One to one maths interventions built for KS4 success
Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons now available
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
2D shapes Angle rules Polygons Regular polygon Irregular polygon Interior angles of a polygon Exterior angles of a polygon How to work out perimeterThis topic is relevant for:

Hexagon Shape
Here we will learn about the hexagon shape including its properties, the different types of hexagon shapes and how to solve problems involving hexagon shapes.
There are also polygon worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is the hexagon shape?
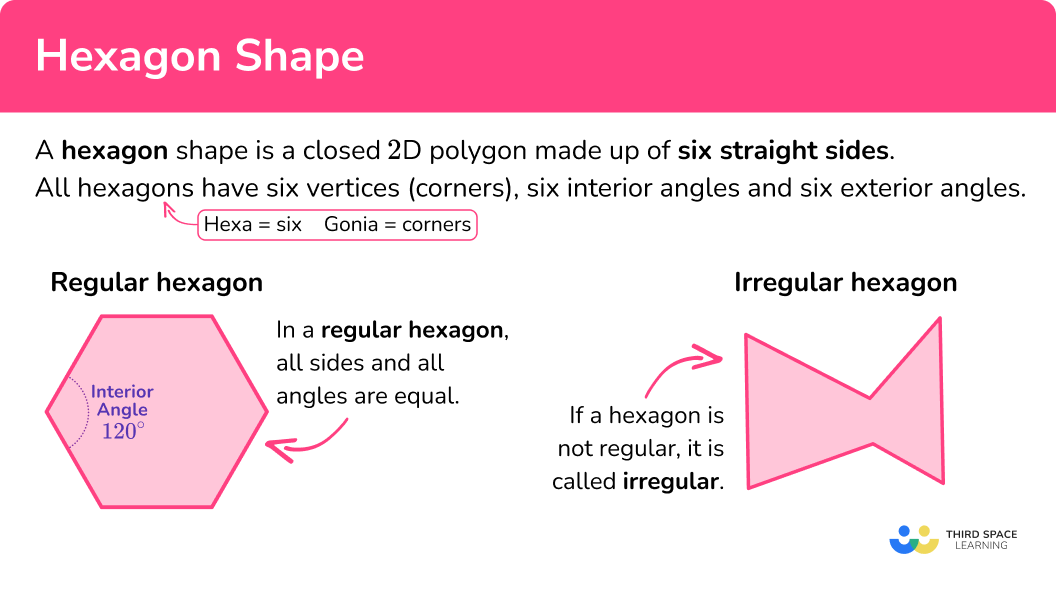
A hexagon shape is a closed two-dimensional polygon made up of six straight sides.
Hexagons have six vertices (corners), six interior angles and six exterior angles. The name hexagon is divided into ‘hexa’ meaning six, and ‘gonia’ meaning apex or corners.
Hexagon shapes can have the same or different dimensions of length.
- A regular hexagon shape has six sides that are equal in length, six interior angles that are equal in size and six exterior angles that are equal in size.
Some examples of real life regular hexagons include floor tiles and honeycomb in beehives which form tessellating hexagonal patterns.

Snowflakes are also hexagonal patterns.

- If a hexagon does not have six equal sides and six equal interior angles, it is called an irregular hexagon.

What is the hexagon shape?
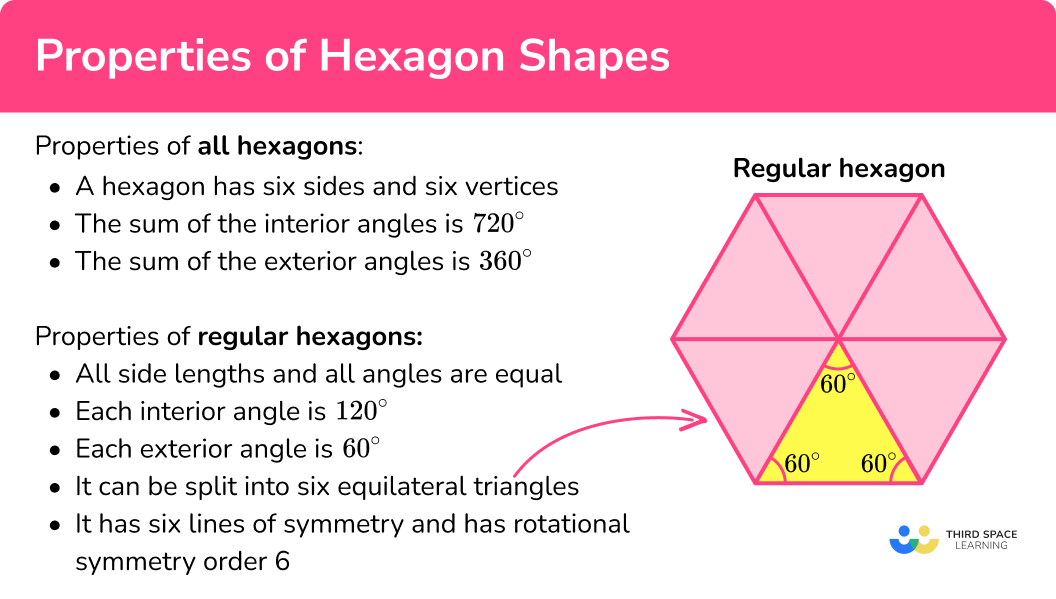
Properties of hexagon shapes
Properties of all hexagons,
- A hexagon has six sides and six vertices.
- The sum of the interior angles is 720^{\circ} .
- The sum of the exterior angles is 360^{\circ} .
Properties of regular hexagons,
- All side lengths and all angles are equal.
- Each interior angle is 120^{\circ} .
- Each exterior angle is 60^{\circ} .
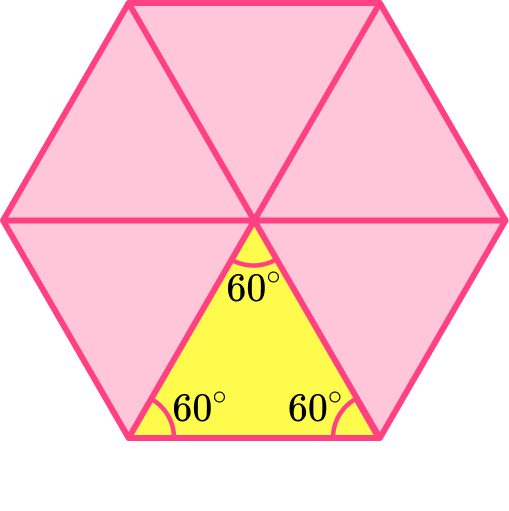
- It can be split into six equilateral triangles.
- It has six lines of symmetry and has rotational symmetry order 6 .
What are the properties of hexagon shapes?
Sides of a hexagon shape
All hexagon shapes have six straight edges that form a closed shape.
Regular hexagons have six equal sides.
Irregular hexagons have six sides that are not all equal in length.
By taking the sum of all six sides of a hexagon, we get the perimeter of the hexagon.
In a regular hexagon, if we know the value of the perimeter, we can calculate the length of each side by dividing the perimeter by six.
For example,
The regular hexagon shape below has a perimeter of 108 \ cm.
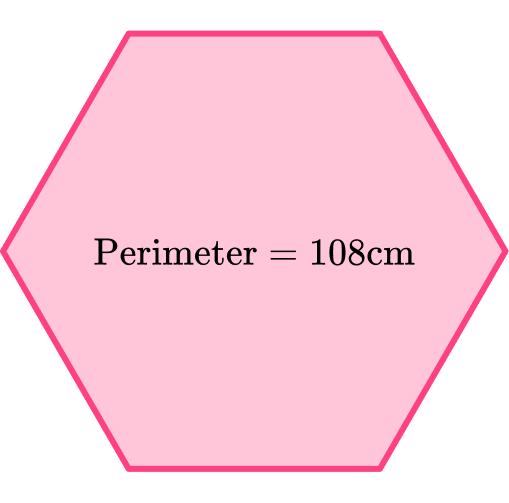
We can calculate the length of each side by
108 \div 6=18 .
So, the length of each side of the regular hexagon shape is 18 \ cm.
Angles of a hexagon shape
All polygons have interior and exterior angles. A pair of interior and exterior angles form a straight line and therefore add to 180^{\circ}
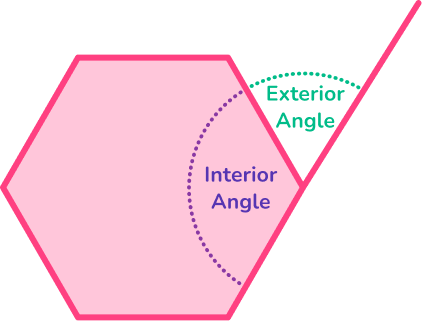
- Interior angles are the angles inside a polygon formed at the apex where two sides meet.
To find the sum of the interior angles of any hexagon,
\text {Sum of the interior angles of a polygon}=(n-2) \times 180 \text {, }where n is the number of sides.
A hexagon has 6 sides, so n=6.
\begin{aligned} \text{Sum of interior angles of a hexagon} &= (6-2) \times 180 \\\\&= 4 \times 180 \\\\ &= 720^{\circ} \end{aligned}The sum of the interior angles of a hexagon shape is 720^{\circ}.
Each of the individual interior angles of a regular hexagon shape is 120^{\circ} each.
Step-by-step guide: Interior angles
- Exterior angles are the angles between a polygon and the extended line from the vertex (corner) of the polygon.
The sum of the exterior angles of any polygon is 360^{\circ}.
The exterior angles of a regular hexagon shape are 60^{\circ} each.
Step-by-step guide: Exterior angles
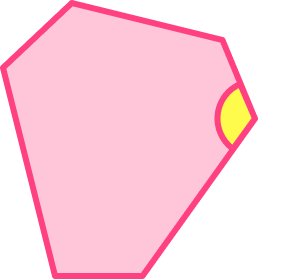
Convex hexagon shapes
A convex hexagon shape has interior angles that all measure less than 180^{\circ}.
Convex hexagons can be regular or irregular. All the vertices (corners) of a convex hexagon are pointed outwards.
For example,
Concave hexagon shapes
A concave hexagon shape has at least one interior angle that is greater than 180^{\circ}.
Concave hexagons have at least one vertex that points inwards.
For example,

How to solve problems involving hexagon shapes
In order to solve problems involving hexagon shapes:
- Identify if the hexagon is regular or irregular.
- Recall the appropriate properties of hexagons in the context of the question.
- Answer the question.
Explain how to solve problems involving hexagon shapes

Hexagon shape worksheet

Get your free hexagon shape worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Hexagon shape worksheet

Get your free hexagon shape worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on polygons
Hexagon shape is part of our series of lessons to support revision on polygons. You may find it helpful to start with the main polygons lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Hexagon shape examples
Example 1: perimeter
Find the perimeter of the hexagon below.
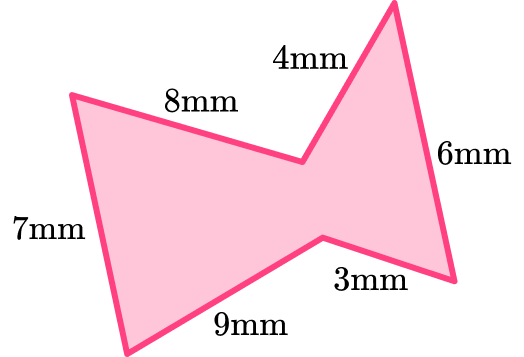
- Identify if the hexagon is regular or irregular.
The hexagon is irregular, all six sides are different lengths.
2Recall the appropriate properties of hexagons in the context of the question.
The appropriate hexagon shape property for this question is, ‘the perimeter can be found by adding the lengths of all six sides’.
3Answer the question.
The perimeter of this hexagon is
7+8+4+6+3+9=37 \mathrm{~mm}.Example 2: missing side
Below is a regular hexagon shape. The perimeter of the shape is 33 \ cm.
Find the side length, a.
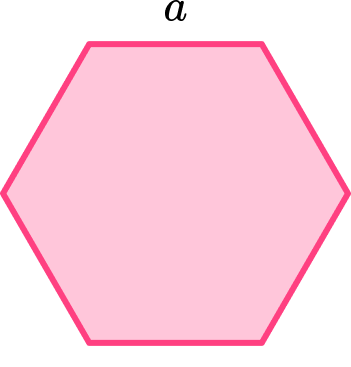
Identify if the hexagon is regular or irregular.
The question states that the hexagon is regular.
Recall the appropriate properties of hexagons in the context of the question.
The appropriate hexagon shape property for this question is, ‘the perimeter can be found by adding the lengths of all six sides’.
We know this is a regular hexagon and that all six sides are equal. We also know that the perimeter is 33 \ cm. To find the side length, a, we can divide the perimeter by the number of equal sides.
Answer the question.
Example 3: exterior angles
What is the size of the exterior angle of a regular hexagon.
Identify if the hexagon is regular or irregular.
The question states that the hexagon is regular.
Recall the appropriate properties of hexagons in the context of the question.
The appropriate hexagon shape property for this question is, ‘the sum of the exterior angles is always equal to 360^{\circ} ‘.
We know this is a regular hexagon and that all six exterior angles are equal.
Answer the question.
Example 4: interior angles
Below is a hexagon. Find the missing angle, x.
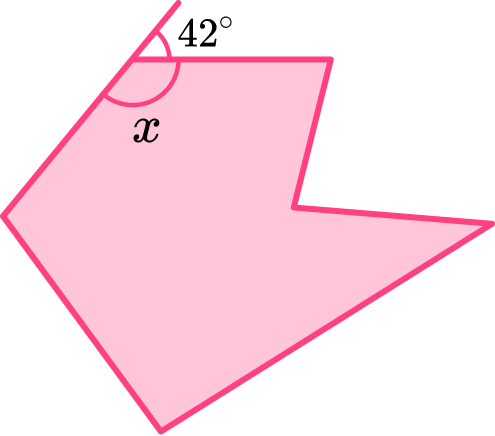
Identify if the hexagon is regular or irregular.
The hexagon is irregular. We know this, because the labelled exterior angle is 42^{\circ}.
If it was a regular hexagon shaped the exterior angles would all be equal, 60^{\circ}.
Recall the appropriate properties of hexagons in the context of the question.
The appropriate hexagon shape property for this question is, ‘interior and exterior angles form a straight line, therefore they add to 180^{\circ} ‘.
Answer the question.
Example 5: length of a long diagonal
Below is a regular hexagon shape. Find the length of the diagonal labelled d.
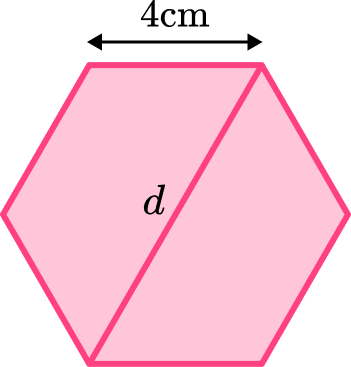
Identify if the hexagon is regular or irregular.
The question states that the hexagon is regular.
Recall the appropriate properties of hexagons in the context of the question.
The appropriate hexagon shape property for this question is, ‘a regular hexagon can be split into six equilateral triangles‘.
Answer the question.
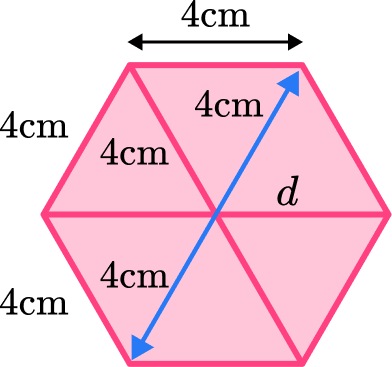
d=2 \times 4=8 \mathrm{~cm}
Example 6: length of a short diagonal
Below is a regular hexagon shape. Find the length of the diagonal labelled d. Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
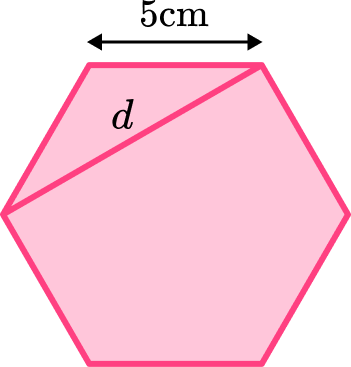
Identify if the hexagon is regular or irregular.
The question states that the hexagon is regular.
Recall the appropriate properties of hexagons in the context of the question.
The appropriate hexagon shape property for this question is, ‘all internal angles are equal to 120^{\circ} in a regular hexagon‘.
Answer the question.
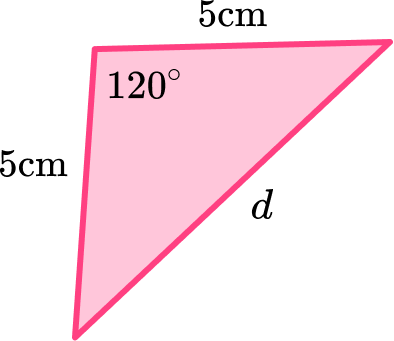
Using the cosine rule,
a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc\cos A .
We can find the length d.
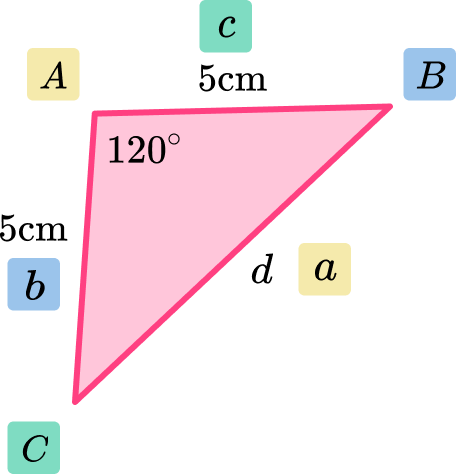
d=\sqrt{5^2+5^2-2\times 5\times 5\times \cos(120)}=5\sqrt{3}=8.66 \mathrm{~cm}
Therefore length d is 8.66 \ cm (to 2 decimal places).
Common misconceptions
- Regular or irregular polygons
We have to be careful to never assume a polygon is regular or irregular. If the question does not tell us, we need to use appropriate properties of polygons to identify regularity or irregularity.
For example, the hexagon below looks regular at a glance, however, we can see from the diagram that two interior angles are labelled, and they are not equal.
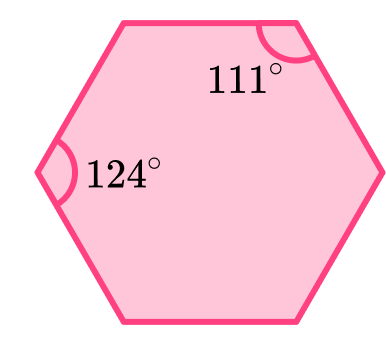
For a polygon to be regular all six interior angles must be equal in size.
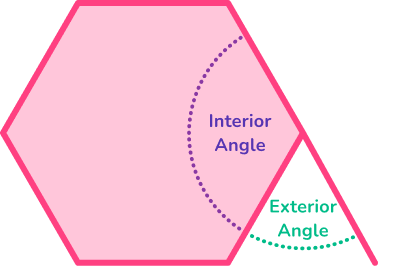
- Interior or exterior angles
Be careful not to confuse interior and exterior angles. Interior angles are formed inside the shape, where two sides meet and form a vertex (corner). Exterior angles are formed between a polygon and the extended line from the vertex (corner) of the polygon.
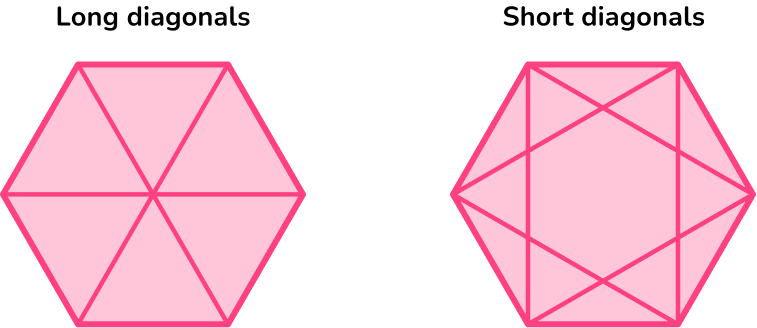
- Diagonals or lines of symmetry
Be careful not to confuse diagonals with lines of symmetry. In a regular hexagon, the three long diagonals are also lines of symmetry, however, the short diagonals are not.
Practice hexagon shape questions
1. Find the perimeter of a regular hexagon shape with side length 8 \ cm.




To find the perimeter of a hexagon shape you add together the six side lengths. This is a regular hexagon, so all six side lengths are equal, at 8 \ cm.
8 \times 6 = 48 \ cm
2. Find the missing angle, a.
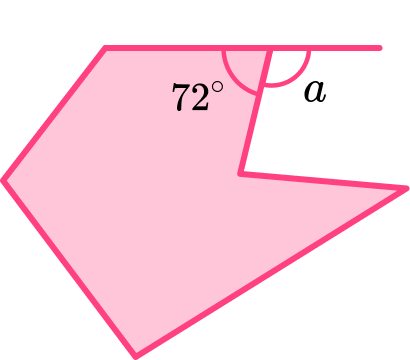




Interior and exterior angles form a straight line, therefore they add to 180^{\circ},
so \ a=180-72=108^{\circ}.
3. The perimeter of this hexagon shape is 50 \ cm. Find the missing side.
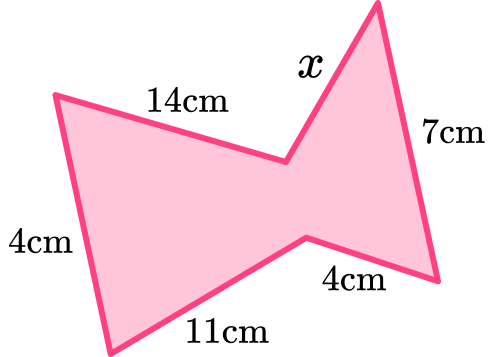




To find the perimeter of a hexagon shape you add together the six side lengths. We know five of the six sides and that the perimeter is 50 \ cm. So, we can subtract the sides we know from the total perimeter to find the missing side.
x=50-14-9-11-4-7=5 \mathrm{~cm}
4. Find the missing angle, p.
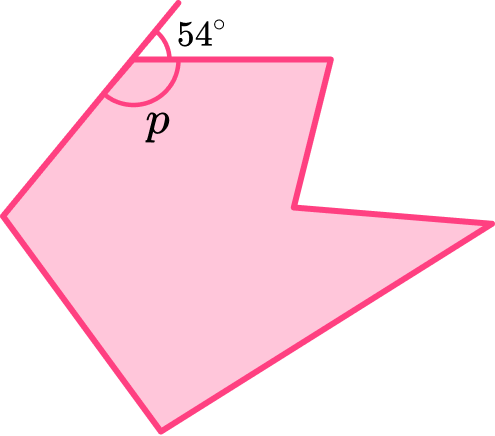




Interior and exterior angles form a straight line, therefore they add to 180^{\circ},
so \ p=180-54=126^{\circ}.
5. Find the length of the diagonal, h.
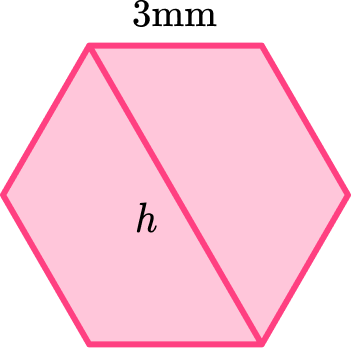




The hexagon shape can be split into 6 regular hexagons to find the length of the long diagonal.
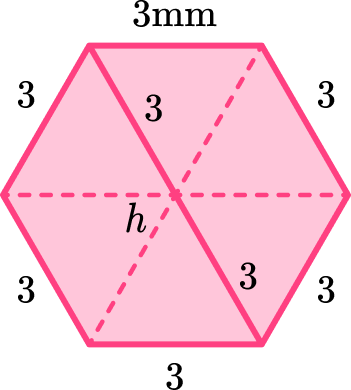
So \ h=2 \times 3=6 \mathrm{~mm}.
6. Find the length of the diagonal, d.
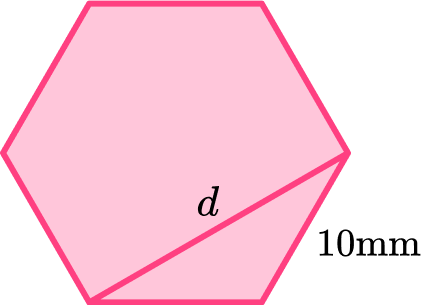




The diagonal d can be found by using the fact that the sides are the same length and the interior angle is 120^{\circ}.
Using the cosine rule,
a^2=b^2+c^2-2bc\cos{A}.
We can find the length d.
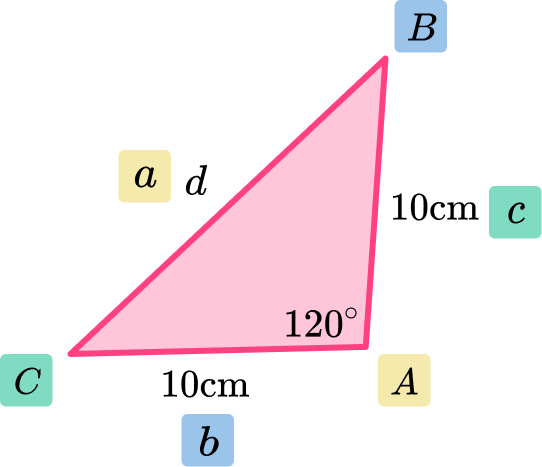
d=\sqrt{10^2+10^2-2\times 10\times 10\times \cos(120)}=10\sqrt{3} \mathrm{~cm}
Hexagon shape GCSE questions
1. (a) Name the polygon below.

(b) It is a convex polygon as it has a reflex angle.
Clearly label the reflex angle with an x.
(2 marks)
(a) Hexagon
(1)
(b)
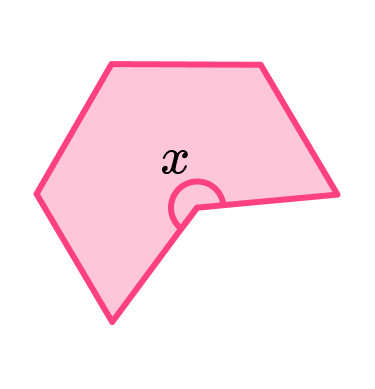
(1)
2. Below is a hexagon. The perimeter of the hexagon is 50 \ cm. Find the missing side length.
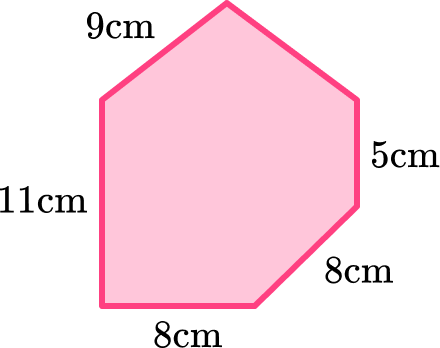
(2 marks)
(1)
9 \ cm(1)
3. Find the angle labelled g.
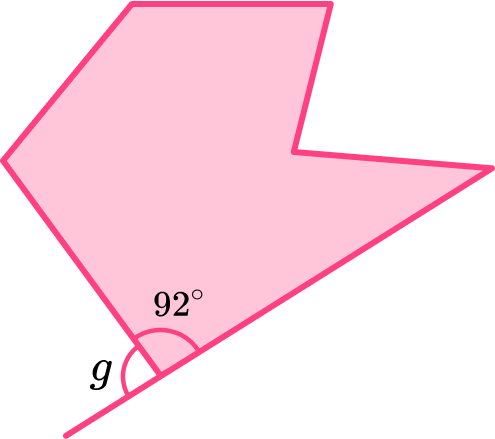
(2 marks)
(1)
88^{ \circ}(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Use properties of hexagons to solve problems
- Find side lengths of a hexagon given a perimeter
- Find the perimeter of a hexagon
- Find the interior angle of a hexagon
- Find the exterior angle of a hexagon
- Find the length of the long diagonal in a regular hexagon
- Find the length of a short diagonal in a regular hexagon
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.