[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
Dividing decimals
Here you will learn about dividing decimals, including how to divide decimals by a whole number, divide decimals by decimals, and divide whole numbers by a decimals. You will learn how to use decimal division to solve word problems.
Students will first learn about dividing decimals as part of their work in number and operations in base ten in fifth grade.
What is dividing decimals?
Dividing decimals is when the divisor, dividend and quotient can be a decimal number. Let’s look at strategies for dividing decimals.
Dividing decimal by whole number
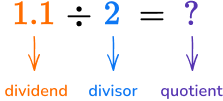 |
| Modeling with a Hundredths Grid |
1.1 = 1.10  Divide into 2 equal groups. 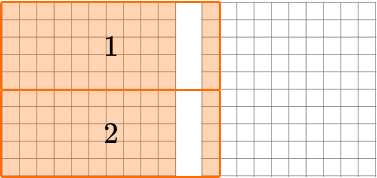 55 squares in each group so the quotient is \textbf{0.55.} |
| Using the Algorithm |
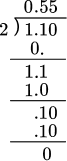 ● Make sure the divisor is a whole number. |
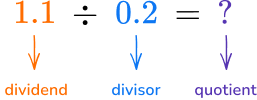
Dividing decimal by a decimal
 |
| Modeling with a Hundredths Grid |
How many groups of 0.2 are there in 1.1? 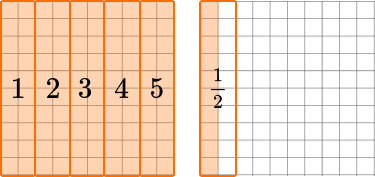 You can see there are 5.5 groups so the quotient is \textbf{5.5.} * \cfrac{1}{2} = 0.5
|
| Using the Algorithm |
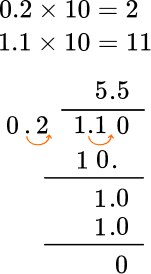 ● Check the divisor, if it’s a whole number start dividing. |
Dividing a whole number by a decimal
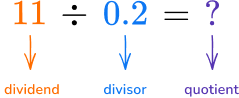 |
How many groups of 0.2 \; (0.20) are there in 11? 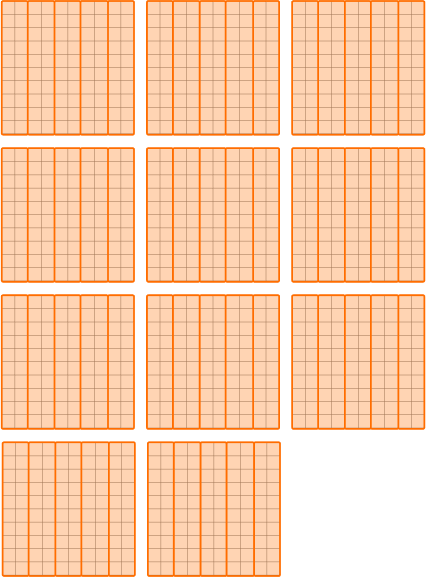 You can see there are 55 groups so the quotient is \textbf{55.} |
| Using the Algorithm |
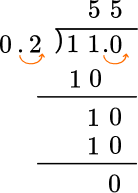 ● Check the divisor, if it’s a whole number start dividing. |
What is dividing decimals?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 5th grade math and 6th grade math?
- Grade 5: Number & Operations Base Ten (5.NBT.B.7)
Add, subtract, multiply, and divide decimals to hundredths, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method and explain the reasoning used.
- Grade 6: The Number System (6.NS.B.3)
Fluently add, subtract, multiply, and divide multi-digit decimals using the standard algorithm for each operation.
How to divide decimals
In order to divide decimals using the algorithm:
- If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 3. If not, decide the power of ten that will make the divisor a whole number.
- Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of \bf{10} .
- If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient. You may need to include zeros as place holders.
- Do long division.
In order to solve real world problems using decimal division:
- Read the problem, identify keywords, and decide which number is the dividend and which number is the divisor.
- If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 4. If not, decide the power of ten that will make the divisor a whole number.
- Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of \bf{10} .
- If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient. You may need to include zeros as place holders.
- Do long division.
- Label your answer appropriately.
![[FREE] Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 4 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Dividing-Decimals-Worksheets-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 4 to 8)
![[FREE] Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 4 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Dividing-Decimals-Worksheets-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 4 to 8 students’ understanding of dividing decimals. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 4 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Dividing-Decimals-Worksheets-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 4 to 8)
![[FREE] Dividing Decimals Worksheets (Grade 4 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/12/Dividing-Decimals-Worksheets-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 4 to 8 students’ understanding of dividing decimals. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEDividing decimals examples
Example 1: dividing a decimal by a whole number using the algorithm
Solve the decimal division problem.
0.16 \div 4 = \; ?- If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 3. If not, decide the power of ten that will make the divisor a whole number.
The divisor is 4 which is a whole number.
3If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient. You may need to include zeros as place holders.
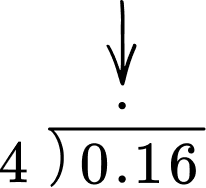
4Do long division.
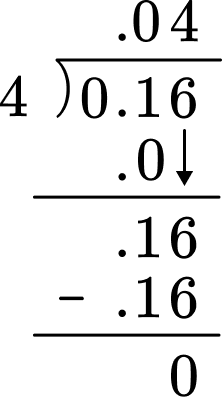
The answer makes sense because on the hundredths grid it shows the quotient to be 0.04. The 4 equal groups have 4 squares. 4 squares = \; 0.04
Example 2: dividing a decimal by a decimal using algorithm
Solve the decimal division problem.
32.85 \div 0.9 = \; ?If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 3. If not, decide the power of ten that will make the divisor a whole number.
The divisor is 0.9, which is not a whole number.
Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of \bf{10} .
Multiply 0.9 \times 10 which is the same as 0.9 \times 10^1
Multiply 32.85 \times 10 which is the same as 32.85 \times 10^1
0.9 \times 10 = 9
32.85 \times 10 = 328.5
If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point and place it on decimal. You may need to add zeros as place holders.
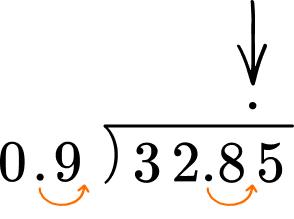
Do long division.
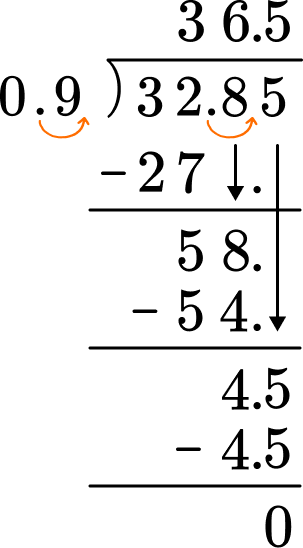
Example 3: dividing a whole number by a decimal using algorithm
Solve the decimal division problem.
77 \div 0.35 = \; ?If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 3. If not, decide the power of ten that will make the divisor a whole number.
The divisor is 0.35, which is not a whole number.
Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of \bf{10} .
Multiply 0.35 \times 100 which is the same as 0.35 \times 10^2
Multiply 77 \times 10 which is the same as 77 \times 10^2
0.35 \times 100 = 35
77 \times 100 = 7700
If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point and place it on decimal. You may need to add zeros as place holders.
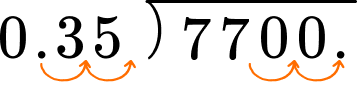
Do long division.
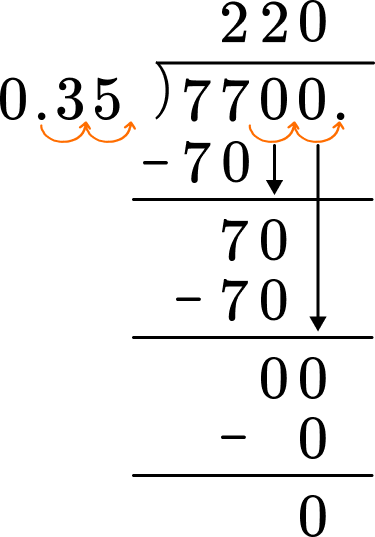
Example 4: decimal division word problem
Carly has 26 meters of rope that she wants to cut into equal pieces that are 0.4 meters in length. How many pieces can she cut?
Read the problem, identify keywords, and decide which number is the dividend and which number is the divisor.
Keywords: equal pieces
26 meters is being cut into equal pieces of 0.4 meters each so the divisor is 0.4 and the dividend is 26.
If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 4. If not, decide the power of ten that will make the divisor a whole number.
The divisor is 0.4, which is not a whole number. Multiply it by 10 to make it a whole number.
Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of \bf{10} .
Multiply 0.4 \times 10 which is the same as 0.4 \times 10^1
Multiply 26 \times 10 which is the same as 26 \times 10^1
0.4 \times 10 = 4
26 \times 10 = 260
If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient. You may need to include zeros as place holders.
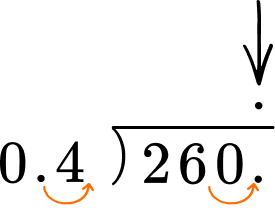
Do long division.
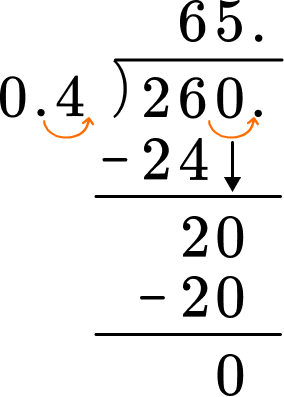
Label your answer appropriately.
The quotient is 65 which represents the pieces of rope.
Carly can cut 65 pieces of rope.
Example 5: decimal division word problem
Julia and her sister are making holiday cookies. They have 0.384 ounces of red food coloring that they want to divide equally into 4 bowls of cookie dough. How much food coloring should there be in each bowl?
Read the problem, identify keywords, and decide which number is the dividend and which number is the divisor.
Keywords: divide equally
0.384 ounces has to be divided equally into 4 bowls so the divisor is 4 and the dividend is 0.384.
If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 4. If not, decide the power of ten that will make the divisor a whole number.
The divisor is a whole number.
If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient. You may need to include zeros as place holders.
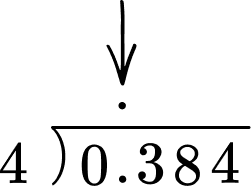
Do long division.
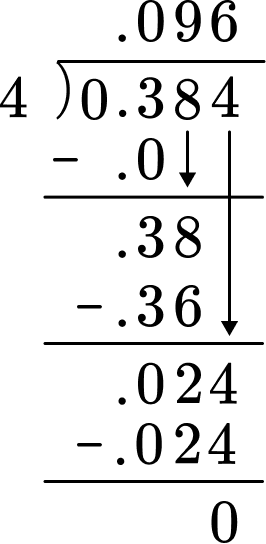
Label your answer appropriately.
The quotient is 0.096 which means that there will be 0.096 ounces of food coloring in each bowl.
Example 6: decimal division word problem
The ice cream sandwiches at school sell for \$1.12. Amelia has \$8.96. How many ice cream sandwiches can she buy?
Read the problem, identify keywords, and decide which number is the dividend and which number is the divisor.
The total amount of \$8.96 will be divided by \$1.12 in order to see how many ice cream sandwiches can be bought.
1.12 is the divisor and 8.96 is the dividend.
If the divisor is a whole number, go to step 4. If not, decide the power of ten that will make the divisor a whole number.
The divisor is 1.12, which is not a whole number. Multiply the divisor by 100 to make it a whole number.
Multiply both the divisor and the dividend by the same power of \bf{10} .
Multiply 1.12 \times 100 which is the same as 1.12 \times 10^2
Multiply 8.98 \times 100 which is the same as 8.98 \times 10^2
1.12 \times 100 = 112
8.98 \times 100 = 896
If the dividend is a decimal number, line up the decimal point of the dividend with the decimal point of the quotient. You may need to include zeros as place holders.
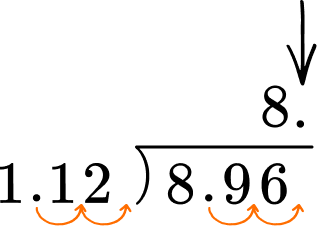
Do long division.
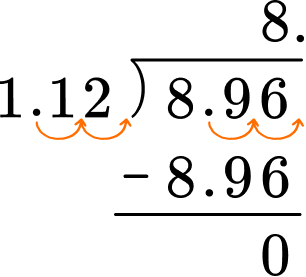
Label your answer appropriately.
The quotient is 8 which represents the amount of ice cream sandwiches. Amelia can buy 8 ice cream sandwiches.
Teaching tips for dividing decimals
- Have students utilize visual models such as hundredths grids or manipulatives such as base ten blocks to build conceptual understanding as opposed to practice worksheets. Division of decimals is a challenging concept for students to master.
- Have students recall and identify patterns with dividing by powers of 10.
- Have students use estimation before doing the algorithm so that they can determine if their answer is reasonable.
- Reinforce place value when dividing.
- Reinforce the essential academic vocabulary such as dividend, divisor, quotient so that it becomes part of students’ everyday math language.
Our favorite mistakes
- Starting the algorithm of long division with a decimal divisor
- Forgetting to move the decimal point of the dividend the same number of decimal places as it moved for the divisor
When multiplying the divisor by a power of ten that will make it a whole number, you have to remember to also multiply the dividend by that same power of ten. In other words, the number of times you move the decimal point in the divisor should be the same as the number of times you move the decimal point in the dividend.
- Forgetting to align the decimal point of the dividend with the quotient
- Thinking that the smaller number is always the divisor
- Confusing the steps of long division
- Not being mindful of place value by forgetting to include \bf{0} ’s as digits for the dividend
Practice dividing decimals questions
1. Solve the decimal division problem.
12.82 \div 0.4 = \; ?




The divisor is 0.4. Multiply the decimal divisor by 10 to make it a whole number.
Also, multiply the dividend by 10.
0.4 \times 10 = 4
12.82 \times 10 = 128.2
Line up the decimal place of the dividend with the decimal place of the quotient.
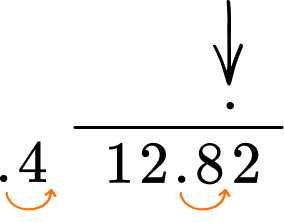
Use the algorithm of long division to divide.
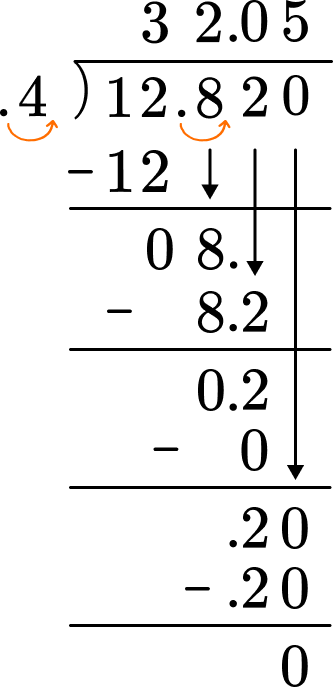
2. Solve the decimal division problem.
17.43 \div 7 = \; ?




The divisor is 7.
Line up the decimal place of the dividend with the decimal place of the quotient. Use the algorithm of long division to divide.
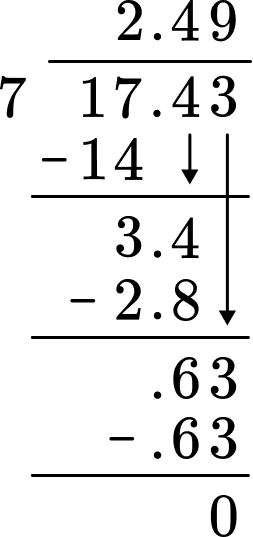
3. Solve the decimal division problem.
105 \div 0.15 = \; ?




The divisor is 0.15 which is not a whole number. Multiply the divisor by 100 to make it a whole number. Also, multiply the dividend by 100.
This is the same as multiplying by 10^2.
Line up the decimal place of the dividend with the decimal place of the quotient.
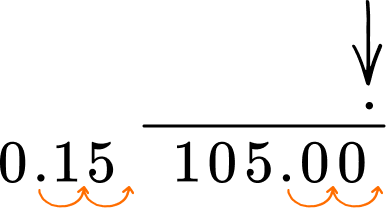
Use the algorithm of long division to divide.
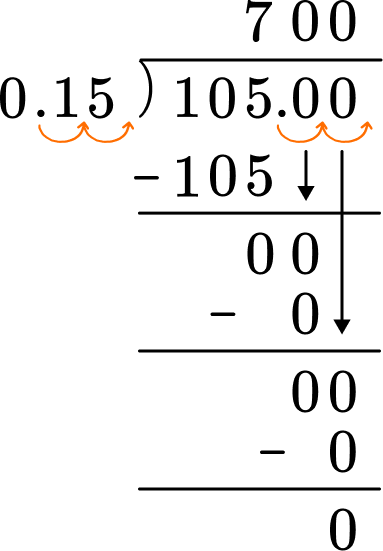
4. Solve the decimal division problem.
87.22 \div 1.4 = \; ?




The divisor is 1.4. Multiply the decimal divisor by 10 to make it a whole number. Also, multiply the dividend by 10 to make it a whole number.
Line up the decimal place of the dividend with the decimal place of the quotient.
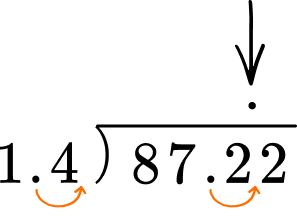
Use the algorithm of long division to divide.
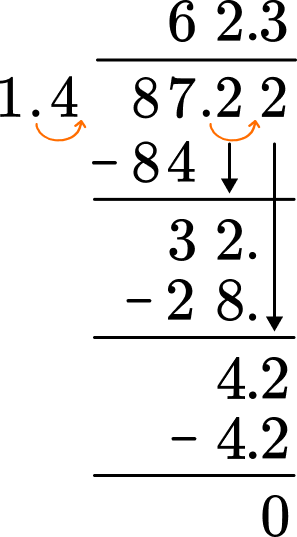
5. Over a three day period, Mila ran a total of 12.36 miles. If she ran the same distance every day, how many miles did she run per day?
4.2 miles

4.12 miles

3.12 miles

4.1 miles

The divisor is 3 and the dividend is 12.36. The divisor is a whole number. Line up the decimal place of the dividend with the decimal place of the quotient. Use the algorithm of long division to divide.
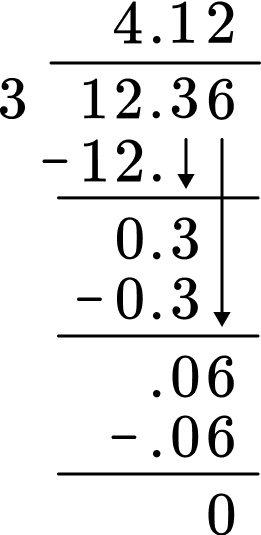
6. William baseball card collector. He has saved up \$54.30 to buy the small packs of baseball cards. If each pack of cards cost \$3.62. How many small packs of cards can he buy?
15 small packs

16 small packs

14 small packs

15.5 small packs

The divisor is 3.62 and the dividend is 54.30. There is a decimal divisor which needs to be multiplied by 100 to make it a whole number. The dividend also needs to be multiplied by 100.
3.62 \times 100 = 362
54.30 \times 100 = 5,430
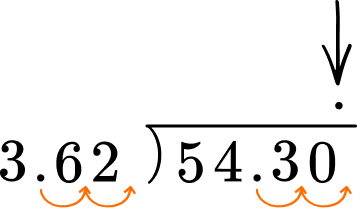
Use the algorithm of long division to divide.
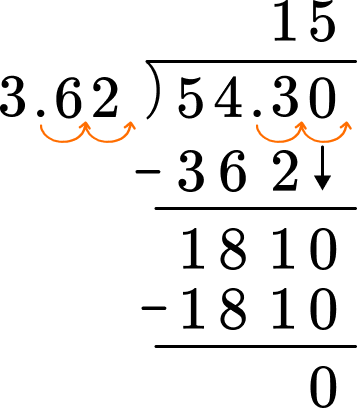
Dividing decimals FAQs:
By multiplying by the appropriate power of ten, you are moving the decimal point. As a shortcut, you can just move the decimal point.
In order to maintain equality, you will have to multiply the dividend by the same power of ten. For example:
1.8 \div 0.2 = 9 is equal to 18 \div 2 = 9
1.8 \div 0.2 = 9 is not equal to 1.8 \div 2 = 0.9
Yes, the divisor doesn’t have to be smaller than the dividend.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!