GCSE Tutoring Programme
Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring.
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Algebraic expressions Maths formulas Area of a quadrilateral Rearranging equationsThis topic is relevant for:

Area of a Right Angled Triangle
Here we will learn about the area of a right angled triangle including how to find the area of a right angled triangle with given lengths and how to calculate those lengths if they are not given.
There are also area of a triangle worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
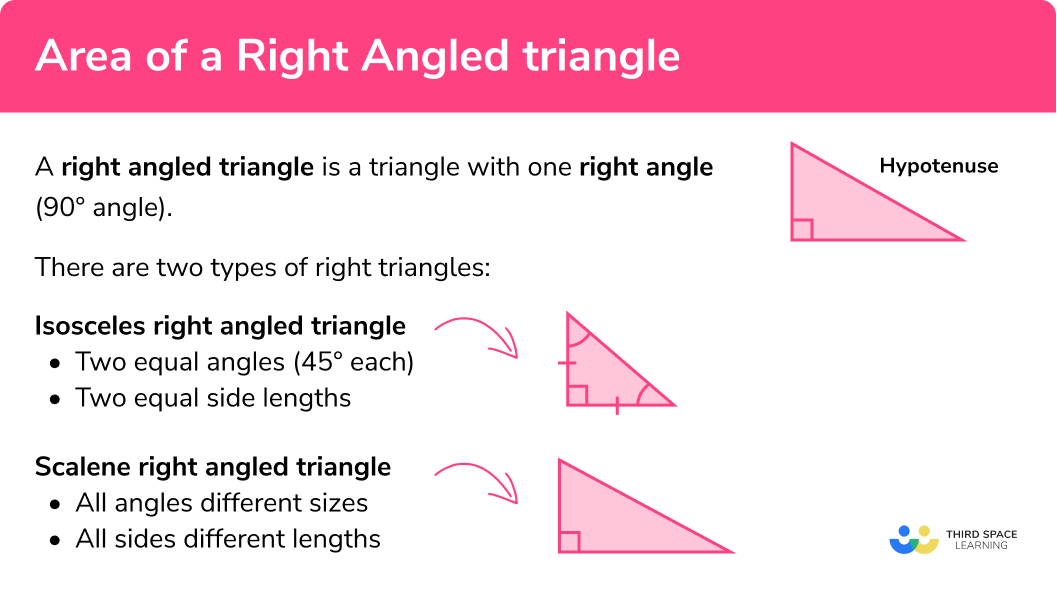
What is a right angled triangle?
A right angled triangle is a triangle with one right angle (
There are two types of right triangles:
Isosceles right angled triangle
-two equal angles (
-two equal side lengths
Scalene right angled triangle
-all angles different sizes
-all sides different lengths
- The relationship between the angles and side lengths of the triangle form the basis of the trigonometric functions sine, cosine and tangent.
Step by step guide: Trigonometry
- The side of the triangle opposite the right angle is the longest side of the triangle and is referred to as the hypotenuse.
Step by step guide: Hypotenuse (coming soon)
- Right triangles are also used in the Pythagorean Theorem:
Step by step guide: Pythagoras’ Theorem (coming soon)
What is a right angled triangle?
How to name a triangle
We can identify a triangle by putting a capital letter on each vertex (corner).
We can then refer to each of the sides of the triangle by using two letters to describe where the line starts and ends.
We can refer to the entire triangle by using all three letters.
E.g.
Name of sides:
side AB, side AC, side BC
Name of triangle:
triangle ABC
How do we find the area of a triangle?
In order to find the area of a triangle, we need to start with the area of a rectangle.
To find the area of a rectangle you must multiply adjacent sides together.
The area of the rectangle below would be calculated by multiplying the base x height
(b x h).
We can split a rectangle into
So the area of each of the right triangles is exactly half the area of the rectangle.
Area of a right angled triangle formula
This can be shortened to
where
Your final answer must be given in units2 (e.g. cm2, m2, mm2).
How to find the area of a right angled triangle
In order to find the area of a right angled triangle:
1Identify the height and base length of your triangle (you might need to calculate these values)
2Write the formula
3Substitute the values for base and height
4Calculate
How to find the area of a right angled triangle


Area Of A Triangle Worksheet

Get your free area of a triangle worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions on area of a right angled triangle.
DOWNLOAD NOW
Area Of A Triangle Worksheet

Get your free area of a triangle worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions on area of a right angled triangle.
DOWNLOAD NOWRelated lessons on area
Area of a right angled triangle is part of our series of lessons to support revision on area. You may find it helpful to start with the main area lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
- Area
- Area of a circle
- Area of a quadrilateral
- Area of a trapezium
- Area of a parallelogram
- Area of compound shapes
- Pi r squared
- Area of a rhombus
- Area of an isosceles triangle
- Area of an equilateral triangle
- Area of a triangle
- How to work out area
- Area of a rectangle
- Area of a hexagon
- Area of a pentagon
Area of right angled triangle examples
Example 1: given base length and height
Find the area of the triangle below:
- Identify the height and base length of the triangle
2Write down the formula
3Substitute the values for the base and height
4Calculate
Remember: Your final answer must be in units squared.
Example 2: given base length and height
Find the area of the triangle below:
Identify the height and base length of the triangle
Note: You have
Write down the formula
Substitute the values for the base and height
Calculate
Remember: Your final answer must be in units squared.
Example 3: missing height
Find the area of triangle ABC below:
Identify the height and base length of the triangle
In this question we are given the length of the hypotenuse which is
Write down the formula
Substitute the values for the base and height
Calculate
Remember: Your final answer must be in units squared.
Example 4: missing length given an angle
Below is a right angled triangle with height of 4 \, cm and an angle of 35^{\circ}.
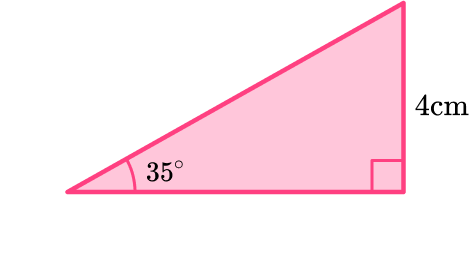
Find the area of the triangle.
Identify the height and base length of your triangle. (You might need to calculate these values)
The height of 4 \, cm is given and an angle of 35^{\circ} so we need to use SOHCAHTOA to find the base.
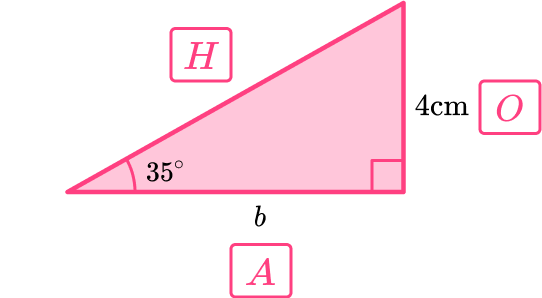
\tan \left( 35 \right)=\frac{4}{b}
So,
\begin{aligned}
b&=\frac{4}{\tan \left( 35 \right)} \\\\
& =5.71 \,cm
\end{aligned}
Write down the formula
Substitute the values for the base and height
Calculate
Example 5: compound shape
Below is the floor plan for a new deck that needs to be painted. One can of paint costs £
Identify the height and base length of the triangle
Split the plan into
For the triangle:
Write down the formula
Substitute the values for the base and height
Calculate
Now you must find the area of the rectangle.
Total Area =
Now we need to divide
This means you have to buy
Now to work out the cost:
The total cost to paint the deck is £
How to find a missing side length given the area
Sometimes a question might give you the area and ask you to work out the height or missing length. In order to do this you must rearrange the formula.
To find a missing length given the area:
1Rearrange the formula
2Substitute in the values you know
3Calculate
Example 6: calculating base length
Triangle XYZ is a right triangle with an area of
Rearrange the formula
to make
Next we need to divide both sides of the formula by
Now substitute the given values
Area =
Height =
Calculate
Common misconceptions
- Identifying the correct information to use
A question may give extra information that is not needed to answer it. Carefully identify the relevant pieces of information.
E.g.
To calculate the area here we only need the base and height.
Base=
Height =
Area=
We can ignore the value of the hypotenuse (
- Units
It is common error to forget the units for area in the final answer. When calculating area, your answer must always have units squared.
Practice area of right angled triangles questions
1. Find the area of the triangle below:




The lengths needed for the base and the height are 9cm and 12cm , so the calculation we need to do is \frac{1}{2} \times 9 \times 12 = 54cm^{2}
2. Find the area of the triangle below:




We need to convert the units so that they are the same.
0.9m=90cm
Then the calculation needed is \frac{1}{2} \times 90 \times 50= 2250cm^{2}
3. Shown below is a outline of a meerkat enclosure. Each meerkat needs a minimum of 9m^{2} to roam around. What is the maximum number of meerkats that can fit into this enclosure?




We can treat the shape as a rectangle with area 3.2 \times 4.5 = 14.4m^{2} and a triangle with area \frac{1}{2} \times 4.5 \times 4.5 = 10.125m^{2}.
This gives a total area of 14.4 + 10.125 = 24.525m^{2}.
By considering multiples of 9 , we conclude that 2 meerkats can fit into the cage.
4. Find the area of the triangle below:




Using Pythagoras’ Theorem to find length AB
AB=\sqrt{18^{2}-6^{2}}
AB=16.97…
The area is then given by \frac{1}{2} \times 6 \times 16.97 = 50.91cm^{2}
5. Triangle PQR is a right angled triangle with an area of 40cm^{2} . The base length of the triangle is 0.1m. Find the height of the triangle.




Starting with the formula for the area of a triangle: Area=\frac{1}{2} \times base \times height
We substitute in the known information (convert lengths to the same units), so
40=\frac{1}{2} \times 10 \times height
40=5 \times height
Therefore:
height = 8cm
Area of a right angled triangle GCSE questions
1. A logo is in the shape of a right angled triangle. It has a base length of 10cm and a height of 4.5cm . Calculate the area of the logo.
(2 marks)
(1)
A=22.5cm^{2}(1)
2. The diagram below shows the plan of a rectangular garden:
Calculate the area of the lawn.
(3 marks)
Area of rectangle:
5 \times 12 = 60m^{2}(1)
Area of triangle:
\frac{1}{2} \times 3 \times 5 = 7.5m^{2}(1)
Area of lawn:
60-7.5=52.5m^{2}(1)
3. The area of the square and the area of the right angled triangle below are equal.
Work out the height of the triangle.
(4 marks)
Area of square:
6 \times 6 = 36cm^{2}(1)
Rearrange area of triangle:
\begin{aligned} A &= \frac{1}{2} bh \\ 2A &= bh\\ h &= \frac{2A}{b} \end{aligned}
(1)
Substitute in values:
h= \frac{2 \times 36}{9} \begin{array}{l} h= \frac{72}{9}\end{array}\begin{array}{l} h=8cm \end{array}(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
-
Apply formula to calculate and solve problems involving the area of triangles
-
Use Pythagoras’ Theorem to solve problems involving triangles
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.