matching place value (ones, tens, hundreds etc).
For example, 352 = 3 x 100 + 5 x 10 + 2 x 1.
F
F
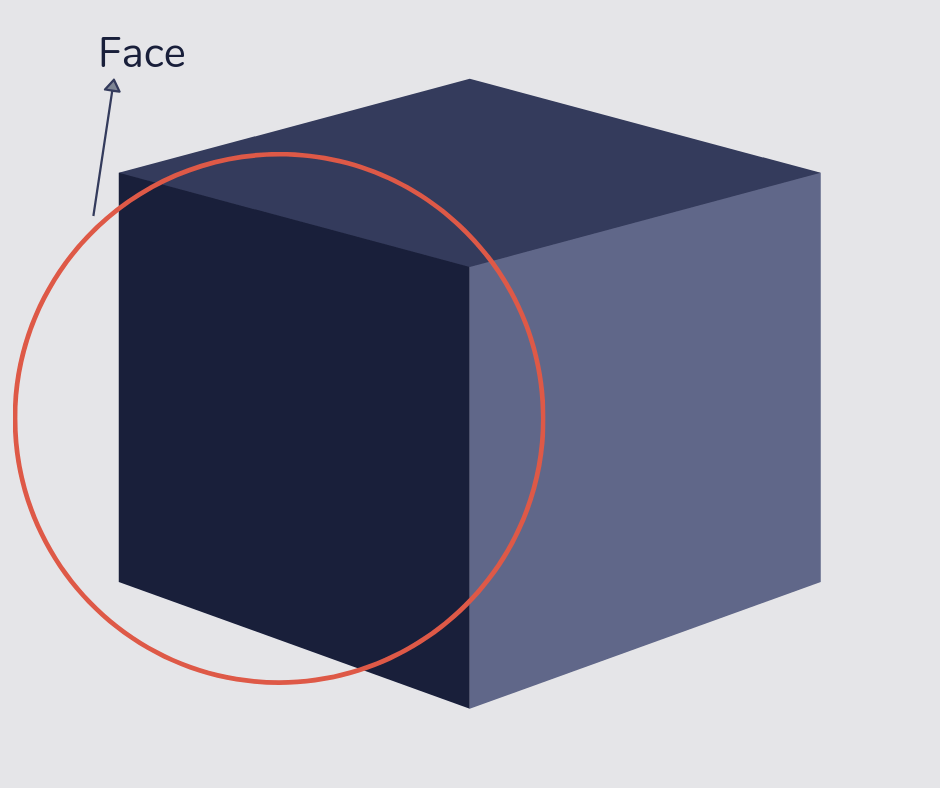
Face
A face is the flat part of a 3D shape.
Factor
A factor is a number that can divide exactly into another number.
For example, 2, 3, 4 and 6 are all factors of 12, as 12 can be divided by them exactly.
Read more: What are factors?
Finding the difference between two numbers
Finding the difference between two numbers is the same as subtracting a smaller number from a larger number. This method is usually taught using a number line, counting the jumps from one number to another.
Formula
A formula is a group of numbers and math symbols that show how to work something out. In elementary school, children will encounter formulas for finding the area and perimeter of 2D shapes and for finding the volume of 3D shapes.
G
G
Geometry
Geometry is the branch of math where children learn about the properties, measurements, position and relationships of points, lines, angles and shapes.
Greatest common factor
The greatest common factor is the largest whole number which is a factor of two or more numbers.
For example, 6 is the greatest common factor of 12 and 18.
Read more: What is the greatest common factor?
Grid method
The grid method is a way for working out multiplication calculations, especially with larger numbers, involving partitioning the numbers, multiplying each part and adding the totals. This is also known as the ‘area model.’
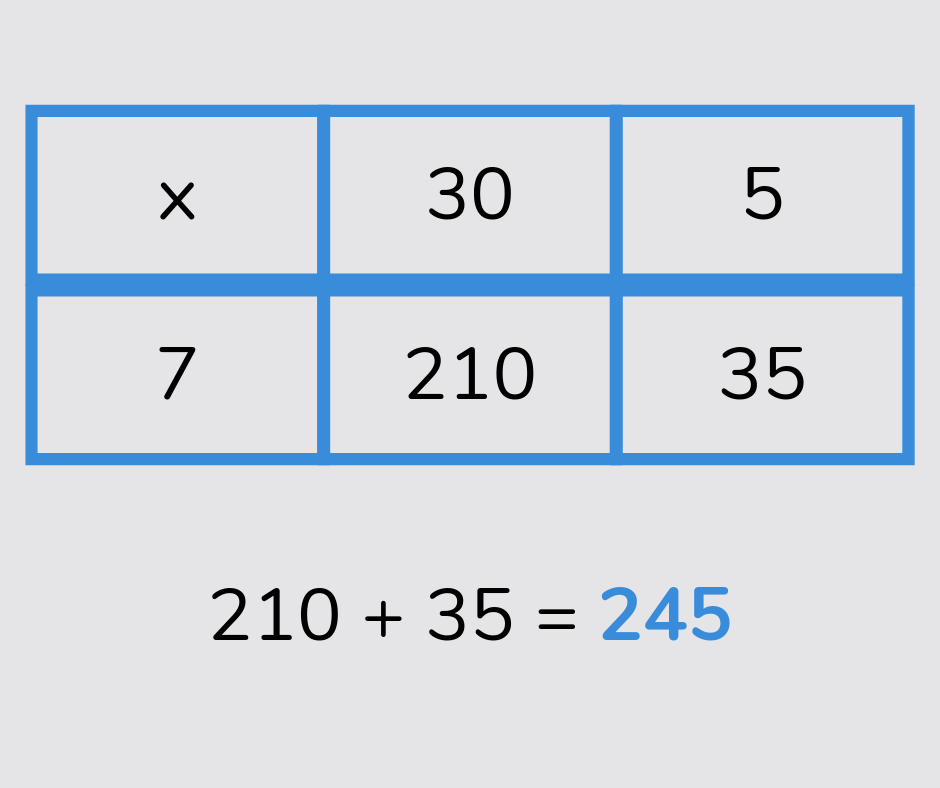
H
H
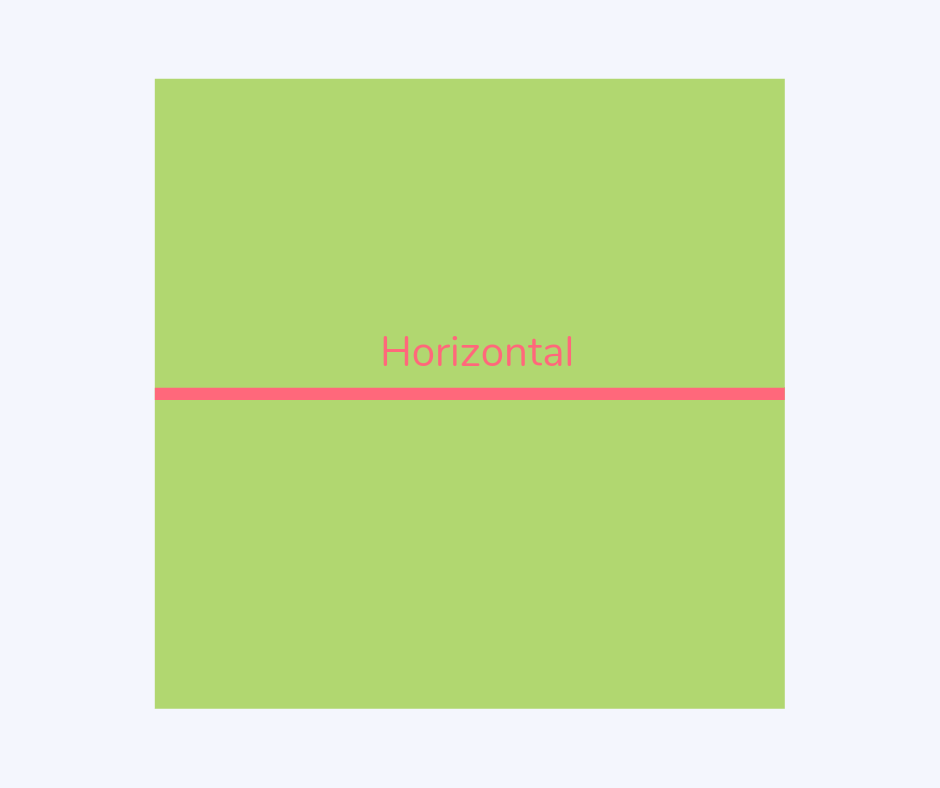
Horizontal
A horizontal line is one that goes from left to right and vice versa.
I
I
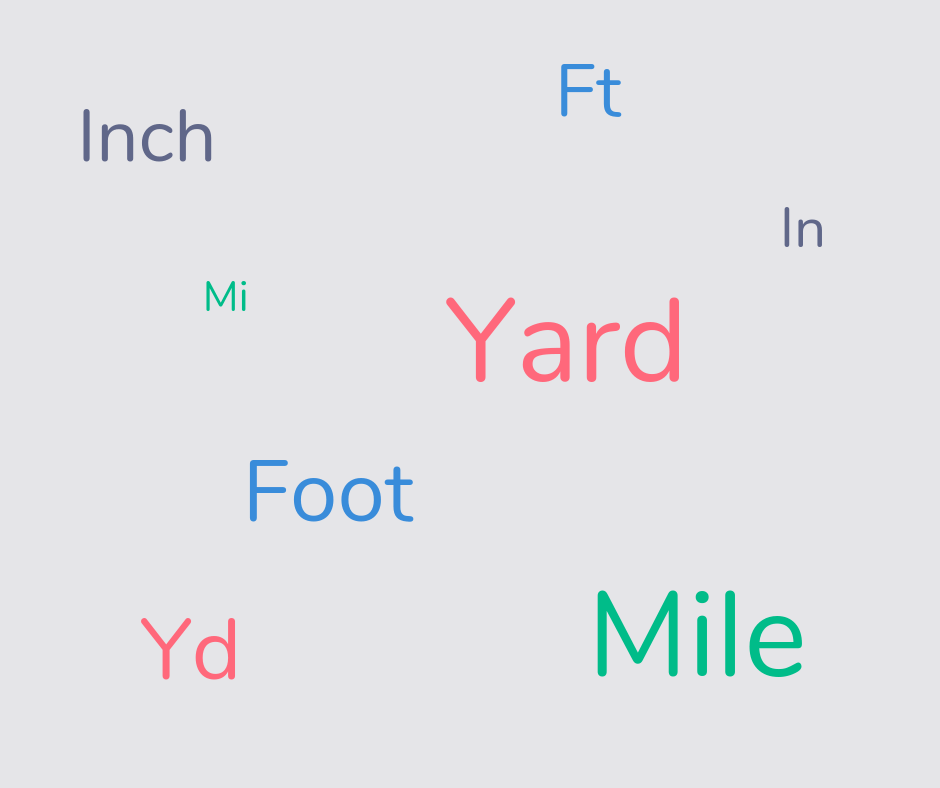
Imperial units
Imperial units are units of measurement commonly used in the US. Children, in elementary school and middle school, will be taught how to convert from, for example, pounds to ounces.
Improper fraction
An improper fraction is one where the numerator is larger than the denominator and is also known as a ‘fraction greater than one.’ For example, 11/4, 6/2 and 21/5 are all improper fractions.
Read more: What Is An Improper Fraction?
Investigation
A mathematical investigation allows children to apply the skills and knowledge they’ve learned to solve problems, which may have more than one way to work them out and more than one answer.
Integer
An integer is simply a whole number, either positive or negative. For example, 8, -23, 502 and -1000 are all integers.
Inverse operation
An inverse operation is another way of saying an opposite operation, which can often be used to check calculations are correct. For example, addition and subtraction are inverse operations, as are multiplication and division.
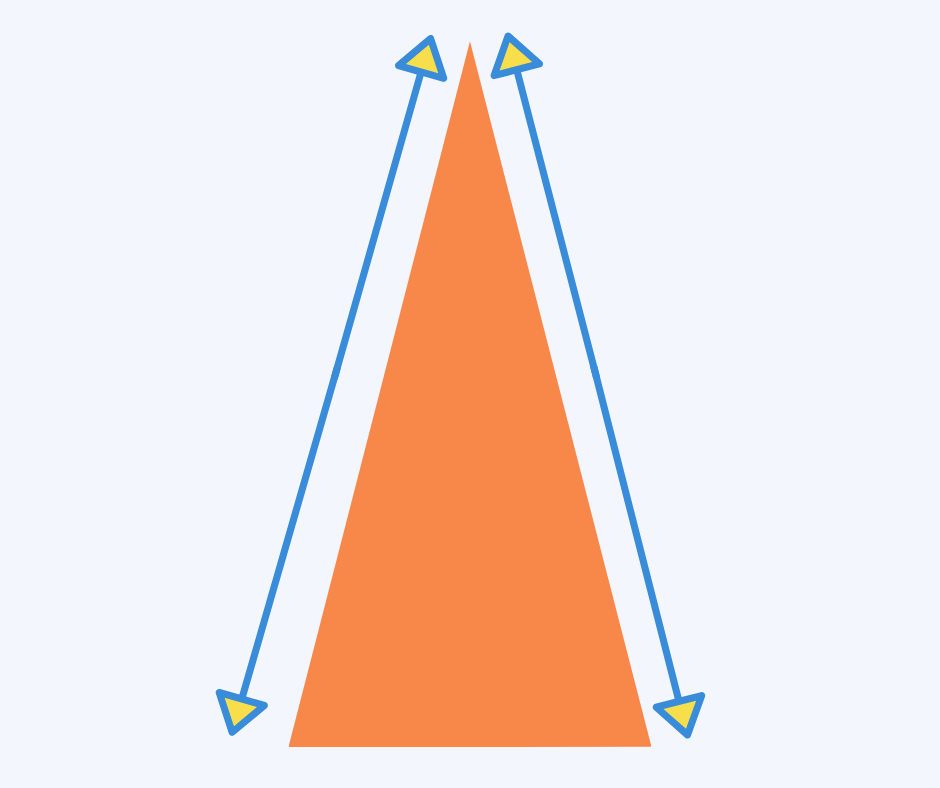
Isosceles triangle
An isosceles triangle is one with two equal sides and two equal angles.
J
J
Jump
A move made when practicing addition or subtraction – forwards or backwards respectively – on a number line.
K
K
Kite
A quadrilateral (four-sided shape) with two pairs of adjacent (next-door) sides that are congruent (equal in length). The diagonals of a kite are perpendicular (meet at a right angle).
L
L
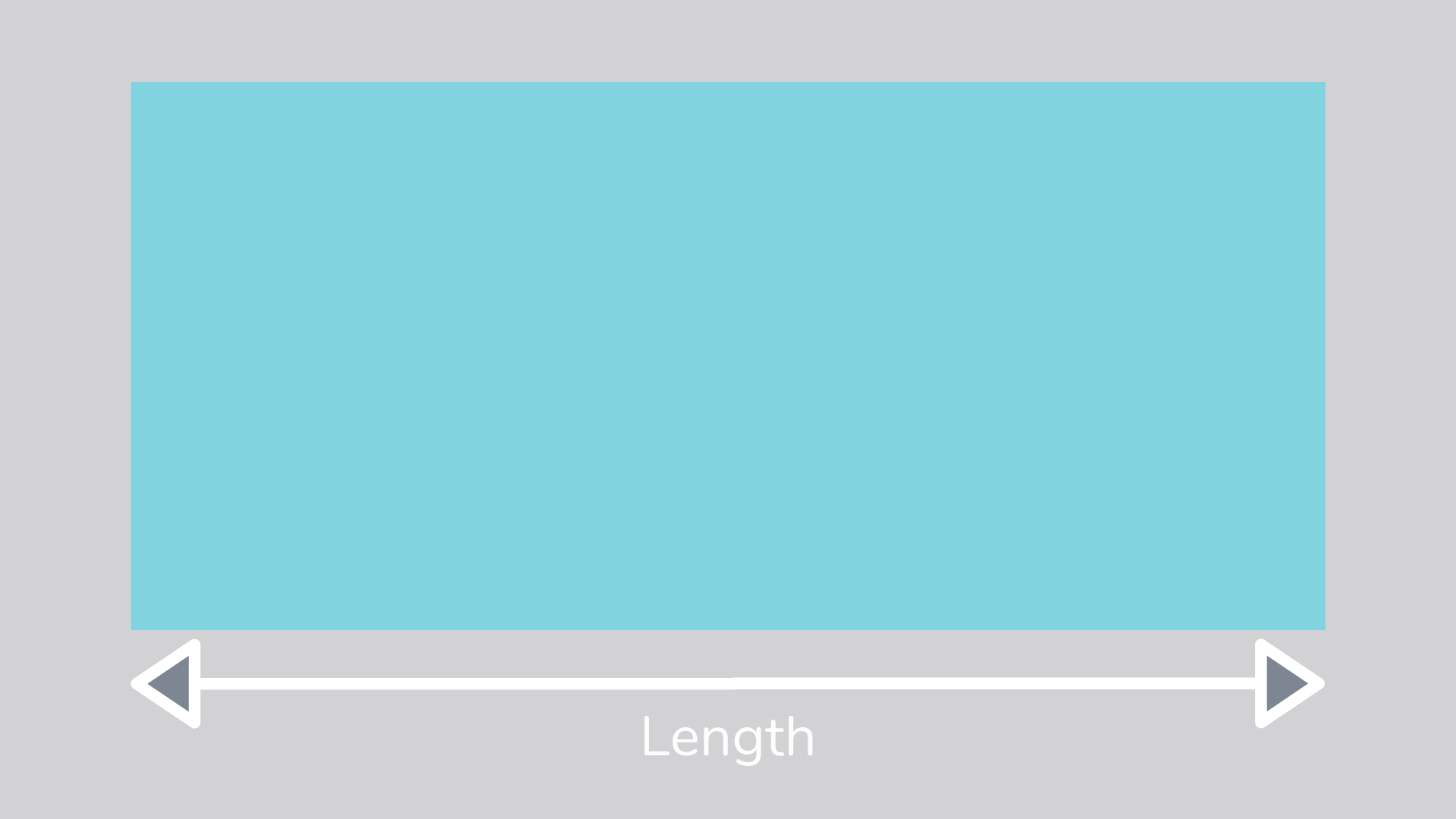
Length
The length of an object is how long or short something is, and is usually measured in units such as centimeters, inches, feet, or yards.
Line graph
A line graph is one where a line connects points, showing how values change over time.
For example, a line graph might show the amount of rainfall over six months.
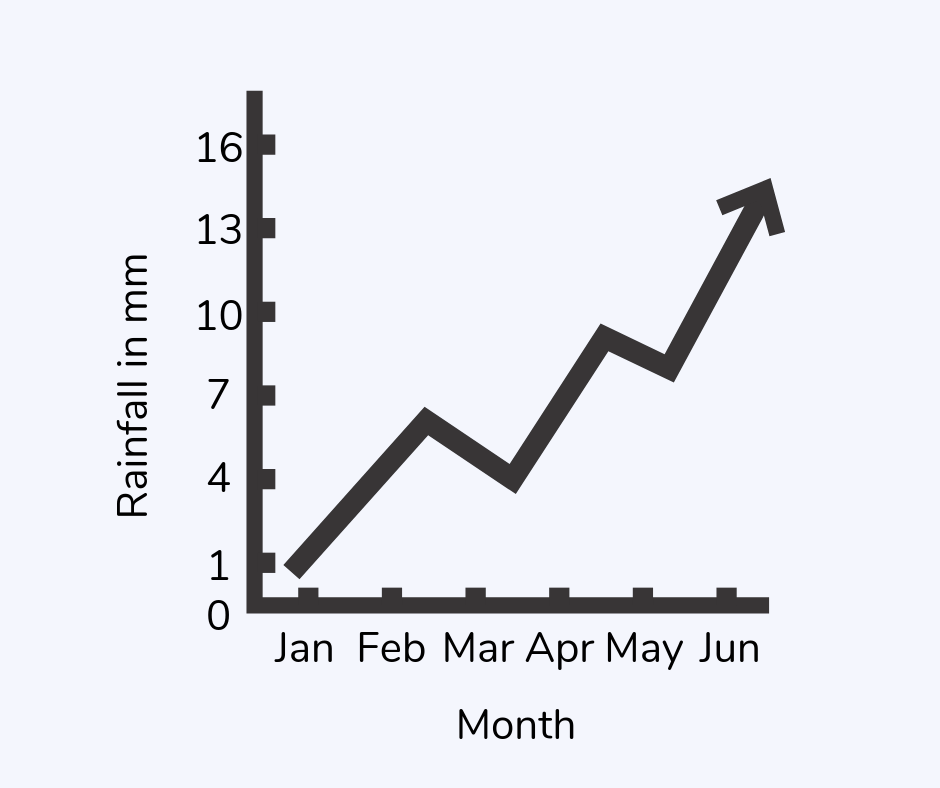
Line of symmetry
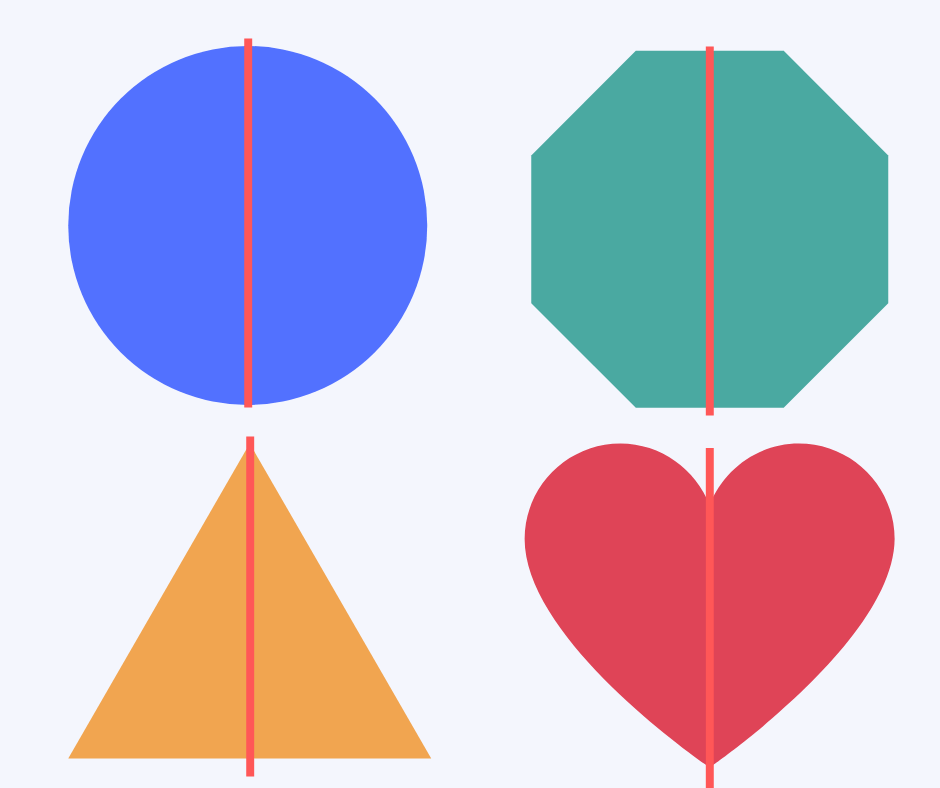
A line of symmetry is a line that can be drawn through the center of a shape or picture to show that both sides are exactly the same.
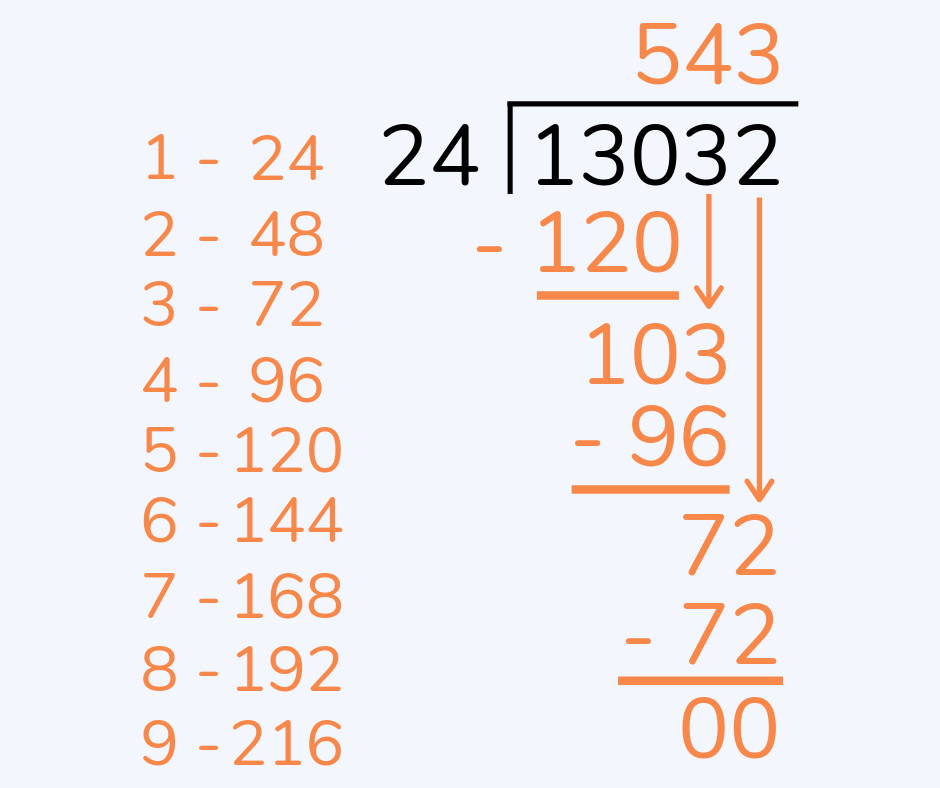
Long division
Long division is a written method showing how to divide larger numbers (such as three or four-digit numbers) by other large numbers. Children will move onto long division in elementary school, once they’ve mastered the partial quotients method.
Long multiplication
Long multiplication, which is sometimes known as column multiplication, is a way of multiplying larger numbers together. Just like column addition and subtraction, the numbers are put in columns according to their place value.
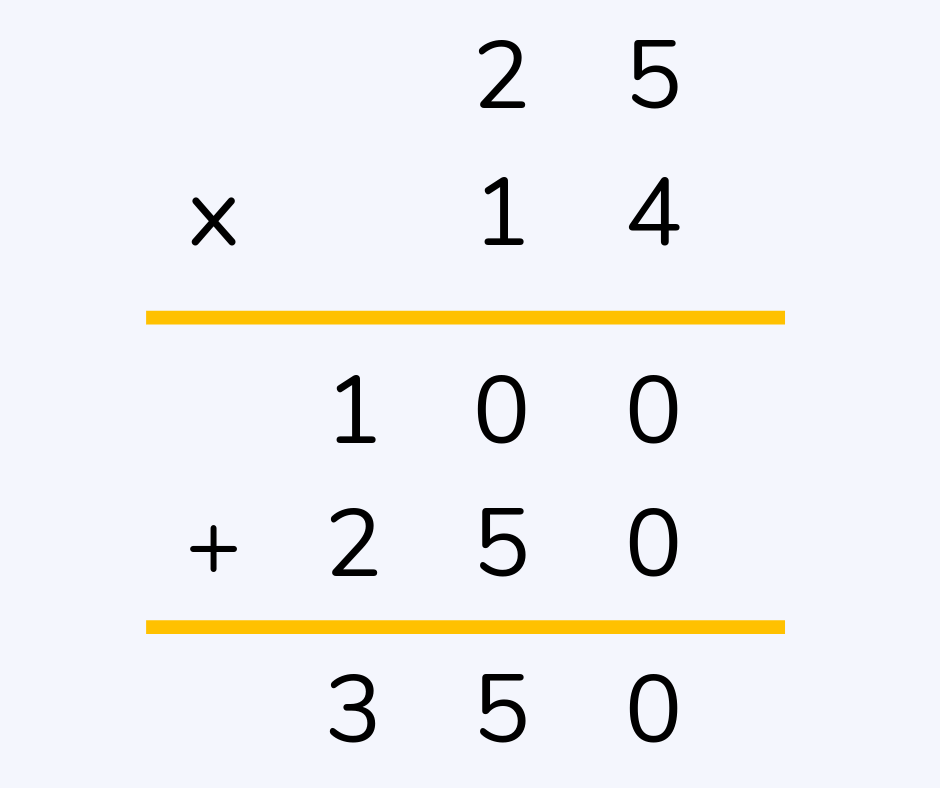
Read more: What is long multiplication?
Lowest common denominator
The lowest common denominator of two or more fractions is the smallest number that can be exactly divided by each denominator.
For example, 12 is the lowest common denominator of \frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{3} and \frac{1}{4}.
Lowest common multiple
The lowest common multiple is the smallest number which is a multiple of two or more numbers.
For example, the lowest common multiple of 4 and 5 is 20.
Read more: What is the lowest common multiple?
M
M
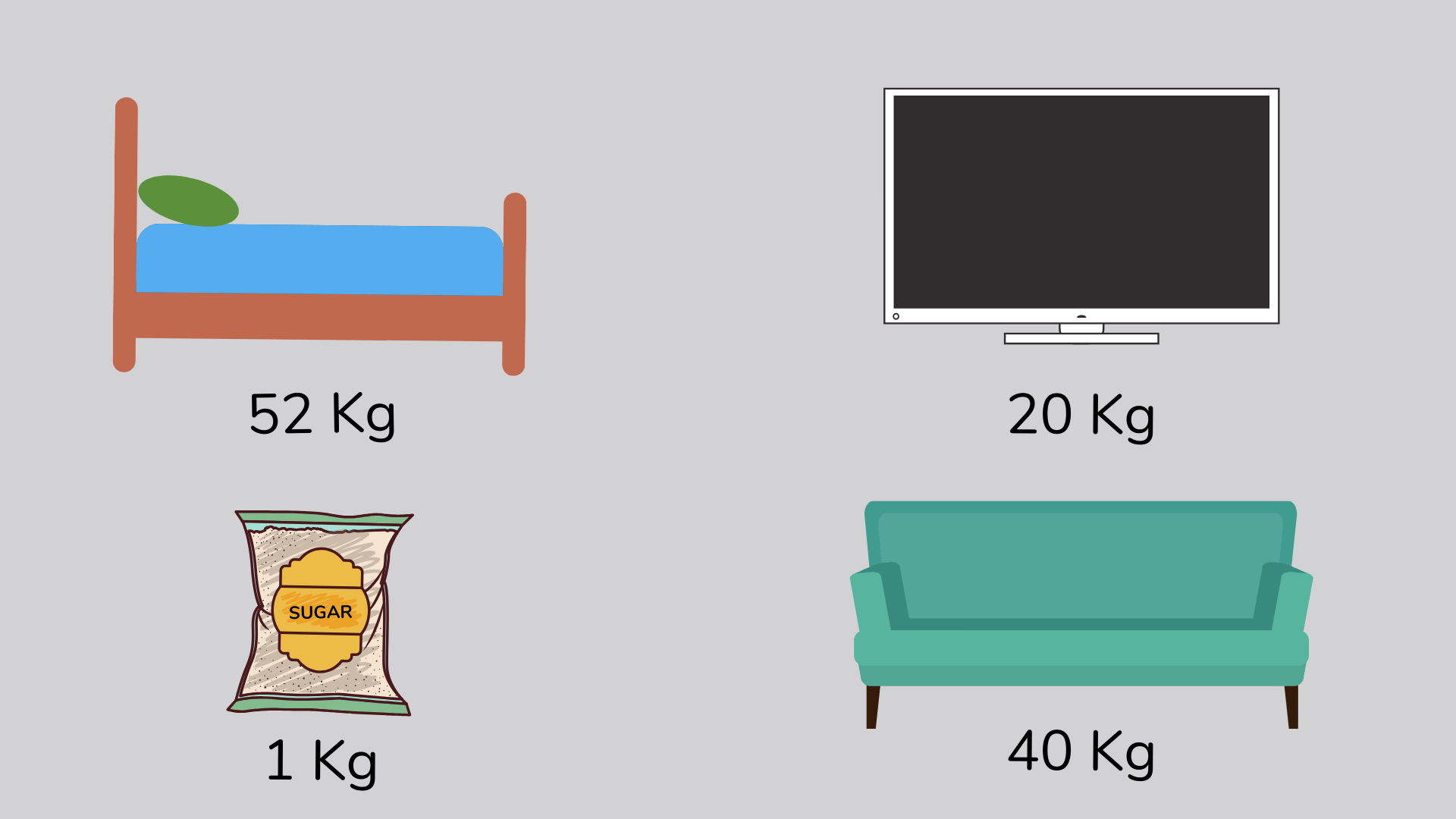
Mass
The mass of an object is how much it weighs and may be measured in pounds, ounces, kilograms, etc.
For example, the mass of a bag of sugar is 1 kg.
Mastery
Having mastery in a math topic means that children not only understand how to work out problems, but can also explain how they worked it out and apply their knowledge to more complicated word problems and investigations.
Mean
Mean is another word for average, and is found by adding a set of values and dividing the total by the number of values in the set.
For example, the mean of 2, 4, 5, 7 and 12 is 6 because (2 + 4 + 5 + 7 + 12 = 30 ÷ 5 = 6)
Read more: What Is Mean In Maths?
Median
The median of a set of numbers is the middle number in that list. The numbers in the list must first be sorted into ascending order (least to greatest), then children can find the median number.
For example, the median of 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 is 4.
Metacognition
Metacognition means to be aware of and analyze your thoughts and learning processes in order to make necessary changes to your learning behavior. Techniques such as modeling problems and getting children to ask questions about their work are ways of improving their metacognition.
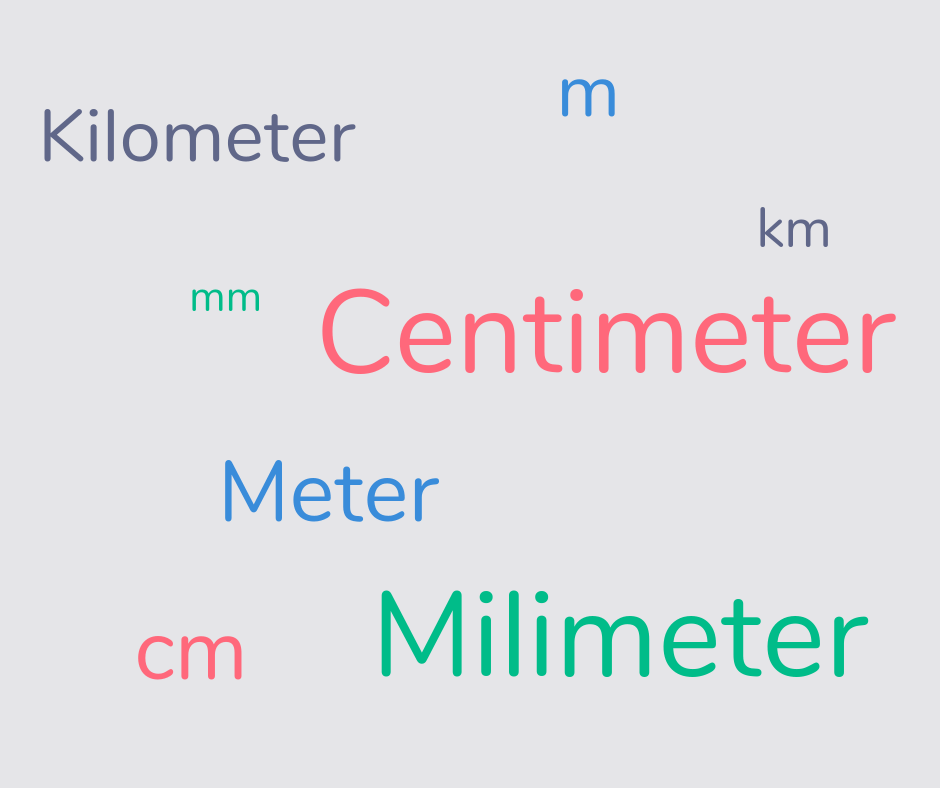
Metric units
Metric units are units of measurement that are common around the world and are based on the metric system. For example, grams, centimeters, liters and seconds are all examples of metric units.
Mixed number
A mixed number is one with both a whole number and a fraction. For example, 8 \frac{2}{3} and 5 \frac{10}{12} are mixed numbers.
Read more: What Is A Mixed Number?
Mode
The mode of a set of numbers is the one that appears most often. For example, the mode of 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7 is 5.
Multiple
A multiple is the result of multiplying one integer by another. Multiples of a number are those in that numbers times table. For example, multiples of 7 include 14, 35, 49 and 84.
Read more: What is a Multiple?
N
N
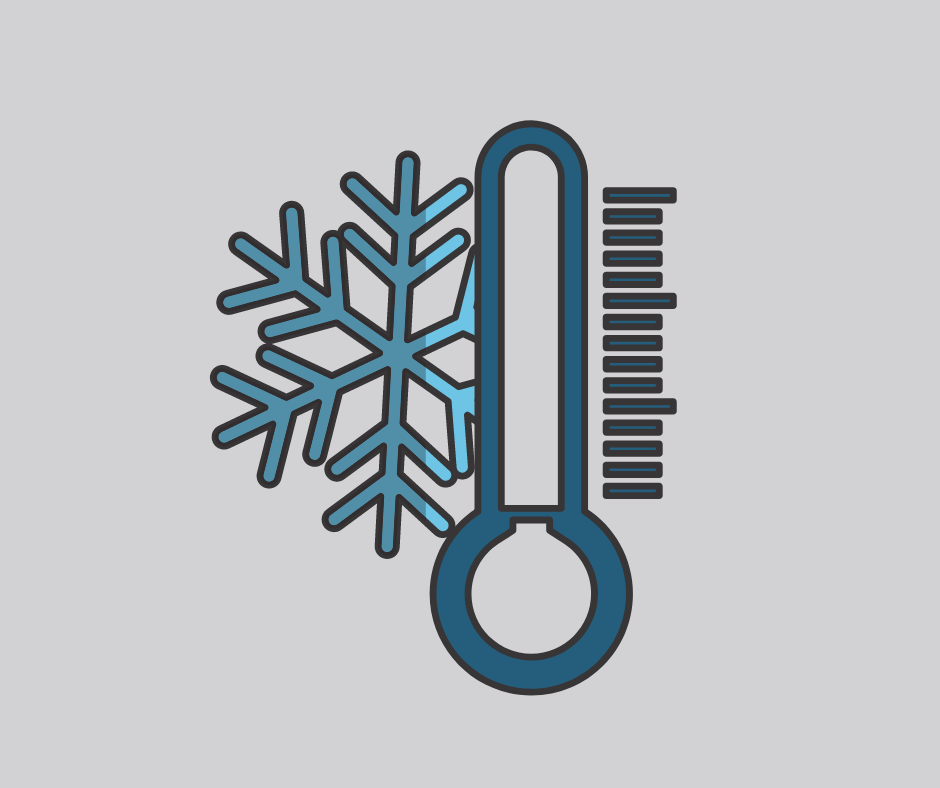
Negative numbers
A negative number is any number lower than 0 and is commonly taught using temperatures. For example, -2, -14, -67.
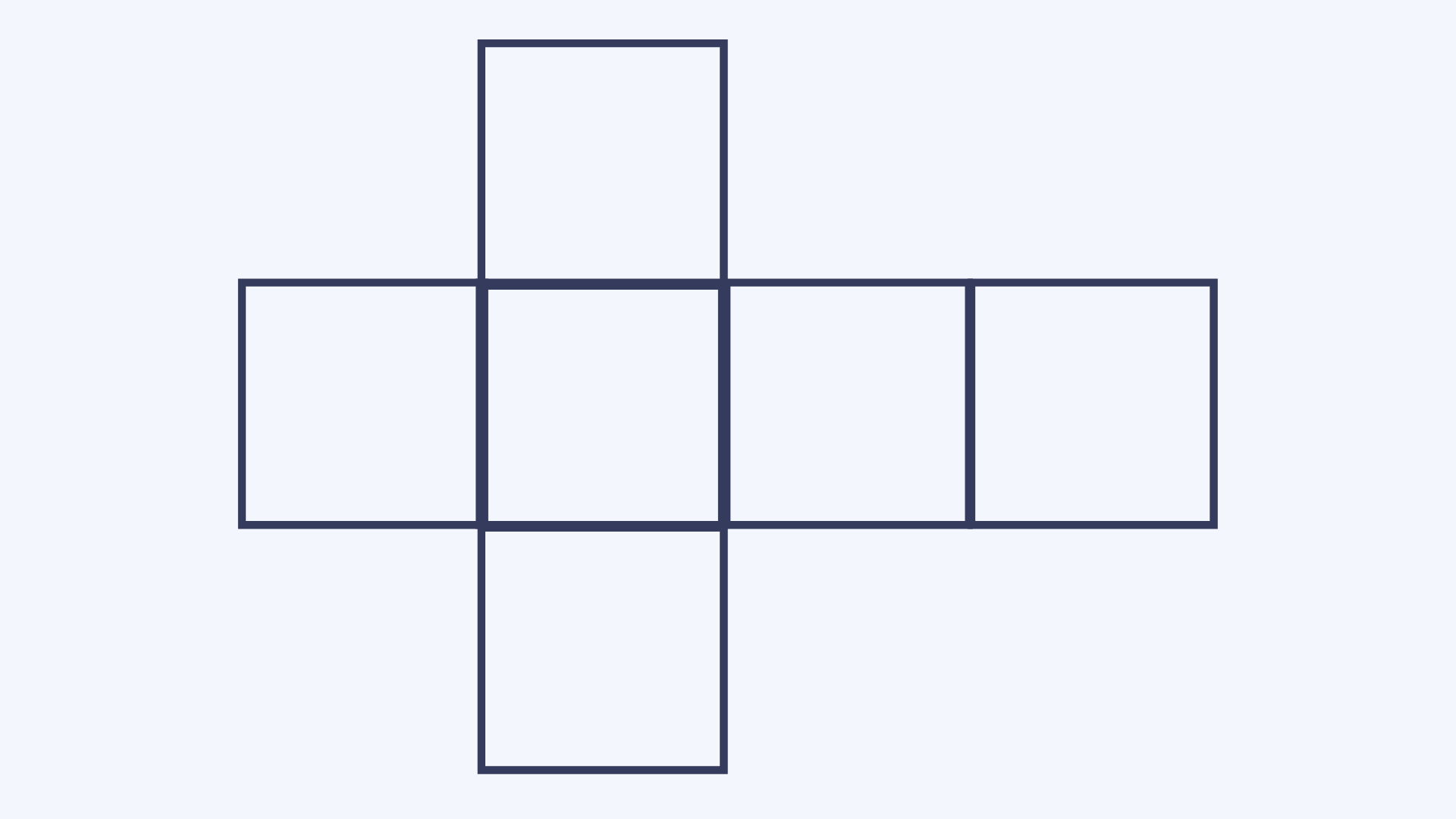
Net
A net is the flat outline of a 3D shape, before it is folded together.
Number bonds
Number bonds are pairs of numbers that add together to make a given number. For example, 2 + 8 and 4 + 6 are number bonds to 10, whereas 43 + 57 and 81 + 19 are number bonds to 100.
Read this: What are number bonds?
Number facts
Number facts are simple addition, subtraction, multiplication and division calculations that children should be able to mentally recall easily. For example, 50 + 50 = 100 or 2 x 2 = 4 are number facts.
Number line and number ladder
A number line is a horizontal line, with numbers going up the bottom of the line. The numbers will typically increase in size and the space between the numbers doesn’t usually matter. Number lines are especially used early in elementary school to teach number bonds and adding using jumping.
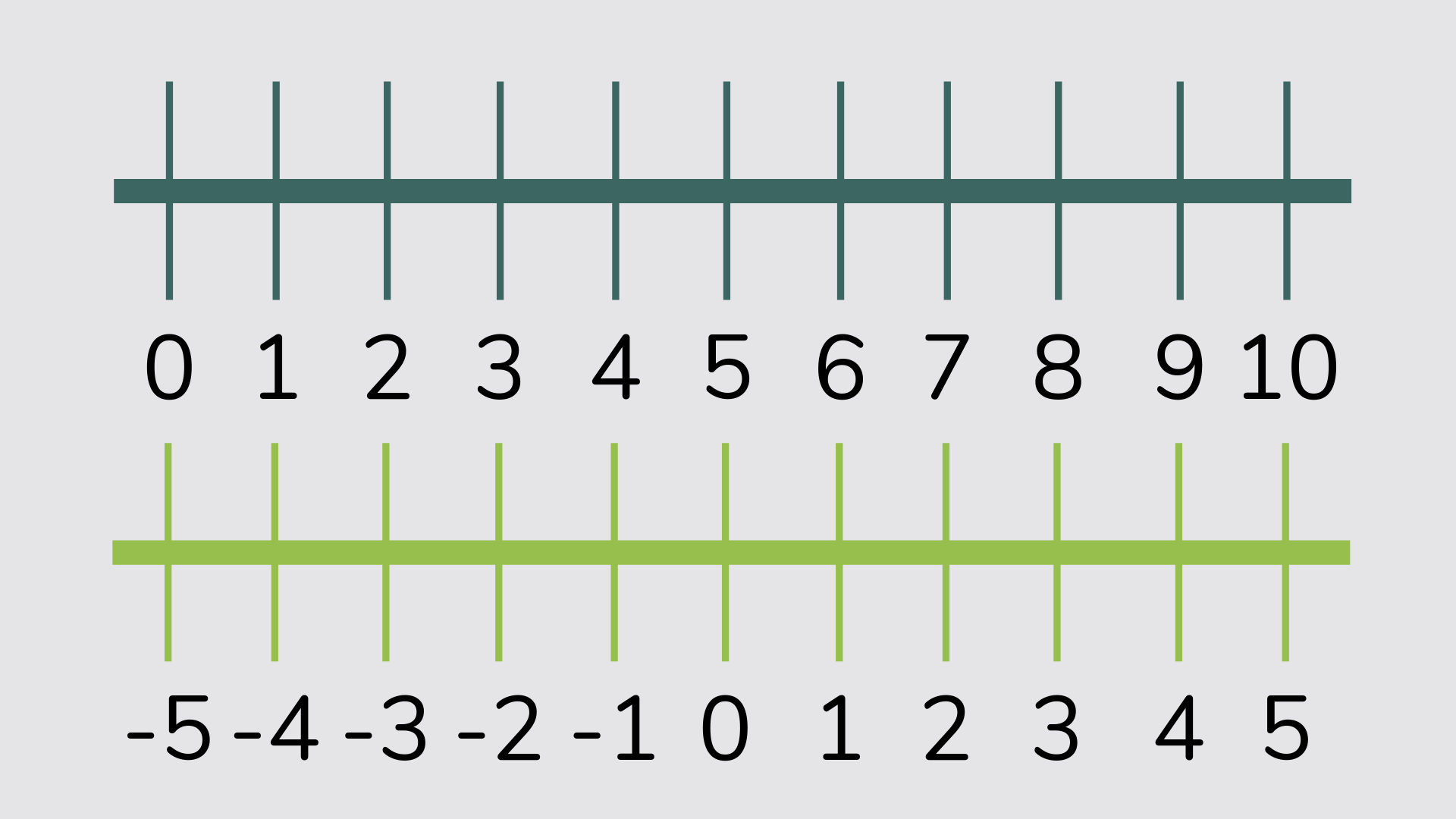
A number ladder is a number line drawn vertically.
Number sentence
A number sentence is how a calculation is written, using numbers and symbols. For example, 5 + 7 = 12 is an addition number sentence.
Read this: What is a number sentence?
Number chart
A number chart is a math aid used in elementary schools, showing numbers in order from 0 up to, for example, 20 or 100. Number charts are useful for helping with counting and seeing patterns in number sequences.
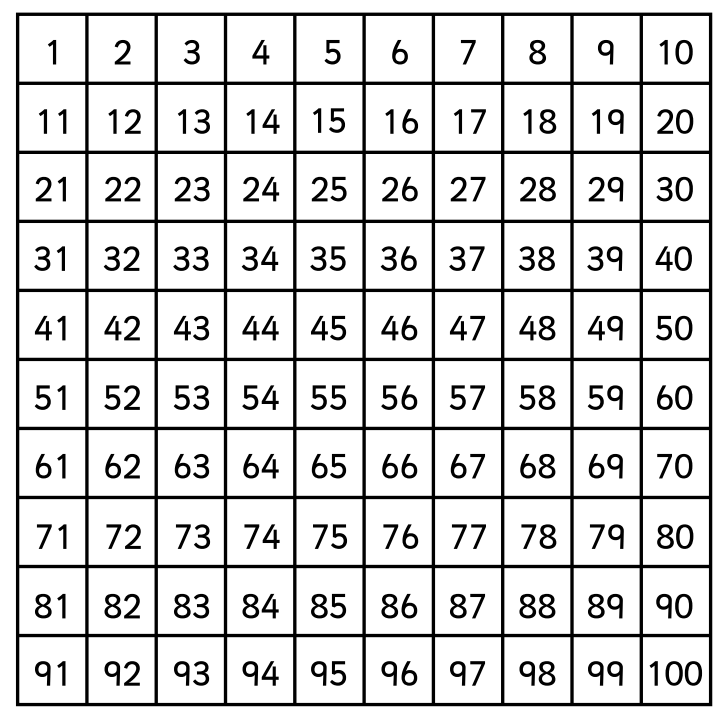
Numerator
A numerator is the name for the top number in a fraction. For example, in the fraction \frac{5}{8}, 5 is the numerator.
O
O
Obtuse angle
An obtuse angle is any angle that measures between 90° and 180°.
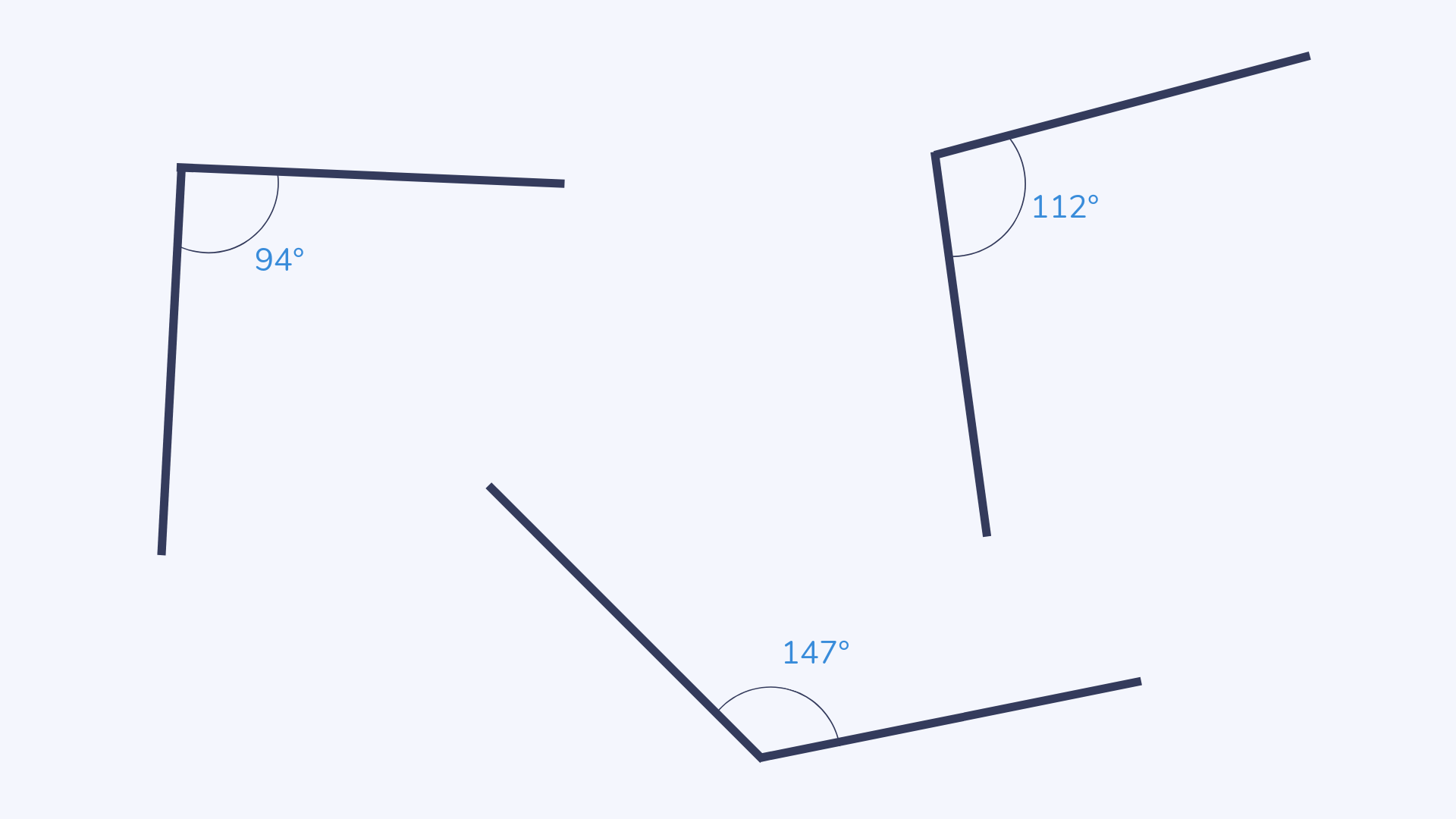
Odd and even numbers
An even number is any number that can be divided into two equal groups and always ends in 0, 2, 4, 6 and 8.
An odd number is any number that can’t be divided into two equal groups and always ends in 1, 3, 5, 7 and 9.
Operation
In math, the four types of operations are addition, subtraction, multiplication and division.
Ordinal numbers
An ordinal number tells us what position something is in a list, often taught using dates or the results of races. For example, Ben finished in 1st place, Chris in 2nd and Alex in 3rd. The contrast of this is a cardinal number.
P
P
Parallel
A parallel line is a straight line that always stays the same distance from another line and never meets. Shapes are often used to teach parallel lines. For example, a square has two pairs of parallel lines.
Partitioning
To partition a number means to separate a number into separate parts (ones, tens, hundreds, thousands etc). This is also known as decomposing. Partitioning makes understanding place value easier and is also used when using column methods or grid methods.
For example, 5,246 can be partitioned into 5 thousands, 2 hundreds, 4 tens and 6 ones or 5000 + 200 + 40 + 6.
Read more: What is partitioning?
Part whole model
A part whole model is a way of representing a number and its composite parts. It is a good way to show the relationship between numbers, and the method uses partitioning. The two main ways part whole model is used are in bar modeling and cherry diagrams.
Read more: What is part whole model?
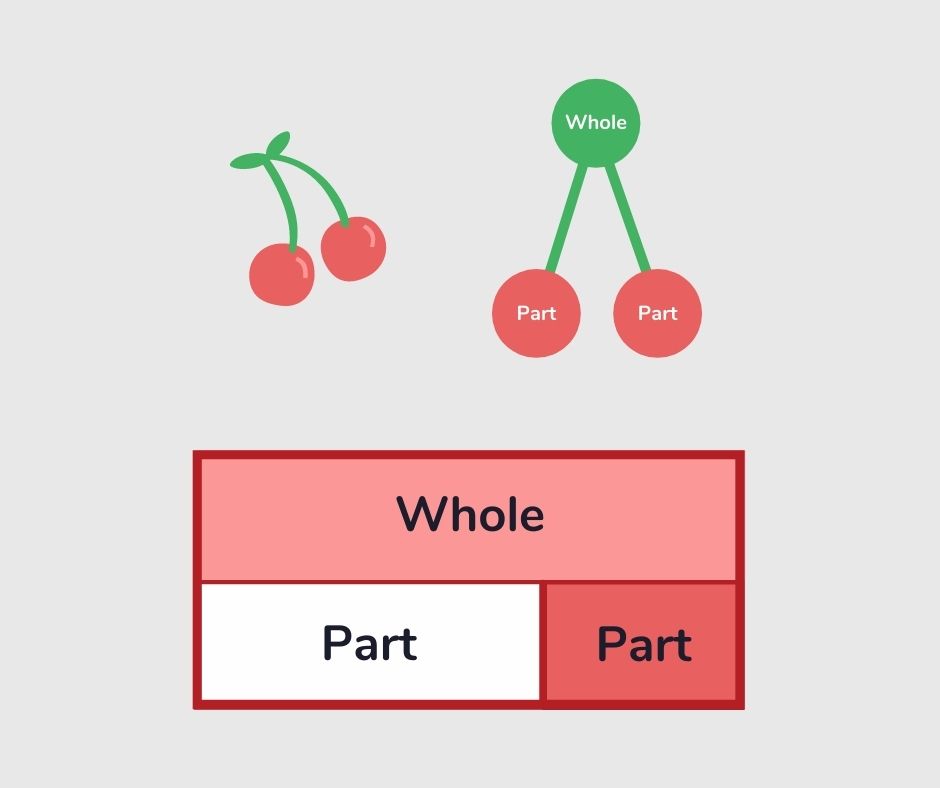
Percentage
Percentage means ‘out of 100’ and is used to show a number or ratio expressed as a fraction of 100. Percents are shown with the symbol %. Students often encounter percentages when talking about sales in shops. For example, this $80 jacket had 20% off in the Christmas sale.
Perimeter
The perimeter is the distance around a 2D shape and is often taught using the example of fences around a field or garden.
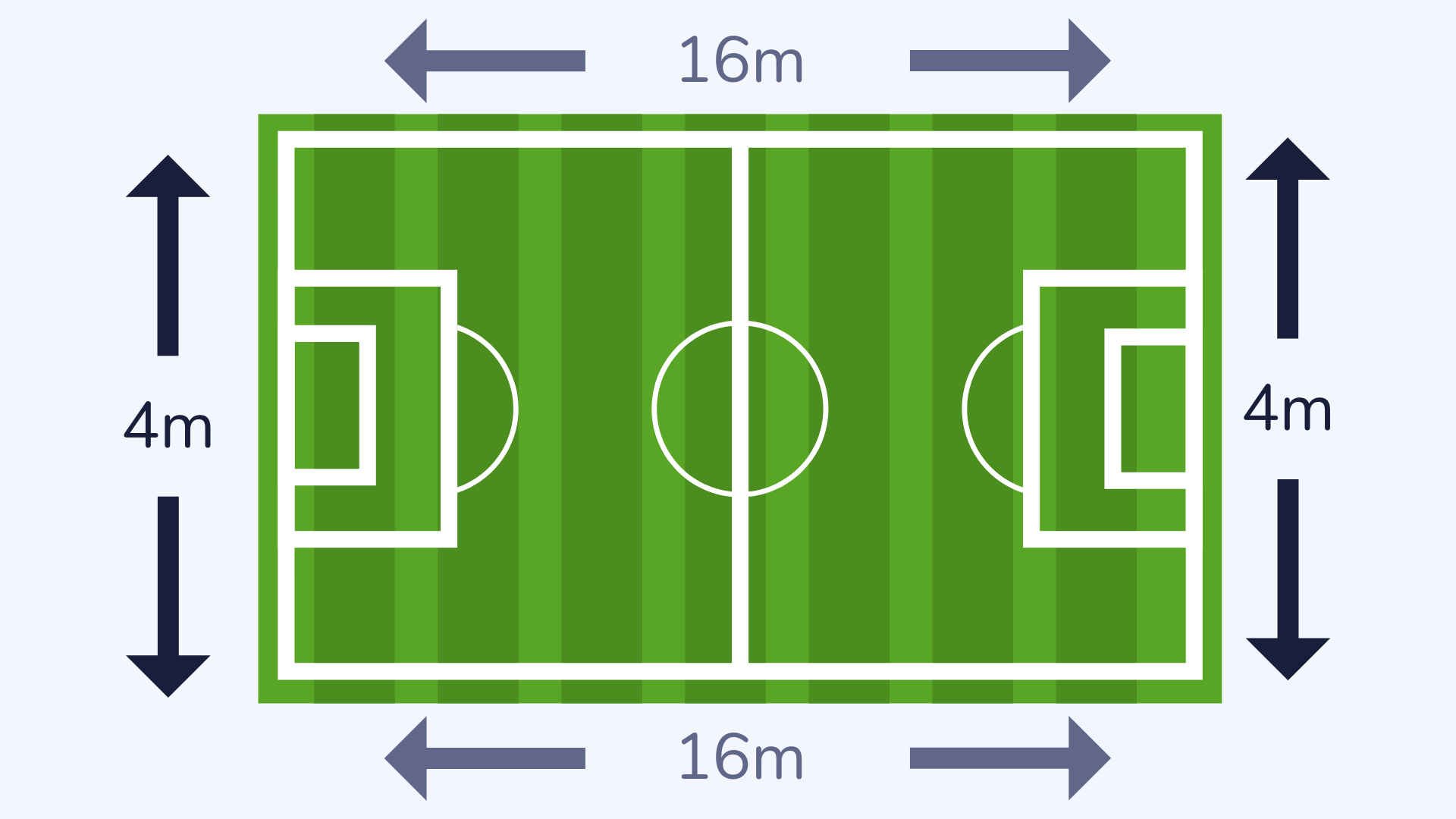
Read more: What is the perimeter?
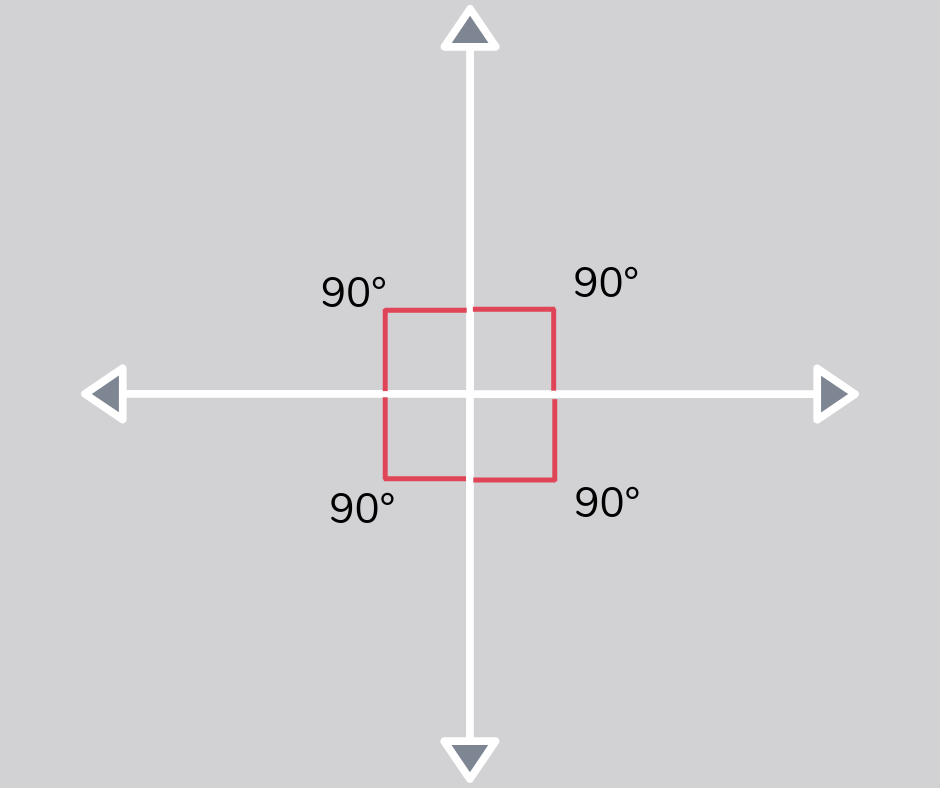
Perpendicular
Perpendicular lines are two lines that meet to create a right angle, often seen in shapes.
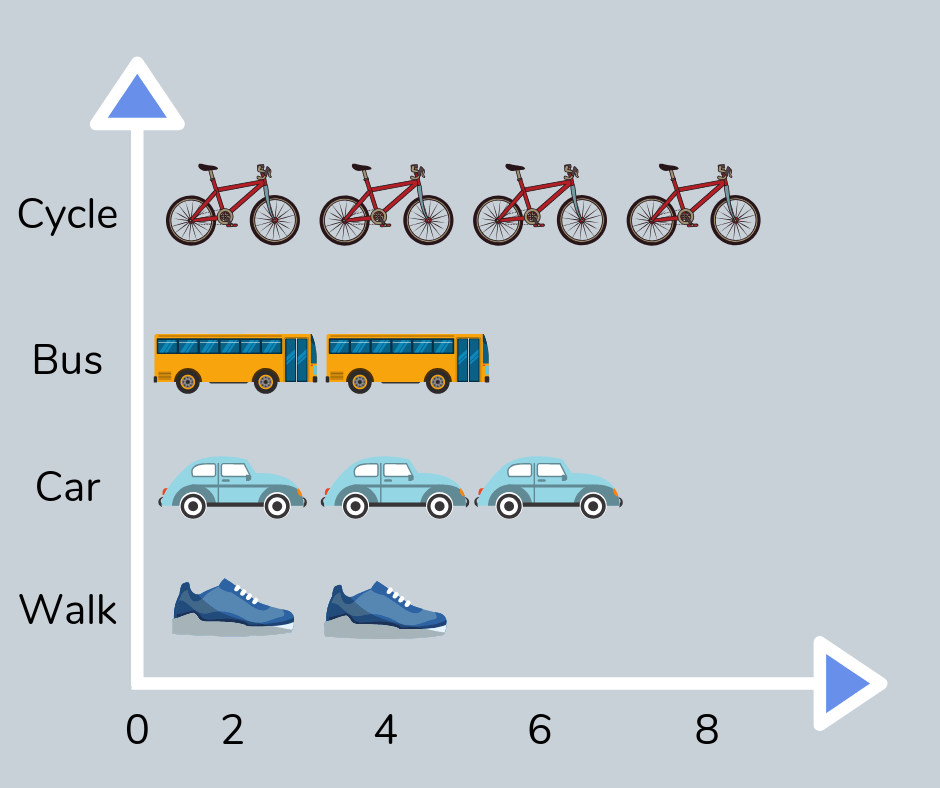
Pictogram
A pictogram, or pictograph, is a type of graph that uses pictures to represent information. These are often taught early in elementary school before moving onto block charts and bar graphs.
Pie chart
A pie chart is a circular chart divided into sections, representing different values, which can be fractions, decimals, percentages or angles.
Place value
The place value of a number is how much each digit in the number represents.
For example, the place value of 157 is 1 hundred, 5 tens and 7 ones.
Read more: What is place value?
Try this: Place value grid to make at home
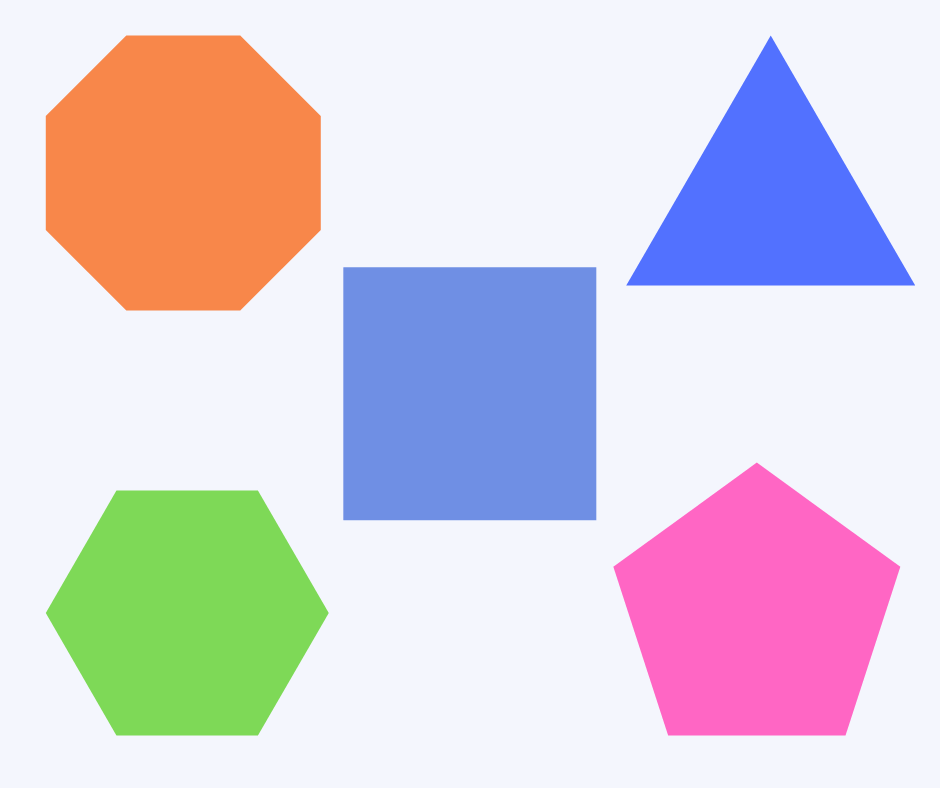
Polygon
A polygon is any 2D shape with straight, closed sides. Any shapes with open or curved sides are not polygons. For example, triangles, squares and parallelograms are polygons, but circles and ovals are not.
Prime number
A prime number is any number greater than 1 that can only be divided equally by itself and 1. For example, 5, 7, 11 and 13 are prime numbers.
Read more:
Prism
A prism is a 3D shape with two identical flat sides and ends. Cubes and cuboids are examples of prisms.
Probability, chance and likelihood
Probability is the study of how likely or how big a chance there is that something will happen. It can be described in words, fractions, percentages or ratios. For example, there is a 20% chance of rain tomorrow.
Product
A product of two numbers is the name for the answer to a multiplication calculation.
For example, 35 is the product of 5 x 7.
Proportion
A proportion is a portion or part of a whole, and is often taught alongside ratio.
Protractor
A protractor is an instrument used to measure angles.
Pyramid
A pyramid is a 3D shape with triangular sides that join at a point, with a polygon base.

Q
Q
Quadrilateral
A quadrilateral is any 2D shape with four sides, including a square, rhombus, kite and trapezium.
R
R
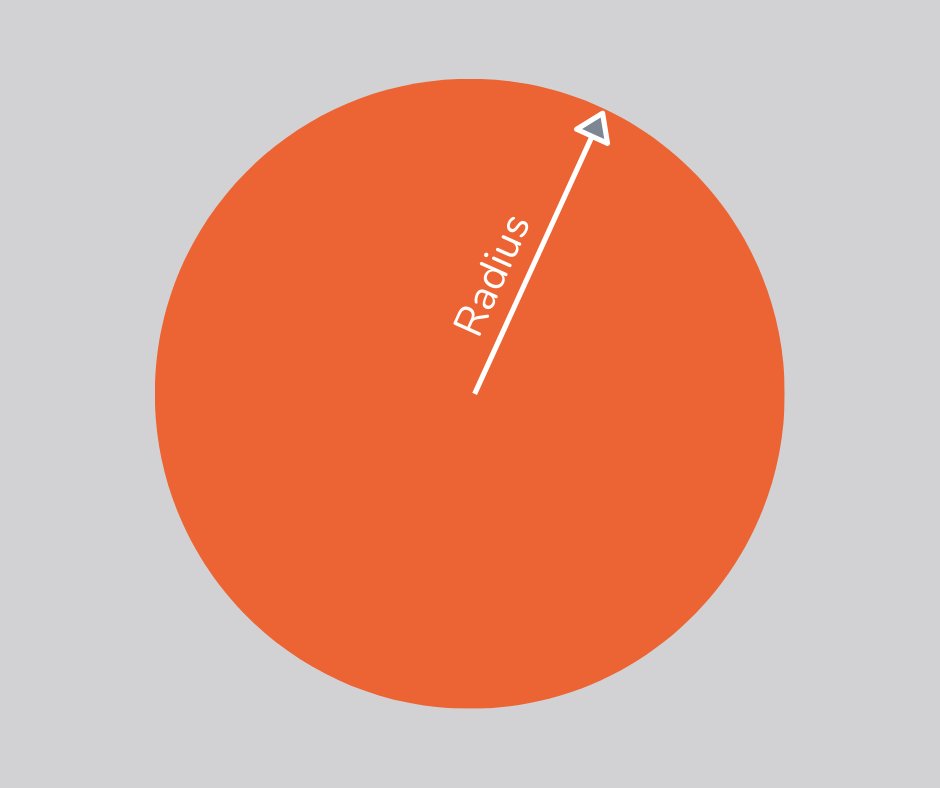
Radius
The radius is the distance from the centre of a circle to its circumference and is half the diameter.
Range
The range of a set of numbers is the difference between the smallest and largest numbers in the set.
For example, in the set of numbers 50 to 60, the range is 10.
Ratio
A ratio is used to compare values, showing the relative value of one to another. It is taught using real-life examples, such as comparing the number of boys to girls in class. For example, the ratio of boys to girls was 2:1, meaning there are two boys for every one girl.
Reflection of shapes
A reflection of a shape is a drawing of a shape reflected in a line of symmetry, with the reflection on the other side of the line but facing in the opposite direction.
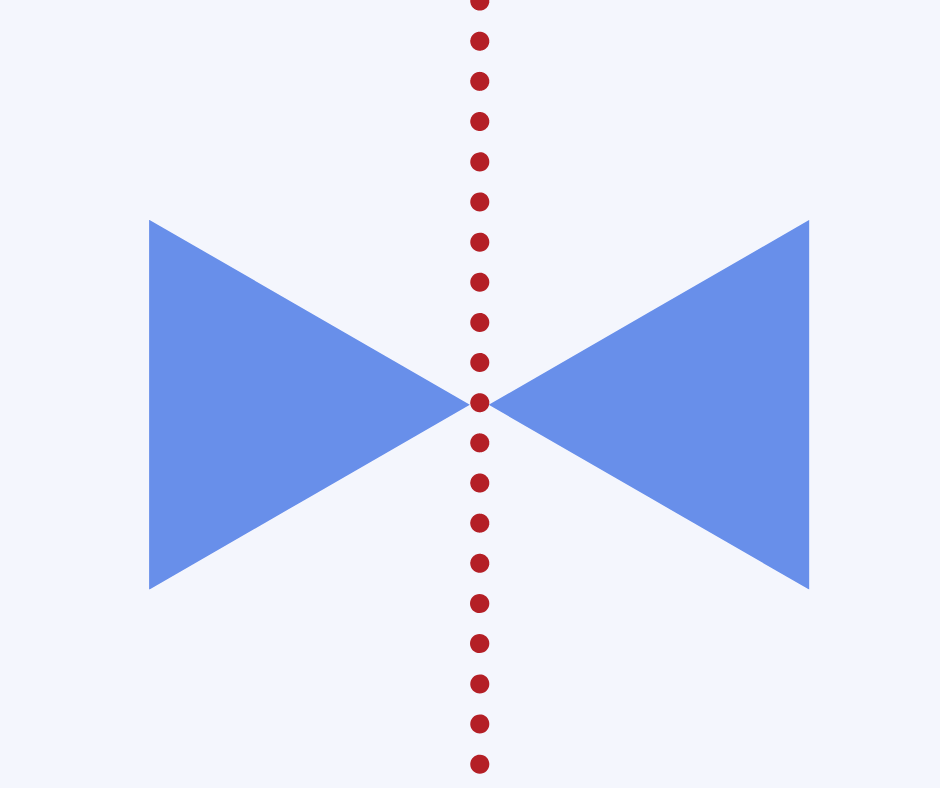
Reflective symmetry
Reflective symmetry is a type of transformation, looking at when a shape or pattern is reflected in a mirror or line of symmetry. The reflected shape should be exactly the same size and distance from the line of symmetry as the original.
Reflex angle
A reflex angle is any angle between 180° and 360°.
Regular and irregular shapes
A regular shape is one where all the sides and interior angles are equal, whereas an irregular shape has sides and angles of different lengths and sizes.
Read more: What are regular and irregular shapes?
Right angle
A right angle is an angle that measures 90°. It is also known as a quarter turn, as it is \frac{1}{4} of a full turn, which measures 360°.
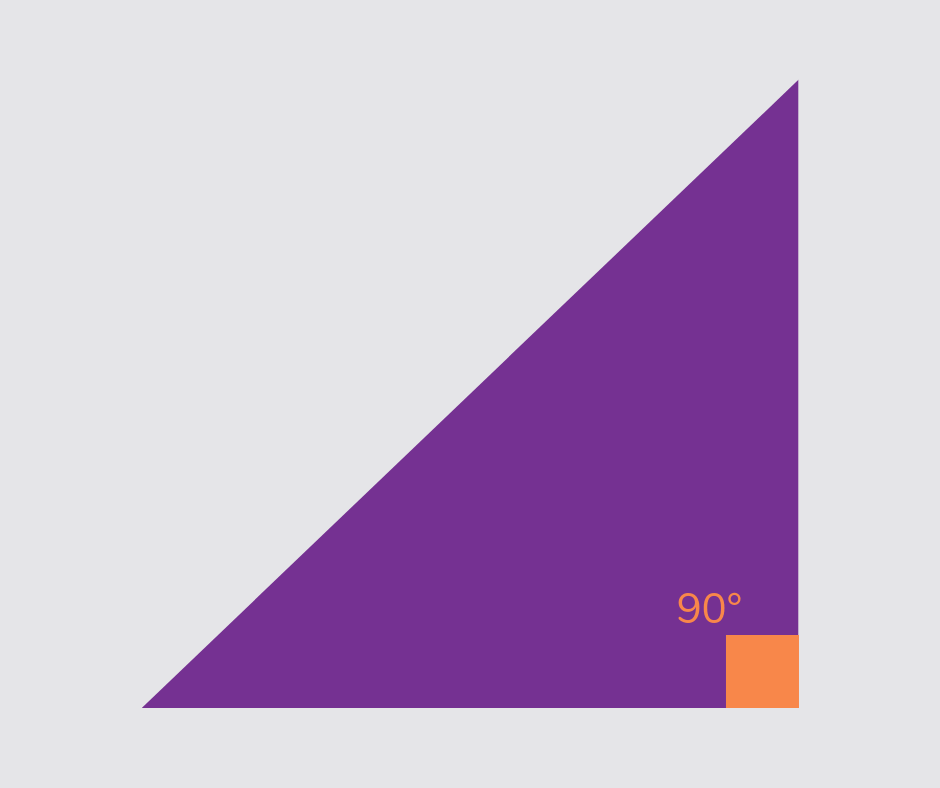
Right-angled triangle
A right-angled triangle is a 2D shape with three sides and one angle that measures 90°.
Roman numerals
Roman numerals are the numbers used in ancient Rome, with letters from the Latin alphabet representing certain numbers. They are commonly taught using years. For example, V = 5, X = 10, C = 100, M = 1000, so 1066 is MLXVI.
Rotation of shapes
A rotation of a shape is when a shape is moved around a fixed point, either clockwise or counterclockwise and by a certain number of degrees. However, the shape doesn’t change size.
Rotational symmetry
Rotational symmetry is a type of transformation, where a shape is turned around a central point, without changing its size.
Rounding numbers
To round a number means to adjust it up or down to a number that makes calculating with it easier. Numbers are usually rounded up to the nearest 10, 100 or 1000, with decimals being rounded to the nearest whole number, tenth or hundredth. There is a rule that if a digit is 4 or less it rounds down and if it is 5 or more it rounds up.
For example, 426 rounds to 430 to the nearest 10, but 400 to the nearest 100.
Repeated addition
Repeated addition is a technique used to teach multiplication in elementary school, where children add ‘lots’ of numbers together.
For example, 3 ‘lots’ of 5 is 5 + 5 + 5 as well as 3 x 5.
S
S
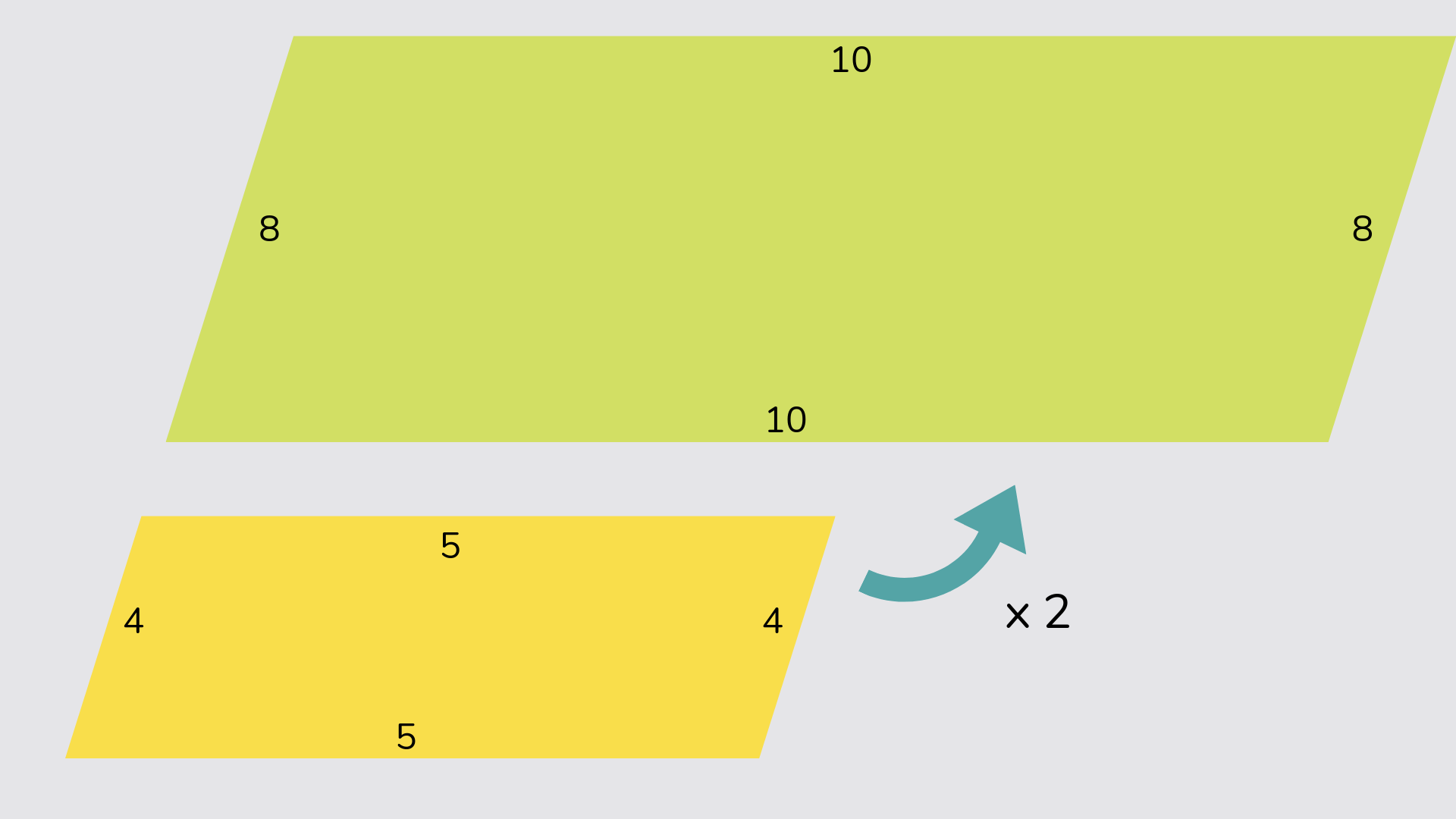
Scale factor
A scale factor is used when we increase or decrease a 2D shape in size, so we make the shape larger or smaller depending on the scale factor. For example, this shape has been increased by a scale factor of 2.
Scalene triangle
A scalene triangle is a 2D three-sided shape where all the sides and angles are unequal.

Shared between
‘Shared between’ is a phrase used when introducing division, to show how a set of objects can be ‘shared’ into equal sized groups.
Simplifying fractions
To simplify a fraction means to reduce it to its lowest form, by dividing the numerator and denominator by the same number. For example \frac{8}{10} can be simplified to \frac{4}{5} by dividing both the numerator and denominator by 2.
Square numbers and Square roots
A square number is the result of multiplying a number by itself. When writing this, we write a small two next to and above the number. For example, 7² = 7 x 7 = 49.
Read more: What is a square number?
Standard and non-standard units
Standard units are the units of measurement we normally use to indicate the length, mass or capacity of an object. For example, inches, yards, cups, pints, etc.
Non-standard units are used when introducing measurement early in elementary school, for example the length of a pencil or hand spans.
Sum
A sum of two numbers is another name for the result of an addition calculation. For example, the sum of 15 and 23 is 38.
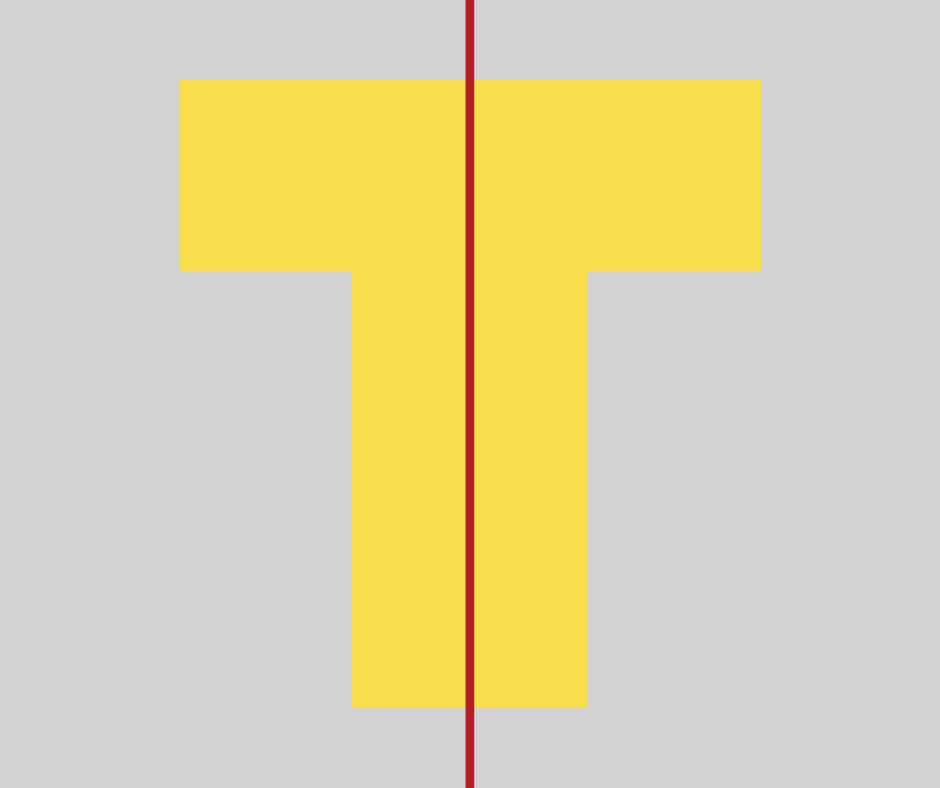
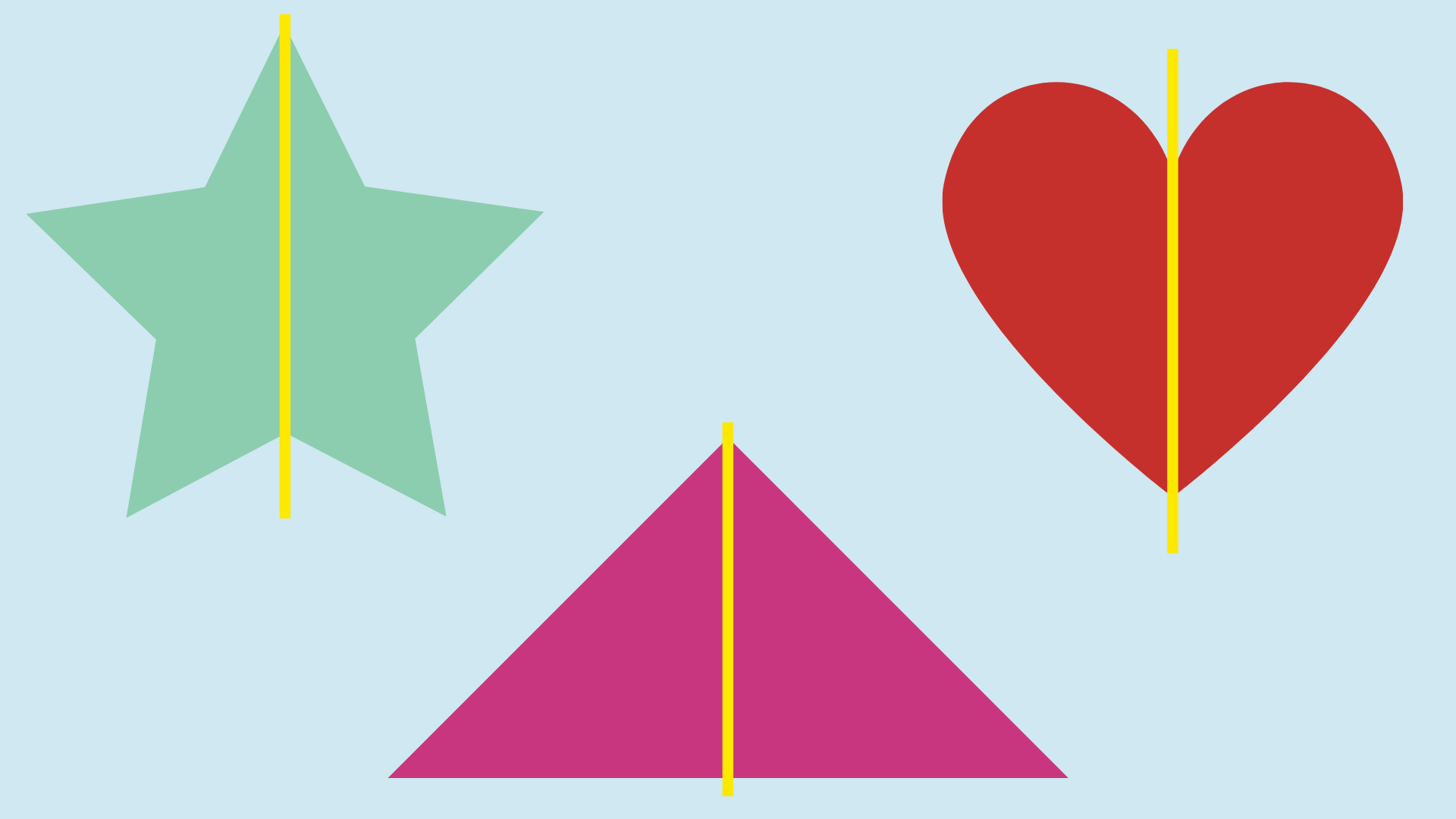
Symmetry
When a picture or shape is the same on both sides, we call it ‘symmetrical’, and this can be shown by drawing a line of symmetry through the center and seeing if both sides are the same.
Read this: What is a line of symmetry?
T
T
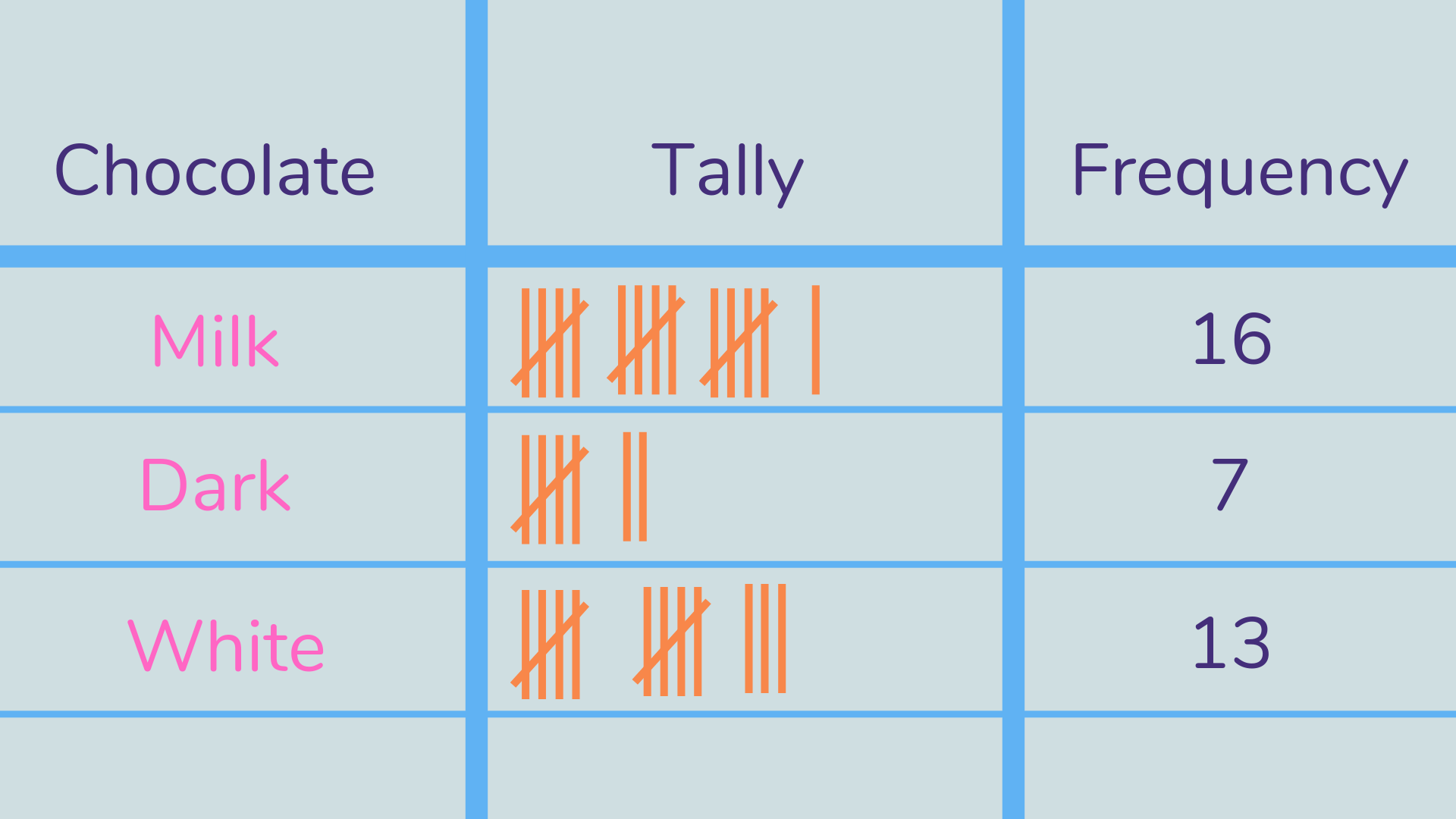
Tally chart
A tally chart uses marks instead of numbers to represent information. One vertical mark is used to represent each one unit, with five being shown as a fifth line crossed through the first four lines.
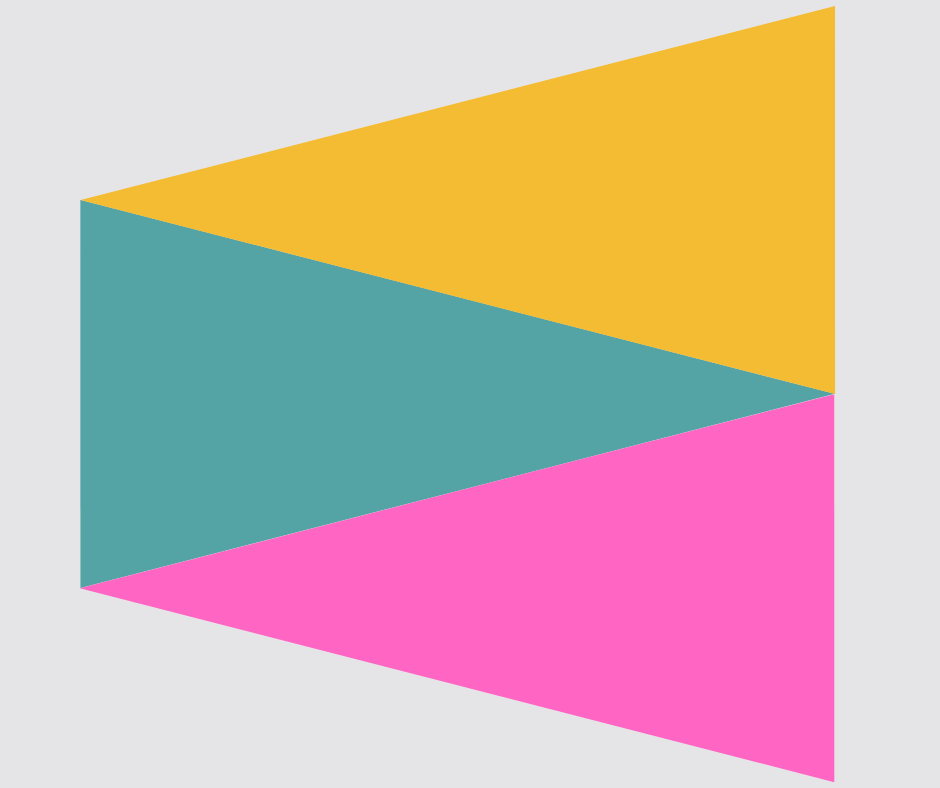
Tessellation
When shapes fit together exactly with no gaps, we call this tessellation. An example of this in real life are floor tiles.
Time intervals
A time interval is the length of time between two times. For example, the time interval between 1:15 and 1:45 is 30 minutes.
Translation of shapes
Translation is a type of transformation, where a shape is moved into a new position, without being changed in any way.
Triangle
A triangle is a 2D shape with three sides, angles and corners.
Triangular number
A triangular number is a number that can make a triangular dot pattern. For example, 1 + 2 = 3, 2 + 3 = 5, 3 + 5 = 8, 5 + 8 = 13 etc.
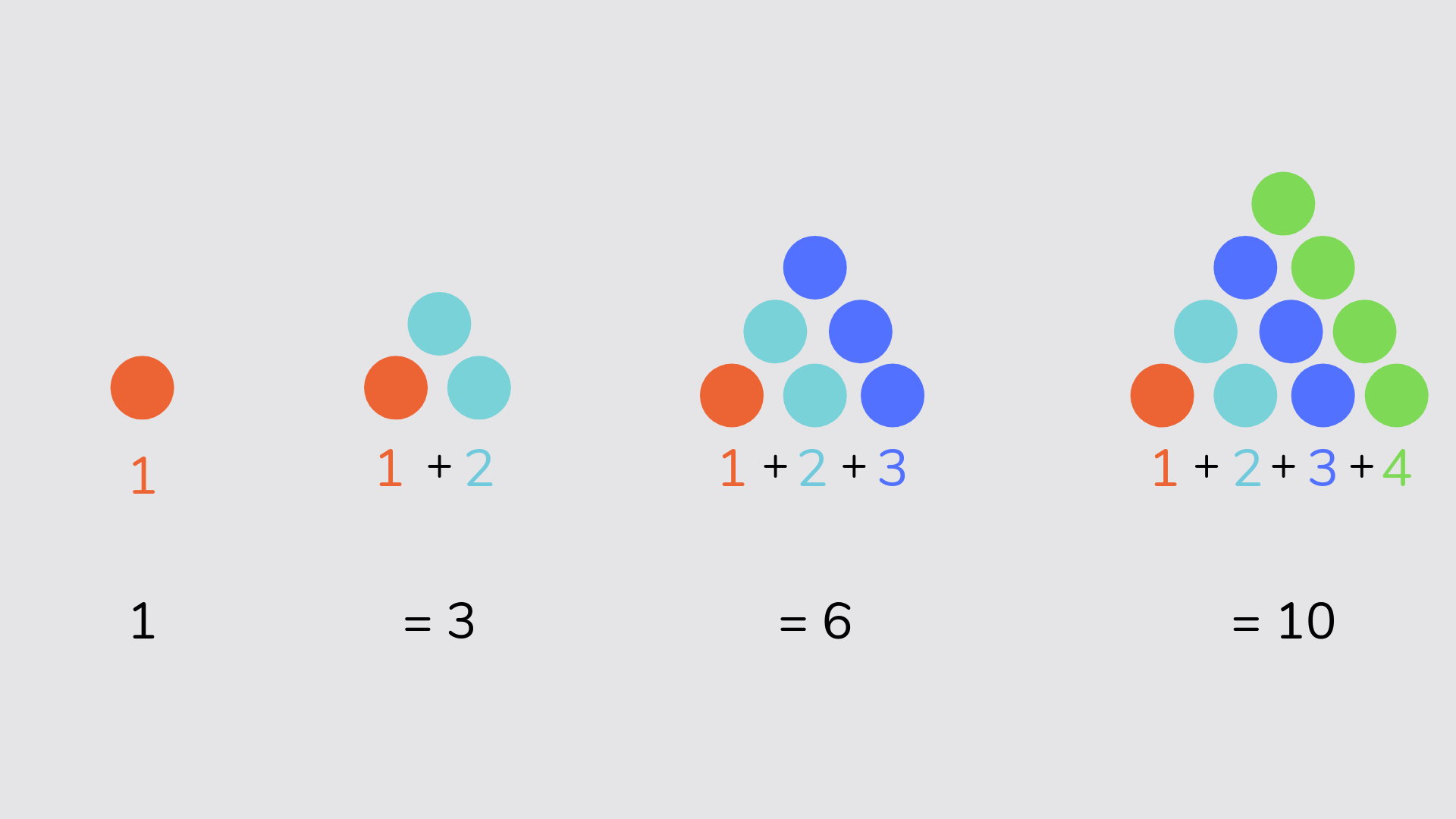
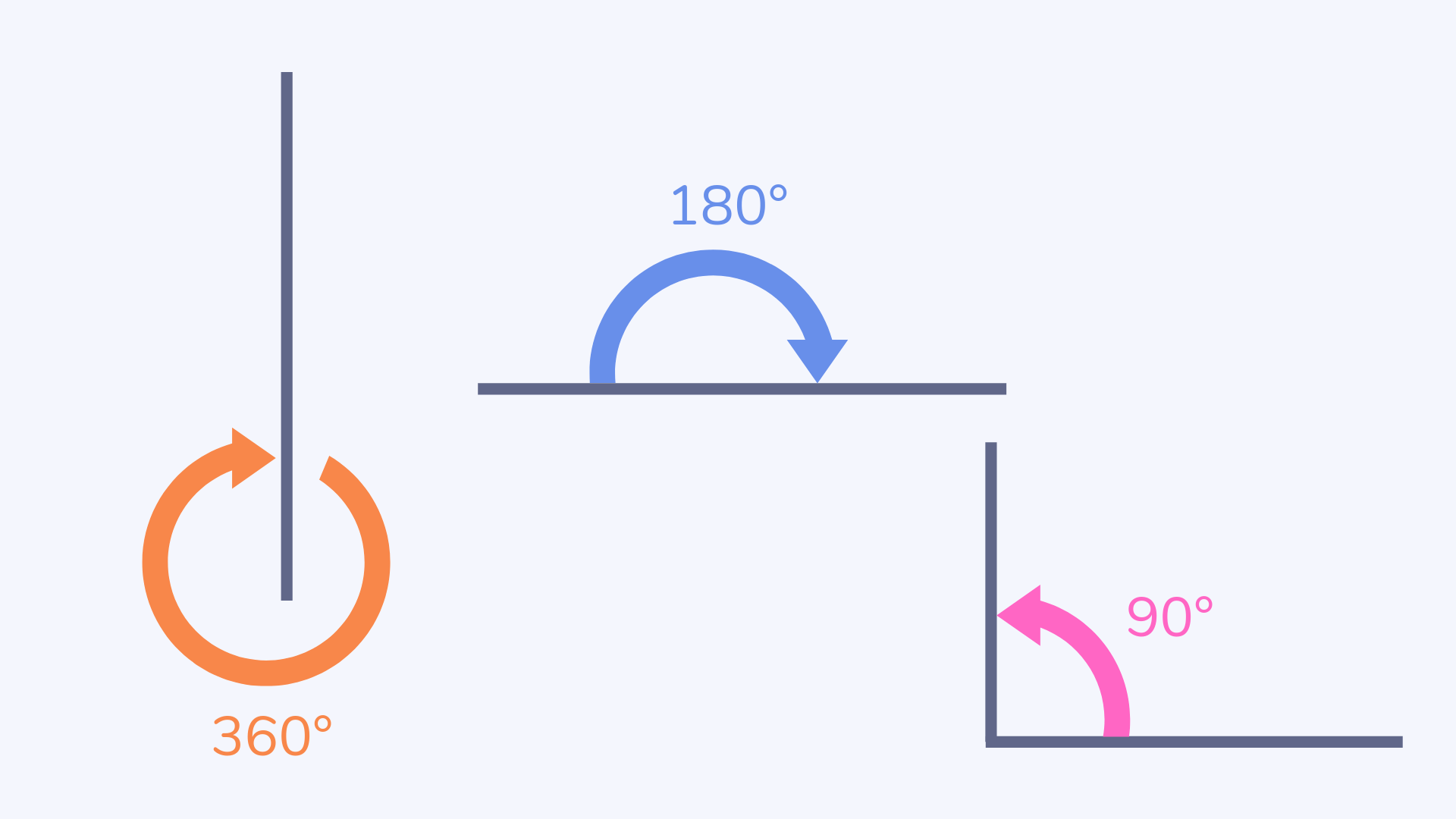
Turns
Turns are a movement in a circle, with a quarter turn being the same as 90°, a half turn as 180° and a full turn as 360°, either clockwise or anticlockwise.
Two-step and multi-step problems
A two-step problem is a word problem which needs two calculations to solve it. A multi-step problem requires more than two calculations to solve it.
Read more: Two step word problems and multi step word problems?
U
U
Unit and non-unit fractions
A unit fraction is any fraction with 1 as the numerator, whereas a non-unit fraction is any fraction with a number greater than 1 as the numerator. For example, ⅙ is a unit fraction, whereas 2/6 is a non-unit fraction.
Read this: What is a unit fraction?
Read more: What is a non-unit fraction?
V
V
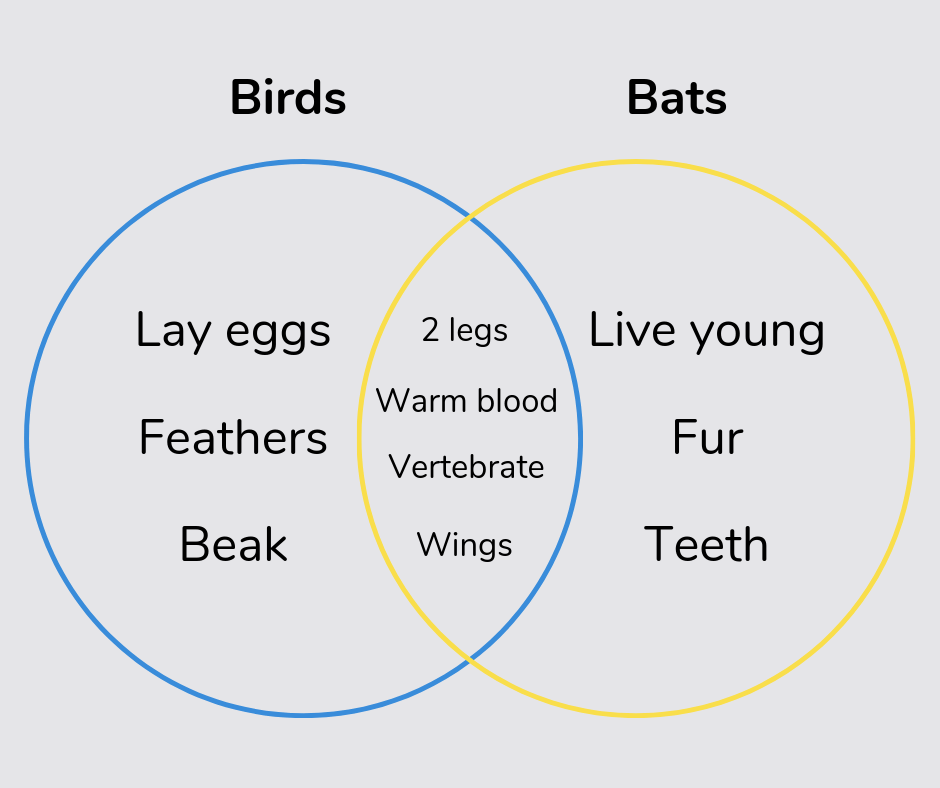
Venn diagram
A Venn diagram is a visual way of sorting different objects or numbers into overlapping circles with different rules, with anything in the overlapping part sharing both rules.
Read this: What Is A Venn Diagram?
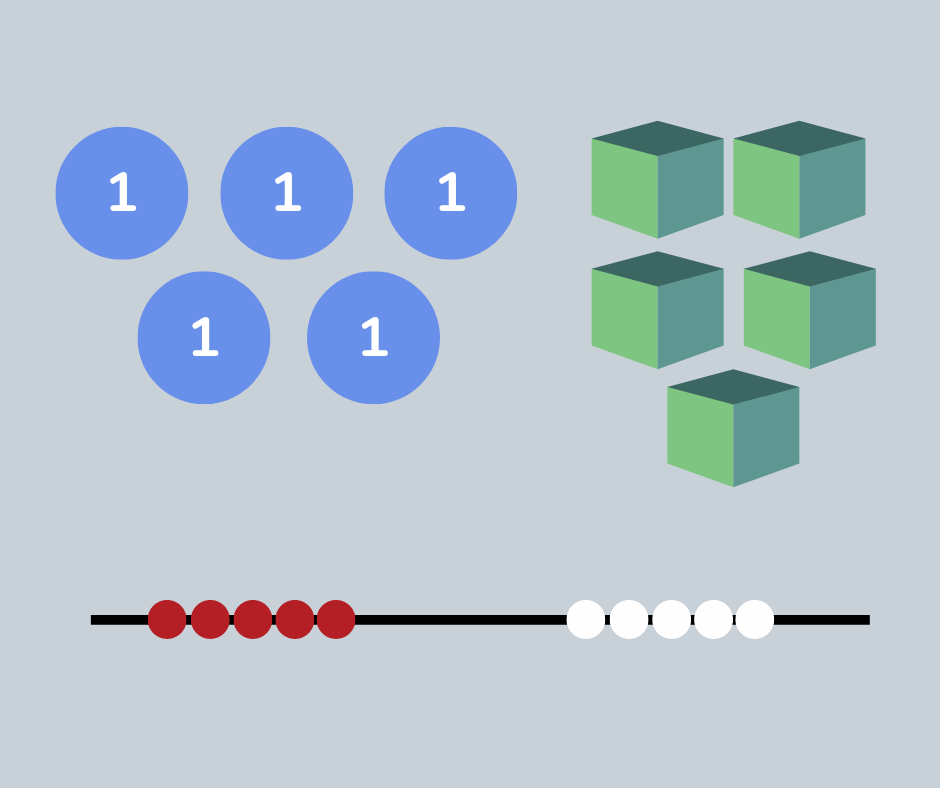
Variation
In elementary school level math, there are two types of variation, conceptual and procedural variation.
Conceptual variation means looking at a math idea in various representations. For example, showing a number using multilink, base ten block, 100 square or partitioned, to explain place value.
Procedural variation is used to support a child’s deeper understanding of a math process by extending a problem by varying the number, varying the processes to solve a problem or varying the problems by applying the same method to a group of similar problems.
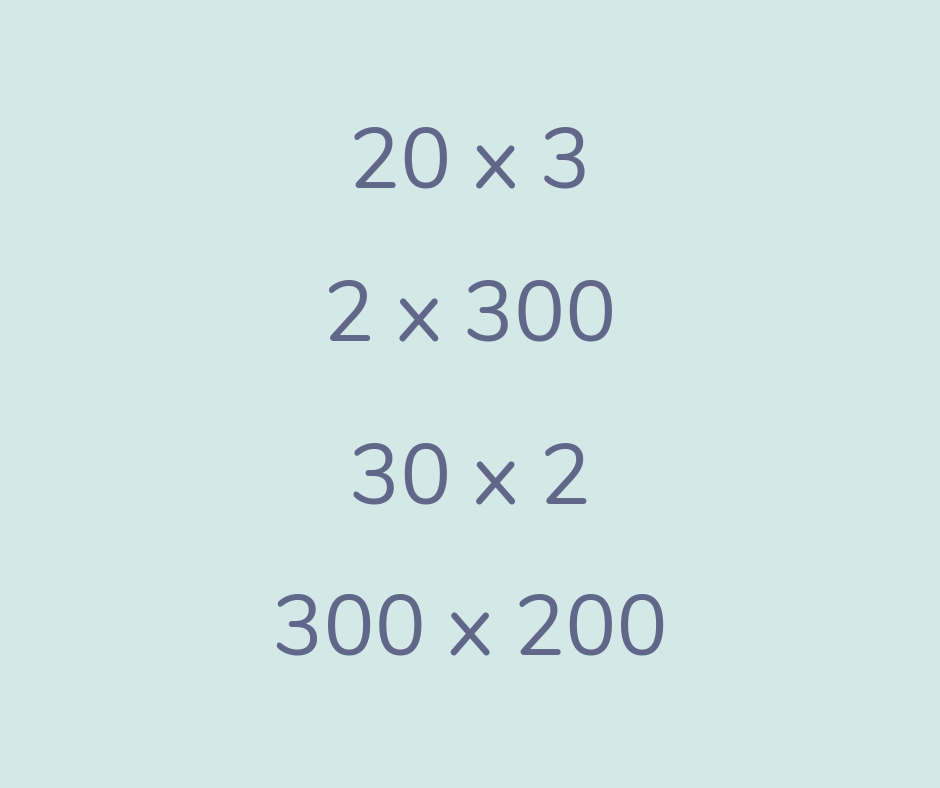
Vertex/vertices
Vertex is another name for a corner of a 2D shape or the points where edges in a 3D shape meet.
Vertical
A vertical line runs up and down, from top to bottom.
Volume
The volume is the amount of space an object occupies, especially 3D shapes. Children will learn the formula for finding the volume of a shape, which is the length x width x height, with the answer having units with a cube number, for example cm³.
W
W
Word problem or story problem
A word problem or a story problem is a real-life situation where a math calculation is needed to solve a problem. For example, ‘If half a class of children have pets and there are 36 children in the class, how many have pets?’
Read this: Word Problems Explained
X
X
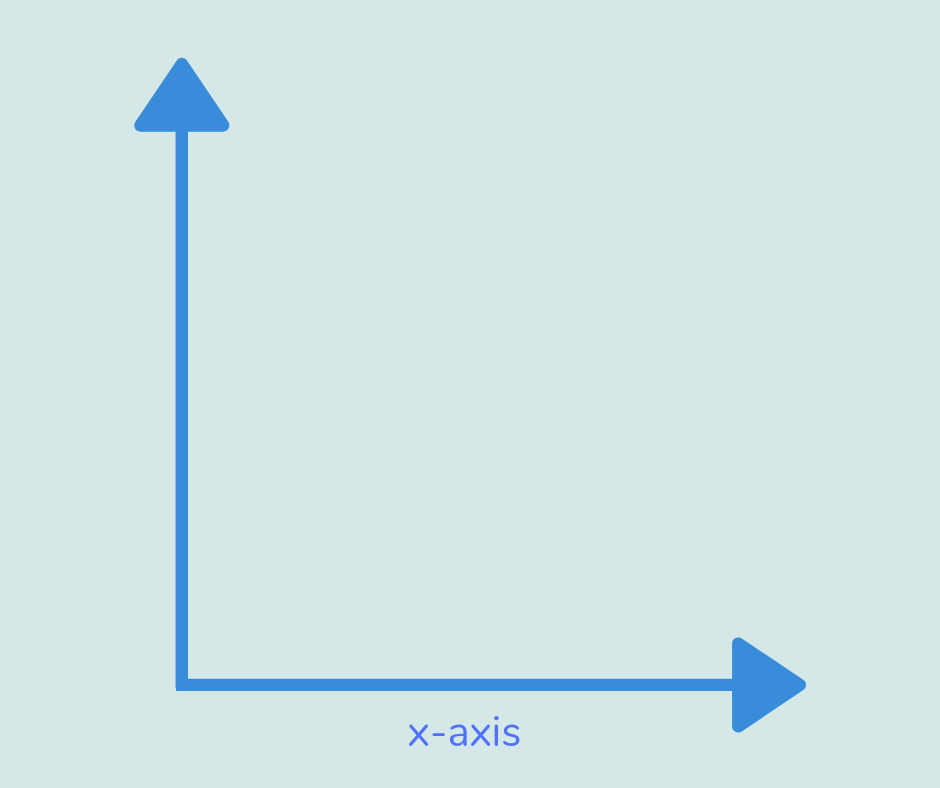
X-axis
The x-axis is the horizontal axis on a graph, along which we find the x-coordinate (by going ‘along the corridor’).
Y
Y
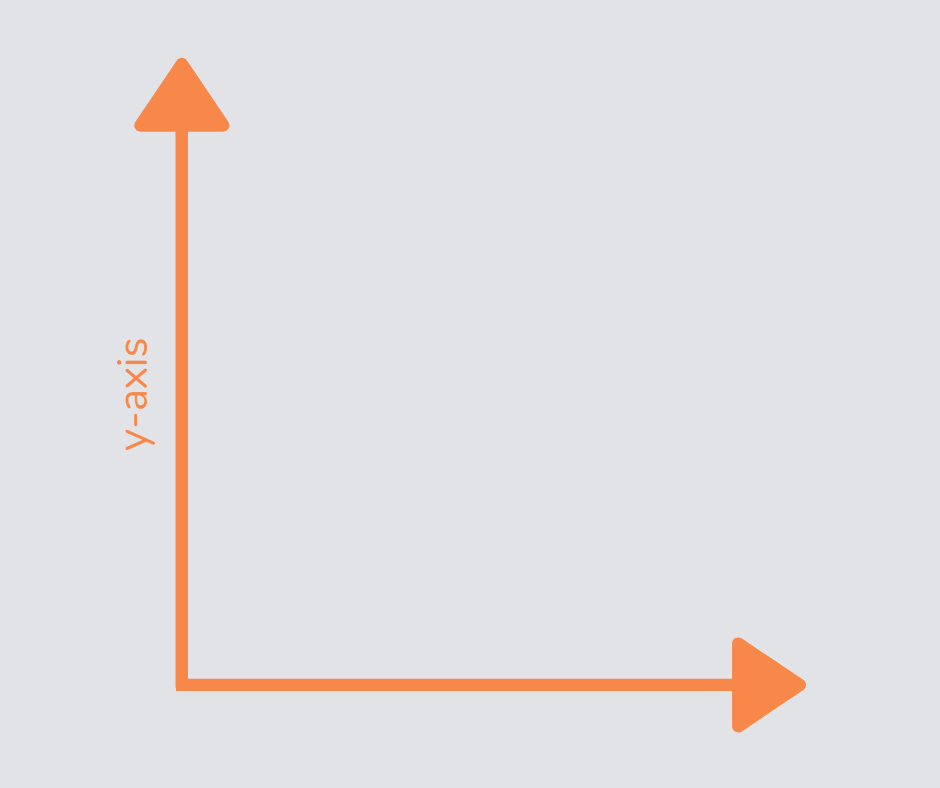
Y-axis
The y-axis is the vertical axis on a graph, along which we find the y-coordinate (by going ‘up the stairs’).
Z
Z
Zero
Zero is a placeholder between +1 and -1, it has no value but changes the value of other numbers. For example, in the number 703 it changes the number 73 to the much larger 703.
In our math dictionary for kids, teachers and parents, we’ve tried to include as much of the math terminology your child will be learning in elementary and middle school as possible, but we know that we may have missed something!
If that is the case, then let us know which numeracy based terms we have missed, and we’ll be more than happy to add them to this A to Z math dictionary!
Do you have students who need extra support in math?
Skye—our AI math tutor built by experienced teachers—provides students with personalized one-on-one, spoken instruction that helps them master concepts, close skill gaps, and gain confidence.
Since 2013, we’ve delivered over 2 million hours of math lessons to more than 170,000 students, guiding them toward higher math achievement.
Discover how our AI math tutoring can boost student success, or see how our math programs can support your school’s goals:
– 3rd grade tutoring
– 4th grade tutoring
– 5th grade tutoring
– 6th grade tutoring
– 7th grade tutoring
– 8th grade tutoring