[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
2D shapes
Here you will learn about 2D shapes, including the attributes of various 2D shapes and symmetry.
Students first learn about 2D shapes in kindergarten and first grade with their work in geometry, identifying and classifying shapes by their properties.
They expand their knowledge of 2D shapes as they progress through elementary and middle school.
What are 2D shapes?
2D shapes are flat shapes that can be drawn on a flat surface (or plane).
They have two dimensions, length and width, and have no thickness.
2D shapes can be grouped by the dimensions they have.
Here are some familiar 2D shapes.

Polygons
Polygons are 2D shapes made from straight lines that meet at points called vertices.
There are two different types of polygons.
| Regular polygons | Irregular polygons |
|---|---|
Regular polygons have equal side Equilateral Triangle  Square  Regular Hexagon  | Irregular polygons do not have all equal Right Triangle  Rectangle  Irregular Hexagon  |
Step-by-step guide: Polygons
Step-by-step guide: Regular polygons
Step-by-step guide: Irregular polygons
Symmetry
Symmetry is when an object can be divided into equal halves, where the two halves are mirror images of each other.
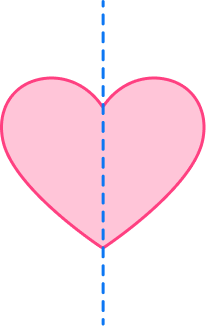
| Line symmetry |
|---|
Line symmetry is when an object can be divided in half with the two halves being |
Square A square has 4 lines of symmetry. 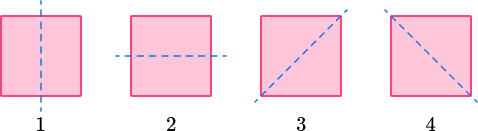 |
Equilateral Triangle An equilateral triangle has 3 lines of symmetry. 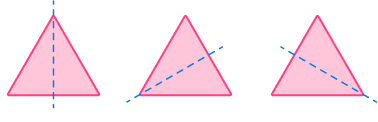 |
Trapezoid This trapezoid is not a regular polygon and has only 1 line of symmetry. 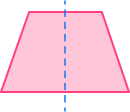 |
Step-by-step guide: Line symmetry
Step-by-step guide: Symmetry
![[FREE] 2D Shape Worksheet (Grade 2 to 4)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/2D-shapes-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] 2D Shape Worksheet (Grade 2 to 4)
![[FREE] 2D Shape Worksheet (Grade 2 to 4)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/2D-shapes-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your 2nd, 3rd, and 4th grade students’ understanding of 2D shape. 10+ questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] 2D Shape Worksheet (Grade 2 to 4)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/2D-shapes-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
[FREE] 2D Shape Worksheet (Grade 2 to 4)
![[FREE] 2D Shape Worksheet (Grade 2 to 4)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/2D-shapes-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image.png)
Use this quiz to check your 2nd, 3rd, and 4th grade students’ understanding of 2D shape. 10+ questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEProperties of 2D Shapes
Let’s look at the properties of some of the most common 2D Shapes.
| Name of polygon | Properties of polygon |
|---|---|
Equilateral triangle  |
● 3 vertices |
Square  |
● 4 vertices |
Regular pentagon  |
● 5 vertices |
Regular hexagon  |
● 6 vertices |
Regular octagon  |
● 8 vertices |
Step-by-step guide: Pentagon (coming soon)
Step-by-step guide: Hexagon shape
Step-by-step guide: How to draw a hexagon
Step-by-step guide: Octagon (coming soon)
What are 2D shapes?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to kindergarten – 5 th grade math?
- Kindergarten: Geometry ( K.G.A.3)
Identify shapes as two-dimensional (lying in a plane, “flat”) or three-dimensional (“solid”).
- Grade 1: Geometry (1.G.A.2)
Compose two-dimensional shapes (rectangles, squares, trapezoids, triangles, half circles, and quarter-circles) or three-dimensional shapes (cubes, right rectangular prisms, right circular cones, and right circular cylinders) to create a composite shape and compose new shapes from the composite shape.
- Grade 2: Geometry (2.G.A.1)
Recognize and draw shapes having specified attributes, such as a given number of angles or a given number of equal faces. Identify triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, and cubes.
- Grade 4: Geometry (4.G.A.3)
Recognize a line of symmetry for a two-dimensional figure as a line across the figure such that the figure can be folded along the line into matching parts. Identify line-symmetric figures and draw lines of symmetry.
- Grade 5: Geometry (5.G.B.4)
Classify two-dimensional figures in a hierarchy based on properties.
How to use 2D Shapes
There are a lot of ways to use 2D shapes. For more specific step-by-step guides, check out the individual pages linked in the “What are 2D shapes?” section above or read through the examples below.
In order to identify a 2D shape, a polygon, or a regular polygon.
- Recall the definition.
- Explain how the 2D shape fits the definition.
2D shapes examples
Example 1: identifying polygons
What type of 2D shape is a stop sign?

- Recall the definition.
A stop sign is a polygon with 8 sides.
2Explain how the 2D shape fits the definition.
Polygons that have 8 sides are called octagons. So, a stop sign is an octagon.
Example 2: identifying a polygon
Is a circle a polygon?
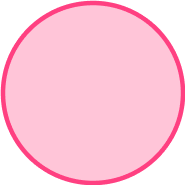
Recall the definition.
A polygon is a 2D shape made up of straight lines that meet at points called vertices.
Explain how the 2D shape fits the definition.
A circle is a 2D shape, but it is not made up of straight lines, so it is not a polygon.
Example 3: identifying polygons
Is a pentagon a polygon?

Recall the definition.
A polygon is a 2D shape made up of straight lines.
Explain how the 2D shape fits the definition.
A pentagon is a 2D shape made up of straight lines, so it is a polygon.
Example 4: regular / irregular polygons
Is the parallelogram a regular polygon?

Recall the definition.
Regular polygons have equal side lengths and equal interior angles.
Explain how the 2D shape fits the definition.
The parallelogram does not have equal side lengths and does not have equal interior angles, so it is not a regular polygon.
Example 5: symmetry
How many lines of symmetry does this rectangle have?

Recall the definition.
Line symmetry is when an object can be divided in half, with the two halves being mirror images or reflections of each other.
Explain how the 2D shape fits the definition.
In this case, the rectangle can be divided down the middle vertically and across the middle horizontally.
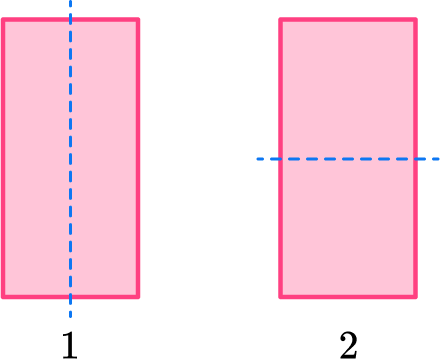
So there are 2 lines of symmetry.
Example 6: symmetry
Name the shape.
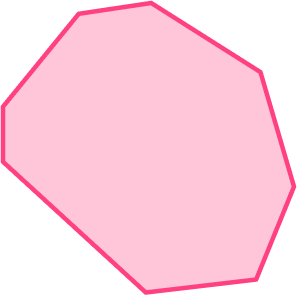
Recall the definition.
Octagons are polygons with 8 sides.
Irregular polygons are polygons that do not have equal sides and equal angles.
Explain how the 2D shape fits the definition.
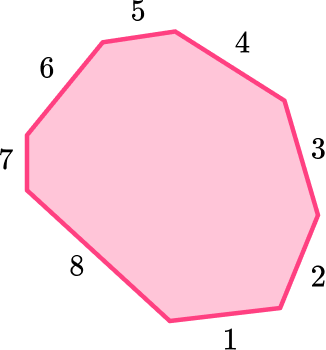
The shape is an octagon because it has eight sides and eight angles. The sides and the angles are not equal, so it is also an irregular polygon. The shape is an irregular octagon.
Teaching tips for 2D shapes
- Instead of relying on worksheets, use manipulatives and real world objects in class so that students can see and understand the different shapes.
- Link art projects to 2D shapes and symmetry so that students can apply the math to creative projects.
- Provide students with cut-outs of the actual shapes so that they can measure the side lengths and angle measurements to develop their understanding of regular shapes versus irregular shapes.
- Include in lesson plans math centers where your learners can rotate through various 2D shape activities that are comprised of hands-on activities with pattern blocks, shape flashcards, and digital activities with math games so that students can learn shapes and their attributes.
- Reinforce essential vocabulary as it pertains to the geometrical shapes so students can recall the shapes names and see how they are used in real life.
Easy mistakes to make
- Confusing the different shapes
For example, thinking that a pentagon is a hexagon or vice versa.
- Thinking that a rectangle is a regular polygon
Squares are the only regular quadrilaterals. Rectangles have the same interior angles, but they do not have the same side lengths.
- Thinking that figures can’t have more than one line of symmetry
2D shapes can have more than one line of symmetry or no lines of symmetry.
- Rotational symmetry/lines of symmetry
Lines of symmetry are often confused with rotational symmetry. A line of symmetry on a two-dimensional shape divides the shape equally into two symmetrical pieces. Rotational symmetry is the number of times a shape fits into itself when rotated around its center.
- Thinking that an irregular hexagon is not a hexagon
If students have too much exposure to regular hexagons and not enough of irregular hexagons, they may believe that a regular hexagon is the only type of hexagon. Be sure to vary their exposure to hexagonal shapes and give them opportunities to work with and draw hexagons that are not regular. This applies to all other types of polygons as well.
Practice 2D shapes questions
1. Which figure below represents a regular polygon?


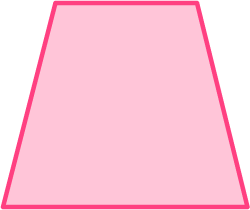

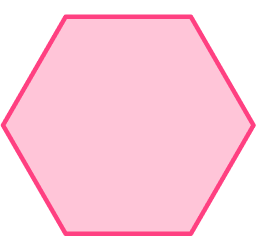

Regular polygons have equal side lengths and equal interior angles.
The only figure that has equal side lengths and equal interior angles is the regular hexagon.
2. Which polygon has 5 vertices?
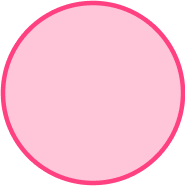



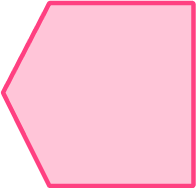

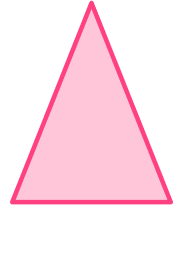

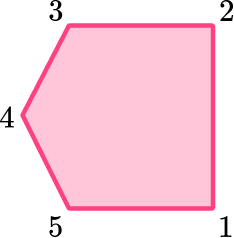
The pentagon has five vertices.
The vertices are the corners of the shape.
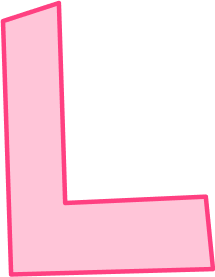
3. Which 2D shape is an irregular hexagon?
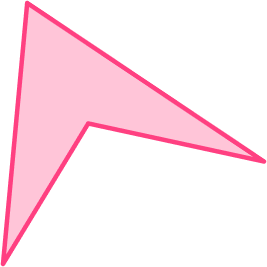

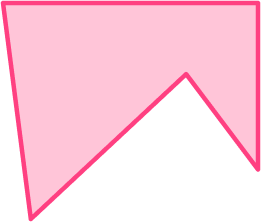

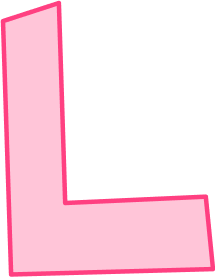


An irregular hexagon is a 6 sided shape that does not have equal side lengths or equal interior angles.
This polygon was the only one with 6 sides.
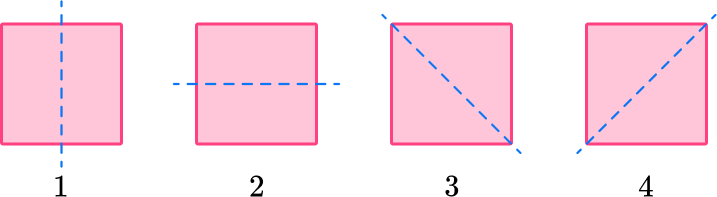
4. Which shape has 4 lines of symmetry?






A square is a regular polygon with four equal sides and four equal interior angles.
So it will have four lines of symmetry.
A rectangle will only have two lines of symmetry, a kite and a parallelogram have no lines of symmetry.
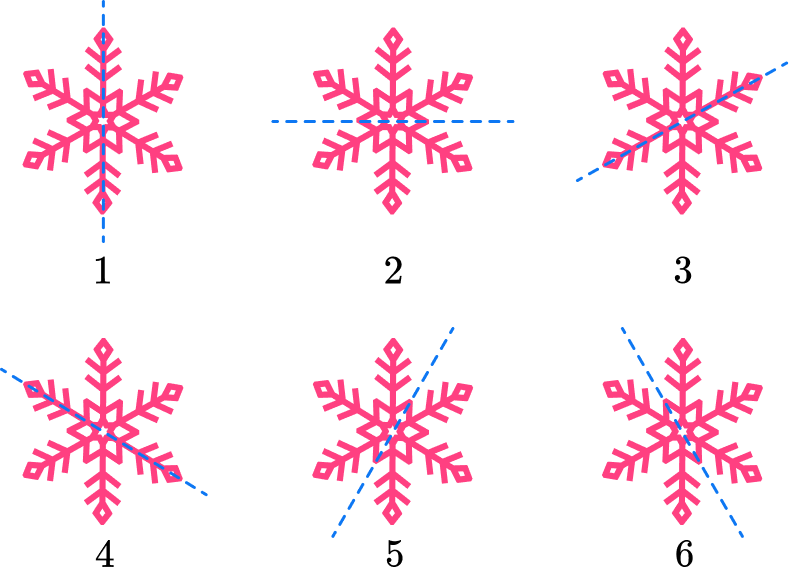
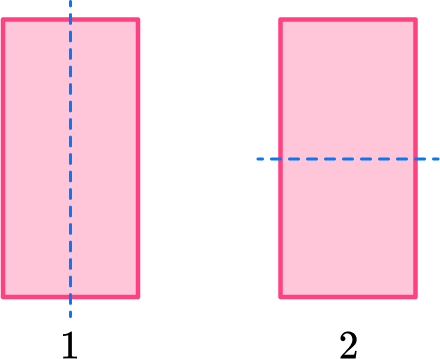
5. How many lines of symmetry does this 2D figure have?





By definition, line symmetry is when an object can be divided in half, with the two halves being mirror images or reflections of each other.
In this case, the snowflake has six lines of symmetry.

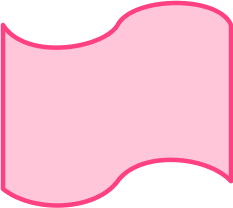
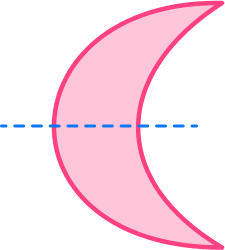
6. Which of the following shapes has only two lines of symmetry?








No lines of symmetry.
Two lines of symmetry
No lines of symmetry
One line of symmetry
2D shapes FAQs
By definition, polygons are enclosed 2D shapes made up of straight lines that meet at points. If a shape has a curved line edge, it will not be a polygon.
Perimeter is the distance around the shapes, so you can just add up the side lengths. The area is the space within the shapes. There are various formulas you will learn to find the areas of shapes such as triangles, squares, rectangles, and parallelograms.
The sum of the interior angles of a polygon is always the number of sides minus 2 times 180 . You will learn this as you move into high school.
A cuboid is another name for a cube, which are 3D shapes where each face is a square.
A rhombus is a parallelogram, so opposite sides are equal and opposite sides are parallel, and in addition to that, all four sides are equal.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
