GCSE Tutoring Programme
"Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring."
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Adding and subtracting negative numbers Arithmetic BIDMAS Laws of indicesThis topic is relevant for:

Multiplying And Dividing Negative Numbers
Here we will learn about multiplying and dividing negative numbers including what negative numbers are and how to multiply and divide them.
There are also negative number worksheets and exam questions at worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are negative numbers?
Negative numbers are any numbers less than zero and have a negative sign (−) in front of them.
Numbers greater than zero are referred to as positive numbers. If there is no sign in front of a number the number is positive.
On the number line below we can see some positive and negative integers (whole numbers):
The numbers in orange are negative and the blue numbers are positive.
Just like you can multiply and divide positive numbers, you can do the same with negative numbers.
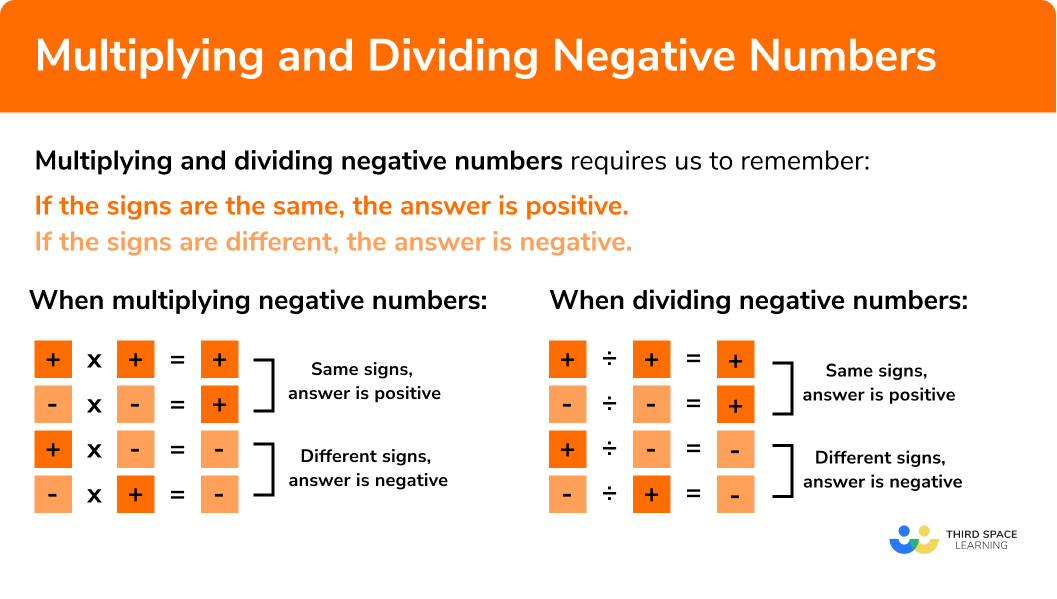
In order to multiply or divide negative numbers you must remember:
If the signs are the same, the answer is positive.
If the signs are different, the answer is negative.
When multiplying negative numbers:
The same rules apply for dividing negative numbers:
Click here to learn about adding and subtracting negative numbers.
What do you need to remember when multiplying and dividing negative numbers?
How to multiply and divide negative numbers
In order to multiply and divide negative numbers:
- Multiply or divide the numbers normally.
- Change the sign as necessary using the rules of multiplying and dividing negative numbers:
If the signs are the same, the answer is positive.
If the signs are different, the answer is negative.
Explain how to multiply and divide negative numbers in 2 steps

Multiplying negative numbers worksheet

Get your free worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions on multiplying and dividing negative numbers.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Multiplying negative numbers worksheet

Get your free worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions on multiplying and dividing negative numbers.
DOWNLOAD FREEMultiplying and dividing negative numbers examples
Example 1: multiplication of negative numbers
Multiply:
- Multiply or divide numbers normally.
2Change the sign using the rules of multiplying and dividing negative numbers:
If the signs are the same, the answer is positive.
If the signs are different, the answer is negative.
In this case we have a number that is positive multiplied by a negative number (minus times positive gives a minus).
The signs are different so we must have a negative answer:
Example 2: division of negative numbers
Divide:
Multiply or divide numbers normally.
Change the sign using the rules of multiplying and dividing negative numbers:
If the signs are the same, the answer is positive.
If the signs are different, the answer is negative.
In this case we have a negative number divided by a negative number.
The signs are the same so we must have a positive answer:
Example 3: order of operations
Solve:
Multiply or divide numbers normally.
In this case we are dealing with three different operations (+, x and ÷). We need to use BIDMAS to determine the order to calculate.
Let’s temporarily ignore the negative signs.
If we start with division:
Next multiplication:
There is an add sign in between so we must add the two numbers once we have dealt with the negatives.
Change the sign using the rules of multiplying and dividing negative numbers:
If the signs are the same, the answer is positive.
If the signs are different, the answer is negative.
For the first part,
So the answer is positive
For the second part
So the answer is
We are left with
Example 4: powers
Solve:
Multiply or divide numbers normally.
Change the sign using the rules of multiplying and dividing negative numbers:
If the signs are the same, the answer is positive.
If the signs are different, the answer is negative.
Remember
If we start with just
If we take that
Example 5: worded problem
The table below shows the temperatures recorded in Manchester at different times of the day. What is the product of the highest and lowest temperatures?
| Time of day | Temperature (℃) |
| 2am | −6 |
| 7am | −4 |
| 1pm | 2 |
| 6pm | −2 |
Multiply or divide numbers normally.
The highest temperature was at 1pm of
The lowest temperature was at 2am of
Change the sign using the rules of multiplying and dividing negative numbers:
If the signs are the same, the answer is positive.
If the signs are different, the answer is negative.
In this case we have a positive number multiplied by a negative number.
The signs are the same so our answer has to be negative.
Common misconceptions
- Greater negative doesn’t mean a larger number
A common error is to assume that the larger a negative number is, the bigger number is.
E.g.
−3 is smaller than 2
- Raising a negative number to a power greater than one
Remember when raising a negative number to a power greater than1 the resulting answer could be positive or negative.
When you raise a negative number to an odd exponent the resulting answer is negative.
When you raise a negative number to an even exponent the resulting answer is positive.
Related lessons
Multiplying and dividing negative numbers is part of our series of lessons to support revision on negative numbers. You may find it helpful to start with the main negative numbers lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Practice multiplying and dividing negative numbers questions
1. Work out -12\times (-6)




The signs are the same therefore the answer is positive:
-12\times (-6)=72
2. Work out 60 \div (-12)




The signs are different therefore the answer is negative:
60 \div (-12)=-5
3. Work out -4 \div 2-7 \times (-8)




We must remember to apply BIDMAS here.
4 \div 2=2
The signs are different so it is -2
7 \times 8=56
We need to be really careful with the signs here. We are subtracting
7 \times (-8)
The signs are different so it is -56 .
The calculation becomes -2 – – 56 .
There is – – together so we change this to a +
4. Work out: (-3)^{4}




(-3)^{4} means (-3) \times (-3) \times (-3) \times (-3)
Starting from the left,
(-3) \times (-3) = 9 (positive since the signs are the same)
9 \times (-3) = -27 (negative since the signs are different)
(-27) \times (-3) = 81 (positive since the signs are the same)
5. The temperature in Greenland was -8^{\circ}\text{C} . The temperature in Antarctica was 3 times as cold as it was in Greenland. What was the temperature in Antarctica?




The calculation we need to do is 3 \times -8
3 \times 8 = 24
The signs are different so the answer is negative.
3 \times -8=-24
Multiplying and dividing negative numbers GCSE questions
The table shows the temperature in different cities across Canada.
| City | Temperature |
| Toronto | −3 |
| Calgary | −12 |
| Ottawa | 2 |
| Quebec City | −6 |
(a) Which city has the lowest temperature?
(b) Find the product between the warmest and the coldest cities.
(3 marks)
a)
Calgary
(1)
b)
Identifying the warmest and coldest temperatures (Ottawa and Calgary).
(1)
Correctly multiplying 2 and −12 to give −24
(1)
2. Mary has the following 6 cards:
She is going to choose 2 cards and multiply them.
(a) What is the largest possible number she can make?
(b) What is the smallest possible number she can make?
(4 marks)
a)
For identifying −9 or −8.
(1)
Correctly multiplying −9 and −8 or 72 seen.
(1)
b)
For identifying −9 or 7.
(1)
Correctly multiplying two numbers or −63 seen.
(1)
3. The temperature in London was −6℃ on Wednesday. On the same day the temperature at the north pole was 4 times as cold as it was in London.
What was the temperature in the North Pole?
(2 marks)
(−6) x 4 seen.
(1)
−24℃ (must have negative and celsius sign).
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
-
Multiply and divide integers both positive and negative
-
Use negative numbers in context and calculate intervals across 0
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.