High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Addition and subtraction Properties of equalityDividing multi digit numbers
Here you will learn how to divide multi digit numbers with strategies, such as the relationship between addition and subtraction, the properties of operations and also how to use the standard algorithm of long division.
Students will first learn about dividing multi digit numbers in 4 th and 5 th grade and how to use the standard algorithm to divide in 6 th grade.
What is dividing multi digit numbers?
Dividing multi digit numbers is dividing large numbers into equal groups.
When first working with multi-digit division, the focus is on using strategies including place value understanding, properties of operations and the relationship between multiplication and division.
For example,
600 \div 15= \; ?
- I know that 15 \times 10=150, so I can see how many 150 s are in 550.
\begin{aligned}& 600-150=450, \\\\ & 450-150=300, \\\\ & 300-150=150, \\\\ & 150-150=0\end{aligned}
There are 4 groups of 15 \times 10 in 600, so there are 40 groups of 15 in 600.
- I know that 600 \div 15=(300+300) \div 15.
Since 30 \div 15=2, then 300 \div 15=20. This means…
\begin{aligned}& (300+300) \div 15 \\\\ & =300 \div 15+300 \div 15 \\\\ & =20+20 \\\\ & =40\end{aligned}
- I can use an area model and what I know about multiplication to solve.
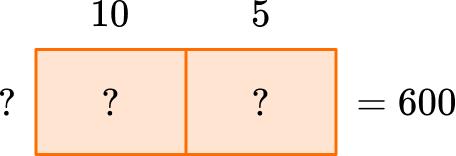
I know that 5 times something is half of 10 times something, so the box for 5 needs to be half the box for 10 – with the sum being 600.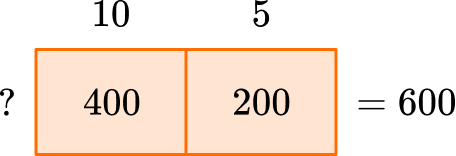
Now I know that 40 \times 10=400 and 40 \times 5=200, so the missing value is 40.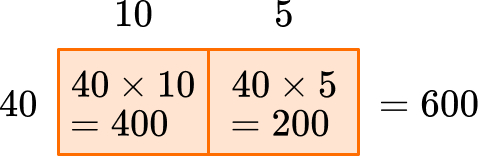
Notice there are many ways to solve the same problem – using partial products and partial quotients, using the distributive property over division and using the area model to work backwards from multiplication.
Knowing the names of each strategy is not important, but understanding why they work and making connections between them is.
After students have had sufficient practice understanding division with multi-digit whole numbers in 4 th and 5 th grade, the standard algorithm is taught in 6 th grade.
For example,
600 \div 15= \; ?
Set up the equation to solve with the algorithm.
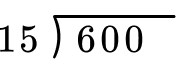
The steps of the algorithm are: divide, multiply, subtract then bring down.
Start with the first digit in the dividend, which is the number with the largest place value. How many wholes are in 6 \div 15?
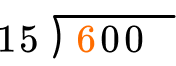
Since there are no wholes, move to include the next digit. How many wholes are in 60 \div 15?

60 \div 15=4. Record the 4 above the 60, in the tens position. Now multiply 4 \times 15 and record the product below.
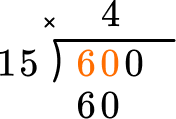
This shows that in 4 groups of 15, there are 60. Now subtract.
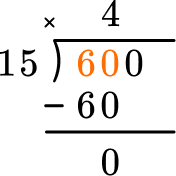
This shows how many are left over – in this case none. Since 4 groups of 15 are 60, there was exactly enough. Now bring down the next digit in the dividend.
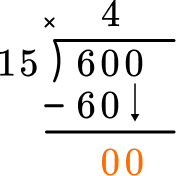
How many wholes are in 0 \div 15? There are 0. Record the 0 above.
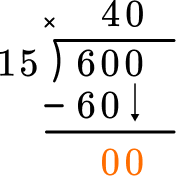
Multiplying 0 \times 15=0, and subtraction shows that there is nothing left over.
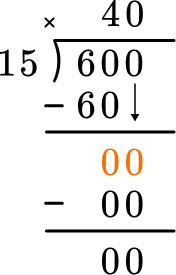
Note: This page does not cover division with decimals. However, students use strategies in fifth grade to divide decimals up to hundredths and use the standard algorithm in 6 th grade to divide all decimals.
See also: Multiplying and dividing decimals
What is dividing multi digit numbers?
Common Core State Standards
How does this apply to 4 th grade math, 5 th grade math and 6 th grade math?
- Grade 4: Numbers and Operations in Base 10 (4.NBT.B.6)
Find whole-number quotients and remainders with up to four-digit dividends and one-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
- Grade 5: Numbers and Operations in Base 10 (5.NBT.B.6)
Find whole-number quotients of whole numbers with up to four-digit dividends and two-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
- Grade 6: Number System (6.NS.B.2)
Fluently divide multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm.
![[FREE] Multiplication and Division Worksheet (Grade 4, 5 and 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Multiplication-and-Division-Check-for-Understanding-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Multiplication and Division Worksheet (Grade 4, 5 and 7)
![[FREE] Multiplication and Division Worksheet (Grade 4, 5 and 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Multiplication-and-Division-Check-for-Understanding-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 4, 5 and 7 students’ understanding of multiplication and division. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 4, 5 and 7 grade multiplication and division topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Multiplication and Division Worksheet (Grade 4, 5 and 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Multiplication-and-Division-Check-for-Understanding-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Multiplication and Division Worksheet (Grade 4, 5 and 7)
![[FREE] Multiplication and Division Worksheet (Grade 4, 5 and 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Multiplication-and-Division-Check-for-Understanding-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 4, 5 and 7 students’ understanding of multiplication and division. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 4, 5 and 7 grade multiplication and division topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEHow to divide multi digit numbers with strategies
In order to divide multi digit numbers with strategies:
- Write the division equation.
- Choose a solving strategy.
- Solve the equation.
Dividing multi digit numbers examples
Example 1: dividing a four-digit number by 1 digit divisor
Solve 9,245 \div 8.
- Write the division equation.
The equation is 9,245 \div 8= \; ?
2Choose a solving strategy.
Since division and multiplication are related, you can use what you know about multiplication to solve.
3Solve the equation.
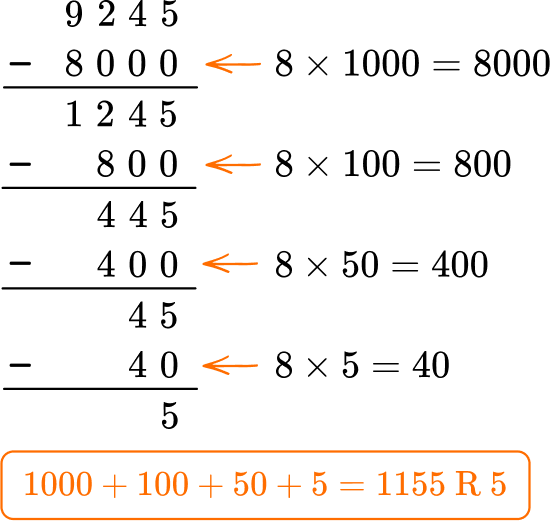
Example 2: dividing a four-digit number by 2 digit divisor
A box fits 20 crayons. There are 4,740 crayons. How many boxes can be filled with crayons?
The equation is 4,740 \div 20= \; ?
Properties of operations can be used to solve.
\begin{aligned} & 4,740 \div 20 \\\\ & =(4,000+600+100+40) \div 20 \\\\ & =4,000 \div 20+600 \div 20+100 \div 20+40 \div 20 \\\\ & =200+30+5+2 \\\\ & =237\end{aligned}
Example 3: dividing a four-digit number by 2 digit divisor
Solve 6,300 \div 25.
The equation is 6,300 \div 25= \; ?
Properties of operations and place value can be used to solve.
Since 63 is 100 times smaller than 6,300 then 6,300 \div 100=63.
Since 100=25 \times 4, there are 4 groups of 63 in the quotient.
63 \times 4=252, so 6,300 \div 25=252.
How to divide multi digit numbers with long division
In order to divide multi digit numbers with long division:
- Write the division equation in long division form.
- Divide part of the dividend (going from largest place value to smallest).
- Multiply the partial quotient and divisor.
- Subtract the product from the dividend.
- Bring down the next largest place value and begin again at Step 2.
Example 4: dividing a two-digit number by 1 digit divisor
Solve 96 \div 4 with the standard algorithm.
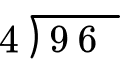
How many wholes are in 9 \div 4?
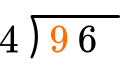
2 \times 4=8, there are 2 whole groups of 4.
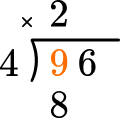
This shows that in 2 groups of 4, there are 8.
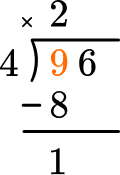
This shows there is 1 left over.
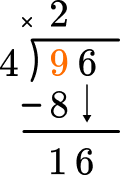
How many wholes are in 16 \div 4?
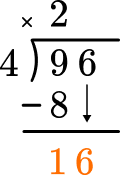
4 \times 4=16, there are 4 whole groups of 16.
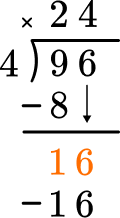
This shows that in 4 groups of 4, there are 16.
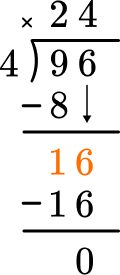
This shows there are 0 left over.
There is nothing left to bring down and there is no remainder.
96 \div 4=24
Example 5: dividing a three-digit number by 1 digit divisor with remainder
Solve 197 \div 7 with the standard algorithm.
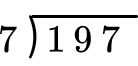
How many wholes are in 1 \div 7?
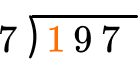
None, so we move to the next place value.
How many wholes are in 19 \div 7?
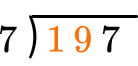
2 \times 7=14, there are 2 whole groups of 7.
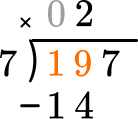
This shows that in 2 groups of 7, there are 14.
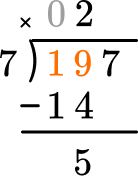
This shows there are 5 left over.
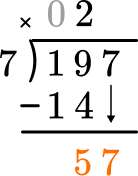
How many wholes are in 57 \div 7?
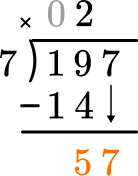
8 \times 7=56, there are 8 whole groups of 7.
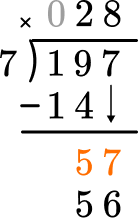
This shows that in 8 groups of 7, there are 56.
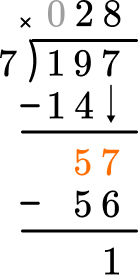
This shows there is 1 left over.
There are no more digits to bring down. There are a few options for recording an answer:
- Record it as a remainder: 197 \div 7=28 \mathrm{~R} \, 1
- Record it as a fraction: 197 \div 7=28 \cfrac{1}{7}
In this case the numerator is the remainder and the denominator is the divisor. - Record it as a decimal: 97 \div 7=28.142 \ldots
This requires you to keep following the steps, by bringing down 0 s from the decimal place values positions.
See also: Dividing decimals
Example 6: dividing a four-digit number by 2 digit divisor
Solve 8,118 \div 18 with the standard algorithm.
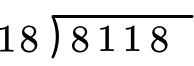
How many wholes are in 8 \div 18?
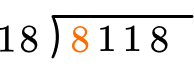
None, so we move to the next place value.
How many wholes are in 81 \div 18?
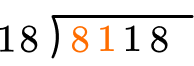
4 \times 18=72, there are 4 whole groups of 18.
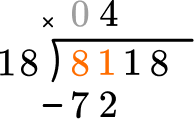
This shows that in 4 groups of 18, there are 72.
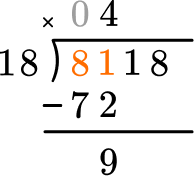
This shows there are 9 left over.
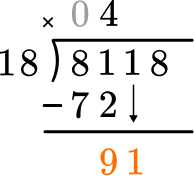
How many wholes are in 91 \div 18?
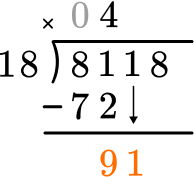
5 \times 18=90, there are 5 whole groups of 18.
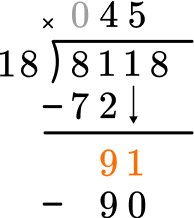
This shows that in 5 groups of 18, there are 90.
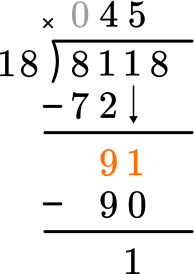
This shows there is 1 left over.
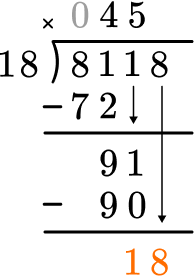
How many wholes are in 18 \div 18?
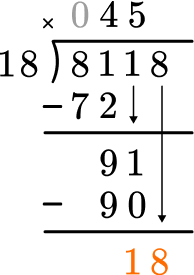
1 \times 18=18, there is 1 whole group of 18.
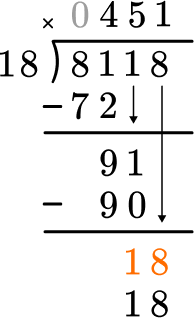
This shows that in 1 group of 18, there are 18.
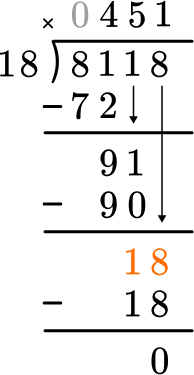
This shows there is 0 left over.
There is nothing left to bring down and there is no remainder.
8,118 \div 18=451
Teaching tips for dividing multi digit numbers
- While worksheets can be useful for this skill, make sure to expose students to all types of division problems. This includes, but is not limited to number problems, word problems, projects, real world scenarios, calculator activities, etc. It is important that students see division problems in many different contexts and solved in many different ways.
- Since solving long division problems involves using a multi-step algorithm, be sure that students have access to a tutorial, notes or webpage (like this one) so they can see the order of the steps and how to use them. This will increase their chances of understanding and memorizing the algorithm.
Easy mistakes to make
- Incorrectly adding partial quotients
When learning to divide large numbers, many students use the partial quotient method. For this method to be successful, students need to keep track of all the partial quotients and add them together at the end. If a student’s work is messy or incomplete, it can lead to mistakes.
- Thinking the first number goes on out the outside when using long division
When performing the standard algorithm for division, the divisor appears first from left to right, then the dividend. This is backwards from how a division expression is written, which can be confusing in the beginning.
For example,
4,571 \div 11 is written as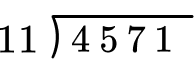
- Thinking that division is always a larger number divided by a small number
Up until 5 th grade, most (if not all) of students’ experience with division is a larger number divided by a smaller number. However, it is important to not make this claim and correct students if they make it.
Something as simple as “All the numbers we are working with are larger numbers divided by smaller numbers, but that doesn’t mean that is the only way to divide.”
You may even engage students in a short activity (or “brain teaser”) about 1 \div 2, by asking them “If you had 1 piece of gum and divided it by 2, what size would each piece be?”
Since dividing 1 item into 2 parts is a common real world occurrence, most elementary students can make sense of this.
While they are not expected to formally operate like this in elementary school, sprinkling a few of these experiences throughout the year can go a long way in preventing students from forming this misconception.
Related multiplication and division lessons
Practice dividing multi digit numbers
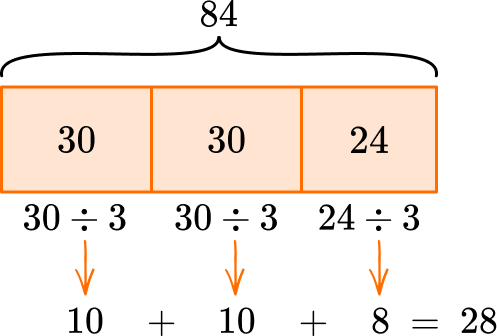
1. Solve 84 \div 3.




You can break 84 up into parts and divide each part by 3.
2. Solve 801 \div 9.




You can think about a related fact.
“Since 9 \times 9=81, then 9 \times 90=810. Taking away one of those groups of 9, moves us from 810 to 801, so that is 89 groups of 9. ”
3. A warehouse has 787 science kits. Each shipping box fits 32 science kits. How many boxes are needed for all the science kits?




Since division and multiplication are related, you can use what you know about multiplication to solve.
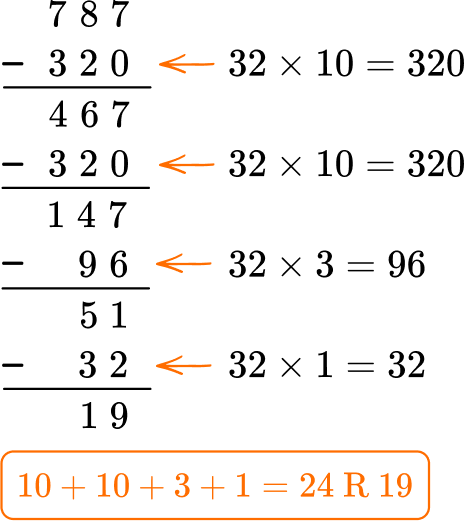
24 boxes still leave 19 science kits without a box, so 25 boxes are needed.
4. Solve 76 \div 4 with the division algorithm (long division).




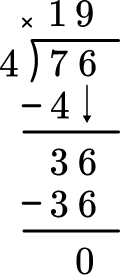
Start with how many wholes are in 74? Record the 1 at the top and subtract the group of 4 to see that there are 3 left over.
Then bring the 6 and decide how many wholes are in 36 \div 4. Record the 9 and subtract the 9 groups of 4 to see that there is nothing left over.
This shows there are 0 left over.
There is nothing left to bring down and there is no remainder.
76 \div 4=19
5. Solve 407 \div 11 with the division algorithm (long division).




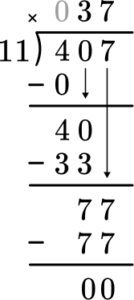
Start with how many wholes are in 4 \div 11? Since there are none, move to 40 \div 11. Record the 3 at the top and subtract the 3 groups of 11 to see that there are 7 left over.
Then bring the 7 and decide how many wholes are in 77 \div 11. Record the 7 and subtract the 7 groups of 11 to see that there is nothing left over.
This shows there are 0 left over.
There is nothing left to bring down and there is no remainder.
407 \div 11=37
6. A movie theater has 5,679 people that subscribe to their account on social media. They expect all the subscribers to come and see a new action movie. If each theater fits 101 people, how many theaters would the subscribers fill (not including any guests)?




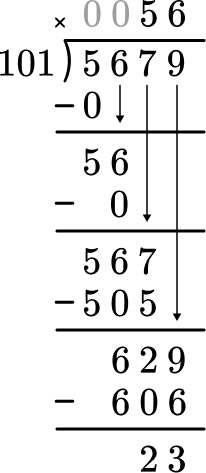
Start with how many wholes are in 5 \div 101? Since there are none, move to 56 \div 101. Since there are none, move to 567 \div 101. Record the 5 at the top and subtract the 5 groups of 101 to see that there are 62 left over.
Then bring the 9 and decide how many wholes are in 629 \div 101. Record the 6 and subtract the 6 groups of 101 to see that there is 23 left over.
5,679 \div 101=56 \text { R } 23
The 23 remaining people will not fill up the entire theater, so the subscribers would fill the theater fully 56 times.
Dividing multi digit numbers FAQs
In third grade, students work with dividing two-digit numbers by one-digit numbers within 100.
Their work with division is directly connected to multiplication. Students start with multi-digit division in fourth grade by dividing 2 -digit numbers, 3 -digit numbers and 4 -digit numbers by 1 -digit divisors.
They extend their learning to 2 -digit divisors in 5 th grade. In all three grade levels, students use their reasoning and understanding of numbers. In 6 th grade, they learn how to divide with the standard algorithm.
Students begin learning both of these skills in 5 th grade.
They use different strategies to solve problems with decimals (all operations), and they learn how to make sense of and model division with unit fractions (a whole number by a unit fraction and a unit fraction by a whole number).
Students learn the corresponding algorithms to these operations in 6 th grade.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!