23 Classroom Management Strategies & Practical Examples For Teachers
Classroom management strategies promote learning by establishing and maintaining a positive and safe learning environment. However, classroom management can be a source of anxiety for educators, especially newly qualified staff. In this article, our author Samantha Dock shares 23 effective classroom management strategies informed by research and her own experience in the classroom.
When I first started my teaching career, I was most nervous about managing my own classroom and students’ behavior. This was fueled by negative depictions in popular media. One scene that came to mind was from the 1990 film, Kindergarten Cop. Detective John, played by Arnold Schwarzenegger, walks into a chaotic kindergarten classroom. Students are screaming, running amok, and painting the walls red, leaving Detective John frozen speechless. He yells at the students, inevitably causing them to cry.
While Detective John resorted to some ineffective classroom management strategies, I developed a repertoire of research-informed techniques to manage my classroom and create productive learning environments.
Below, I share with you 23 teacher-tested classroom management strategies, grounded in research, to assist educators in successfully navigating classroom management.
What are classroom management strategies?
Classroom management strategies are the tools and techniques teachers use to ensure a smooth and productive learning environment. These strategies are designed to support both academic progress and social-emotional development by addressing disruptions and student misbehavior in a proactive and effective manner.
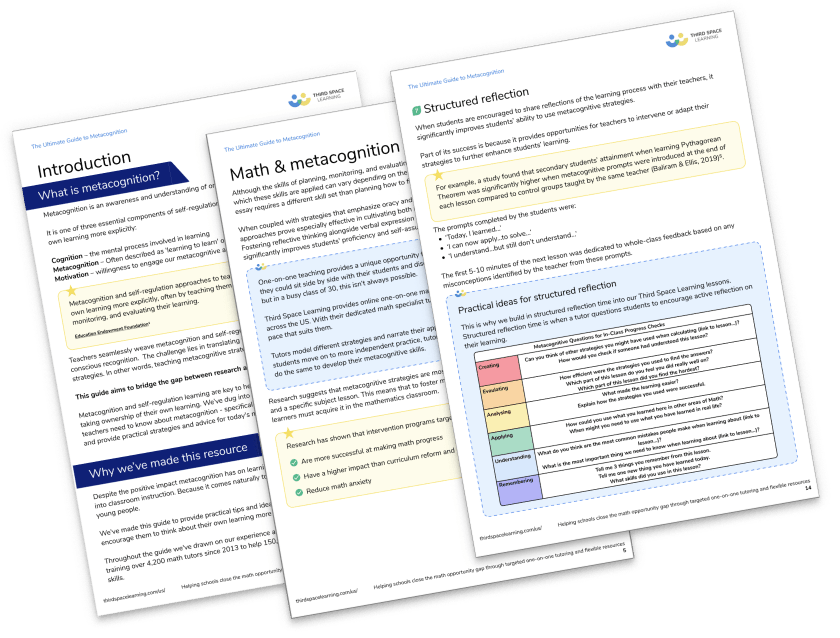
13 teaching Strategies Poster
13 tried and tested strategies to help teachers maximise student progress with best classroom management practice.
Download Free Now!Benefits of classroom management strategies
Researchers have been studying effective classroom management strategies since the 1950s and have identified a number of benefits. A well-managed classroom leads to:
- Improved behavior
- Reduced problem behavior (Oliver et al., 2011)
- Increased student engagement (Gage and MacSuga-Gage, 2017)
- Improved learning outcomes and academic achievement (Adeyemo, 2012)
However, it’s important to note that a classroom management strategy in isolation will not impact all students’ behavior. Teaching is an art, not a science. Teachers must develop a repertoire of strategies and know how and when to use them effectively. That’s why we’ve compiled this list of 23 research-informed techniques for you to implement and adapt as necessary for you and your students’ needs.

Meet Skye, the voice-based AI tutor making math success possible for every student.
Built by teachers and math experts, Skye uses the same pedagogy, curriculum and lesson structure as our traditional tutoring.
But, with more flexibility and a low cost, schools can scale online math tutoring to support every student who needs it.
Find out more23 effective and practical classroom management techniques for educators
1. Establish classroom rules and expectations
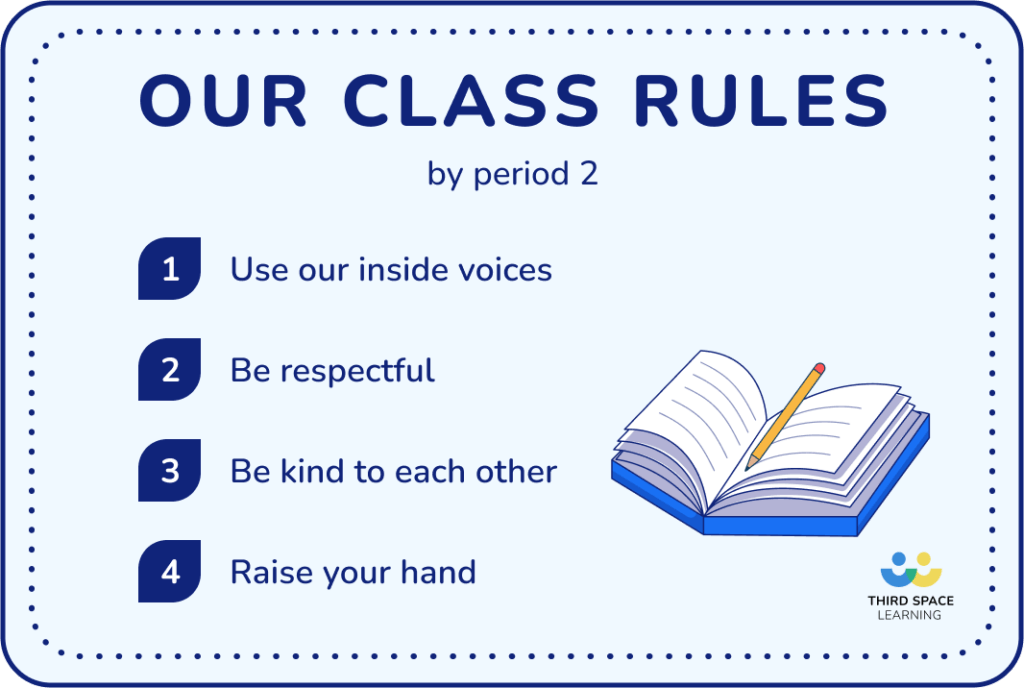
Establishing classroom rules and expectations is fundamental for creating a structured learning environment. Clearly outlining expectations from the first day of school sets the tone for behavior and academic engagement.
For example, a teacher might establish rules such as “Raise your hand before speaking” and “Respect your classmates.” This clarity helps students understand boundaries and fosters a sense of security, which in turn supports better classroom management by reducing disruptions and conflicts.
2. Build relationships with students
Building relationships with students is essential for creating a positive classroom atmosphere and promoting good behavior. Showing genuine interest in students’ lives and interests, helps teachers establish trust and rapport.
This simple strategy is particularly effective for reducing subject-specific anxiety, such as math anxiety.
3. Keep specific student needs in mind
Keeping specific student needs in mind allows teachers to provide targeted support and accommodations. Recognizing and addressing individual differences in learning styles, interests, and backgrounds helps create a more inclusive and responsive learning environment.
For example, providing additional resources or modifying assignments to accommodate students with diverse learning needs or cultural backgrounds promotes equity in education and enhances classroom management by fostering a sense of belonging and engagement for all students.
Putting student’s needs first
At Third Space Learning, students work one-on-one with Skye, the AI math tutor. Skye is an adaptive, dialog-driven AI math tutor designed and developed by teachers. Skye uses diagnostic and formative assessment to adapt pitch, pace, and teaching style according to each student’s needs. Because the one to one teaching is targeted to each child’s gaps, students make accelerated progress and find lessons more engaging and fun.
The range of interactive tools in the virtual classroom allows students to communicate their critical thinking with Skye in a way they are comfortable with.
4. Build relationships with parents
Parental engagement is crucial for gaining support and cooperation in managing classroom behavior. Communicating regularly with parents about their child’s progress and behavior helps build trust and understanding.
For example, sending home weekly newsletters or making phone calls can develop positive relationships with parents, keeping them informed and involved. Ensuring the first time parents hear from you is good news helps to lead to a collaborative effort if you do reach out for support to maintain a conducive learning environment.
5. Use time effectively
Effective use of time is key to maximizing instructional minutes and minimizing disruptions. Lesson planning with clear objectives and transitions helps keep students focused and on task.
For instance, breaking down lessons into manageable chunks with built-in opportunities for student interaction and group work can prevent boredom, keep students’ attention and reduce off-task behavior, contributing to smoother classroom management.
6. Arrange classroom furniture purposefully
Arranging classroom furniture purposefully can impact the flow of instruction and student behavior. Creating a layout that facilitates movement and encourages collaboration can enhance engagement and minimize distractions.
For example, arranging desks in clusters or circles promotes group discussions and cooperative learning, encouraging a sense of community and reducing disruptions.
Make sure that you have a garbage can in the front and back of the room to further lessen students moving all around the room.

7. Set clear consequences
Transparency about consequences helps students to understand the outcomes of their actions and encourages accountability. Clearly communicate the consequences of both positive and negative behavior. This will promote consistency and fairness.
For example, a teacher might establish a behavior chart with clear expectations and corresponding rewards or consequences for behavior issues, empowering students to make informed choices and ultimately improving classroom management.
8. Be consistent
Consistency in enforcing rules and consequences establishes predictability and fairness, which are essential for effective classroom management. Consistency helps students to understand what is expected of them and reduces confusion and resentment.
For example, consistently enforcing rules for tardiness or incomplete homework sends a clear message about the importance of responsibility and respect for classroom norms.
9. Establish classroom procedures (and practice them!)
Establishing classroom procedures and practicing them throughout the school year helps to streamline routines and minimize disruptions. Teaching students the steps for common tasks such as entering the classroom, transitioning between activities, and packing up at the end of the day promotes efficiency and order.
For example, practicing a morning routine that includes greeting the teacher, turning in homework, and completing a warm-up activity sets a positive tone for the day and reinforces expectations for behavior and participation.
10. Incorporate brain breaks
Incorporate brain breaks into the daily schedule to help maintain student focus and productivity. Short, structured breaks between activities or lessons give students opportunities to recharge and refocus, reducing restlessness and improving overall engagement.
For example, incorporate brief stretching exercises, mindfulness activities, or quick games to help students release energy and to improve attention span, leading to more effective learning.
11. Engage students in learning
Engaging students in learning promotes active participation and reduces off-task behavior. Use a variety of teaching strategies such as hands-on activities, group discussions, and multimedia presentations to cater to different learning strategies and interests, keeping students invested in the lesson. Teaching doesn’t always mean direct instruction.
For example, incorporate real-world examples and multimedia resources. This can make abstract concepts more relatable and engaging, fostering curiosity and enthusiasm for learning. Helping students understand how to learn math, you can include real math, fun math activities and outdoor math to engage learners.
12. Give students responsibility
Giving students responsibility empowers them to take ownership of their learning and behavior. Assigning tasks such as classroom jobs, peer tutoring, or leading discussions promote a sense of belonging and encourages positive behavior.
For example, allowing students to take turns leading morning meetings or organizing classroom supplies promotes leadership skills and reinforces the importance of cooperation and accountability.
13. Be flexible
Being flexible and adaptable allows teachers to respond effectively to unexpected situations and individual student needs. Flexibility in lesson planning, classroom routines, and behavior management strategies helps to accommodate diverse learning styles and personalities.
For example, be open to modifying assignments or allowing extra time for struggling students. This will demonstrate empathy and promote a supportive learning environment.
14. Use behavior-specific praise
Using behavior-specific praise (BSP) reinforces positive behavior and encourages students to continue making good choices. Providing specific and genuine praise for effort, cooperation, and achievement boosts students’ self-esteem and motivation. Gage and MacSuga-Gage (2017) found that BSP had a statistically significant impact on positive student behavior.
For example, acknowledge students for helping a classmate, “Well done for helping them to complete the task”, or for completing a challenging task, “You did well to keep trying and try different approaches”. This rewards effort and positive attitudes, in addition to academic achievement. BSP demonstrates appreciation and encourages continued positive behavior, contributing to a more harmonious classroom environment.
15. Use teacher-directed opportunities to respond
Teacher-directed opportunities to respond involve strategically prompting students to participate and engage in classroom activities. Actively soliciting student responses through effective questioning, comments, or prompts means teachers create a dynamic learning environment where every student has the opportunity to contribute.
For example, a teacher might ask open-ended questions during a discussion or call on individual students to share their thoughts, ensuring that all voices are heard and encouraging active participation. This strategy not only promotes a sense of ownership and responsibility among students but also provides valuable feedback for the teacher to assess understanding and adjust instructional strategies as needed, thus enhancing overall classroom management.
16. Prompt for behavioral expectations
Prompting for behavioral expectations reminds students of classroom rules and encourages self-monitoring of behavior. Using visual cues, verbal reminders, or nonverbal signals helps redirect off-task behavior and reinforces expectations.
For example, using a hand signal to remind students to raise their hand before speaking or displaying a visual timer to indicate remaining time for an activity prompts students to stay focused and on track, enhancing classroom management.
17. Lesson plan
Lesson planning with clear objectives and engaging activities supports effective instruction and classroom management. Planning lessons that are relevant, challenging and use differentiation strategies helps maintain student interest and participation.
For example, incorporating interactive technology, cooperative learning tasks, or hands-on experiments aligns with students’ diverse learning needs and preferences, leading to a more dynamic and orderly classroom environment.
18. Be cognizant of your voice
Being cognizant of your voice tone, volume, and pacing can positively influence classroom dynamics. Using a calm and confident tone conveys authority and fosters a respectful atmosphere.
For example, speaking clearly and at a moderate volume ensures that all students can hear and understand instructions, minimizing confusion and disruptions.
19. Consider proximity
Considering the proximity to students during instruction and classroom management situations can enhance teacher-student interactions and behavior management. Moving around the classroom and positioning oneself near students who need extra support or redirection helps maintain focus and deter off-task behavior.
For example, standing near students who are working independently or quietly reminding a distracted student of expectations reinforces classroom norms and encourages positive behavior.
20. Practice compassion
Practicing compassion and empathy towards students promotes a supportive and inclusive classroom environment. Recognizing and validating students’ feelings and experiences helps build trust and rapport.
For example, acknowledging a student’s frustration with a difficult assignment or offering encouragement during challenging times demonstrates empathy and cultivates a sense of belonging, contributing to better classroom management and student well-being.
21. Model ideal behavior
Modeling ideal behavior sets a positive example for students and reinforces classroom expectations. Demonstrating respect, kindness, and perseverance in interactions with students and colleagues establishes a culture of mutual respect and cooperation.
For example, acknowledging and apologizing for mistakes, actively listening to students’ perspectives, and demonstrating a growth mindset in overcoming challenges helps create a positive classroom climate and promote effective classroom management.
22. Promote a growth mindset
Promoting a growth mindset encourages students to embrace challenges and persist in their efforts to learn and grow. Emphasizing the value of effort, resilience, and learning from mistakes fosters a school culture of continuous improvement.
For example, praising students for their perseverance in tackling difficult tasks or providing opportunities for reflection and goal-setting empowers students to take ownership of their learning and behavior, leading to better classroom management outcomes.
23. Use tangible and intangible rewards
Using both tangible and intangible rewards reinforces positive behavior and motivation. Offering praise, recognition, privileges, or small incentives for following classroom rules and meeting academic goals encourages students to stay on task and make positive choices.
For example, implementing a reward system such as a whole class token economy or individual behavior charts with opportunities to earn privileges promotes a positive classroom environment and supports effective behavior management.
If you’re looking for a way to encourage students to complete their homework, you can use the homework surprise board. If everyone in the class does their homework, they get a letter. The goal is to spell out the word “homework.” Once your class spells “homework” the entire class gets to choose a class prize!

Classroom management tips for new teachers
Classroom management can be one of the most daunting challenges for new teachers. From navigating disruptive behavior to fostering a positive learning environment, rookies often find themselves overwhelmed.
However, with the right strategies and support, managing a classroom can become a rewarding aspect of teaching.
New teachers
Here are some quick tips for new teachers, regardless of your students’ grade:
- Implement positive reinforcement for desired behaviors. For example, praise a student aloud for following the directions on the board.
- Establish clear and consistent classroom rules and expectations. Here’s a pro tip: have students be a part of the process of creating rules! This helps to create a positive classroom culture and they get to feel like their voice is heard.
- Utilize proactive strategies such as behavior contracts or token systems. It can be helpful to students to physically see their progress and reward they are working towards.
- Address issues with students individually. Students can become embarrassed and act out if their behavior is addressed in front of their peers.
- Foster a sense of community and respect among students to mitigate disruptive behavior. This will help promote positive behavior between peers and enhance the classroom environment.
Grade-level
Here are some grade-level specific tips, great for new teachers or teachers transitioning to a different school phase.
- High school: Incorporate student voice and choice in classroom activities to enhance engagement, provide opportunities for student leadership roles and responsibilities, and offer real-world connections to course content to increase relevance
- Middle school: Utilize interactive and hands-on learning activities to keep students engaged, implement frequent transitions and movement breaks to maintain focus, and foster peer relationships and collaborative learning experiences
- Elementary school: Establish consistent routines and visual schedules to promote predictability, use positive reinforcement and praise to reinforce desired behaviors, and incorporate games and interactive elements into lessons to keep young learners engaged
- Pre-k: Use visual schedules, picture cues, and verbal reminders to support understanding and communication, and incorporate plenty of hands-on, sensory-rich activities to engage young learners and promote exploration and discovery
- Special education: Provide visual supports and communication tools to facilitate understanding, and collaborate closely with support staff and parents to ensure consistency and alignment across settings
Professional development for classroom management
Ongoing professional development opportunities play a pivotal role in empowering teachers to enhance their classroom management skills and stay updated on best practices. In today’s dynamic educational landscape, where student’s needs and behavior patterns continually evolve, teachers must continuously refine their strategies to maintain an effective learning environment.
Professional development provides educators with access to the latest research, techniques, and resources tailored to address classroom management challenges. By participating in workshops, seminars, and collaborative learning experiences, teachers can access resources, tools, and support networks to address challenges effectively.
Ultimately, investing in ongoing professional development empowers teachers to cultivate a supportive and engaging classroom environment and enables teachers to adapt their practices to meet the diverse needs of their students and foster a positive learning environment.
If you are an educator struggling with misbehavior, here are some recommendations:
1. Seek professional development opportunities
Attend workshops, conferences, and online courses specifically focused on classroom management techniques. Look for training sessions that offer practical strategies and real-life scenarios to help address misbehavior effectively.
- IRIS Center: PD Activity Learning the Components of a Comprehensive Behavior Management Plan
- PBS Learning Environment
- Teaching Strategies For Supporting Children With ADHD In The Classroom
- Ask your administration if there is any professional development offered through the district regarding classroom management
2. Observe experienced teachers
Arrange to observe experienced teachers in action, particularly those known for their effective classroom management skills.
During teacher observation, take note of their strategies, techniques, and approaches to handling challenging behaviors, and consider how you can adapt them to suit your own teaching style and classroom context.
3. Utilize mentorship programs
Participate in mentorship programs where you can be paired with a more experienced teacher who can provide guidance, support, and feedback on managing misbehavior. Engaging in regular discussions and reflections with your mentor can offer valuable insights and personalized advice tailored to your specific needs and circumstances.
Effective classroom management is crucial for creating a conducive learning environment, and it’s achievable through various proven strategies. It’s essential for teachers to continuously invest in professional development opportunities and seek mentorship to refine their classroom management skills.
Importantly, schools and teachers should collaborate to promote a positive classroom culture, recognizing that teachers are not alone in this endeavor. By implementing these strategies and fostering a supportive learning environment, educators can empower students to thrive academically and socially.
Classroom management strategies FAQ
The four classroom management styles are authoritarian, authoritative, permissive, and indulgent. Of these four, the most effective style is authoritative. An authoritative teacher practices a balance of teacher control and student involvement. Authoritative teachers are supportive, flexible, assertive, and warm. All of which are qualities of an extraordinary and successful educator.
The Big 8 classroom management strategies are the following:
1. Expectations
2. Cueing
3. Attention prompt
4. Signals
5. Tasking
6. Voice
7. Proximity
8. Time limits
The 4 Cs of classroom management are the following:
1. Critical thinking
2. Communication
3. Collaboration
4. Creativity
It is imperative that these strategies are implemented into the classroom at a young age. Students cannot wait until middle or high school to be introduced to these skills.
References
Oliver et al. 2018. Teacher classroom management practices: effects on disruptive or aggressive student behavior.
Gage and MacSuga-Gage. 2017. Salient Classroom Management Skills: Finding the Most Effective Skills to Increase Student Engagement and Decrease Disruptions.
Adeyemo. 2012. The Relationship Between Effective Classroom Management and Students’ Academic Achievement.