[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Decimals Fractions Addition and subtraction Multiplication and division Exponents Order of operations (PEMDAS) Algebraic expressionsSubstitution
Here you will learn about substitution, including what it is and how to use it to solve algebraic equations, expressions and inequalities.
Students will first learn about substitution as part of expressions and equations in 6th grade.
What is substitution?
Substitution means replacing the variables in an algebraic expression, equation or inequality.
You can substitute values to solve general mathematical formulas.
For example,
Use the formula A= \cfrac{1}{2} \, bh to find the area of the triangle.
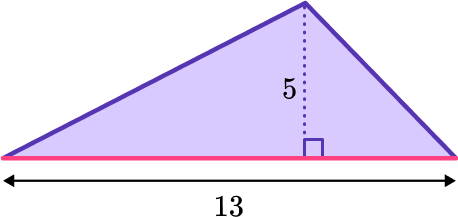
Substitute 5 for h and 13 for b and follow the order of operations:
\begin{aligned} &A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h \\\\ & A=\cfrac{1}{2} \times 13 \times 5 \\\\ & A=32.5 \text { units }^2 \end{aligned}
You can also use substitution in any mathematical expression, equation or inequality with unknowns (variables) to find the solution.
For example,
Does x = 2 satisfy the equation 4x+1=3 ?
Substitute 2 for x and follow the order of operations:
4 \times 2+1=8 + 1
8+1=9
9
Substituting 2 for x, does not satify the equation, so 2 is not a solution for 4x+1=3.
For example,
Does y = -4 satify the inequality y < 3 ?
Substitute -4 for y :
-4 < 3
Substituting -4 for y satisfies the inequality, so -4 is a solution for y < 3.
*Note that there are an infinite amount of solutions for this inequality – any number less than 3 will satisfy the inequality.
What is substitution?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6th grade math?
- Grade 6 – Expressions and Equations (6.EE.B.5)
Understand solving an equation or inequality as a process of answering a question: which values from a specified set, if any, make the equation or inequality true? Use substitution to determine whether a given number in a specified set makes an equation or inequality true.
How to use substitution to solve
In order to use substitution to solve an algebraic expression, equation or inequality:
- Substitute each variable with its given value.
- Solve using the order of operations.
![[FREE] Substitution Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Substitution-worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Substitution Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)
![[FREE] Substitution Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Substitution-worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 6 to 8 students’ understanding of substitution. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Substitution Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Substitution-worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Substitution Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)
![[FREE] Substitution Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Substitution-worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 6 to 8 students’ understanding of substitution. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREESubstitution examples
Example 1: basic formula, volume
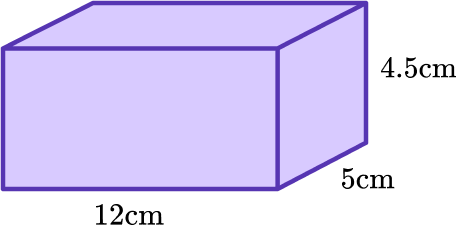
Find the volume of the rectangular prism using the formula, V=l \times w \times h.
- Substitute each variable with its given value.
V=12 \times 5 \times 4.5
2Solve using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & V=12 \times 5 \times 4.5 \\\\ & V=60 \times 4.5 \\\\ & V=270 \mathrm{~cm}^3 \end{aligned}
Example 2: basic expression, one variable and fractions
Find the value of 20-\cfrac{m}{5} \, when m=35.
Substitute each variable with its given value.
20-\cfrac{35}{5}
Solve using the order of operations.
\cfrac{35}{5} \, is an improper fraction and can be simplified to 7.
20-7=13
Example 3: basic inequality
Does d = -8 satisfy the inequality d \geq -9 ?
Substitute each variable with its given value.
-8 \geq-9
Solve using the order of operations.
There is nothing to calculate, but you read the inequality ‘-8 is greater than or equal to -9.’
Substituting -8 for d satisfies the inequality, so -8 is a solution for d \geq -9.
*Note that there are an infinite amount of solutions for this inequality – any number greater than or equal to -9 will satisfy the inequality.
Example 4: basic expression, two variables
Does x=4 and y=2 satify the equation 3 x-5 y=2 ?
Substitute each variable with its given value.
3 \times 4-5 \times 2
Solve using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 3 \times 4-5 \times 2 \\\\ & 12-10=2 \\\\ & 2=2 \end{aligned}
Substituting 4 for x and 2 for y satisfies the equation, so x=4 and y=2 is a solution for 3x-5y=2.
Example 5: expression with parentheses
Find the value of 2 (q-r) when q=15 and r=6.
Substitute each variable with its given value.
2(15-6)
Solve using the order of operations.
2(9)=18
Remember 2(9) is the same as 2\times 9
The value of the expression is 18
Example 6: exponents
Find the value of s^2(20-t) when s=2 and t=9.
Substitute each variable with its given value.
2^2(20-9)
Solve using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 2^2(20-9) \\\\ & =2^2(11) \\\\ & =4(11) \quad \quad \text{ **Remember } 4(11) \text{ is the same as } 4 \times 11 \\\\ & =44 \end{aligned}
Teaching tips for substitution
- Take time to make sure that students understand how algebraic equations, expressions, and inequalities are formed and what they represent before asking students to use them to solve. A great way to do this is through hands-on activities with algebra tiles or other manipulatives.
- Give students opportunities to create algebraic equations, expressions, and inequalities based on a real-world problem. For example, if you want to create playlists with 10 songs each, make the expression that would show how many playlists you would need depending on s, the number of songs you wanted to use.
- When introducing substitution, make sure that students are comfortable using related terms, such as coefficient and solution set, so terminology does not become a barrier. For this, students can create their own dictionary of math terms, which can include synonyms or examples for terms that are hard to remember. You can also display a word list in the classroom.
- Don’t place all the emphasis on “finding the answer,” but instead give students time to explore what numbers are and are not included in the solution set. At this stage in their development, they are still building foundational ideas about algebraic expressions, equations, and inequalities, so it is important not to rush them to “the answer.”
- Give students time to explore ideas around the number of solutions an algebraic equation, expression, or inequality may have. For example, give them the equation 3x+1=4 and ask them to find all the solutions. Then give them the equation 3x + 1 =y and ask them to find all solutions. Have students compare and contrast their solving strategies and make conjectures about why the second equation has infinitely more solutions.
Easy mistakes to make
- Confusing the meaning of a coefficient in front of a variable
Remember in algebraic expressions, 3k means 3 multiplied by k, not the number 3 written after the number represented by k.
For example,
- Not applying order of operations (PEMDAS)
Always solve parentheses first, then exponents, then multiplication and division from left to right, and then addition and subtraction from left to right.
For example,
Solve 4x+10 \div 2 when x=1.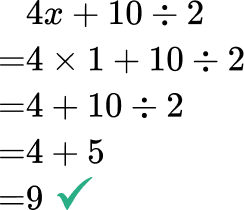
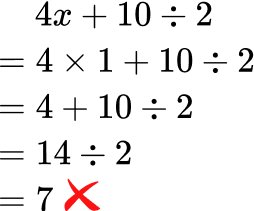
- Mixing up the values when there is more than one variable
Pay attention to which value goes with which variable. Mixing them up will lead to a different answer.
For example,
Solve 4x+\cfrac{3}{4} \, y when x=1 and y=4.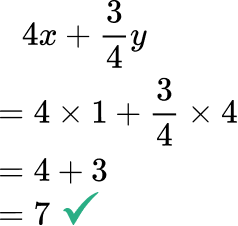
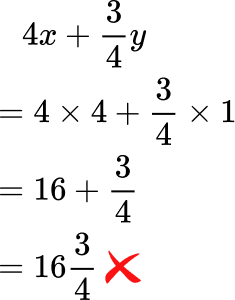
- Using the wrong formula to solve
The more formulas you know, the easier it is to get them confused or use the wrong one out of habit.
For example,
Find the area of a triangle with a base of 10 inches and a height of 3 inches.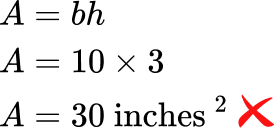
The correct formula for the area of a triangle is A=\cfrac{1}{2} \, b h, so the area of the triangle in the example is 15 \text { inches }^2.
Related math equations lessons
This substitution topic guide is part of our series on math equations. You may find it helpful to start with the main math equations topic guide for a summary of what to expect or use the step-by-step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other topic guides in this series include:
- Math equations
- Rearranging equations
- How to find the equation of a line
- Linear equations
- Writing linear equations
- Solving equations
- Identity math
- One step equations
- Solve equations with fractions
Practice substitution questions
1. Find the volume of the cube using the formula, V=s^3.
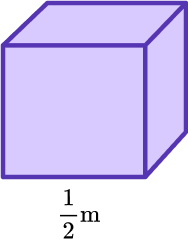




Substitute each variable with its given value.
Remember, s^3=s \times s \times s.
V=\left(\cfrac{1}{2}\right)^3
Solve using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & V=\left(\cfrac{1}{2}\right)^3 \\\\ & V=\cfrac{1}{2} \times \cfrac{1}{2} \times \cfrac{1}{2} \\\\ & V=\cfrac{1}{4} \times \cfrac{1}{2} \\\\ & V=\cfrac{1}{8} \, m^3 \end{aligned}
2. Find the value of 7 x-10 when x=5.




Substitute each variable with its given value.
7 \times 5-10
Solve using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 7 \times 5-10 \\\\ & =35-10 \\\\ & =25 \end{aligned}
3. Which number is not a solution for x \leq-56?




Substitute each variable with its given value and then read each inequality:
-55 \leq-56… ‘-55 is less than or equal to -56’
-56 \leq-56… ‘-56 is less than or equal to -56’
-57 \leq-56… ‘-57 is less than or equal to -56’
-112 \leq-56… ‘-112 is less than or equal to -56’
Substituting -55 for x does not make the inequality true, so -55 is not a solution for x \leq-56.
4. Find the value of \cfrac{y}{4}+8 r when y=20 and r=3.




Substitute each variable with its given value.
\cfrac{20}{4}+8 \times 3
Solve using the order of operations.
\cfrac{20}{4} is an improper fraction and can be simplified to 5.
\begin{aligned} & \cfrac{20}{4}+8 \times 3 \\\\ & =5+8 \times 3 \\\\ & =5+24 \\\\ & =29 \end{aligned}
5. Find the value of 6 g \, (3 h-9) when g=10 and h=5.




Substitute each variable with its given value.
6 \times 10(3 \times 5-9)
Solve using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 6 \times 10(3 \times 5-9) \\\\ & =6 \times 10(15-9) \\\\ & =6 \times 10(6) \\\\ & =6 \times 10 \times 6 \\\\ & =60 \times 6 \\\\ & =360 \end{aligned}
6. Find the value of 3 e^2+8 when e=4.




Substitute each variable with its given value.
3 \times 4^2+8
Solve using the order of operations.
Remember, 4^2=4 \times 4.
\begin{aligned} & 3 \times 4^2+8 \\\\ & =3 \times 16+8 \\\\ & =48+8 \\\\ & =56 \end{aligned}
Substitution FAQs
Like the everyday definition of substitution, it is the act of replacing something with something else.
In other grades, students will learn how to use substitution in simultaneous equations, such as linear systems, which can include graphing.
No, by substituting numbers you are not changing the overall value of the equation, but seeing if the substituted number keeps the equation true.
No, factoring is finding the factors of algebraic expressions or equations by using properties of operations. This is different from using substitution to see if a number is within the solution set.
The substitution method is another way to say substitution. It can be used for simple equations, such as the ones shown on the page, all the way up to more complicated equations, such as solving systems of equations in algebra or finding derivatives in calculus.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!