One to one maths interventions built for KS4 success
Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons now available
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Ratio Types of angles Angle rules Coordinates mathsThis topic is relevant for:

Similar Shapes
Here we will learn about similar shapes in maths, including what they are and how to identify similar shapes. We will also solve problems involving similar shapes where the scale factor is known or can be found.
There are similar shapes worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What are similar shapes?
Similar shapes are enlargements of each other using a scale factor.
All the corresponding angles in the similar shapes are equal and the corresponding lengths are in the same ratio.
E.g.
These two rectangles are similar shapes.
The scale factor of enlargement from shape A to shape B is 2 .
The angles are all 90^o
The ratio of the bases is 2:4 which simplifies to 1:2
The ratio of the heights is also 1:2
E.g.
These two parallelograms are similar shapes.
The scale factor of enlargement from shape A to shape B is 3.
The corresponding angles are all equal, 45^o and 135^o .
The ratio of the bases are 3:9 which simplifies to 1:3
The ratio of the perpendicular heights is also 1:3
See also: Enlargement
What are similar shapes?
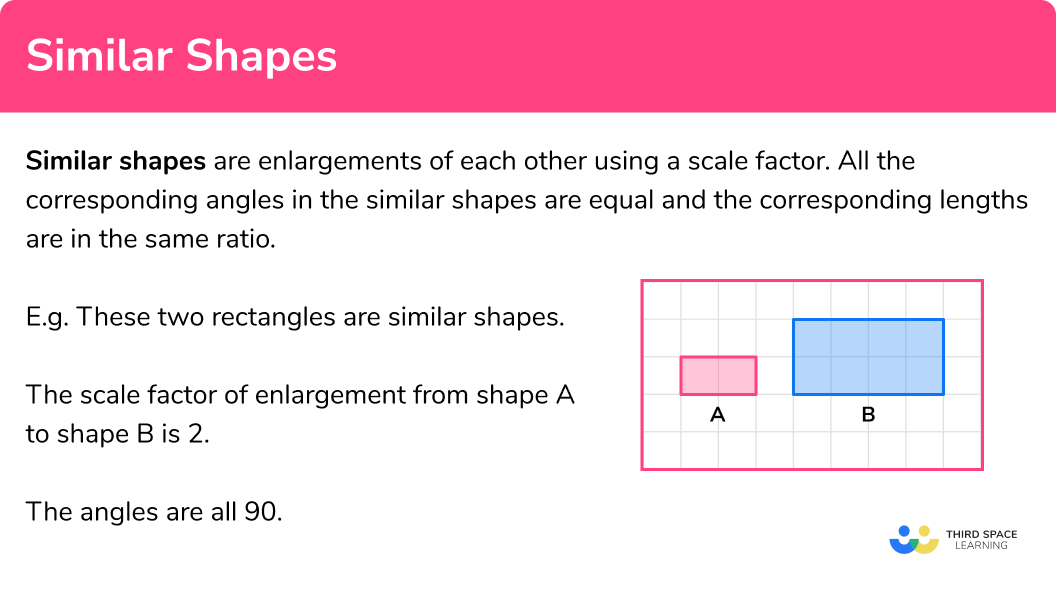
Scale factor for length, area and volume
The scale factors for length, area and volume are not the same.
In Higher GCSE Maths similar shapes are extended to look at area scale factor and volume scale factors
To work out the length scale factor we divide the length of the enlarged shape by the length of the original shape.
To work the area scale factor we square the length scale factor.
To work the volume scale factor we cube the length scale factor.
E.g.
- Comparing length A and length B we can work out the scale factor to be 3 .
- Comparing area A and area B we can work out the scale factor to be 9 .
This is the same as 3^2 .
- Comparing volume A and volume B we can work out the scale factor to be 27 .
This is the same as 3^3 .
Step-by-step guide: Scale factor
Scale factor for length, area and volume
How to decide if shapes are similar
In order to decide if shapes are similar:
- Decide which sides are pairs of corresponding sides.
- Find the ratios of the sides.
- Check if the ratios are the same.
Explain how to decide if shapes are similar

Similar shapes worksheet

Get your free similar shapes worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Similar shapes worksheet

Get your free similar shapes worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREERelated lessons on congruence and similarity
Similar shapes is part of our series of lessons to support revision on congruence and similarity. You may find it helpful to start with the main congruence and similarity lesson for a summary of what to expect, or use the step by step guides below for further detail on individual topics. Other lessons in this series include:
Similar shapes examples
Example 1: decide if shapes are similar
Are these shapes similar?
- Decide which sides are pairs of corresponding sides.
The bases of the rectangles are a pair of corresponding sides.
The heights of the rectangles are a pair of corresponding sides.
2Find the ratios of the sides.
When writing the ratios the order is very important.
Here the ratio is length A : length B
The ratio of the bases is 1:2
The ratio of the heights is 2:4 which simplifies to 1:2
3Check if the ratios are the same.
The rectangles are similar shapes. The ratios for the corresponding lengths are the same 1:2.
The scale factor of enlargement for shape A to shape B is 2 .
Example 2: decide if shapes are similar
Are these shapes similar?
Decide which sides are pairs of corresponding sides.
The bases of the triangles are a pair of corresponding sides.
The heights of the triangles are a pair of corresponding sides.
Find the ratios of the sides.
When writing the ratios the order is very important.
The ratio of the heights is 5:15 which simplifies to 1:3
The ratio of the bases is 7:20 this can be written as 1: \frac{20}{7} or 1:2.857...
Check if the ratios are the same.
The triangles are NOT similar shapes. The ratios for the corresponding lengths are NOT the same.
How to find a missing length
In order to find a missing side in a pair of similar shapes:
- Decide which sides are pairs of corresponding sides.
- Find the scale factor.
- Use the scale factor to find the missing length.
How to find a missing length

Missing length examples
Example 3: finding a missing length
Here are two similar shapes. Find the length QR.
Decide which sides are pairs of corresponding sides.
Pair up the sides that have measurements. Make sure you pair up the side mentioned in the question.
The sides AB and PQ are a pair of corresponding sides.
The sides BC and QR are a pair of corresponding sides.
Find the scale factor.
The ratio of the lengths AB : PQ is 9:27 which simplifies to 1:3
This gives a scale factor of enlargement from rectangle ABCD to rectangle PQRS of 3.
Use the scale factor to find the missing length.
The ratio of the lengths BC : QR is also 1:3
We can use the scale factor 3 as a multiplier to find the missing length.
The missing side has been found. QR = 12 cm
Alternatively an equation may be formed and solved:
Example 4: finding a missing length
Here are two similar triangles. Find the length BC.
Decide which sides are pairs of corresponding sides.
Pair up the sides that have measurements. Make sure you pair up the side mentioned in the question. Use the angles to help you.
The sides AB and DE are a pair of corresponding sides.
The sides BC and EF are a pair of corresponding sides.
Find the scale factor.
The ratio of the lengths AB : DE is 12.5 : 25 which simplifies to 1 : 2
This gives a scale factor of enlargement from triangle ABC to triangle DEF of 2.
But we want a scale factor from DEF to ABC which will be \frac{1}{2} .
Use the scale factor to find the missing length.
The ratio of the lengths BC : EF is also 1:2
We can use the scale factor \frac{1}{2} as a multiplier to find the missing length.
18\times\frac{1}{2}=9
The missing side has been found. BC = 9 \; cm
Alternatively an equation may be formed and solved:
How to find a missing length in a triangle
In order to find a missing side in a pair of triangles when you are not told that the triangles are similar:
- Use angle facts to determine which angles are equal.
- Redraw the triangles side by side.
- Decide which sides are pairs of corresponding sides.
- Find the scale factor.
- Use the scale factor to find the missing length.
How to find a missing length in a triangle

Missing length in a triangle examples
Example 5: finding a missing length in a triangle
Work out the value of x.
Use angle facts to determine which angles are equal.
Look for equal angles.
angle ACB = angle DCE as vertically opposite angles are equal
There are a pair of parallel sides – AB and DE. This means that there are equal angles as there are alternate angles.
Angle ABC = angle CED (alternate angles)
Angle BAC = angle CDE (alternate angles)
Redraw the triangles side by side.
It makes the problem much easier if you redraw the triangles side-by-side so that it is easier to pair up the corresponding sides.
Decide which sides are pairs of corresponding sides.
Pair up the sides that have measurements. Make sure you pair up the side mentioned in the question. Use the angles to help you.
The sides AC and DC are a pair of corresponding sides.
The sides BC and EC are a pair of corresponding sides.
Find the scale factor.
The ratio of the lengths AC : DC is 4 : 10 which simplifies to 1 : 2.5
This gives a scale factor of enlargement from ABC to CDE of 2.5
Use the scale factor to find the missing length.
The ratio of the lengths BC : EC is also 1 : 2.5
We can use the scale factor 2.5 as a multiplier to find the missing length.
x=5 \times 2.5=12.5
The value of x has been found, x=12.5
Alternatively an equation may be formed and solved:
Example 6: finding a missing length in a triangle
Work out the value of x.
Use angle facts to determine which angles are equal.
Look for equal angles.
angle EAB = angle DAC as they are common to both triangles
There are a pair of parallel sides – EB and DC. This means that there are equal angles as there are corresponding angles.
angle AEB = angle ADC (corresponding angles)
angle ABE = angle ACD (corresponding angles)
Redraw the triangles side by side.
It makes the problem much easier if you redraw the triangles side-by-side so that it is easier to pair up the corresponding sides.
Decide which sides are pairs of corresponding sides.
Pair up the sides that have measurements. Make sure you pair up the side mentioned in the question. Use the angles to help you.
The sides AE and AD are a pair of corresponding sides.
The sides EB and DC are a pair of corresponding sides.
Find the scale factor.
The ratio of the lengths AE : AD is 5 : 8 which simplifies to 1 : \frac{8}{5} or 1 : 1.6
This gives a scale factor of enlargement from ABE to ACD of 1.6
Use the scale factor to find the missing length.
The ratio of the lengths EB : DC is also 1 : 1.6
We can use the scale factor 1.6 as a multiplier to find the missing length.
x=7 \times 1.6=11.2
The value of x has been found, x=11.2
Alternatively an equation may be formed and solved:
How to find an area or volume using similar shapes
In order to find an area or volume using similar shapes:
- Find the scale factor.
- Use the scale factor to find the missing value.
How to find an area or volume using similar shapes

Area or volume using similar shapes examples
Example 7: finding an area or volume
These two figures are similar.
The area of shape A is 60 \; cm^2 .
Find the area of shape B:
Find the scale factor.
Use the given information to write a ratio and work out the scale factor.
When writing the ratios the order is very important.
\begin{aligned} \text{The ratio of the lengths is} \ \text{length} \; A&: \text{length} \; B\\\\ 5&:10\\\\ \text{which simplifies to} \quad 1&:2 \end{aligned}
The scale factor of enlargement from shape A to shape B is 2
Use the scale factor to find the missing value.
As we are finding an area we need to square the ratio of the lengths, and square the scale factor.
\begin{aligned} \text{The ratio of the lengths is -} \ \text{length} \ A&:\text{length} B\\\\ 1&:2\\\\ \text{The ratio of the areas is -} \ \text{area} \ A&:\text{area} \ B\\\\ 1^2&:2^2\\\\ \text{which simplifies to -}\ \ \ \ \ \ 1&:4 \end{aligned}
We can use the area scale factor 2^2 or 4 as a multiplier to find the missing area.
60\times 4=240
The area of shape B is 240 \; cm^2
Alternatively you can form an equation to solve:
Example 8: finding an area or volume
These two shapes are similar.
The volume of shape A is 400 \; cm^3 .
Find the volume of shape B:
Find the scale factor.
Use the given information to write a ratio and work out the scale factor.
When writing the ratios the order is very important.
\begin{aligned} \text{The ratio of the lengths is} \ \text{length } A&: \text{length } B\\\\ 10&:15\\\\ \text{which simplifies to} \quad 1&:1.5 \end{aligned}
The scale factor of enlargement from shape A to shape B is 1.5
Use the scale factor to find the missing value.
As we are finding a volume we need to cube the ratio of the lengths, and cube the scale factor.
\begin{aligned}
\text{The ratio of the lengths is -} \ \text{length} \ A&:\text{length} B\\\\
1&:1.5\\\\
\text{The ratio of the volumes is -} \ \text{volume} \ A&:\text{volume} \ B\\\\
1^3&:1.5^3\\\\
\text{which simplifies to -}\ \ \ \ \ \ 1&:3.375
\end{aligned}
We can use the volume scale factor 1.5^3 or 3.375 as a multiplier to find the missing volume.
400\times 3.375=1350
The volume of shape B is 1350 \; cm^3
Alternatively you can form an equation to solve:
Common misconceptions
- Take care with the order of ratios
Make sure that you are consistent with your ratios.
E.g.
In this example, always write the A value first, and then the B value.
1 : 3 and 2 : 6.
The ratios are equal, so these shapes are similar shapes.
- In most diagrams the diagrams are NOT drawn to scale
Often diagrams for questions involving similar shapes are NOT drawn to scale. So, use the measurements given, rather than measuring for yourself.
- Shapes can be similar but in different orientations
The second shape may be in a different orientation to the first shape. The shapes can still be similar.
E.g.
Here shape A and Shape B are similar.
Shape B is an enlargement of shape A by scale factor 2.
Here shape B has been rotated to make the similarity easier to see.
- Scaling up or down
If you are finding a missing length in the larger shape you can multiply by the scale factor. The scale factor will be a number greater than 1 .
If you are finding a missing length in the smaller shape you can multiply by the scale factor, but the scale factor will be a number between 0 and 1.
Practice similar shapes questions
1. Consider if these shapes are similar:
Yes – sides in ratio 1:4

No – sides in ratio 1:3 and 1:4

No – sides in ratio 1:3 and 1:2

Yes – sides in ratio 1:3

The shapes are similar as the ratio of the corresponding sides are the same.
The ratio of the bases is \;\; 3:9
which simplifies to \quad \quad \;\; 1:3
the ratio of the heights is \; 1:3
2. Consider if these shapes are similar:
Yes – sides in ratio 2:1

Yes – sides in ratio 3:1

No – sides in ratio 2:1 and 1:2

No – sides in ratio 3:1 and 2:1

The shapes are similar as the ratio of the corresponding sides are the same.
The ratio of the short sides is \;\; 4:2
which simplifies to \quad \quad \quad \quad \;2:1
the ratio of the long sides is \quad 8:4
which simplifies to \quad \quad \quad \quad \;2:1
3. These shapes are similar. Find the value of x.




The ratio of the bases is \;\; 6:12
which simplifies to \quad \quad \;\,1:2
The scale factor of enlargement is 2
x=5 \times 2 =104. These shapes are similar. Find the value of x.




The ratio of the bases is \;\; 6:9
which simplifies to \quad \quad \;\,1:\frac{9}{6}
or \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \;\;1:1.5
The scale factor of enlargement is 1.5
x=8 \times 1.5=125. Find the value of x.




Use the parallel lines to identify equal angles.
Then we can find pairs of corresponding sides.
The ratio of the corresponding sides is \;\; 4:12
which simplifies to \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \;\;\; 1:3
The scale factor of enlargement is \; 3
x=3 \times 3= 9
6. Find the value of x.




Use the parallel lines to identify equal angles.
Then we can find pairs of corresponding sides.
The ratio of the corresponding sides is \;\; 9:6
which simplifies to \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \quad \;\;\; 1:\frac{2}{3}
The scale factor of enlargement is \; \frac{2}{3}
x=12 \times \frac{2}{3}= 8
Similar shapes GCSE questions
1. Which shape is similar to shape X?
(1 mark)
Shape D
(1)
2. Triangles ABC and DEF are similar.
(a) Write down the size of angle y
(b) Work out the value of x
(3 marks)
(a)
y=56
(1)
(b)
x:11=4:8 the scale factor is \frac{1}{2}
(1)
x=11\times \frac{1}{2}=5.5(1)
3.
ABC and AED are straight lines.
BE is parallel to CD.
AD = 10.5 \;cm
AE = 7.5 \; cm
BE = 6.8 \; cm
Work out the length CD
(2 marks)
10.5\div 7.5=1.4
(1)
CD=6.8\times 1.4 = 9.52(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
- Compare lengths using ratio notation and/or scale factors
- Solve problems with similar shapes using ratio notation and/or scale factors
- Solve problem with areas and volumes using ratio notation and/or scale factors (HIGHER)
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.