18 Word Problems For Year 5: Develop Pupils’ Problem Solving Skills Across Single and Mixed KS2 Topics
Word problems for Year 5 involve increasingly complex, multi step calculations that require reasoning and problem-solving skills alongside fluency. Teachers should provide regular, targeted practice that integrates all three of these areas to ensure pupils are well-prepared for any KS2 problem-solving context.
To support your planning, our team of expert primary teachers have created this collection of 18 word problems for Year 5 maths. The problems are curriculum-aligned and cover a range of KS2 topics.This resource is designed to fit in with your day to day teaching. The questions are great to use as lesson starters, as extension tasks for pupils who finish work quickly or who need an extra challenge, or as homework. This article also includes worked examples, teaching ideas and links to Year 5 maths worksheets and further free and premium resources.
All Kinds of Word Problems
Download this free pack of multiplication word problems to help your Year 5 class grow their problem solving skills
Download Free Now!Year 5 maths word problems in the national curriculum
Word problems are an important element of the Year 5 curriculum. By Year 5, the national curriculum states that pupils should develop their ability to solve a wider range of problems, including:
- Increasingly complex properties of numbers and arithmetic.
- Problems demanding efficient written and mental methods of calculation.
- Solving more complex two-step and multi-step word problems.
Children should also begin to use the language of algebra to solve these problems.
Place value
Solve number and practical problems involving:
- ordering and comparing numbers to at least 1,000,000
- counting forwards or backwards in steps of powers of 10
- interpreting negative numbers in context and rounding to the nearest 10, 100, 1000, 10,000 and 100,000
Addition and subtraction
Solve addition and subtraction word problems and a combination of these, including understanding the meaning of the equals sign.
Multiplication and division
Solve problems involving multiplication and division, including using knowledge of:
- Factors
- Multiples
- Squares and cubes
- Scaling by simple fractions
Fractions, decimals and percentages
Fractions, decimal and percentage word problems involve solving problems involving numbers up to 3 decimal places and problems which require knowing percentage and decimal equivalents.
Measurement
Solve time word problems, including converting between units of time, and problems involving measure (for example, length, mass, volume and money word problems) using decimal notation and scaling.
Statistics
Solve comparison, sum and difference problems, using information presented in a line graph.
Addition word problems for Year 5
In Year 5, addition word problems can involve whole numbers with over 4 digits and decimal numbers. Children should be able to round number to check the accuracy and begin to solve two step number problems.
Addition question 1
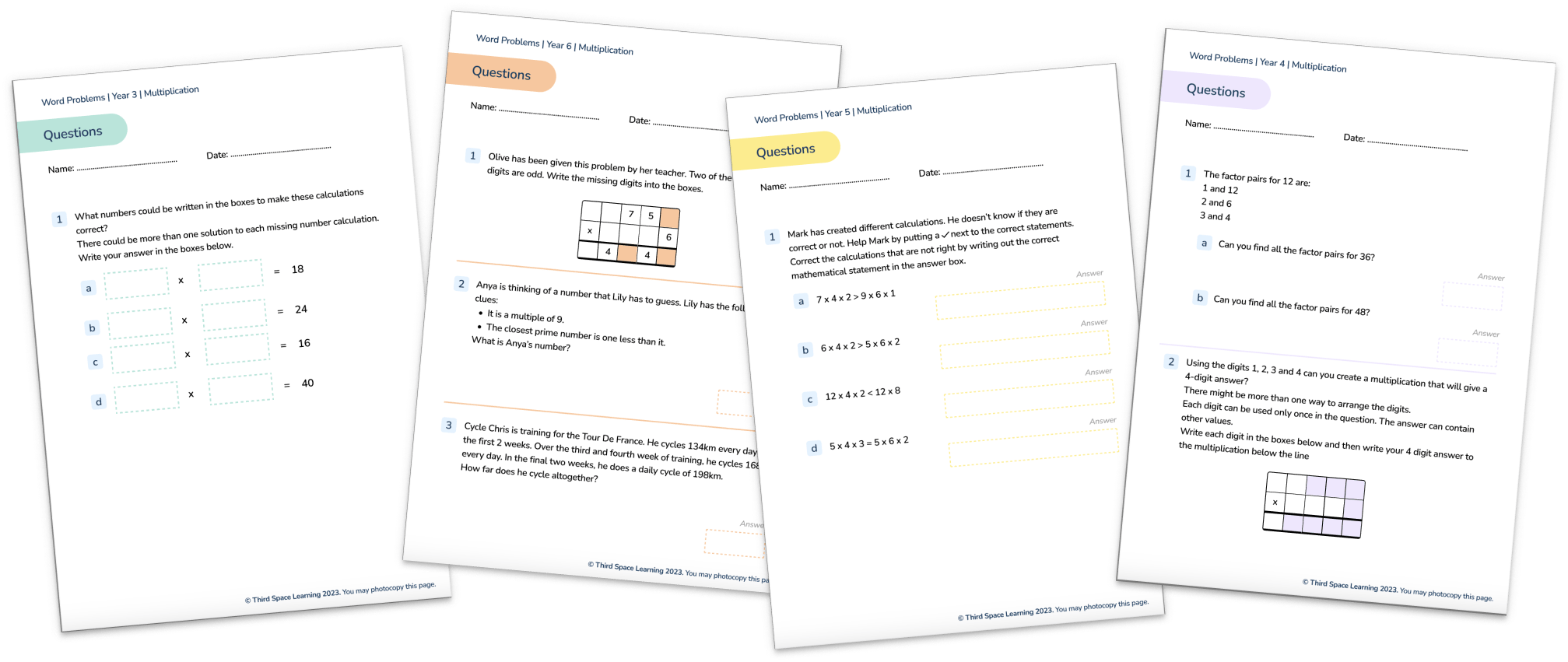
Gemma picks two cards from the cards below and adds them together.
She is able to make three different totals. What will they be?
2365 6281 9782
Answer (2 marks): 12,147 16,063 8646
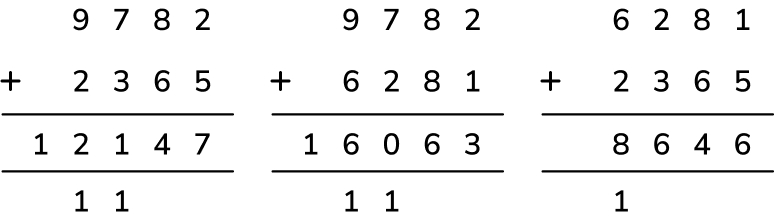
Addition question 2: Addition with regrouping
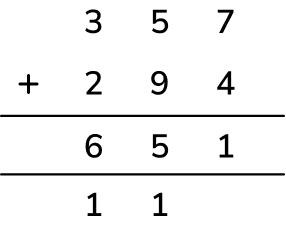
Ahmed adds two of these numbers mentally.
357 280 294 232
In his calculation, he exchanges twice to create one ten and one hundred.
Write Ahmed’s calculation and work out the total.
Answer (1 mark): 357 + 294 = 651
Addition question 3: Multiples of 10
Change one digit in the calculation below, so that the answer is a multiple of 10.
726 + 347
Answer (1 mark): 723 + 347 = 1070
Subtraction word problems for Year 5
Subtraction word problems in Year 5 require pupils to be confident subtracting numbers over 4 digits and problems involving decimal numbers. Pupils need to be able to round numbers to check accuracy and to use subtraction when solving mixed word problems.
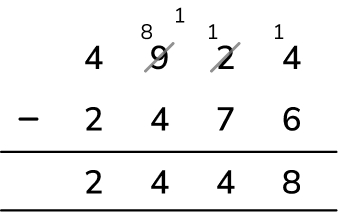
Subtraction question 1: Subtracting 4-digit numbers (distance)
A coach is travelling 4924 km across the USA
It has 2476 km to go.
How many kilometres has the coach already travelled?
Answer (1 mark): 2448 km
Subtraction question 2: Subtracting 4-digit numbers
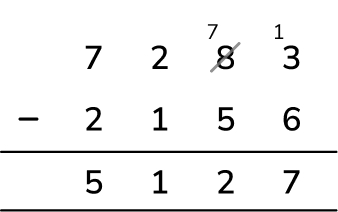
A primary school printed 7283 maths worksheets in the Summer term. 2156 were for Key Stage 1 pupils. How many were printed for Key Stage 2?
Answer (1 mark): 5127 worksheets
Subtraction question 3: Subtracting 5-digit numbers (money)
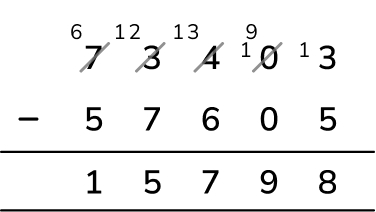
A clothing company made £57,605 profit in 2021 and £73,403 in 2022.
How much more profit did the company make in 2022 than in 2021?
Answer (1 mark): £15,798
Multiplication word problems for Year 5
In Year 5, multiplication word problems involve:
- combining multiplication with other operations in order to solve two-step word problems
- times tables
- multiplying whole numbers up to 4-digits by 1 or 2-digit numbers
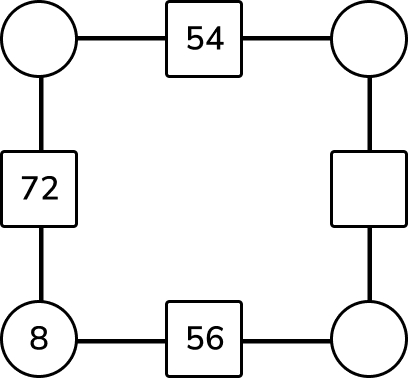
Multiplication question 1: Multiplication facts
In this diagram, the numbers in the circles are multiplied together to make the answer in the square between them.
Complete the missing numbers.
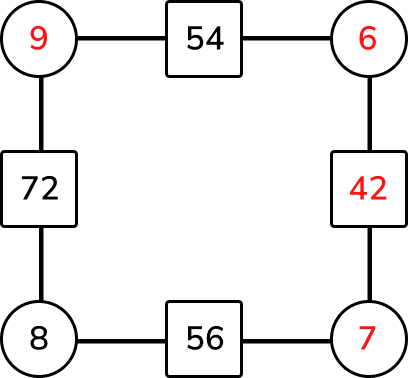
Answer (1 mark)
Multiplication question 2: Multi step word problem
Mrs Jones was printing the end of year maths test. Each test had 18 pages and 89 pupils were sitting the test. Mrs Jones also needed to print out 12 copies for the teachers and teaching assistants who were helping to run the test.
How many pieces of paper did Mrs Jones need to put in the photocopier, to make sure she had enough for all the tests?
Answer (1 mark)
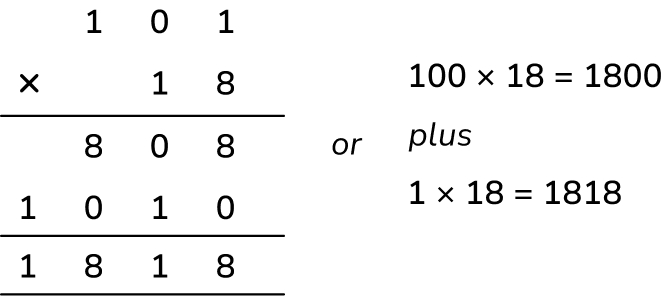
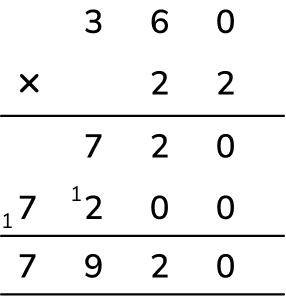
Multiplication question 3: Multi step multiplication (3-digit by 2-digit)
A school is booking a trip to Alton Towers. Tickets cost £22 per pupil.
There are 120 children in each year group and all the children from 3 year groups will be going.
What will be the total price for all the tickets?
Answer (2 marks): £7920
Division word problems for Year 5
In Year 5, division word problems involve:
- whole numbers up to 4-digits being divided by 1-digit numbers
- interpreting remainders
Division question 1: Dividing 2-digit numbers
Tom has 96 cubes and makes 12 equal towers.
Masie has 63 cubes and makes 9 equal towers.
Whose towers are tallest and by how many cubes?
Answer (2 marks): Tom
Tom’s tower has more cubes. His towers have 1 more cube than Maise’s towers.
96 ÷ 12 = 8
63 ÷ 9 = 7
Division question 2: Interpreting the remainder
A cake factory has made cakes to deliver to a large event.
265 cakes have been baked. How many boxes of 8 cakes can be delivered to the event?
Answer (2 marks): 33 boxes
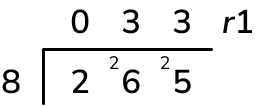
Division question 3: Dividing 4-digit numbers by 1-digit numbers
Lily collected 1256 stickers. She shared them between her 8 friends. How many stickers did each friend get?
Answer (1 mark): 157 stickers
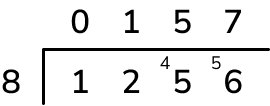
Fraction and decimal word problems for Year 5
In Year 5, fractions word problems and decimals involve:
- Converting between fractions and decimals
- Ordering fractions and decimals
- Adding and subtracting fractions and decimals
Fraction and decimal question 1: Finding a fraction of an amount
Isobel collected 24 conkers.
She gave \frac{1}{8} of the conkers to her brother.
How many conkers did she have left?
Answer (1 mark): 21 conkers left
\frac{1}{8} of 24 = 3
24 – 4 = 21
Fraction and decimal question 2: Multi step subtraction
Ahmed counted out 32 sweets. He gave \frac{1}{4} of the sweets to his brother and \frac{3}{8} of the sweets to his friend.
How many sweets did he have left?
Answer (2 marks): 12 sweets
\frac{1}{4} of 32 = 8
\frac{3}{8} of 32 = 12
He gave away 20 sweets, so had 12 left for himself.
Fraction and decimal question 3: Adding mixed numbers and fractions
Two friends shared some pizzas, 1 ate 1 \frac{1}{2} pizzas, whilst the other ate \frac{5}{8} of a pizza. How much did they eat altogether?
Answer (1 mark): 2 \frac{1}{8} of pizza
1 \frac{1}{2} = \frac{12}{8}
\frac {12}{8} + \frac{5}{8} = \frac{17}{8} = 2 \frac{1}{8} pizzas
Mixed four operation word problems for Year 5
Problems with mixed operations, or ‘multi-step’ word problems, require two or more operations to solve them. A range of concepts can be covered within mixed problems, including:
- the four operations
- fractions
- decimals
- measures
These are worth more marks than some of the more straightforward, one-step problems.
Mixed operation question 1: Multi step money problem
At the cake sale, Sam buys 6 cookies and a cupcake. He pays £2.85 altogether.
Naya buys 2 cookies and pays 90p altogether.
How much does the cupcake cost?
Answer (2 marks): 60p for one cupcake

Mixed operation question 2: Mixed multiplication and addition word problem
Large biscuit tin – 48 biscuits
Small biscuit tin – 30 biscuits
Ben bought 2 large tins of biscuits and 3 small tins.
How many biscuits did he buy altogether?
Answer (2 marks): 186 biscuits
2 x 48 = 96
3 x 30 = 90
96 + 90 = 186 biscuits
Mixed operation question 3: Multi step money problem (profit)
The owner of a bookshop bought a box of 15 books for £150.
He sold the books individually for £12 each.
How much profit did he make?
Answer (2 marks)

How to teach problem solving in Year 5
Children need to be taught the skills to make sense of word problems and tackle them successfully. Some teachers encourage students to use acronyms, such as RUCSAC (Read, Underline, Calculate, Solve, Answer, Check) to provide a structured approach. While these do simplify the process, it can encourage a formulaic approach, rather than deep mathematical thinking. It is beneficial however to provide pupils with some structure, such as:
1. Read the question carefully and identify the key information needed to solve it
2. Draw a picture or visual representation to understand the question
3. Identify which calculations are required for solving it
Once pupils reach an answer, they should use strategies to check it, for example:
- Using mental maths skills to round and estimate to check whether the final answer is realistic.
- Calculating the inverse
READ MORE: Mental maths Year 5

This structured method is the same approach Skye, the AI maths tutor, takes in Third Space Learning’s AI maths tutoring. In this Year 5 lesson on solving multi-step addition and subtraction problems, Skye models the following stages:
- Careful reading: Skye first models reading the problem carefully and helps the pupil identify the key information needed to solve it.
- Visualisation: Bar models are used to help pupils visualise the problem and work out what calculation is needed to answer the question, supporting the development of abstract understanding.
- Reasoning: Skye then uses spoken prompts to encourage pupils to verbalise their calculation steps and reasoning, ensuring deep conceptual understanding.
This approach ensures Year 5 pupils develop not only fluency skills by completing calculations correctly, but also the transferable strategies needed to succeed in complex, multi-step problem-solving.
Word problems for Year 5: Worked examples
Subtracting and adding 3- and 4-digit numbers
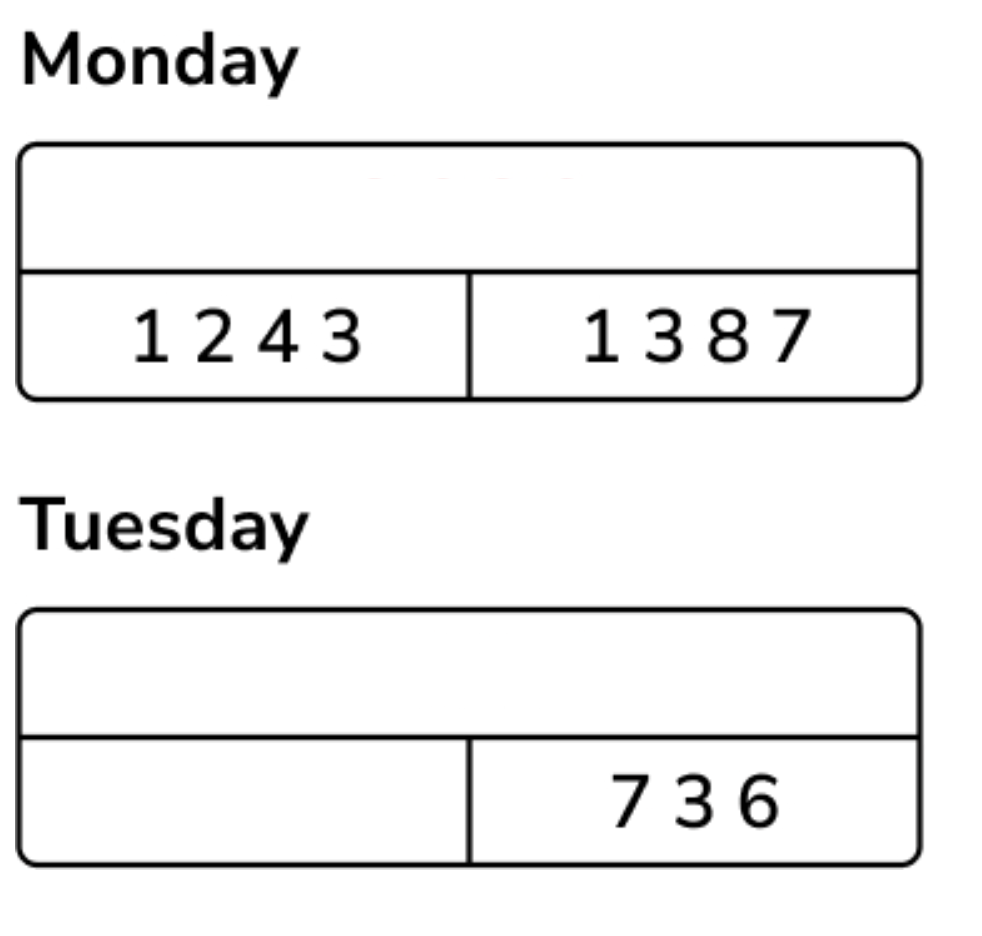
A transport museum has 1243 visitors on Monday morning and another 1387 visitors in the afternoon. On Tuesday 736 fewer visitors go to the museum than who visited on Monday.
How many visitors were there altogether on Tuesday?
1. Read the question carefully and identify the key information needed to solve it
- The number of visitors on Monday morning and Monday afternoon are given separately. They need to be added together to give the total number of visitors for Monday.
- ‘Fewer’ means I will need to subtract the number of fewer visitors on Tuesday from the total number of visitors on Monday.
2. Draw a picture or visual representation to understand the question
We can draw a bar model to represent this problem:
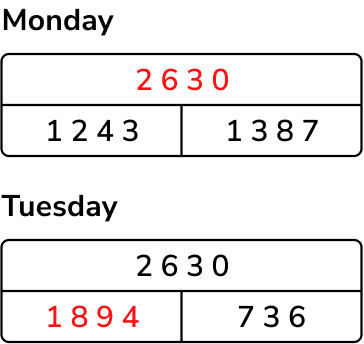
3. Identify which calculations are required for solving it
Column addition and subtraction are required to solve this question.
- To calculate the total number of visitors on Monday, we need to add 1243 and 1387 together. 1243 + 1387 = 2630
- The number of fewer visitors on Tuesday needs to be subtracted from Monday’s total: 2630 – 736 = 1894.
- The total number of visitors on Tuesday was 1894.
Finding a fraction of an amount
A farmer has 145 sheep. He sells \frac{3}{5} of his sheep at the market.
How many sheep did the farmer sell?
1. Read the question carefully and identify the key information needed to solve it
- The total number of sheep is 145.
- We need to find \frac{3}{5} of this total.
- The denominator (5) tells us how many equal parts the total needs to be divided into. The numerator (3) tells us how many of those parts the farmer sold.
2. Draw a picture or visual representation to understand the question
We can draw a bar model to represent the whole number (145) divided into 5 equal parts
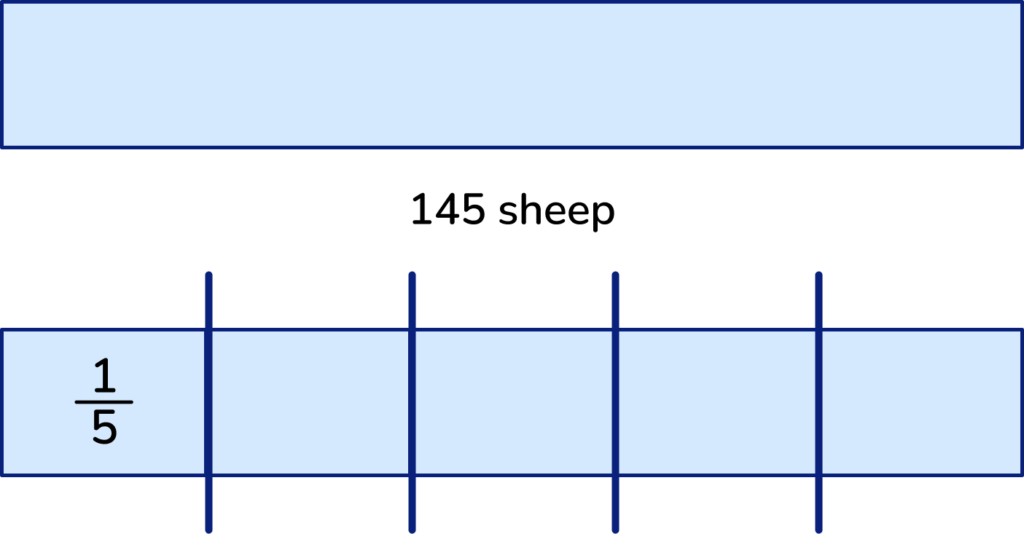
3. Identify which calculations are required for solving it
- We need division to find the size of one part (\frac{1}{5}).
- Then, we need multiplication to multiply by the numerator (3).
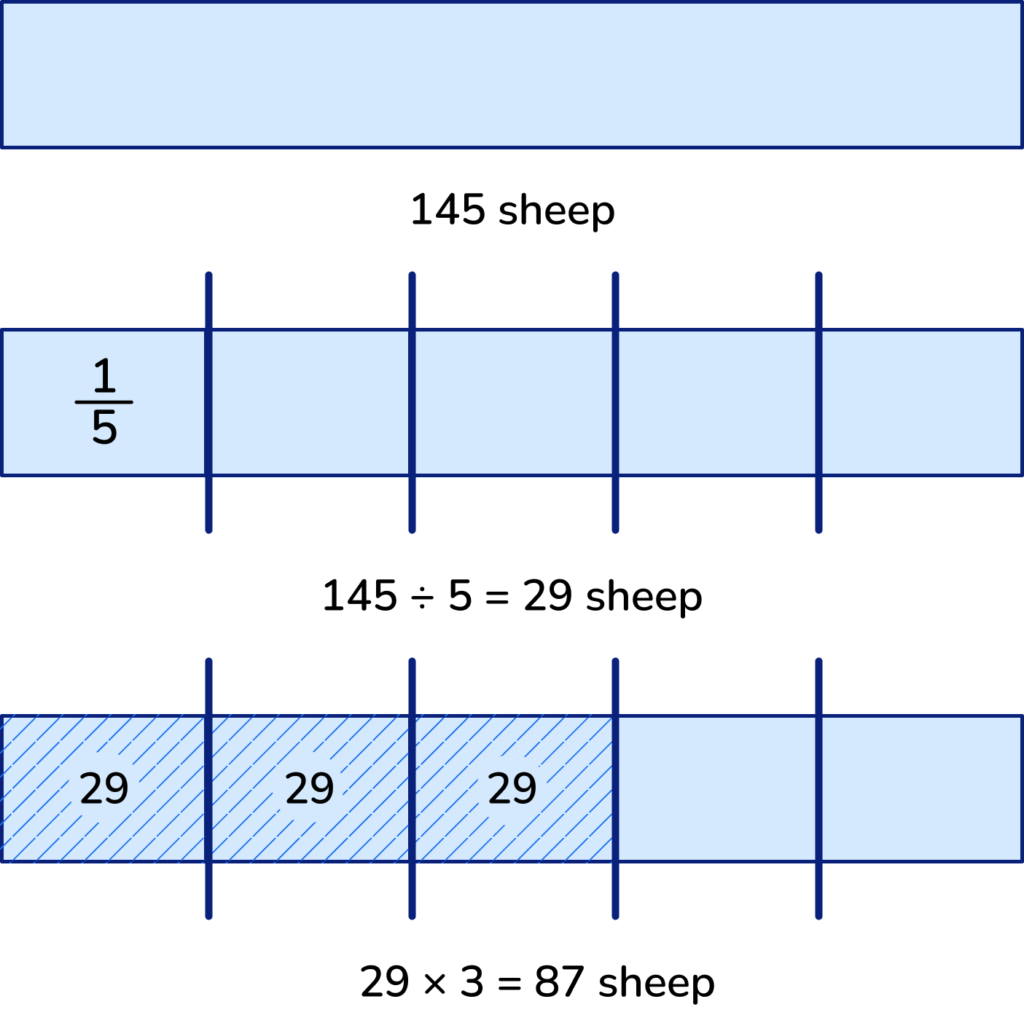
- To find the value of one part (\frac{1}{5}): 145 ÷ 5 = 29
- To find the value of three parts (\frac{3}{5}): 29 x 3 = 87
- The farmer sold 87 sheep at the market.
Long multiplication: Multiplying 4-digits by 2-digits
A library orders 27 copies of a popular new children’s book that costs £14.59 each.
What is the total cost of the order? £_____
1. Read the question carefully and identify the key information needed to solve it
- The cost of one book is £14.59, which is the same as 1459p.
- The number of copies ordered is 27.
- The final answer must use the £ unit.
2. Consider drawing a picture or visual representation to understand the question
You can use a number line to show two benchmark calculations: rounding down and rounding up.
- Round down (lower estimate): £14.00 x 20 = £280
- Round up (upper estimate): £15.00 x 30 = £450
The actual answer must be between £280 and £450. This can help alert pupils to common misconceptions, for example if a pupil gets £39.39 or £3939.30, the visual check on the number line instantly alerts them that their answer is incorrect.

3. Identify which calculations are required for solving it
This is a single calculation that requires long multiplication (multiplying a 4-digit number by a 2-digit number).
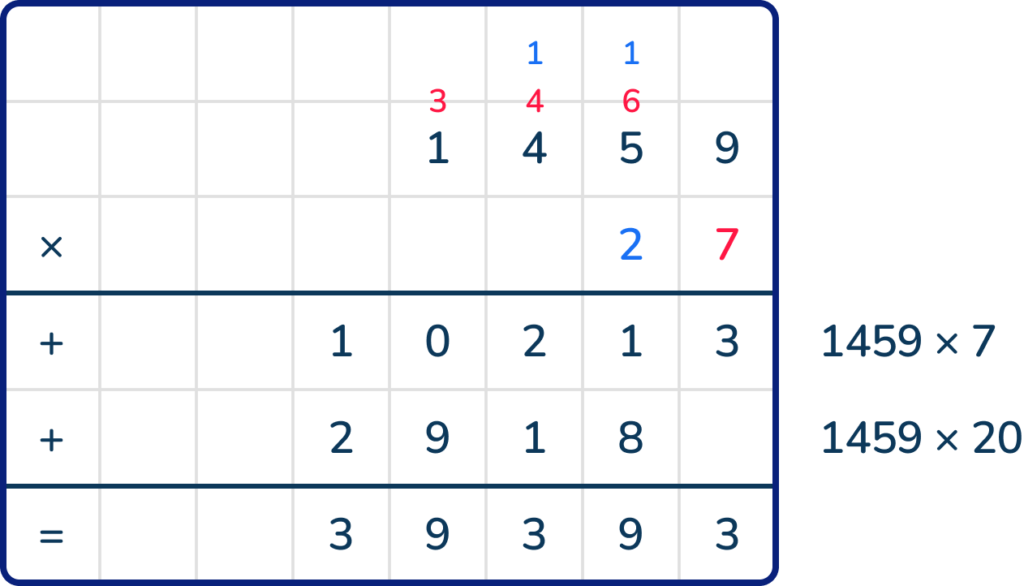
- First, multiply 1459 by 7 (the unit digit). 1459 x 7 = 10213
- Next, multiply 1459 by 20 (the tens digit), remembering to place a zero as a placeholder. 1459 x 20 = 29180
- Finally, add the two results together: 10213 + 29180 = 39393
The total cost of the order is £393.93, which is between the pupils’ estimates on the number line.
More word problem resources
Third Space Learning offers a wide array of free maths and word problems resources for other year groups:
Support your pupils’ learning and provide them with even more problem-solving practice with these KS2 topical maths packs and answer sheets. The following worksheets focus on real life problems, themes and dates across the academic year:
DO YOU HAVE STUDENTS WHO NEED MORE SUPPORT IN MATHS?
Skye – our AI maths tutor built by teachers – gives students personalised one-to-one lessons that address learning gaps and build confidence.
Since 2013 we’ve taught over 2 million hours of maths lessons to more than 170,000 students to help them become fluent, able mathematicians.
Explore our AI maths tutoring or find out about a primary school maths tutor for your school.