High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Types of data Primary dataDrawing graphs and charts
Interpreting graphs and chartsSecondary data
Here you will learn about secondary data, including what it is and how to use it in the statistical process.
Students first learn to work with secondary data in 6 th grade and expand their knowledge and use of data as they progress through the grades.
What is secondary data?
Secondary data is data that was collected and then used by another person for another purpose.
Secondary data can be collected from many sources, such as:
- publications
- books
- websites
- government records
- past surveys
- past questionnaires
The most important thing to remember is that secondary data is data used by a person who did not collect it.
Secondary data can be graphed, which provides a visualization of the data.
For example,
Adam was researching the difference in rainfall between two cities. He graphs from a weather website that shows the total rainfall each month for the cities.
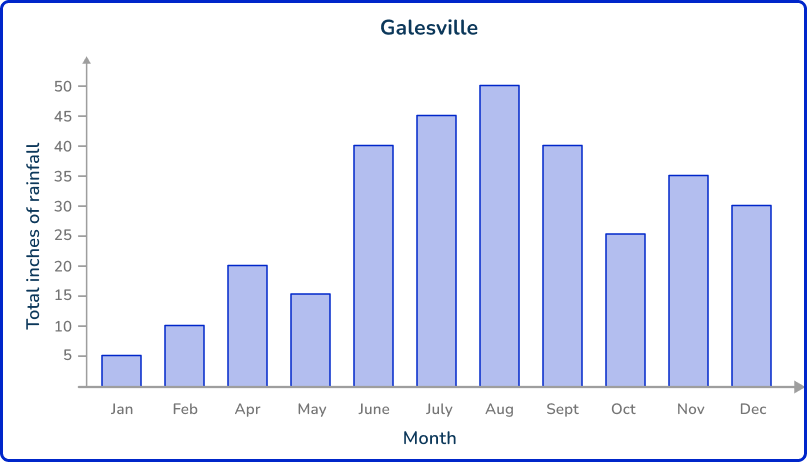
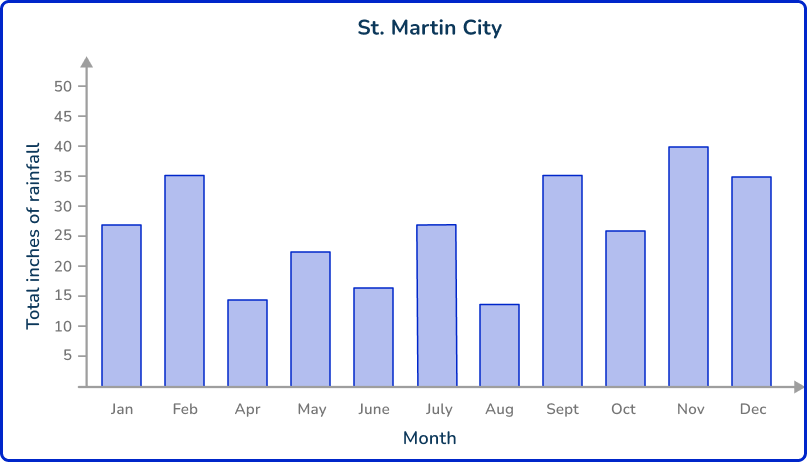
Since Adam is using data by someone else, this is secondary data.
Now that Adam has found the data, he can use it to complete his research…
- What is the difference between rainfall in January for Galesville and St. Martin City? 20 inches
What is secondary data?

Common Core State Standards
How does this apply to 6 th grade math?
- Grade 6 – Statistics and Probability (6.SP.B.5a and 6.SP.B.5b)
Recognize a statistical question as one that anticipates variability in the data related to the question and accounts for it in the answers. For example, “How old am I?” is not a statistical question, but “How old are the students in my school?” is a statistical question because one anticipates variability in students’ ages.
- Grade 6 – Statistics and Probability (6.SP.B.5a and 6.SP.B.5b)
Summarize numerical data sets in relation to their context, such as by:- Reporting the number of observations.
- Describing the nature of the attribute under investigation, including how it was measured and its units of measurement.
![[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Types-of-Data-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)
![[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Types-of-Data-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 to 7 students’ understanding of types of data. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th and 7th grade types of data topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Types-of-Data-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)
![[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Types-of-Data-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 to 7 students’ understanding of types of data. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th and 7th grade types of data topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEHow to recognize secondary data
In order to recognize secondary data:
- Identify the data collected.
- Identify the source of the data and the user.
Secondary data examples
Example 1: real world example of healthcare research
Professor Lee is a researcher studying the effects of exercise on mental health. He reviews a published study that analyzed data from hundreds of people who participated in different fitness programs, tracking changes in their mental well-being.
Using the study’s findings, Professor Lee decides which fitness program to recommend for his own research. Is this an example of secondary data? Explain.
- Identify the data collected.
In this case, the data was collected in a study that measured how exercise impacted mental health.
2Identify the source of the data and the user.
Now we need to identify who collected and used the data. The context tells us that Professor Lee used data from a study. It does not indicate that Professor Lee was involved in the study, so we will assume he was not.
This means Professor Lee was analyzing and using data he did not collect. Professor Lee used secondary data sources.
Example 2: real world example of market research
Huong is a marketing analyst studying what people like about new smartphones. She looks at a report from a tech company that asked thousands of customers about their favorite features and what they buy.
Using the report, Huong decides which features to highlight in her ads. Is this an example of secondary data? Explain.
In this case, the data was from a tech company’s report that surveyed smartphone customers about the features they like and buy.
Now we need to identify who collected and used the data. The context tells us that Huong used data from a report.
It does not indicate that Huong was involved in the report, so we will assume she was not. This means Huong was analyzing and using data she did not collect. Huong used secondary data sources.
Example 3: real world example of healthcare research
Jamal wants to write a blog about how small business owners solve problems. He talks to a group of local business owners and asks them questions in personal interviews.
Then he uses their answers to write a blog post and shares it online. Is this an example of secondary data? Explain.
In this case, the data was collected by personal interviews of people who own small businesses.
Now we need to identify who collected and used the data. The context tells us that Jamal identifies the group of people he wanted to collect data from. He also created the research questions and performed the interviews.
Jamal then used the raw data to create a summary video. Since Jamal’s data sets and data analysis used only primary sources, this is an example of primary data.
How to analyze secondary data
In order to analyze secondary data:
- Collect secondary data.
- Choose a graph or measure of center to calculate.
- Answer questions based on the data analysis.
Example 4: collecting and analyzing secondary research
Ishana is completing a research project. Ishana wants to know, “What is the average lifespan for wild cats?”
Ishana uses a book from the library that gives the following data:
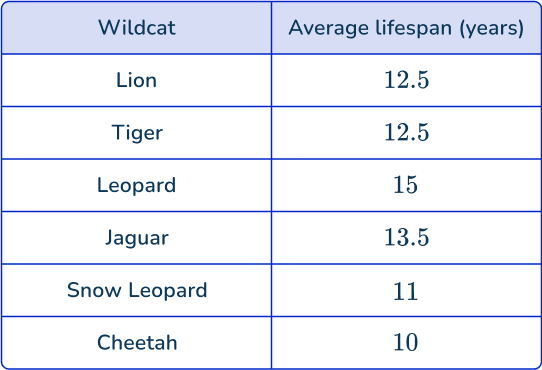
Ishana decides to show the data with a bar graph.
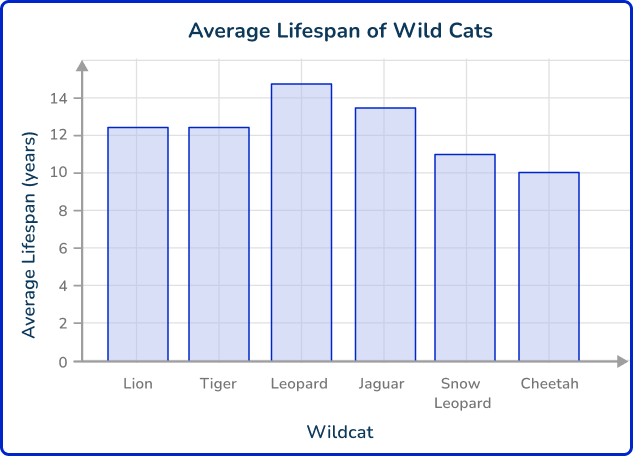
Some examples of questions Ishana can answer with the data are:
- On average, how much longer do leopards live than cheetahs? 5 years
- Which animals live the same, on average? Lions and Tigers
Example 5: secondary data analysis of census data
Aubrey is completing a project for work. Aubrey needs to know the average value of houses in a neighborhood.
Aubrey uses data collected by a government survey to create the following table:
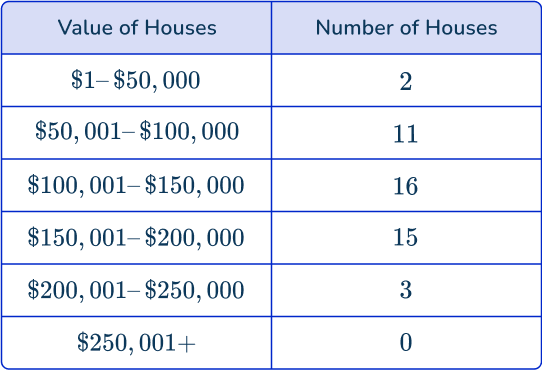
Aubrey decides to show the data with a histogram.
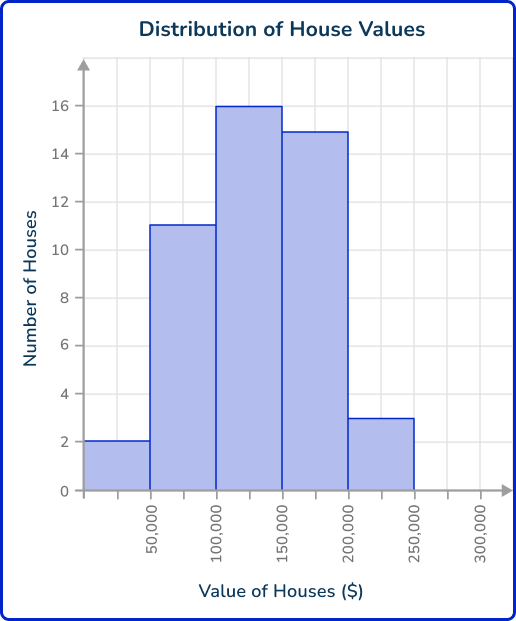
Some examples of questions Aubrey can answer with the data are:
- What is the median bin for the value of houses in this neighborhood?
\$ 100,001 \, – \, \$ 150,000 - How many houses were included in the data set? 47
Example 6: secondary data collection for social media, involving qualitative data
For a Social Science class project, Arrow wants to create a social media post about the kinds of news stories major news companies share.
Arrow looks at a study that chose 200 random news stories and sorted them into three groups: negative, neutral, or positive. He also analyzes the average number of words in each story.
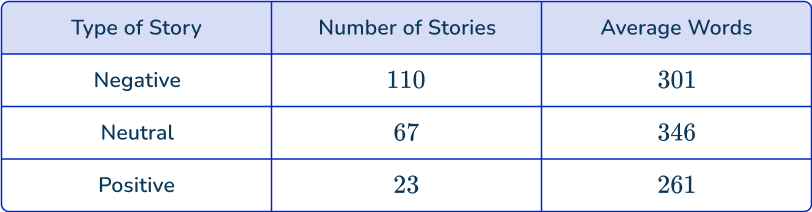
The data collected is secondary data as it is from a study that he did not collect the data for.
Arrow decides to analyze the frequency of the type of story and the average number of words.
Some examples of questions Arrow can answer with the data are:
- How many more negative stories were in the sample than positive? 87
- What percent of the sample were neutral stories? 33.5 \%
- Which type of story was longer, on average? Neutral
Teaching tips for secondary data
- When teaching students to identify secondary data, emphasize the importance of exploring existing data from reliable sources, such as public datasets or reports.
Encourage students to consider how the formats of these datasets (for example, spreadsheets, charts, or written summaries) align with their research questions, helping them choose data that is accurate, relevant and easy to analyze.
- Expose students to a variety of types of data and demographics within datasets. Along with this, give them opportunities to engage in both quantitative and qualitative research, by creating their own research questions and hypotheses, before using secondary data.
Easy mistakes to make
- Choosing unreliable sources of secondary data
Since the data is not collected by the person using it, it is important to ensure that the research data comes from a trusted source. Secondary research is only as valuable as the data quality used within it.
Teach students how to identify reputable sources or provide them with a list of data resources and repositories to use, such as the U.S. Census Bureau.
- Not checking for outdated information
Using data that no longer aligns with the current context, can lead to mismatches with your research design, research purpose, and chosen research methods and ultimately result in a research product that is not useful.
Always search for the origin date of the research and confer with experts when necessary, to ensure that the data you are using is the most recent and relevant to your research purposes.
Related types of data lessons
Practice secondary data questions
1. Ivy is planning the research methods for her next project. She will gather data from various sources. Which source is an example of secondary data?
Ivy will randomly choose 5 people and complete case studies.

Ivy will create a survey to send out to random participants.

Ivy will use the data from a government survey completed last year.

Ivy will place rain gauges throughout the city and collect data from them each week.

Let’s look at each source of data…
- Ivy will randomly choose 5 people and complete case studies.
- This is NOT secondary data, since Ivy will choose the people and collect the data.
- Ivy will create a survey to send out to random participants.
- This is NOT secondary data, since Ivy will create the survey and collect the data.
- Ivy will use the data from a government survey completed last year.
- This IS secondary data, since Ivy did not complete the survey.
- Ivy will place rain gauges throughout the city and collect data from them each week.
- This is NOT secondary data, since Ivy is the one collecting the data.
2. Odion is working on a data management plan for her healthcare research project. He will gather data from various sources. Which source is an example of secondary data?
Odion will analyze health records from a national database collected over the past five years.

Odion will interview 10 patients about their recent hospital visits.

Odion will create a new questionnaire to collect information on patient satisfaction.

Odion will monitor patient vitals in a clinic over the next three months.

Let’s look at each source of data…
- Odion will analyze health records from a national database collected over the past five years.
- This IS secondary data, since Odion is using government collected data, not his own data.
- Odion will interview 10 patients about their recent hospital visits.
- This is NOT secondary data, since Odion will complete the interviews himself.
- Odion will create a new questionnaire to collect information on patient satisfaction.
- This is NOT secondary data, since Odion will create the questionnaire and collect the data.
- Odion will monitor patient vitals in a clinic over the next three months.
- This is NOT secondary data, since Odion will collect the data himself.
3. Which is NOT an example of secondary data?
James writes a literature review analyzing published studies and reports on consumer trends from the past decade.

A clothing store conducts a focus group with 12 participants to discuss their shopping habits.

Maria uses census data to decide 5 possible locations of a new daycare center.

A zoologist reviews elephant studies from the last 10 years to design a new elephant habitat at the zoo.

Let’s look at each source of data…
- James writes a literature review analyzing published studies and reports on consumer trends from the past decade.
- This IS secondary data, since James is using previously published data.
- A clothing store conducts a focus group with 12 participants to discuss their shopping habits.
- This is NOT secondary data, since the store is collecting the data themselves.
- Maria uses census data to decide 5 possible locations of a new daycare center.
- This IS secondary data, since Maria is using data previously collected by the government.
- A zoologist reviews elephant studies from the last 10 years to design a new elephant habitat at the zoo.
- This IS secondary data, since the zoologist is using data collected by other people.
4. Yusuf uses data published on four grocery store’s websites, to compare the price of bananas at each store over time. Then Yusuf created the following graph:
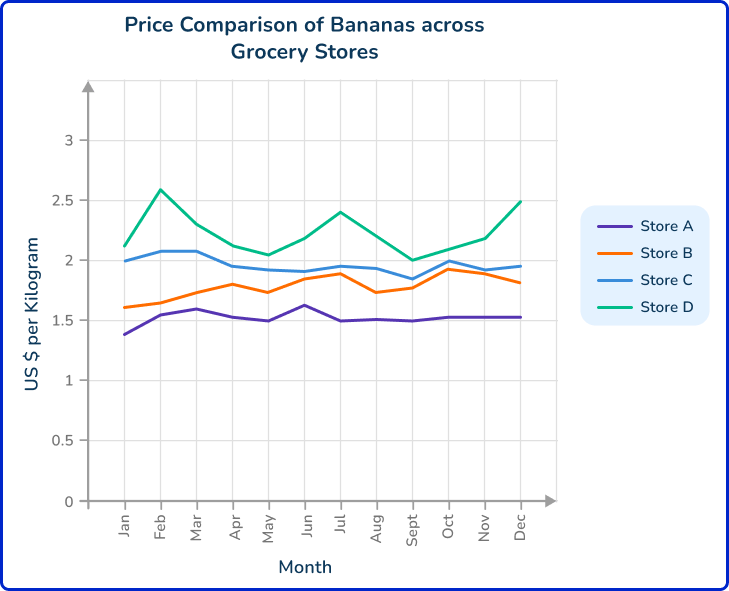
Why is this an example of secondary data?
The data was collected online.

Yusuf created a graph with the data.

The data was quantitative.

Yusuf used data collected by someone else.

Secondary data is data that was collected and then used by another person for another purpose.
This is an example of secondary data because Yusuf did not collect the data himself.
The data was collected by the stores and then published online.
Secondary data can be collected offline, as well as online. It may involve graph, but this is not a requirement. Secondary data can be quantitative or qualitative.
5. Kayce used a thermometer to measure the temperature outside her house throughout the day and created the following graph:
Why is this NOT an example of secondary data?
The graph does not have numbers labeled on the axes.

Kayce collected the data herself.

Only one data source was used for the graph.

Kayce did not use random samples.

Secondary data is data that was collected and then used by another person for another purpose.
This is NOT an example of secondary data because Kayce collected the data herself.
Secondary data can have only one data source and the graph of secondary data may or may not have numbers labeled on the axes. Secondary data may involve random samples, but this is not a requirement.
6. Last year, Derek collected data on how many slices of pizza each person ate at his birthday party.
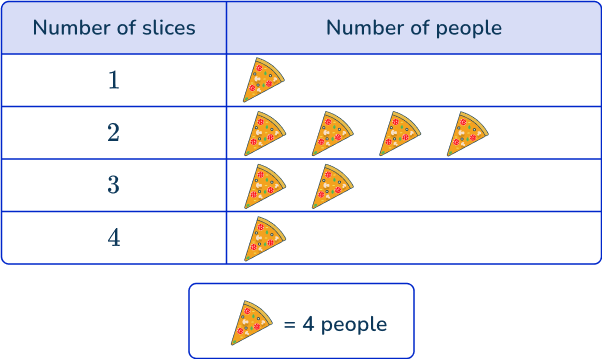
This year, his uncle uses the data to decide how many pizzas to order. If each pizza has 8 slices, how many pizzas should Derek’s uncle order, according to last year’s data?




Each pizza represents 4 people.
4 people had 1 slice: 4 \times 1=4 slices
16 people had 2 slices: 16 \times 2=32 slices
8 people had 3 slices: 8 \times 3=24 slices
4 people had 4 slices: 4 \times 4=16 slices
So last year, 4+32+24+16=76 slices were eaten in total.
76 slices \div \, 8 slices per pizza =9.5 pizzas, rounded up to 10 pizzas.
Secondary data FAQs
Primary data collection can be time-consuming and often requires an in-depth process. With secondary data, the work of collecting the data has already been completed, so you can start analyzing the data much sooner.
Some disadvantages include a limited control over the original methodology, which might not align with your research. The data could also be outdated, biased, or contain errors.
Additionally, it may lack the detail needed to fully address your research questions, limiting its usefulness for specific studies.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!