High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Multiplication and division Multiplying multi-digit numbers Dividing multi-digit numbersMultiplying and dividing decimals
Here you will learn about multiplying and dividing decimals, including how to multiply and divide decimals by whole numbers, multiply and divide decimals by decimals, and divide whole numbers by decimals.
Students will first learn about multiplying and dividing decimals as part of their work in number and operations in base 10 in 5th grade. They continue to build on this knowledge by learning the algorithm as a part of their work in the number system in 6th grade.
What is multiplying and dividing decimals?
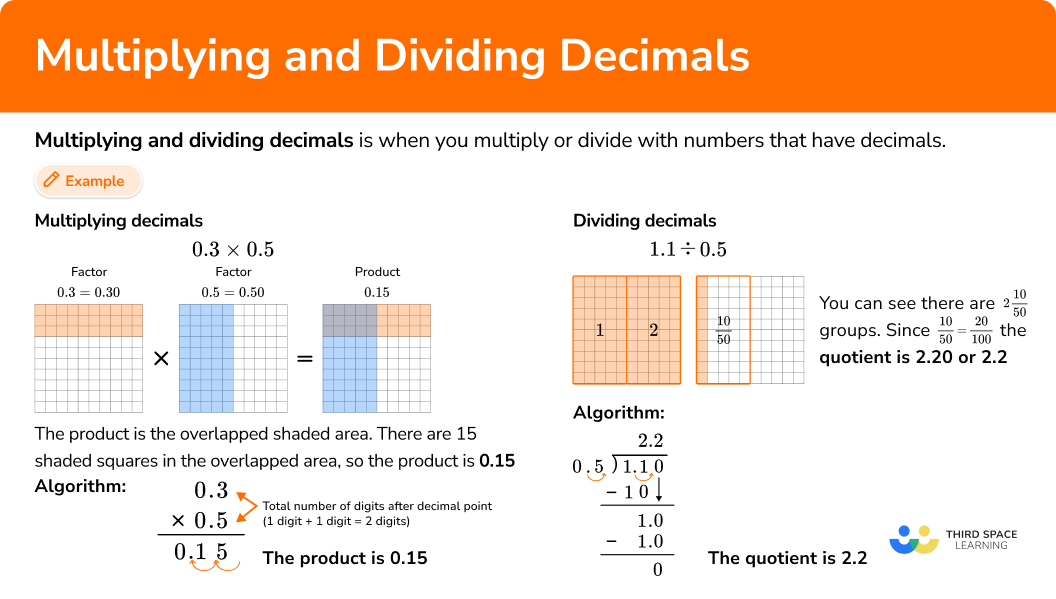
Multiplying and dividing decimals is when you multiply or divide with numbers that have decimals.
For example,
| Multiplying decimal number by decimal number |
|---|
| Modeling with a Hundredths Grid |
\hspace{1.3cm} Factor \hspace{2.7cm} Factor \hspace{2.7cm} Product
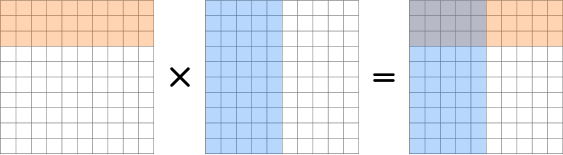 The product is the overlapped shaded area. There are 15 shaded squares in the overlapped area, so the product is \bf{0.15} |
| Using the Algorithm |
Use the algorithm for multi-digit multiplication to multiply decimal numbers. 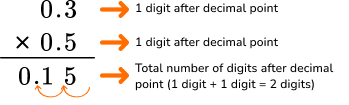 |
| Multiplying a whole number by decimal number |
|---|
| Modeling with a Hundredths Grid |
5 groups of 0.25 or 5 groups of 25 shaded squares (hundredths) 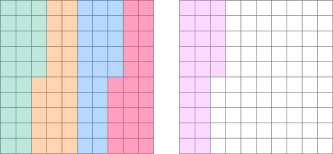 The product is the sum of all the shaded squares, which is 125 hundredths. The product is \bf{1.25} |
| Using the Algorithm |
Use the algorithm for multi-digit multiplication to multiply decimal numbers. 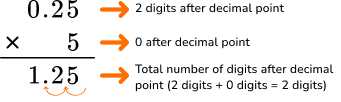 |
For example,
| Dividing a decimal by a whole number |
|---|
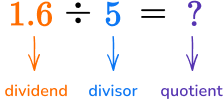 |
| Modeling with a Hundredths Grid |
1.6 = 1.60 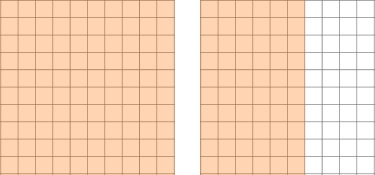 Divide into 5 equal groups. 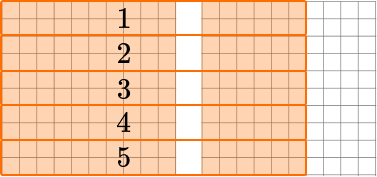 32 hundredth squares in each group so the quotient is \bf{0.32} |
| Using the Algorithm |
 Divide the way you would whole numbers. |
| Dividing a decimal by a decimal |
|---|
 |
| Modeling with a Hundredths Grid |
How many groups of 0.5 are there in 1.1? 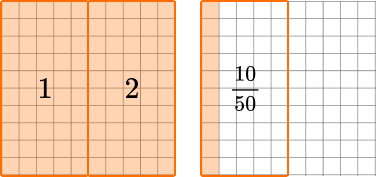 You can see there are 2\cfrac{10}{50} \, groups. Since \cfrac{10}{50} \, = \cfrac{20}{100} \, the quotient is \bf{2.20} or \bf{2.2} |
| Using the Algorithm |
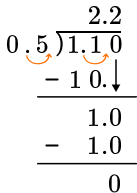 ● Check the divisor; if it’s a whole number, start dividing. |
| Dividing a whole number by a decimal |
|---|
 |
| Modeling with a Hundredths Grid |
How many groups of 0.2 \; (0.20) are there in 3? 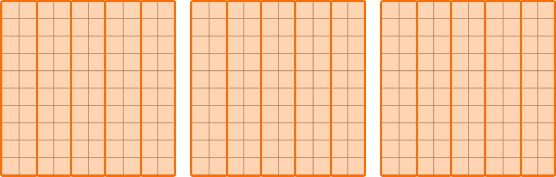 You can see there are 15 groups so thequotient is \bf{15.} |
| Using the Algorithm |
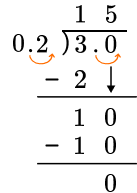 ● Check the divisor; if it’s a whole number, start dividing. |
What is multiplying and dividing decimals?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 5th grade math and 6th grade math?
- Grade 5: Number & Operations Base Ten (5.NBT.B.7)
Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used.
- Grade 6: The Number System (6.NS.B.3)
Fluently add, subtract, multiply, and divide multi-digit decimals using the standard algorithm for each operation.
How to multiply decimals
In order to multiply decimals using the standard algorithm.
- Stack the number with the most digits on top.
- Multiply the same as multi-digit whole numbers, regrouping when necessary.
- Count the number of digits after the decimal point for each factor.
- Put the same number of digits behind the decimal point for the product.
In order to solve decimal multiplication word problems.
- Create an equation to model the problem.
- Stack the number with the most digits on top.
- Multiply the same as multi-digit whole numbers, regrouping when necessary.
- Count the number of digits after the decimal point for each factor.
- Put the same number of digits behind the decimal point for the product.
- Label the product.
![[FREE] Multiplying and Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 5 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Multiplying-and-Dividing-Decimals-Worksheets-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Multiplying and Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 5 to 6)
![[FREE] Multiplying and Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 5 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Multiplying-and-Dividing-Decimals-Worksheets-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 5 to 6 students’ understanding of multiplying decimals. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Multiplying and Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 5 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Multiplying-and-Dividing-Decimals-Worksheets-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Multiplying and Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 5 to 6)
![[FREE] Multiplying and Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 5 to 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Multiplying-and-Dividing-Decimals-Worksheets-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 5 to 6 students’ understanding of multiplying decimals. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEMultiplying decimals examples
Example 1: multiplying a decimal number by a decimal number
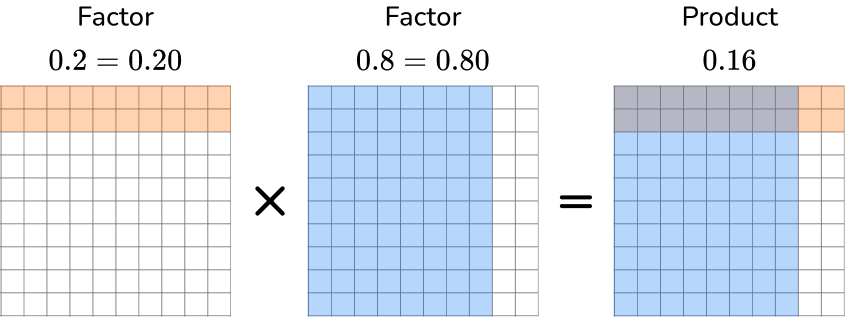
Find the product of 0.2 \times 0.8
- Stack the number with the most digits on top.
Both factors have the same number of digits, so it does not matter which one is on top.
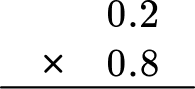
2Multiply the same as multi-digit whole numbers, regrouping when necessary.
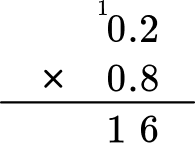
3Count the number of digits after the decimal point for each factor.
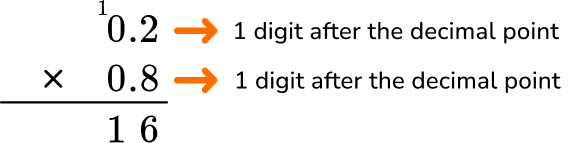
In total, the factors have 2 decimal points.
4Put the same number of digits behind the decimal point for the product.
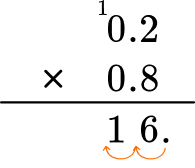
Move the decimal point two decimal places. The product will have two digits after the decimal point.
The product is 0.16.
On the hundredths grid, look at the overlapped shaded region. There are 16 hundredth squares or 0.16.
Example 2: multiplying a decimal number by a whole number
Find the product of 3 \times 1.03
Stack the number with the most digits on top.
1.03 has more digits than 3, so 1.03 will be on top.
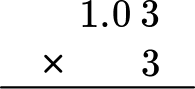
Multiply the same as multi-digit whole numbers, regrouping when necessary.
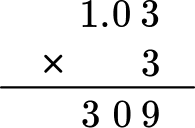
Count the number of digits after the decimal point for each factor.

In total, the factors have two decimal places.
Put the same number of digits behind the decimal point for the product.
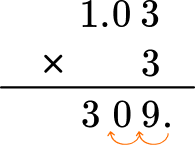
Move the decimal point two decimal places. The product will have two digits after the decimal point.
The product is 3.09.
Looking at the hundredths grids, you can see there are 3 groups of 1.03 that represent 309 shaded hundredth squares or 3.09.
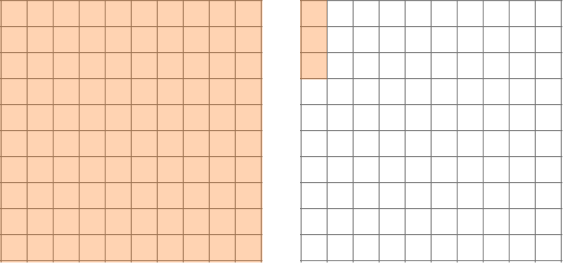
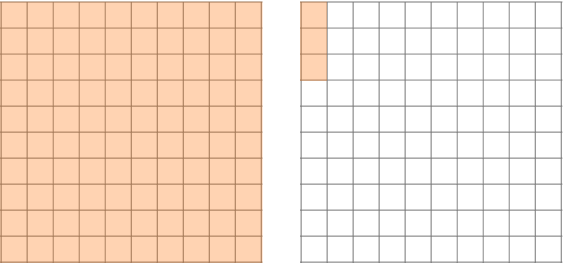
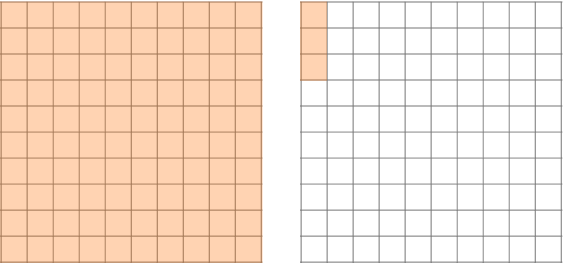
Example 3: multiplying a decimal by a decimal
Find the product of 5.7 \times 8.09.
Stack the number with the most digits on top.
8.09 has more digits than 5.7, so it will go on top.
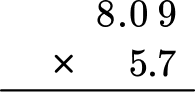
Multiply the same as multi-digit whole numbers, regrouping when necessary.
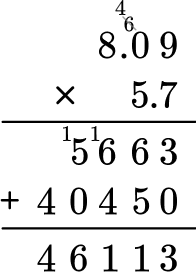
Count the number of digits after the decimal point for each factor.
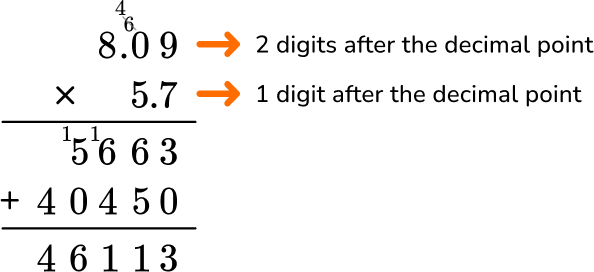
In total, the factors have 3 decimal points.
Put the same number of digits behind the decimal point for the product.
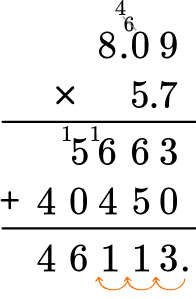
Move the decimal point three decimal places. The product will have three digits after the decimal point.
The product is 46.113.
Example 4: word problem multiplying decimal by a decimal
Mark wants to paint a wall in his kitchen. It has a length of 12.5 feet and a width of 8.25 feet. How much paint, in square feet, does Mark need to paint the wall?
Create an equation to model the problem.
12.5 \times 8.25 = \; ?
Stack the number with the most digits on top.
Both factors have the same number of digits, so it does not matter which one is on top.
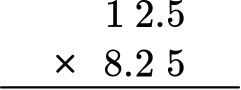
Multiply the same as multi-digit whole numbers, regrouping when necessary.
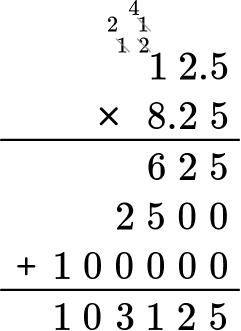
Count the number of digits after the decimal point for each factor.
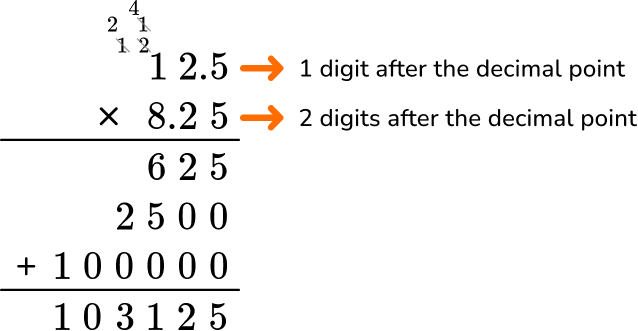
In total, there are three decimal places after the decimal point.
Put the same number of digits behind the decimal point for the product.
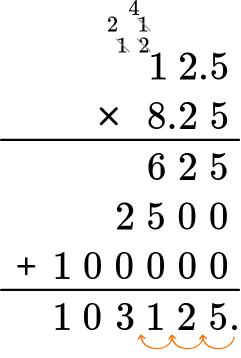
Move the decimal point three decimal places. The product will have three digits after the decimal point.
The product is 103.125.
Label the product.
Mark will need 103.125 feet ^{2} of paint to paint the wall.
How to divide decimals
In order to divide decimals using the algorithm:
- If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 3. If not, decide the power of 10 to multiply it by that will make it a whole number.
- Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of 10 .
- If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient.
- Do long division.
In order to solve real world problems using decimal division:
- Read the problem, identify keywords, and decide which number is the dividend and which number is the divisor.
- If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 4. If not, decide the power of 10 that will make the divisor a whole number.
- Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of 10 .
- If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient.
- Do long division.
- Label your answer appropriately.
Dividing decimals examples
Example 5: dividing a decimal by a whole number
Solve the decimal division problem.
0.56 \div 7 = \; ?
If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 3. If not, decide the power of 10 to multiply it by that will make it a whole number.
The divisor is 7 which is a whole number → go to step 3.
If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient.
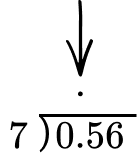
Do long division.

The answer makes sense because 56 hundredths on the grid is 7 groups of 8 hundredths.
Example 6: dividing a decimal by a decimal
Solve 24.36 \div 2.1 = \; ?
If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 3. If not, decide the power of 10 to multiply it by that will make it a whole number.
The divisor is 2.1, which is not a whole number. It needs to be multiplied by 10^1.
Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of 10 .
Multiply 2.1 \times 10 which is the same as 2.1 \times 10^1=21.
Multiply 24.36 \times 10 which is the same as 24.36 \times 10^1=243.6.
If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient.
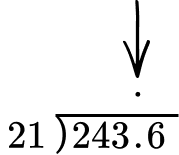
Do long division.
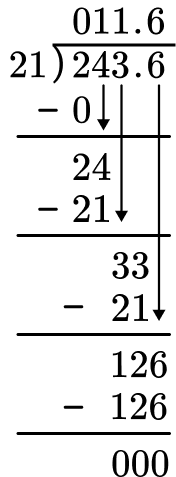
Example 7: dividing a whole number by a decimal
Solve 9 \div 0.15 = \; ?
If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 3. If not, decide the power of 10 to multiply it by that will make it a whole number.
The divisor is 0.15 which is not a whole number. It needs to be multiplied by 10^2.
Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of 10 .
Multiply 0.15 \times 100 which is the same as 0.15 \times 10^2=15.
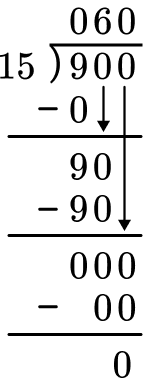
Multiply 9 \times 100 which is the same as 9 \times 10^2=900.
If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient.
The new equation is 900 \div 15, so there is no decimal in the dividend.
Do long division.
Example 8: Decimal division word problem
A recipe calls for 5.6 ounces of flour. How many complete recipes can be made with 265.44 ounces of flour?
Read the problem, identify keywords, and decide which number is the dividend and which number is the divisor.
Each recipe has 5.6 ounces and we need to find how many times 5.6 ounces goes into 265.44 ounces → 265.44 \div 5.6
If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 4. If not, decide the power of 10 to multiply it by that will make it a whole number.
The divisor is 5.6. It needs to be multiplied by 10^1.
Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of 10 .
Multiply 5.6 \times 10 which is the same as 5.6 \times 10^1=56.
Multiply 265.44 \times 10 which is the same as 265.44 \times 10^1=2,654.4.
If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient.
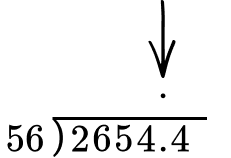
Do long division.

Label your answer appropriately.
The quotient is 47.4, which means that 47 complete recipes can be made with the flour.
Teaching tips for multiplying and dividing decimals
- Students who are just learning how to multiply and divide with decimals should use visual models, such as hundredths grids, to solve. This helps them see the equal groups and consider the size of the products and quotients.
- Give students opportunities to use different strategies to solve these decimal operations, such as partial products or the relationship between multiplication and division. It is important that students have a deep understanding of multiplying and dividing decimals before being introduced to the algorithm. In time, provide opportunities for them to make connections between their strategies and the standard algorithm. This helps students understand why the steps work for all decimal numbers.
- Encourage students to use mental math to estimate what the product or quotient should be. This will help them catch simple mistakes, like a wrong calculation or placing the decimal point in the wrong position.
- Do not rely on only practice worksheets for these skills. Furthermore, when using practice worksheets, value understanding over speed. Decimal calculations take time to do by hand. Do not expect students to answer rapidly, but instead encourage them to take their time to estimate, solve and understand what they are doing.
Easy mistakes to make
- Putting the decimal point in the wrong position in the product
The total number of decimal positions in the numbers being multiplied is how many the product should have.
For example,
5.6 \times 0.7
There are 2 decimal positions being multiplied, so the product should also have 2 decimal positions.
- Forgetting to add back the decimal after multiplying
The algorithm for multiplying decimals is the same as whole numbers, except there is an additional step. The decimal needs to be added back to the product. Forgetting to do so, leads to the wrong final answer.
For example,
5.6 \times 0.7
There are 2 decimal positions being multiplied, so the product should also have 2 decimal positions.
- Lining up the decimal points of the products before multiplying
The decimals do not need to be lined up when using the standard algorithm to multiply, like they do when adding and subtracting. Doing so is not incorrect, but can create extra work and more room for errors.
For example,
2 \times 1.23
Without lining up the decimals: Lining up the decimals: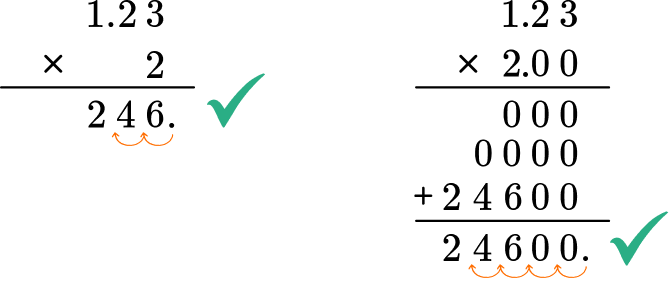
- Switching the dividend and the divisor when using long division
The dividend goes on the inside and the divisor goes on the outside.
For example,
0.58 \div 2
- Not moving the decimal point of the dividend and divisor the same amount
In order to keep the equations equivalent, the decimal needs to move the same amount for both the dividend and divisor. This is the same multiplying the dividend and divisor by the same power of 10.
For example,
2 \div 0.5
- Forgetting to align the decimal point of the dividend with the quotient
For example,
0.8 \div 2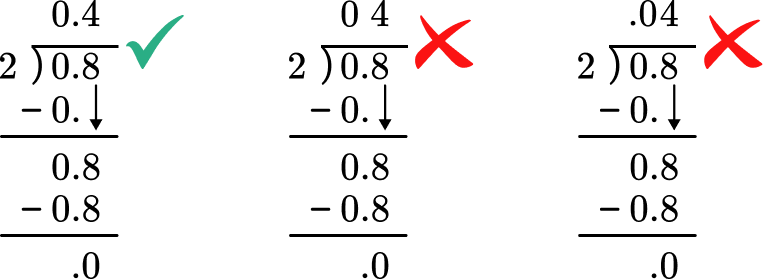
- Thinking that the larger number is always the dividend
Smaller numbers can be, and often are, divided by larger numbers.
For example,
A gardener has 0.3L of water for his 3 plants. If the gardener will water the plants equally, how much water does each plant get?
- Not being mindful of place value by forgetting to divide zeros in the dividend
All digits in the dividend need to be divided when using the standard algorithm, including zeros. Otherwise the place value positions of the digits shifts, changing the value.
For example,
0.15 \div 9 = 15 \div 900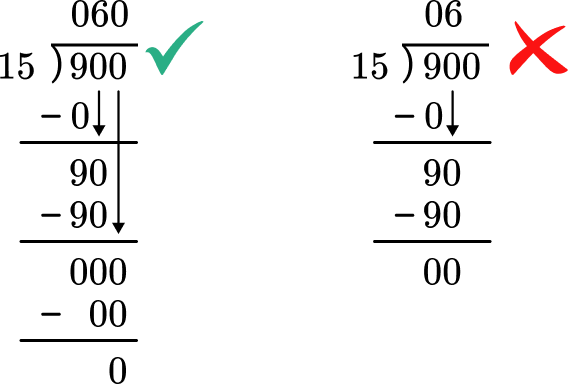
Practice multiplying and dividing decimals questions
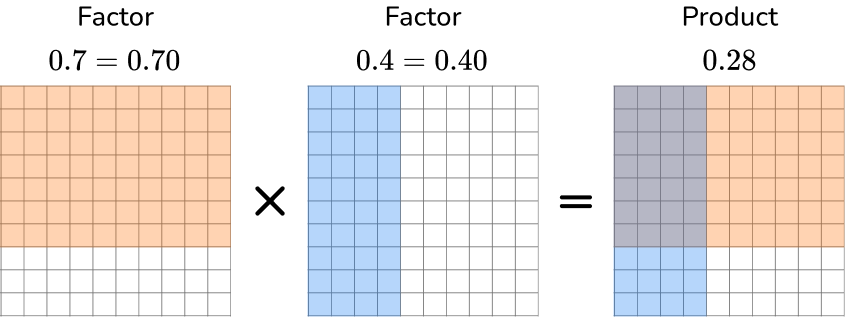
1. Solve 0.7 \times 0.4 = \; ?




Both factors have the same number of digits, so it does not matter which one is on top.

In total, the factors have 2 decimal points.
Move the decimal point two decimal places. The product will have two digits after the decimal point.
The product is 0.28.
On the hundredths grid, look at the overlapped shaded region. There are 28 hundredth squares or 0.28.
2. Solve 17 \times 5.08 = \; ?




5.08 has more digits than 17, so it will go on top.
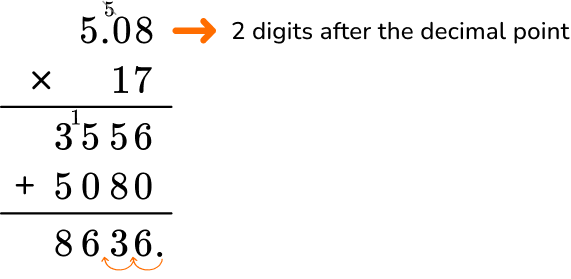
In total, the factors have 2 decimal points. The product will have two digits after the decimal point.
The product is 86.36.
3. Solve 9.1 \times 0.23 = \; ?




0.23 has more digits than 9.1, so it will go on top.
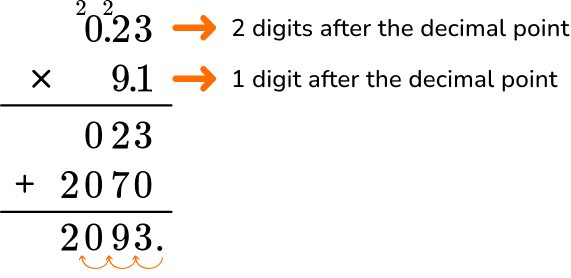
In total, the factors have 3 decimal points. The product will have three digits after the decimal point.
The product is 2.093.
4. A grocery store has 13.2 pounds of apples. They have 2.5 times more bananas than apples. How many pounds of bananas does the grocery store have?
0.33 pounds

33 pounds

3.3 pounds

33.33 pounds

There are 2.5 times more bananas → 13.2 \times 2.5
13.2 has more digits than 2.5, so it will go on top.
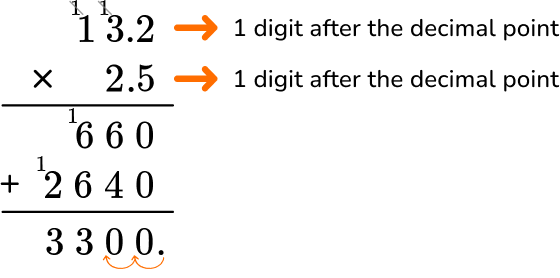
In total, the factors have 2 decimal points. The product will have two digits after the decimal point.
The product is 33. The grocery store has 33 pounds of bananas.
5. Solve 0.85 \div 5 = \; ?




The divisor is 5 which is a whole number, so we set up the long division. Line up the decimal place of the dividend with the decimal place of the quotient.
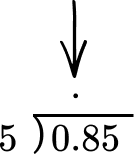
Use the algorithm of long division to divide.

The answer makes sense because 85 hundredths on the grid is 5 groups is 17 hundredths.
6. Solve 4.41 \div 1.5 = \; ?




The divisor is 1.5. Multiply the decimal divisor by 10 to make it a whole number. Also, multiply the dividend by 10.
1.5 \times 10=15
4.41 \times 10=44.1
Line up the decimal place of the dividend with the decimal place of the quotient.
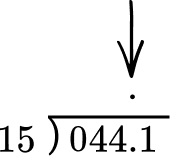
Use the algorithm of long division to divide.

7. Solve 0.6 \div 20 = \; ?




The divisor is 20 which is a whole number, so we set up the long division.
Line up the decimal place of the dividend with the decimal place of the quotient.
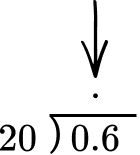
Use the algorithm of long division to divide.

8. Twelve pizzas cost \$85.44. If each pizza costs the same, how much did one pizza cost?




\$85.44 has to be divided equally into 12 pizzas → 85.44 \div 12.
Line up the decimal place of the dividend with the decimal place of the quotient.
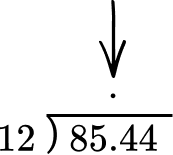
Use the algorithm of long division to divide.
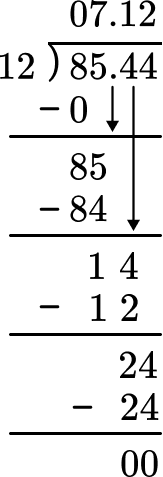
The quotient is 7.12 which means one pizza costs \$7.12.
Multiplying and dividing decimals FAQs:
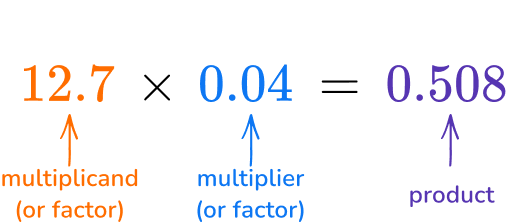
No, most whole number strategies will work with decimals, including partial products.
For example,
2.2 \times 3.4 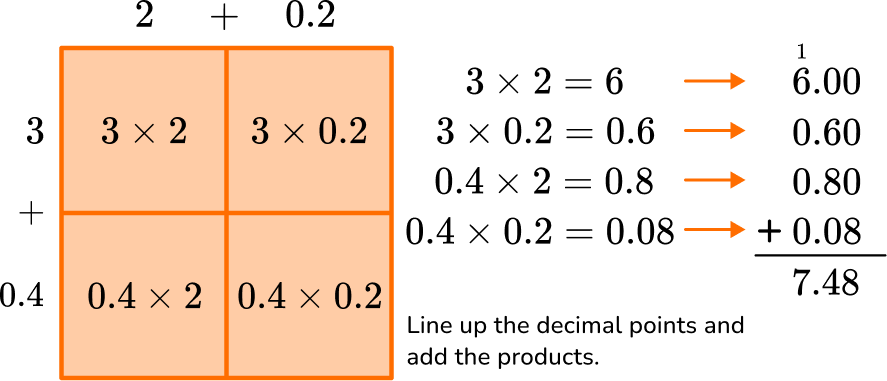
Students will spend most of their time multiplying numbers with decimals in the tenths place, hundredths place and the thousandths place. However, once they learn the standard algorithm, students can multiply with any number of decimal positions.
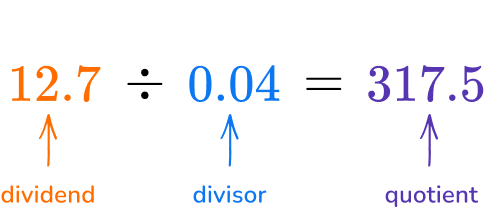
Multiplying by the powers of ten increases the value of each digit in a number and therefore moves the decimal point. As a shortcut, you can just move the decimal point, but you must move it the same amount of times for both the divisor and the dividend to keep the equation equivalent.
Yes, the divisor can be smaller than the dividend. This will result in an answer that has no whole numbers, only decimals.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!
