High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
Primary data
Here you will learn about primary data, including what it is and how to use it in the statistical process.
Students first learn to work with primary data in 6 th grade and expand their knowledge and use of data as they progress through the grades.
What is primary data?
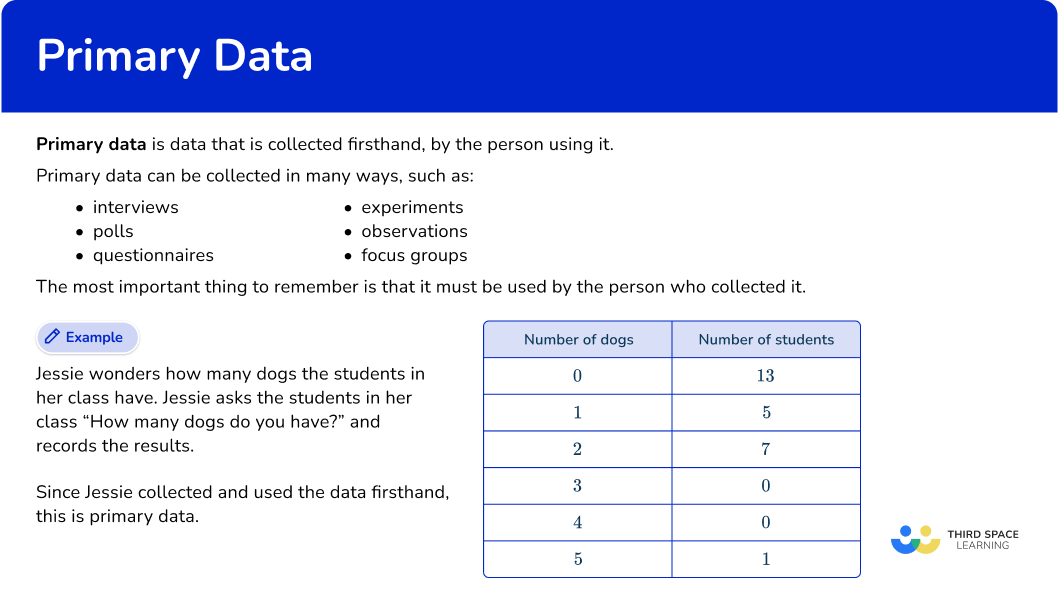
Primary data is data that is collected firsthand, by the person using it.
Primary data can be collected in many ways, such as:
- interviews
- polls
- questionnaires
- experiments
- observations
- focus groups
The most important thing to remember is that it must be used by the person who collected it.
Once the data has been collected, it can be graphed, which provides a visualization of the data.
For example,
Jessie wonders how many dogs the students in her class have. Jessie asks the students in her class “How many dogs do you have?” and records the results.
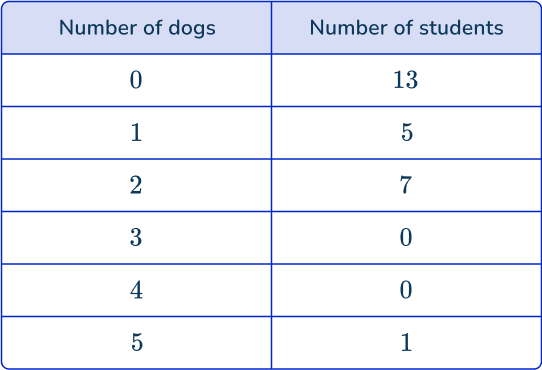
Since Jessie collected and used the data firsthand, this is primary data.
Once the data is collected, Jessie can use a bar graph to display it.
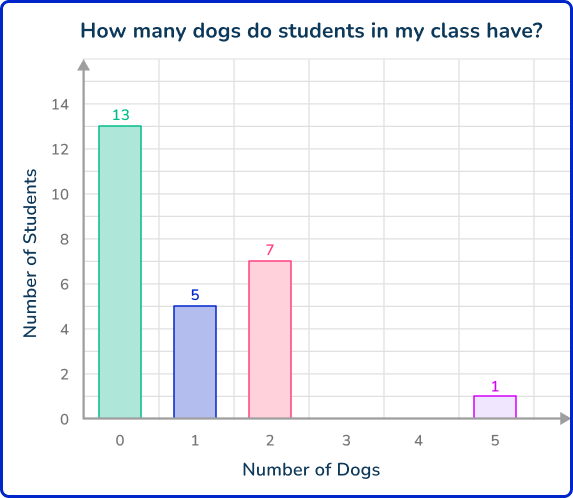
Now, Jessie can use the data in the table and the bar graph to answer questions like…
- What is the most common number of dogs? 0 dogs
- What is the most number of dogs? 5 dogs
- How many more students have 2 dogs than 1 dog? 2 students
What is primary data?
Common Core State Standards
How does this apply to 6 th grade math?
- Grade 6 – Statistics and Probability (6.SP.B.5a and 6.SP.B.5b)
Recognize a statistical question as one that anticipates variability in the data related to the question and accounts for it in the answers. For example, “How old am I?” is not a statistical question, but “How old are the students in my school?” is a statistical question because one anticipates variability in students’ ages.
- Grade 6 – Statistics and Probability (6.SP.B.5a and 6.SP.B.5b)
Summarize numerical data sets in relation to their context, such as by:
- Reporting the number of observations.
- Describing the nature of the attribute under investigation, including how it was measured and its units of measurement.
![[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Types-of-Data-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)
![[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Types-of-Data-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 to 7 students’ understanding of types of data. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th and 7th grade types of data topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Types-of-Data-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)
![[FREE] Types of Data Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/11/Types-of-Data-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 to 7 students’ understanding of types of data. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th and 7th grade types of data topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEHow to recognize primary data
In order to recognize primary data:
- Identify the data collected.
- Identify the source of the data and the user.
Primary data examples
Example 1: real world example of market research
Khalil works for a shoe company and was tasked with researching how many customers might buy again. He created a digital survey asking, “How likely are you to buy shoes from us again?” which appears on the website after a purchase.
The website creates a list of respondents and their answers. Khalil uses the data to prepare a report for his boss. Is this an example of primary data? Explain.
- Identify the data collected.
In this case, the data was collected through a digital survey and that asks customers to respond to the question “How likely are you to buy shoes from us again?”
2Identify the source of the data and the user.
The context tells us that Khalil created the question, took part in the data collection process and then completed the data analysis. Khali was involved with each step of the process, so this is an example of primary data.
Note: Primary data does not have to occur in-person. In this case, the primary data collection method was digital – an online survey.
Example 2: real world example of healthcare research
Dr. Adisa is a doctor trying to figure out the best pill to give patients with chronic pain. She looks at a study that used data from thousands of people who took different medications, checking how well they worked and their side effects.
Using the study’s results, Dr. Adisa chooses which pill to recommend. Is this an example of primary data? Explain.
Identify the data collected.
In this case, the data was collected in a study that measured how well different medicines worked for chronic pain and what their side effects were.
Identify the source of the data and the user.
The context tells us that Dr. Adisa used data from a study. It does not indicate that Dr. Adisa was involved in the study, so we will assume she was not.
This means Dr. Adisa was analyzing and using data she did not collect. This is not an example of primary data. In this example, Dr. Adisa used secondary data sources.
Example 3: real world example of healthcare research
Raelyn wants to create a video of advice from people who have lived in more than one country. She identifies a group of people and conducts personal interviews with each of them.
Then she compiles the best advice into a video and posts it on her social media accounts. Is this an example of primary data? Explain.
Identify the data collected.
In this case, the data was collected by personal interviews of people who had lived in more than one country.
Identify the source of the data and the user.
The context tells us that Raelyn identifies the group of people she wanted to collect data from. She also created the research questions and performed the interviews.
Raelyn then used the raw data to create a summary video. Since Raelyn’s data sets and data analysis used only primary sources, this is an example of primary data.
How to analyze primary data
In order to analyze primary data:
- Collect primary data.
- Choose a graph or measure of center to calculate.
- Answer questions based on the data analysis.
Example 4: collecting and analyzing data from a small group
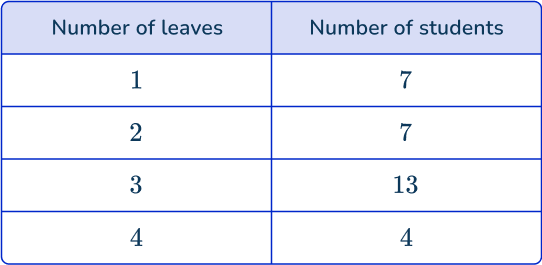
Scenario: Students in your class use leaves as a part of an art project. You wonder, “How many leaves did students in my class use for the art project?”
Collect primary data.
Ask each student in the class how many leaves they used and record the answers in a table.
Choose a graph or measure of center to calculate.
You decide to graph the different values on a pictograph.
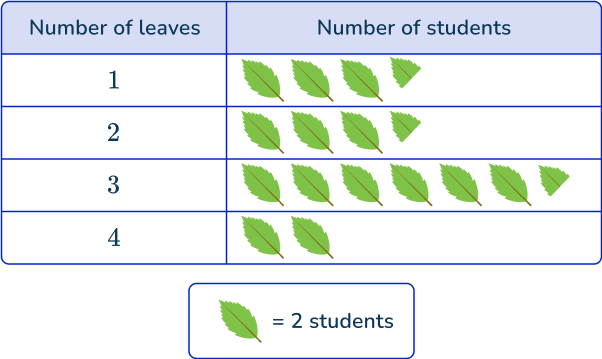
Answer the question based on the data analysis.
Some examples of questions we can answer with the data are:
- How many students used 3 leaves? 13 students
- How many more students used 1 leaf than 4 leaves? 7-4=3 students
- How many students completed the art project? 7+7+13+4=31 students
Note: This is an example of primary research, because the data collector is the one using the data.
Example 5: collecting and analyzing original data
Scenario: A grocery store keeps track of how many new products are sold each day.
Collect primary data.
They place the data from each day into a table.
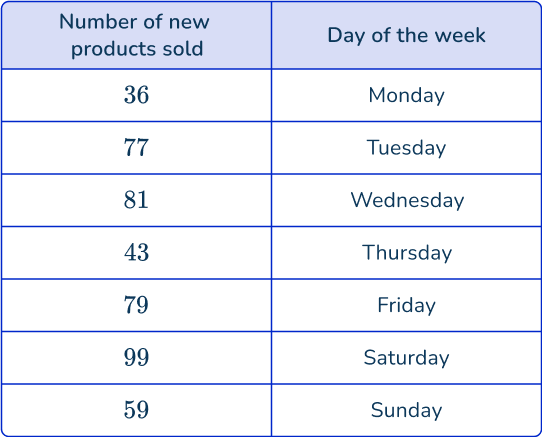
Note: This data gathering process is an example of primary data, since the store using the data is the same store collecting the data.
Choose a graph or measure of center to calculate.
You decide to graph the different values on a bar graph.
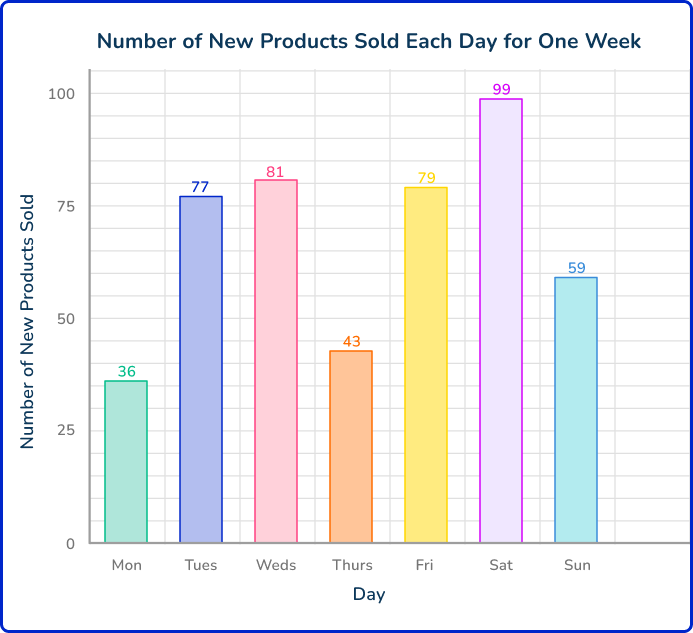
Answer the question based on the data analysis.
Some examples of questions we can answer with the data are:
- Which day sold the most new products? Saturday
- What was the difference between the new products sold on Tuesday and Thursday? 34
- Which day had the least amount of new products sold? Monday
Example 6: collecting and analyzing data from a research project
For a history class project, you need to answer the question “What year were my family members who are older than me born?”
Collect primary data.
Ask each family member older than you what year they were both and record the answers in a table.
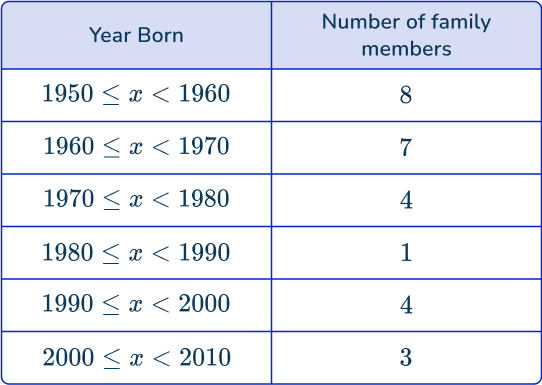
Choose a graph or measure of center to calculate.
You decide to graph the different values on a histogram.
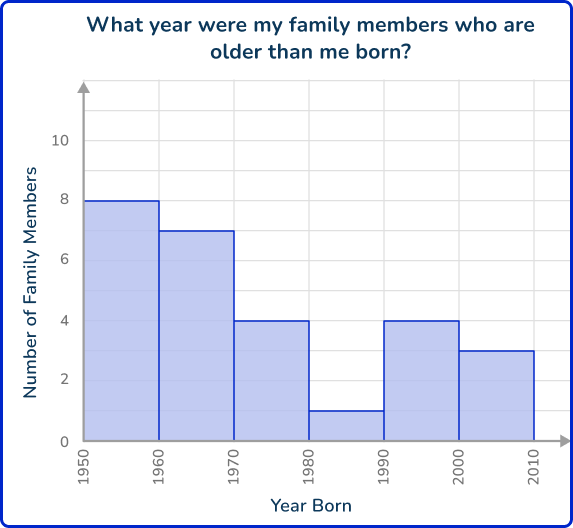
Answer the question based on the data analysis.
Some examples of questions we can answer with the data are:
- How many family members were surveyed? 27
- What is the most common decade? The 1950s
- What is the median decade? The 1960s
Teaching tips for primary data
- Introduce this topic by having students complete primary data collection for different types of data; both quantitative data and qualitative data.
- Make sure you choose activities and worksheets that expose students to different types of research design and methodology.
- Discuss the pros and cons of using primary data. For example, a con is that it can be time-consuming to collect your own data, since high-quality data collection is often an in-depth process.
- Give struggling students examples of primary data they can refer back to.
Easy mistakes to make
- Thinking all data is primary
Remember that reading about or using data is not the same as collecting it.
Always consider who collected the original research and whether it was specifically collected for the current research purpose.
- Incorrectly identifying the source of published surveys or data
Never assume surveys or other data published by other organizations are their primary data. It is possible the source that published the data was not the one that collected it.
Related types of data lessons
Practice primary data questions
1. Lorenzo is planning the research methods for her next project. He will gather data from various sources. Which source is an example of primary data?
Lorenzo will use the data from a survey another company completed last year.

Lorenzo will collect data from 5 books written by various authors.

Lorenzo will randomly choose 5 people and complete case studies.

Lorenzo will randomly choose 5 different businesses and collect data from their public tax information.

Let’s look at each source of data:
- Lorenzo will use the data from a survey another company completed last year.
- NOT primary data, since Lorenzo did not complete the survey.
- Lorenzo will collect data from 5 books written by various authors.
- NOT primary data, since Lorenzo is using books written by other people.
- Lorenzo will randomly choose 5 people and complete case studies.
- This IS primary data, since Lorenzo is the one collecting the data directly from the sources.
- Lorenzo will randomly choose 5 different businesses and collect data from their public tax information.
- This is NOT primary data, since this data was previously collected by others for a different reason.
2. Amara is planning the research methods for her next project. She will gather data from various sources. Which source is an example of primary data?
Amara will interview 10 patients about their experiences with a new treatment.

Amara will analyze reports from a health organization published last year.

Amara will use statistics from three government studies on public health.

Amara will review data from medical journals about past clinical trials.

Let’s look at each source of data…
- Amara will interview 10 patients about their experiences with a new treatment.
- This IS primary data, since Amara is the one collecting the data directly from the sources.
- Amara will analyze reports from a health organization published last year.
- This is NOT primary data, since Amara did not collect the data in the reports.
- Amara will use statistics from three government studies on public health.
- This is NOT primary data, since Amara is using data she did not collect herself.
- Amara will review data from medical journals about past clinical trials.
- This is NOT primary data, since Amara is collecting her data from the work of others.
3. Which is NOT an example of primary data?
A restaurant surveys customers about their dining experience.

A researcher analyzes data from a government report on unemployment rates.

Researchers collect data from volunteers during a clinical trial.

A biologist observes and records bird behavior in the wild.

Let’s look at each source of data…
- A restaurant surveys customers about their dining experience.
- This IS primary data, since the restaurant is collecting the data themselves.
- A researcher analyzes data from a government report on unemployment rates.
- This is NOT primary data, since the researcher is using data that came from the work of others.
- Researchers collect data from volunteers during a clinical trial.
- This IS primary data, since the researchers are collecting the data themselves.
- A biologist observes and records bird behavior in the wild.
- This IS primary data, since the biologist is collecting the data themselves.
4. Syrus asked each student in 8 th grade whether they were going on the field trip. Syrus created the following graph from the data:
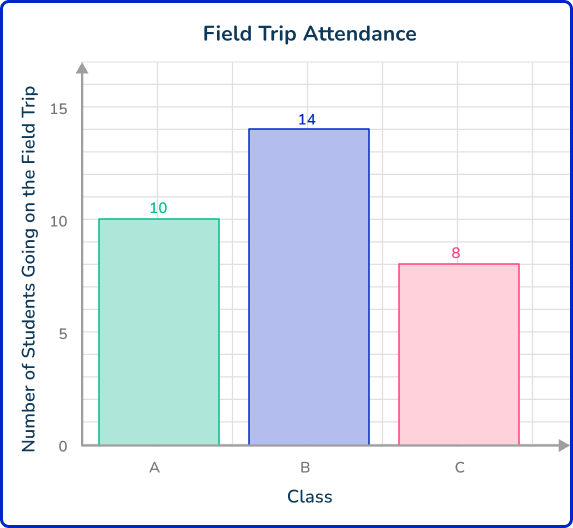
Why is this an example of primary data?
The data was collected offline.

The research process involved a graph.

The sample size was small.

The data was collected by Syrus.

Primary data is data that is collected firsthand, by the person using it.
This is an example of primary data because Syrus collected the data himself.
Primary data can be collected offline, but it can also be collected online. It may involve graph, but this is not a requirement. Primary data can involve small or large samples or the entire population.
5. Berk used the data from a weather website to create the following graph:
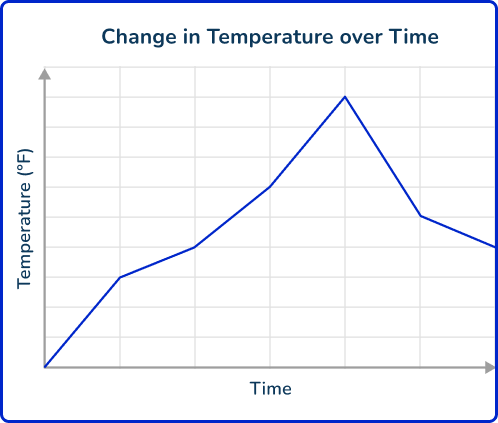
Why is this NOT an example of primary data?
Berk is using data collected by someone else.

Only one data source was used for the graph.

The graph does not have numbers labeled on the axes.

Berk needs to include a table along with the graph.

Primary data is data that is collected firsthand, by the person using it.
This is NOT an example of primary data because Berk did not collect the data that he is using.
Primary data can have only one data source and the graph of primary data may or may not have numbers labeled on the axes.
6. Pablo collected data on how many slices of pizza each person ate at his birthday party.
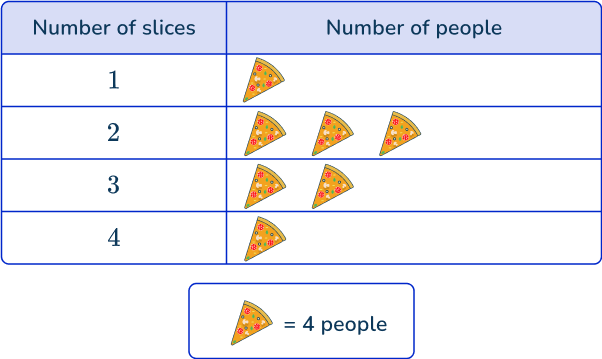
How many more people ate exactly 2 slices than exactly 4 slices?




Each pizza represents 4 people.
So 12 people had exactly 2 slices and 4 people had exactly 4 slices.
12 slices – \; 4 slices =8 slices
Primary data FAQs
Primary data is used to address specific research needs and research objectives. It helps gather firsthand information tailored to the study’s focus. By collecting types of primary data, such as surveys or experiments, researchers can analyze the effectiveness of interventions and make informed decisions.
Secondary research involves analyzing existing data collected for other purposes. It is used to gather insights for specific research questions by reviewing sources like reports, studies, or historical data, rather than collecting real-time data.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!