High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Multiplication Decimals Fractions How to write a ratioUnit rate math
Here you will learn about unit rate math problems, including the rates that involve whole numbers, decimals, integers, and fractions, and how to use unit rate math to make comparisons between rates.
Students will first learn about unit rate math problems as part of ratios and proportions in 6 th grade and 7 th grade.
What is unit rate math?
Unit rate math problems involve creating equivalent ratios where one part of the ratio is 1. A rate is a ratio comparison of different units that can be used to create different quantities.
For example,
The rate of 500 miles to 2 hours, can be used to create the unit rate of 250 miles per hour or mph. In this case, the original rate is 500\text{:}2 and the equivalent unit rate is 250\text{:}1.
Unit rates are also a key part of converting between different measurement systems.
For example,
The conversions 1 foot =12 inches or 100 centimeters =1 meter are examples of unit rates that can be used for problems involving measurement.
Let’s look at a few examples of solving unit rate math problems below.
For example,
A bag of 5 apples costs \$ 6.00. What is the price per apple?
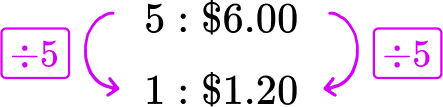
The original rate is 5 to \$ 6.00. To find the price per apple ( 1 apple), both sides of the rate are divided by 5, leaving the equivalent ratio 1 to \$ 1.20. Each apple costs \$ 1.20.
Unit rates can also be used to compare different quantities to decide things like, which rate is cheaper.
For example,
A grocery store sells 3 pounds of green apples for \$ 2.34 and 2 pounds of red apples for \$ 1.86. Which apples have the better unit price?
Unit price means the price per 1 unit. In this case, the units are pounds of apples.
Divide each side of the green apples rate by 3, to create a rate for 1 pound of green apples.
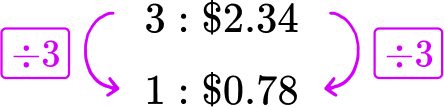
Each pound of green apples costs \$ 0.78.
Divide each side of the red apples rate by 2, to create a rate for 1 pound of red apples.
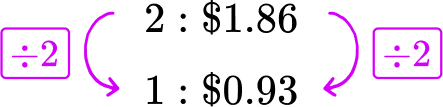
Each pound of red apples costs \$ 0.93.
The green apples have a better unit price, because they cost less per pound than the red apples.
What is unit rate math?
![[FREE] Unit Rate Worksheet (Grade 6 and 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Grade-6-to-8-Unit-rate-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Unit Rate Worksheet (Grade 6 and 7)
![[FREE] Unit Rate Worksheet (Grade 6 and 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Grade-6-to-8-Unit-rate-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your 6th and 7th grade students’ understanding of unit rate. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Unit Rate Worksheet (Grade 6 and 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Grade-6-to-8-Unit-rate-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Unit Rate Worksheet (Grade 6 and 7)
![[FREE] Unit Rate Worksheet (Grade 6 and 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/11/Grade-6-to-8-Unit-rate-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your 6th and 7th grade students’ understanding of unit rate. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREECommon Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6 th grade math and 7 th grade math?
- Grade 6 – Ratios and Proportional Relationships (6.RP.A.2)
Understand the concept of a unit rate \cfrac{a}{b} associated with a ratio a\text{:}b with b≠ 0, and use rate language in the context of a ratio relationship. For example, “This recipe has a ratio of 3 cups of flour to 4 cups of sugar, so there is \cfrac{3}{4} cup of flour for each cup of sugar.” “We paid \$ 75 for 15 hamburgers, which is a rate of \$ 5 per hamburger.”
- Grade 6 – Ratios and Proportional Relationships (6.RP.A.3b)
Solve unit rate problems including those involving unit pricing and constant speed. For example, if it took 7 hours to mow 4 lawns, then at that rate, how many lawns could be mowed in 35 hours? At what rate were lawns being mowed?
- Grade 7 – Ratios and Proportional Relationships (7.RP.A.1)
Compute unit rates associated with ratios of fractions, including ratios of lengths, areas and other quantities measured in like or different units. For example, if a person walks \cfrac{1}{2} mile in each \cfrac{1}{4} hour, compute the unit rate as the complex fraction \cfrac{\cfrac{1}{2}}{\cfrac{1}{4}} miles per hour, equivalently 2 miles per hour.
How to solve unit rate math problems
In order to solve unit rate math problems:
- Write the original rate.
- Use multiplication or division to create a unit rate.
- Use the unit rate to answer the question.
Unit rate math examples
Example 1: unit rate calculation – whole number
6 snack bars cost \$ 18. If all the bars cost the same, what is the price per bar?
- Write the original rate.
6 snack bars cost \ \$ 18 → 6 \text{:}\$ 18
2Use multiplication or division to create a unit rate.
The price ‘per bar’ refers to 1 bar. Divide each side of the rate by 6, to create a rate for 1 bar.
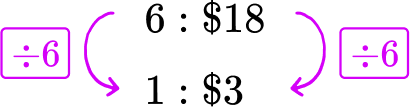
3Use the unit rate to answer the question.
One bar costs \$ 3.
Example 2: unit rate calculation – decimal
A car travels 256 miles in 5 hours. If the car travels the same number of miles each hour, what is the miles per hour rate?
256 miles in 5 hours → 256\text{:}5
The miles ‘per hour’ refers to 1 hour. Divide each side of the rate by 5, to create a rate for 1 hour.
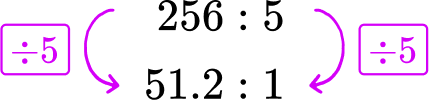
The car travels 51.2 miles each hour.
Example 3: unit rate calculation – mixed number
A recipe calls for 3 cups of sugar and 4 cups of flour. What is the rate of cups of flour per cup of sugar?
3 cups of sugar and 4 cups of flour → 3\text{:}4
The cups of flour ‘per cup of sugar’ refers to 1 cup of sugar. Divide each side of the rate by 3, to create a rate for 1 cup of sugar.
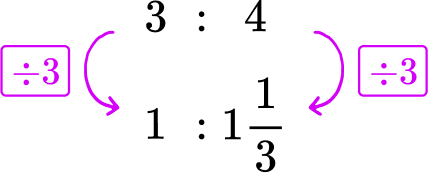
There are 1 \cfrac{1}{3} cups of flour for every cup of sugar.
Example 4: unit rate comparison – decimals
A grocery store sells 3 pounds of green grapes for \$ 3.72 and 4 pounds of purple grapes for \$ 4.80. Which has the better unit price?
3 pounds of green grapes for \$ 3.72 → 3\text{:}\$ 3.72
4 pounds of purple grapes for \$ 4.80 → 4\text{:}\$ 4.80
Unit price means the price per 1 unit. In this case, the units are pounds of grapes.
Divide each side of the green grapes rate by 3, to create a rate for 1 pound of green grapes.
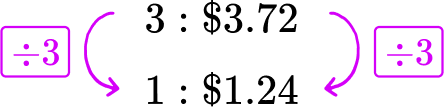
Divide each side of the purple grapes rate by 4, to create a rate for 1 pound of purple grapes.
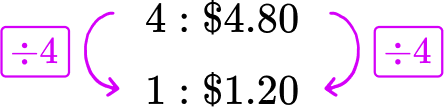
The green grapes cost \$ 1.24 per pound. The purple grapes cost \$ 1.20 per pound, which is less. The purple grapes have a better unit price.
Example 5: unit rate comparison – integers
Temperature gauge A changed by -49 degree in 7 hours. Temperature gauge B changed by -80 degrees in 10 hours. Which gauge showed a slower degree change in temperature per hour?
-49 degree in 7 hours → -49\text{:}7
-80 degrees in 10 hours → -80\text{:}10
The degree change in temperature ‘per hour’ refers to 1 hour. Divide each side of the gauge A rate by 7, to create a rate for 1 hour.
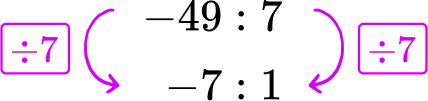
Divide each side of the gauge B rate by 10, to create a rate for 1 hour.
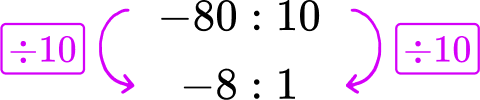
Gauge A dropped 7 degrees each hour. Gauge B dropped 8 degrees each hour.
Gauge A had a slower degree change per hour.
Example 6: unit rate calculation – fractions
Kai walks 1 \cfrac{1}{2} miles in \cfrac{3}{4} of an hour. If his rate is steady, how many miles does Kai walk in 1 hour?
1 \cfrac{1}{2} miles in \cfrac{3}{4} of an hour → 1 \cfrac{1}{2}\text{:}\cfrac{3}{4}
To create the rate for 1 hour, you need to go from \cfrac{3}{4} to 1. This can be done with division or multiplication:
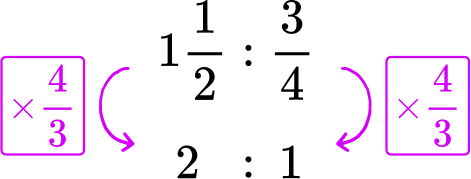
See also: Multiplying fractions
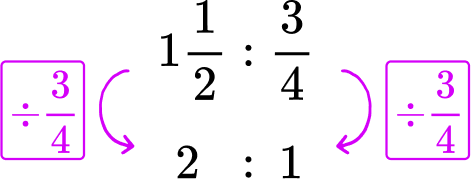
See also: Dividing fractions
Kai walks 2 miles in 1 hour.
Example 7: unit rate comparison – fractions
A sink leaks \cfrac{1}{3} of a cup of water every 5 minutes. A shower leaks \cfrac{2}{5} of a cup of water every 8 minutes. Which leaks faster per minute?
\cfrac{1}{3} of a cup every 5 minutes → \cfrac{1}{3}\text{:}5
\cfrac{2}{5} of a cup every 8 minutes → \cfrac{2}{5}\text{:}8
The leak rate ‘per minute’ refers to 1 minute. Divide each side of the sink rate by 5, to create a rate for 1 minute.
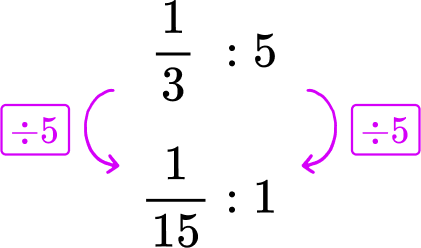
*Note: You can also multiply each side by \cfrac{1}{5}.
Multiply each side of the shower rate by \cfrac{1}{8}, to create a rate for 1 minute.
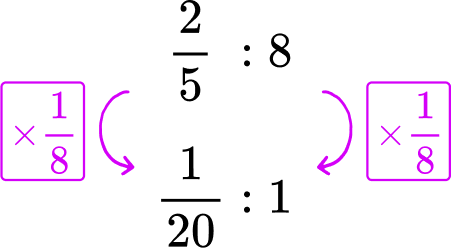
*Note: You can also divide each side by 8.
The sink leaks \cfrac{1}{15} of a cup per minute. The shower leaks \cfrac{1}{20} of a cup per minute.
The sink has a faster leak rate per minute.
Teaching tips for unit rate math
- The topic unit rate has endless real-world connections, so it is easy to introduce it through a relevant example and continue to bring in new real world examples as students progress in their understanding.
- Worksheets can be useful, but be sure to include worksheets that include word problems and a variety of solving strategies.
- Students who are struggling may find a step-by-step guide helpful, like the one provided on this page.
Easy mistakes to make
- Calculating the wrong unit rate
For example, if 10 tennis balls cost \$ 5, the price per ball would be \$ 5 \div 10=\$ 0.50.
An alternative would be to calculate 10 \div 5=2, which is the number of balls per dollar.
Each solving method is correct, but they solve for different unit rates. Always pay attention to which unit rate you are being asked to find.
- Adding and subtracting to find a unit rate
Ratios and rates represent a multiplicative relationship, so multiplication or division can be used to calculate equivalent rates. Adding or subtracting will lead to the incorrect unit rate.
Practice unit rate math questions
1. A grocery store is selling 8 watermelons for \$ 16. What is the per price watermelon?




8 watermelons cost \$ 16 → 8\text{:}\$ 16
The price ‘per watermelon’ refers to 1 watermelon. Divide each side of the rate by 8, to create a rate for 1 watermelon.
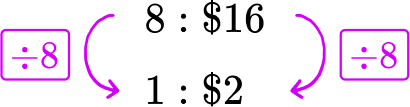
One watermelon costs \$ 2.
2. A boat travels 58 miles in 3 hours. If the boat drove a consistent speed, how many miles did it travel per hour?
19 miles

18 miles

19 \cfrac{1}{3} miles

18 \cfrac{2}{3} miles

58 miles in 3 hours → 58\text{:}3
The miles ‘per hour’ refers to 1 hour. Divide each side of the rate by 3, to create a rate for 1 hour.
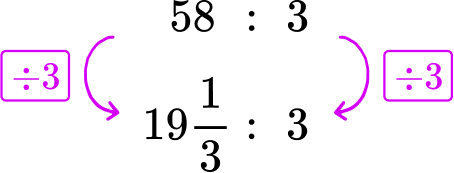
The boat travels 19 \cfrac{1}{3} miles per hour.
3. A pizza shop has 3 different offers. Which one is the cheapest per pizza?
Offer \textbf{A} \hspace{1cm} Offer \textbf{B} \hspace{1cm} Offer \textbf{C}
3 pizzas \hspace{1cm} 5 pizzas \hspace{1cm} 15 pizzas
\$ 24 \hspace{1.5cm} \$ 35 \hspace{1.6cm} \$ 135
Offer A

Offer B

Offer C

All offers are the same price per pizza

Offer A : 3 pizzas for \$ 24 → 3\text{:}\$ 24
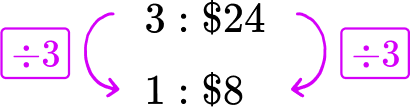
Each pizza in Offer A costs \$ 8.
Offer B : 5 pizzas for \$ 35 → 5\text{:}\$ 35
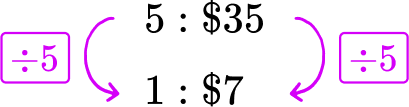
Each pizza in Offer B costs \$ 7.
Offer C : 15 pizzas for \$ 135 → 15\text{:}\$ 135
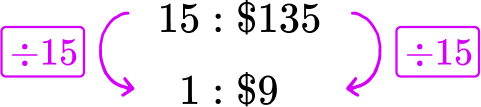
Each pizza in Offer C costs \$ 9.
Offer B has the cheapest cost per pizza.
4. A shop is selling the same pens in two different packs.
Which pack is better value for money and how much cheaper is it per pen?
Pack \textbf{A} : 2 pens cost \$ 3.20
Pack \textbf{B} : 3 pens cost \$ 4.65
Pack A ; it is \$ 0.05 cheaper per pen

Pack B ; it is \$ 0.50 cheaper per pen

Pack A ; it is \$ 0.50 cheaper per pen

Pack B ; it is \$ 0.05 cheaper per pen

Pack A : 2 pens for \$ 3.20 → 2\text{:}\$ 3.20
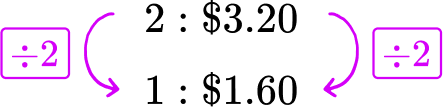
Each pen in Pack A costs \$ 1.60.
Pack B : 3 pens for \$ 4.65 → 3\text{:}\$ 4.65
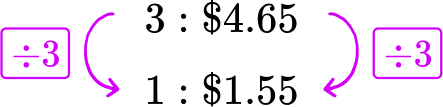
Each pen in Pack B costs \$ 1.55.
\$1.60-\$1.55 = \$0.05.
Pack B costs \$ 0.05 cheaper than Pack A.
5. \cfrac{2}{3} of an ounce of water evaporates every \cfrac{3}{5} of a second. What is the rate of evaporation per second?
2 ounces per second

\cfrac{9}{10} ounces per second

1 \cfrac{1}{9} ounces per second

\cfrac{2}{5} ounces per second

\cfrac{2}{3} of an ounce of water every \cfrac{3}{5} of a second → \cfrac{2}{3}\text{:} \cfrac{3}{5}.
The rate ‘per second’ refers to 1 second. Divide each side of the rate by \cfrac{3}{5}, to create a rate for 1 second.
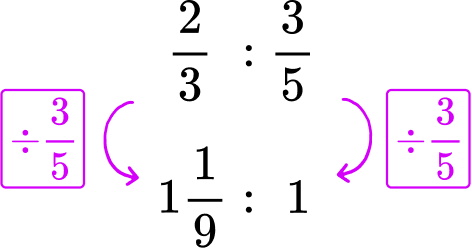
*Note: You can also multiply each side by \cfrac{5}{3}.
1 \cfrac{1}{9} ounces of water evaporates every second.
6. Machine A creates \cfrac{2}{3} of a blanket every 3 minutes. Machine B creates \cfrac{2}{5} of a blanket every 5 minutes. What is the rate of minutes per sweater for the fastest machine?
11 minutes on Machine B

2 minutes on Machine A

4 \cfrac{1}{2} minutes on Machine A

12 \cfrac{1}{2} minutes on Machine B

Machine A : \cfrac{2}{3} of a blanket every 3 minutes → \cfrac{2}{3}\text{:} 3
Machine B : \cfrac{2}{5} of a blanket every 5 minutes → \cfrac{2}{5}\text{:} 5
Divide each side of the Machine A rate by \cfrac{2}{3}, to create a rate for 1 minute.
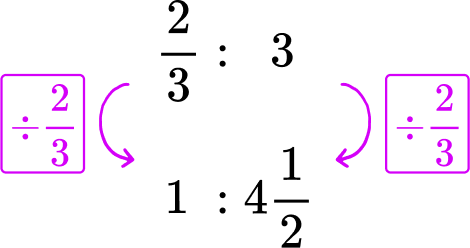
*Note: You can also multiply each side by \cfrac{3}{2}.
Machine A makes one sweater in 4 \cfrac{1}{2} minutes.
Divide each side of the Machine B rate by \cfrac{2}{5}, to create a rate for 1 minute.
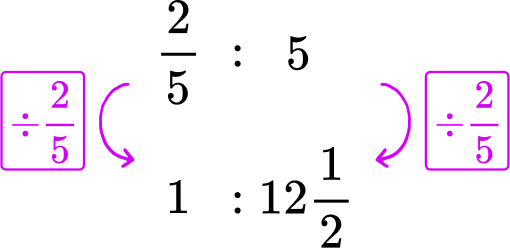
*Note: You can also multiply each side by \cfrac{5}{2}.
Machine B makes one sweater in 12 \cfrac{1}{2} minutes.
Unit rate math FAQs
In middle school, solving unit rate begins with rates involving whole numbers. This sometimes leads to fractional unit rates, but not always (as shown in examples 1\text{-}3 on this page).
Then the topic progresses to include rates with rational numbers, including rates with the original number of units as decimals, integers and fractions. Working with these rates requires solving rational operations to calculate the unit rate (as shown in examples 4\text{-}8 on this page).
Yes, the numerator would represent the unit rate and denominator would be 1.
When working with linear graphs in pre-algebra, the unit rate is the slope of a line.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!