[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
Integers
Here you will learn about integers, including how to identify integers, integers on a horizontal number line, and integers on a vertical number line.
Students will first learn about integers as part of the number system in 6th grade.
What are integers?
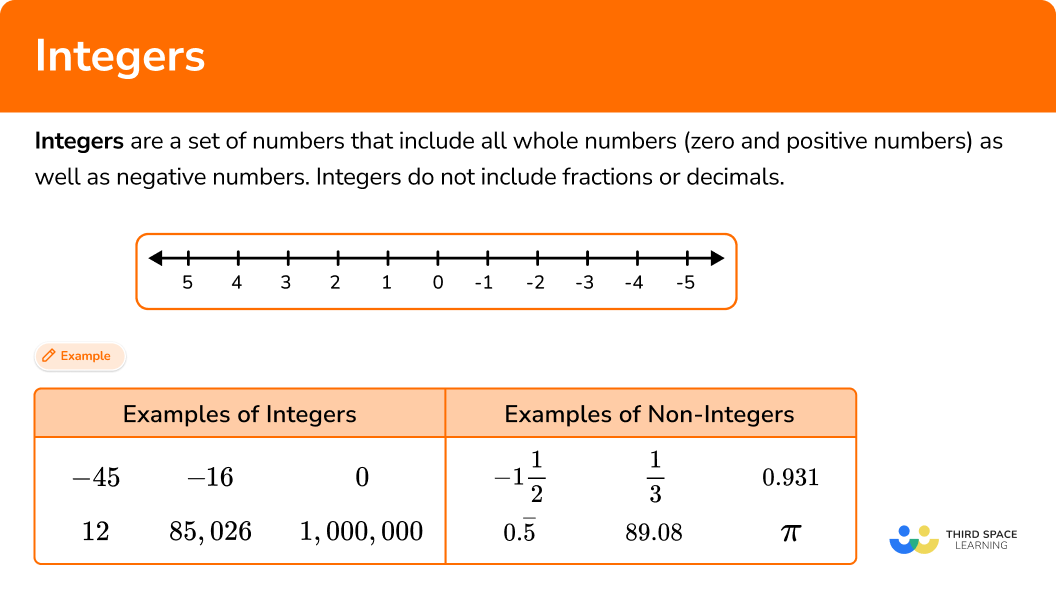
Integers are a set of numbers that include all whole numbers (zero and positive numbers) as well as negative numbers. Integers do not include fractions or decimals.
For example, here are some integers on a horizontal number line

All whole numbers are integers, but not all integers are whole numbers since integers also include negative numbers. Both whole numbers and integers are rational numbers and real numbers.
Natural numbers (also known as counting numbers) are a subset of integers.
For example,
| Examples of Integers | Examples of Non-Integers |
|---|---|
-45 \hspace{.8cm} -16 \hspace{1.6cm} 0 \hspace{.9cm} 12 \quad \quad 85,026 \quad \quad 1,000,000 | -1\cfrac{1}{2} \quad \quad \quad \cfrac{1}{3} \quad \quad 0.931
0.\overline{5} \quad \quad \; 89.08 \quad \quad \pi |
What are integers?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6th grade math?
- Grade 6 – The Number System (6.NS.6c)
Find and position integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram; find and position pairs of integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane.
How to identify integers
In order to identify integers:
- Recall the definition of the type of number needed.
- Show whether the number fits or does not fit the definition.
![[FREE] Types of Number Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 2, 4 and 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Types-of-number-check-for-understanding-listing-image.jpg)
[FREE] Types of Number Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 2, 4 and 6)
![[FREE] Types of Number Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 2, 4 and 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Types-of-number-check-for-understanding-listing-image.jpg)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 students’ understanding of types of numbers. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 2nd, 4th and 6th grade types of numbers topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Types of Number Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 2, 4 and 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Types-of-number-check-for-understanding-listing-image.jpg)
[FREE] Types of Number Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 2, 4 and 6)
![[FREE] Types of Number Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 2, 4 and 6)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Types-of-number-check-for-understanding-listing-image.jpg)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 students’ understanding of types of numbers. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 2nd, 4th and 6th grade types of numbers topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEIntegers examples
Example 1: identifying integers
Which of the following are integers?
–124, \, 254, \, –1.9, \, –7, \, 0, \, 2 \, \cfrac{1}{4} \, , \, – \, \cfrac{2}{3} \, , \, 583- Recall the definition of the type of number needed.
Integers include all whole numbers (positive numbers and zero) and their corresponding negative numbers. You can eliminate the following numbers based on this definition:
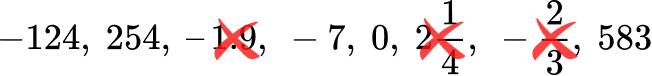
2Show whether the number fits or does not fit the definition.
The remaining numbers are –124, 254, –7, 0, and 583, all of which are integers.
Example 2: identifying integers
Grace says –21 is not an integer, but it is a whole number. Her friend Isaiah says –21 is not a whole number but an integer. Who is correct?
Recall the definition of the type of number needed.
Integers include all whole numbers (positive numbers and zero) and their corresponding negative numbers. Integers do not include fractions or decimals.
Show whether the number fits or does not fit the definition.
Isaiah is correct because –21 is a negative number; it does not include a decimal or a fractional part.
Whole numbers only include zero and positive numbers. Therefore, it is an integer.
Example 3: integers on a number line
Find the missing integer on the number line.
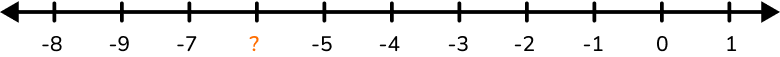
Recall the definition of the type of number needed.
Integers include all whole numbers (positive numbers and zero) and their corresponding negative numbers. Integers do not include fractions or decimals.
This means the missing number will not be a fraction or decimal and will be a negative number.
Show whether the number fits or does not fit the definition.
The missing number is –6.
If you continue counting on the number line, the number in between –7 and –5 would be –6.
Example 4: integers on a number line
There are two integers missing from the number line. Which missing integer is a positive integer?

Recall the definition of the type of number needed.
Integers include all whole numbers (positive numbers and zero) and their corresponding negative numbers. Integers do not include fractions or decimals.
In this case, you are looking for a non-negative integer or positive integer only.
Show whether the number fits or does not fit the definition.
The missing integers are –15 and 20.
The missing positive integer is 20.
Example 5: integers on a vertical number line
The vertical number line is missing two integers; one positive integer and one negative integer. What are they?
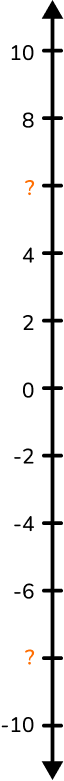
Recall the definition of the type of number needed.
Integers include all whole numbers (positive numbers and zero) and their corresponding negative numbers. Integers do not include fractions or decimals.
Show whether the number fits or does not fit the definition.
There is one negative number and one positive number missing from the vertical number line.
The negative numbers are on the bottom half (counting downwards from zero by 2 ) and the positive numbers are on the top half (counting upwards from zero by 2 ).
Therefore, the missing integers are –8 and 6.
Example 6: integers on a vertical number line
Look at the set of integers on the vertical number line. Fill in the boxes to complete the set.
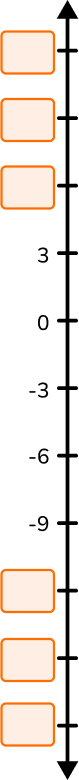
Recall the definition of the type of number needed.
Integers include all whole numbers (positive numbers and zero) and their corresponding negative numbers. Integers do not include fractions or decimals.
Show whether the number fits or does not fit the definition.
The set of integers included on the number line is, in numeric order, –9, –6, –3, 0, 3.
This means you are counting by 3.
So the missing positive numbers are 6, 9, and 12.
The missing negative numbers are –12, –15, and –18.
Teaching tips for integers
- Using a horizontal or vertical number line will help students build their foundation of understanding integers, especially negative numbers. It will also help them understand that negative numbers are the additive inverses of positive numbers.
- Students should master identifying and understanding integers on a number line before moving on to performing arithmetic operations with negative numbers and including negative numbers in algebraic equations.
Easy mistakes to make
- Thinking that integers and whole numbers are the same
Integers and whole numbers are similar, but they are not the same. Whole numbers are a subset of integers. While whole numbers and integers include zero and positive numbers and do not include fractions or decimals, integers also include negative numbers.
- Thinking that zero is not an integer
Zero, while not negative or positive, is an integer as well as a whole number.
- Thinking that a negative number with a larger digit is a larger number than a negative number with a smaller digit
With negative numbers, the smaller digit will be a larger number, and larger digits will be a smaller number. For example, –2 is a larger number than –8.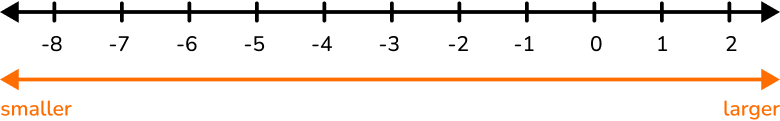
Related types of numbers lessons
Practice integers questions
1. Which of the following is a non-negative integer?




Integers include all whole numbers (positive numbers and zero) and all negative numbers.
Integers do not include fractions or decimals.
2. Which set of numbers are all integers?




The last set of numbers is the only set that does not contain any fractions or decimals and is therefore, a set of integers.
3. Amir’s teacher asked him to plot all of the integers from –4 to 6 on a number line. Which number line is correct?
![]()

![]()

![]()

![]()

Integers include all negative numbers, positive numbers, and zero.
On a horizontal number line, the negative numbers are shown to the left of zero while the positive numbers are shown to the right.
Since negative numbers are the additive inverse of positive numbers, the negative and positive numbers should mirror each other on opposite sides of the zero.
4. Fill in the missing integers to complete the number line.

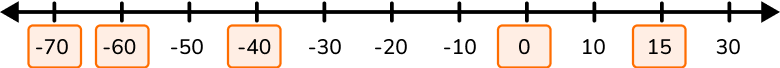

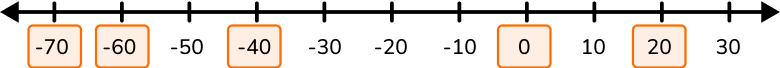





On the horizontal number line, negative numbers count left from zero while positive numbers count right from zero.
The scale, or amount between each number, should be the same.
On this number line, you are counting by 10.
So the missing integers in numeric order are –70, –60, –40, 0, and 20.
5. Plot the numbers –8 to 2 on a vertical number line.
![]()

![]()

![]()

![]()

On the vertical number line, negative numbers count down from zero, while positive numbers count up from zero.
The scale, or amount between each number, should be the same.
On this number line, you are counting by 1.
So in numeric order starting at the top of the number line, the integers should be 2, 1, 0, –1, –2, –3, –4, –5, –6, –7, –8.
6. Fill in the missing integers to complete the vertical number line.
![]()
![]()

![]()

![]()

![]()

On the vertical number line, negative numbers count down from zero, while positive numbers count up from zero.
The scale, or amount between each number, should be the same.
On this number line, you are counting by 5.
So in numeric order starting at the top of the number line, the missing integers should be 15, 5, –5, 20 .
Integers FAQs
An integer is a positive number, a negative number, or the number zero. An integer does not contain decimal digits or fractional parts.
Negative numbers are the additive inverses of the corresponding positive numbers. For example, the additive inverse of –3 is 3, the additive inverse of –12 is 12, etc.
All four basic arithmetic operations – addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division – can be performed on integers. However, mathematicians performing these arithmetic operations on negative numbers may follow different rules than performing them on whole numbers.
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!