High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Multiplication and division 2D shapes QuadrilateralCenter of dilation
Here you will learn about the center of dilation, including how to enlarge or reduce a shape about a point. You will also learn about fractional scale factors and negative scale factors.
Students will first learn about the center of dilation as part of geometry in 8 th grade.
What is the center of dilation?
The center of dilation is the fixed point from which all points of a figure are resized in a dilation.
A dilation is a type of transformation where you change the size of the original shape to make it bigger or smaller by multiplying it by a scale factor while keeping the same proportions.
To use a center of dilation, you need to draw lines from the center of dilation through the vertices of the original shape. These are called ray lines.
For example,
Here, triangle ABC has been enlarged by scale factor 2 about a center of dilation point O. The new triangle is labeled A’B’C’.
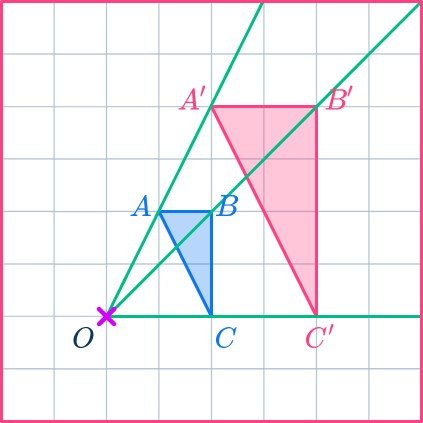
The lengths of the sides of the dilated image are double the lengths of the sides of the original shape.
The pairs of corresponding sides are parallel lines.
The angles in the two shapes are the same and the triangles are similar triangles (or similar figures).
For example,
Here, triangle ABC has been reduced by scale factor \cfrac{1}{3} about a center of dilation point O.
If a scale factor is between 0 and 1, the shape becomes smaller. The new triangle is labeled A’B’C’.
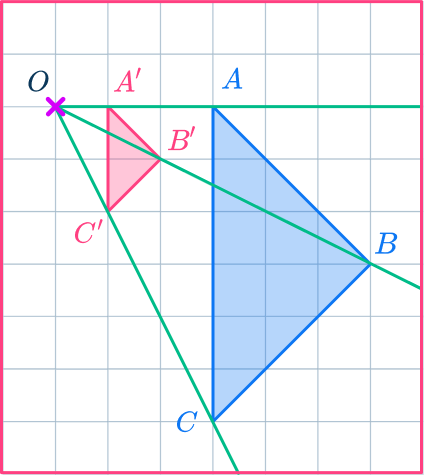
The lengths of the sides of the dilated triangle are a third of the lengths of the sides of the original triangle.
The pairs of corresponding sides are parallel lines.
The angles in the two shapes are the same and the triangles are similar triangles.
![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)
![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 8 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents. 40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)
![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 8 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents. 40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
DOWNLOAD FREENegative scale factors
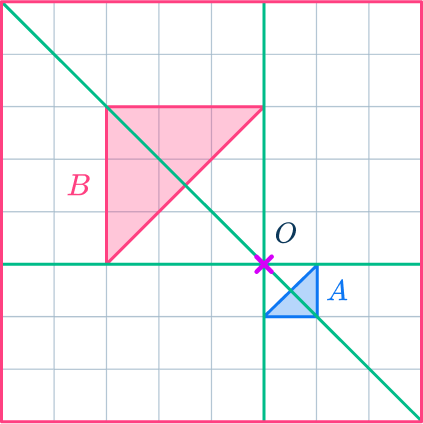
Negative scale factors produce an image on the other side of the center of dilation with the shape upside down.
Negative scale factors are in the higher grade levels only. These are an extension of positive scale factors.
For example,
Triangle A has been enlarged by scale factor - \, 3 about the point O.
What is the center of dilation?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 8 th grade math and high school math?
- Grade 8 – Geometry (8.G.A.3)
Describe the effect of dilations, translations, rotations, and reflections on two-dimensional figures using coordinates.
- High School – Geometry – Similarity, Right Triangles, & Trigonometry (HS.G.SRT.A.1a)
A dilation takes a line not passing through the center of the dilation to a parallel line, and leaves a line passing through the center unchanged.
- High School – Geometry – Similarity, Right Triangles, & Trigonometry (HS.G.SRT.A.1b)
The dilation of a line segment is longer or shorter in the ratio given by the scale factor.
How to enlarge or reduce a shape using a center of dilation
In order to enlarge or reduce a shape using a center of dilation:
- Draw a ray line.
- Mark the new point.
- Mark the other new points.
- Complete the shape.
Center of dilation examples
Example 1: on a grid
Enlarge the triangle ABC by scale factor 2 about the point O.
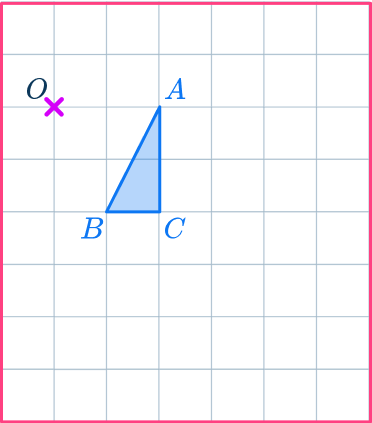
- Draw a ray line.
Choose a point to start with. Point A is a good place to start as it is across from the center of dilation, point O. Draw a ray line from point O through point A and extend the line.
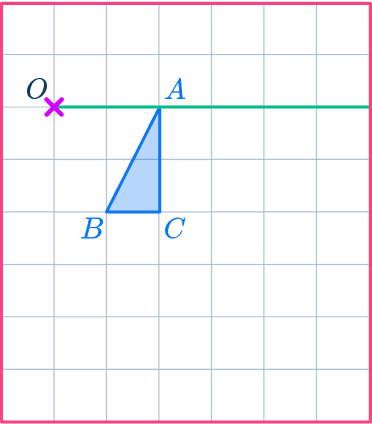
2Mark the new point.
Measure the distance from point O to point A.
Multiply the distance by the scale factor 2.
Measure this new distance from point O and put a mark for the new point.
OA’=2\times OA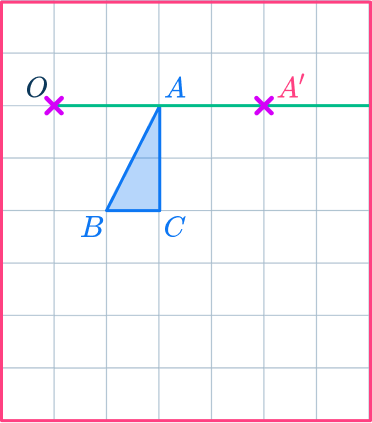
3Mark the other new points.
Draw ray lines going through point B and point C.
Measure the distances of these points from the center of dilation, point O.
Multiply the distances by the scale factor 2.
Measure these new distances from point O and put marks for the new points.
OB’=2\times OB OC’=2\times OC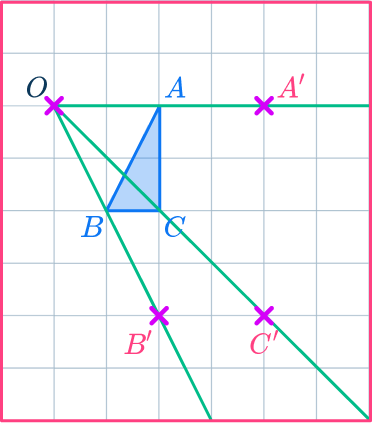
4Complete the shape.
Join up the points to make the new triangle A’B’C’.
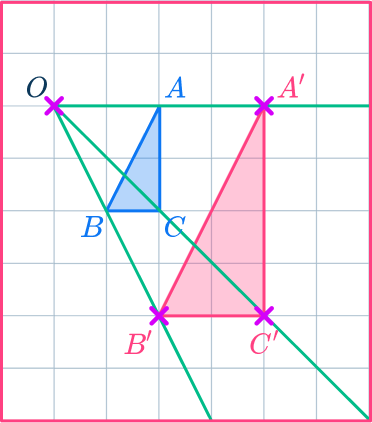
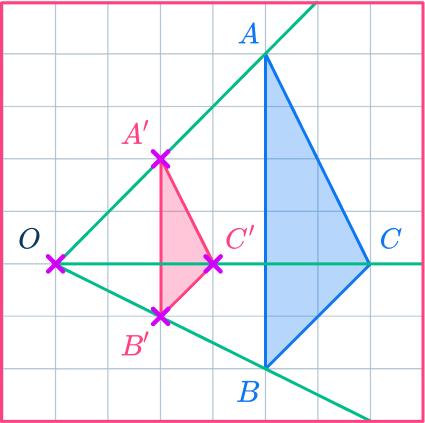
Example 2: on a grid
Reduce triangle ABC by scale factor \cfrac{1}{2} about the point O.
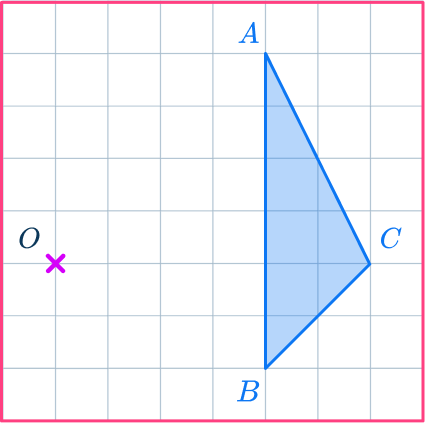
Draw a ray line.
Choose a point to start with. Point C is a good place to start as it is across from the center of dilation, point O.
Draw a ray line from point O through point C and extend the line.
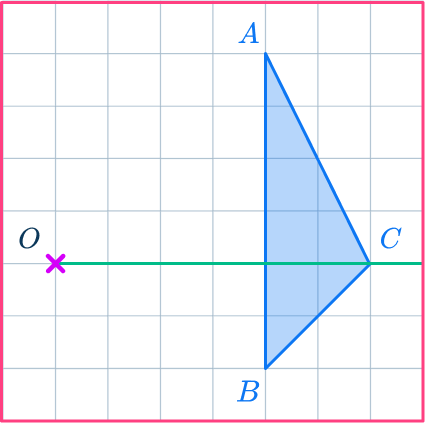
Mark the new points.
Measure the distance from point O to point C.
Multiply the distance by the scale factor \cfrac{1}{2} (or divide by 2 ).
Measure this new distance from point O and put a mark for the new point.
OC’=\cfrac{1}{2}\times OC
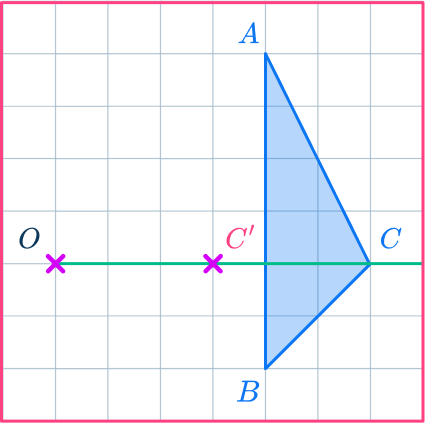
Mark the other new points.
Draw ray lines going through point A and point B.
Measure the distances of these points from the center of dilation, point O.
Multiply the distances by the scale factor \cfrac{1}{2}.
Measure these new distances from point O and put marks for the new points.
OA’=\cfrac{1}{2}\times OA
OB’=\cfrac{1}{2}\times OB
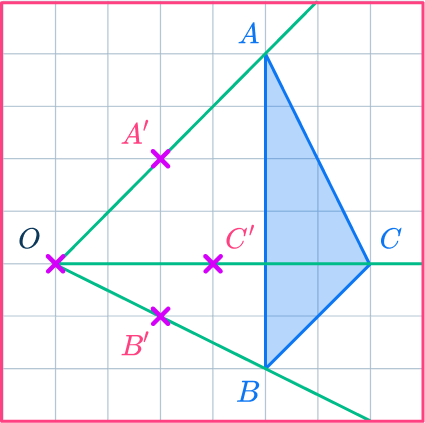
Complete the shape.
Join up the points to make the new triangle A’B’C’.
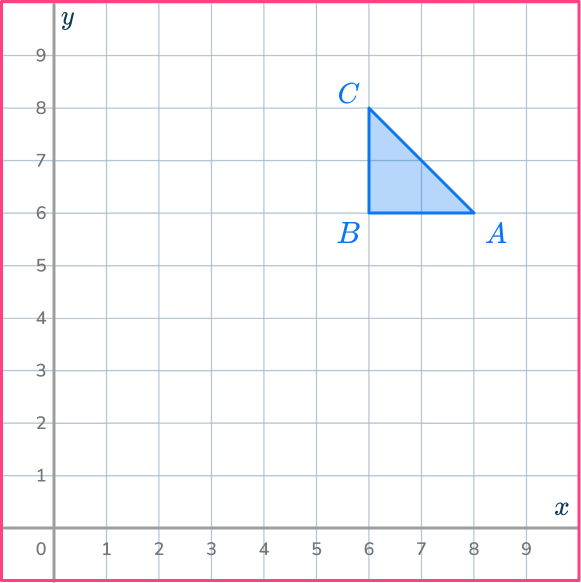
Example 3: on a coordinate plane
Enlarge the triangle ABC by scale factor 3 about the point P \, (8,8).
Mark the center of dilation.
On the diagram mark the center of dilation. The center of dilation is point P.
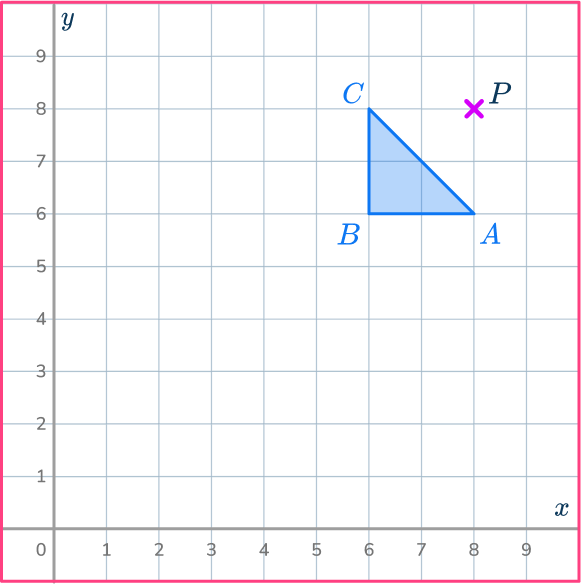
Draw a ray line.
Choose a point to start with.
Point A is a good place to start as it is straight down from the center of dilation, point P.
Draw a ray line from point P through point A and extend the line.
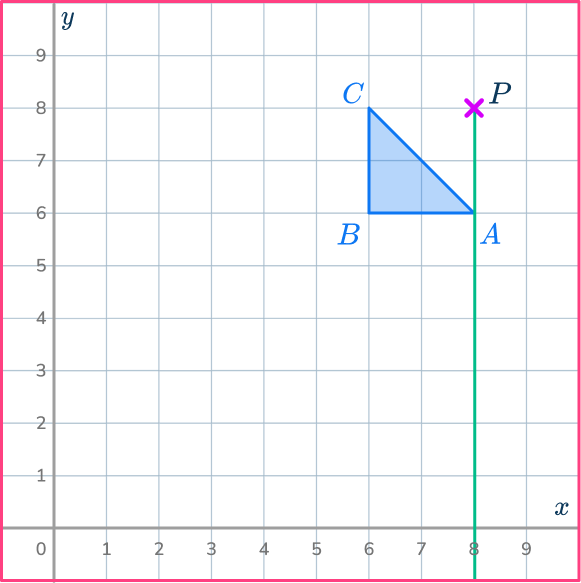
Mark the new point.
Measure the distance from point P to point A.
Multiply the distance by the scale factor 3.
Measure this new distance from point P and put a mark for the new point.
PA’=3\times PA
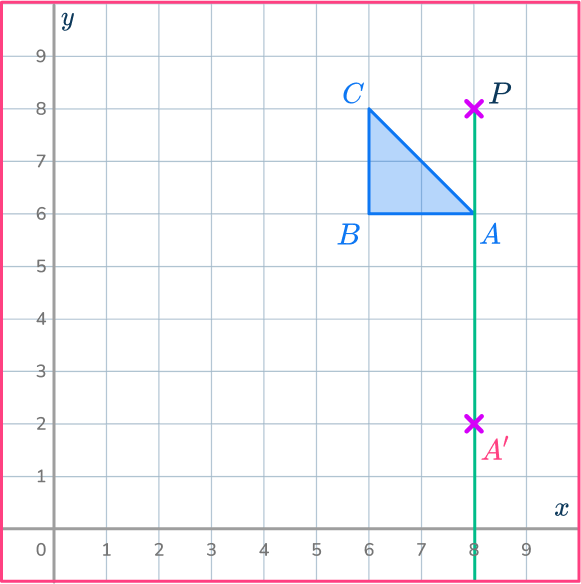
Mark the other new points.
Draw ray lines going through point B and point C.
Measure the distances of these points from the center of dilation, point P.
Multiply the distances by the scale factor 3.
Measure these new distances from point P and put marks for the new points.
PB’=3\times PB
PC’=3\times PC
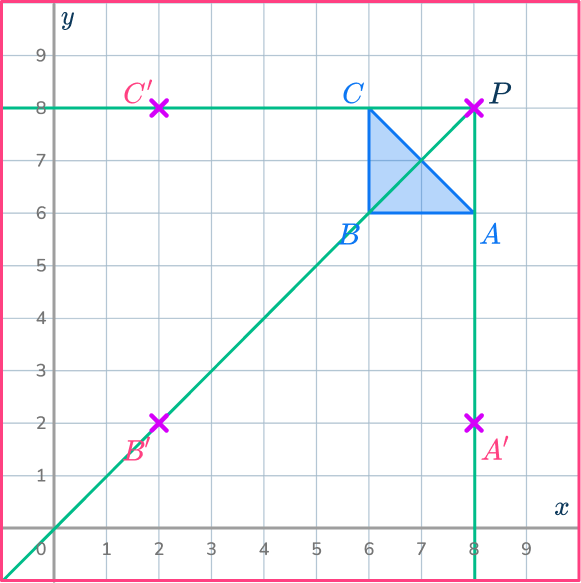
Complete the shape.
Join up the points to make the new triangle A’B’C’.
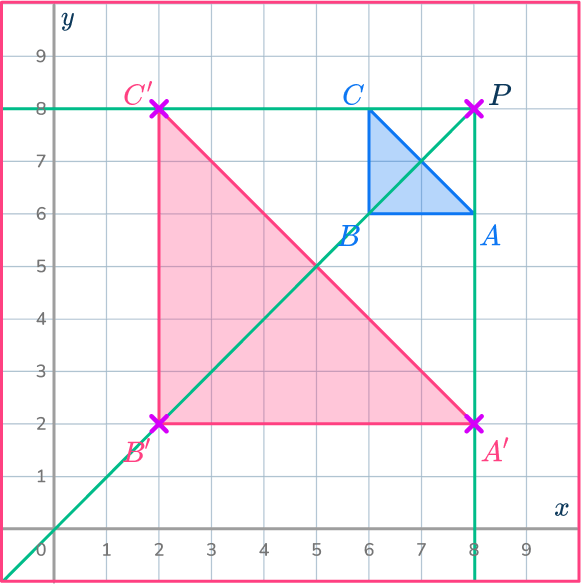
Example 4: on a coordinate plane
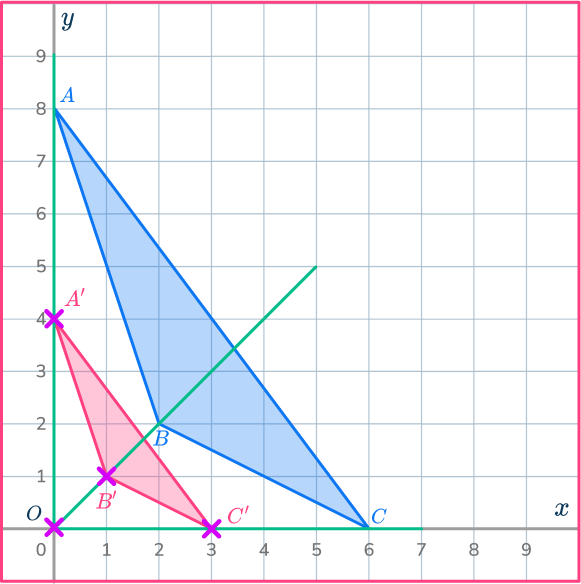
Reduce the triangle ABC by scale factor \cfrac{1}{2} about O.
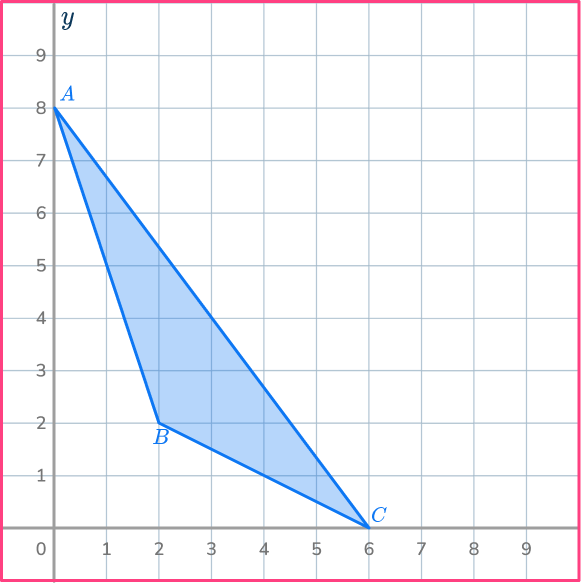
Mark the center of dilation.
On the diagram mark the center of dilation.
The center of dilation is point O, the origin.
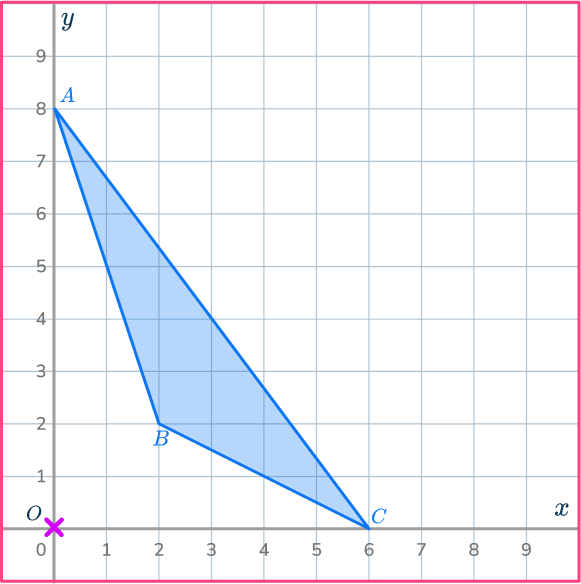
Draw a ray line.
Choose a point to start with.
Point A is a good place to start as it is straight up from the center of dilation, point O.
Draw a ray line from point O through point A and extend the line.
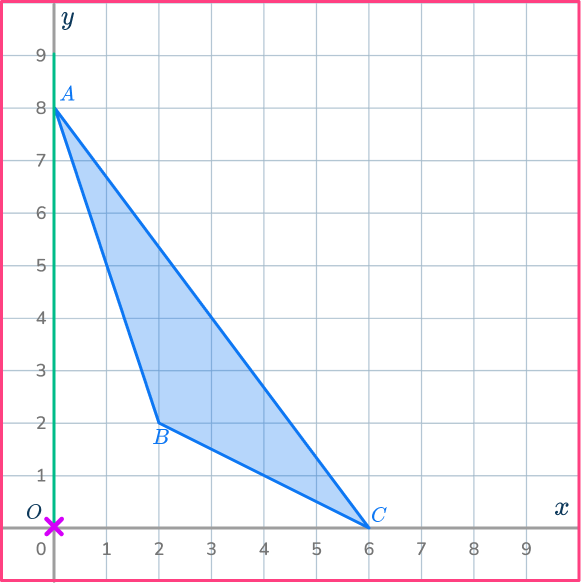
Mark the new point.
Measure the distance from point O to point A.
Multiply the distance by the scale factor \cfrac{1}{2}.
Measure this new distance from point O and put a mark for the new point.
OA’=\cfrac{1}{2}\times OA
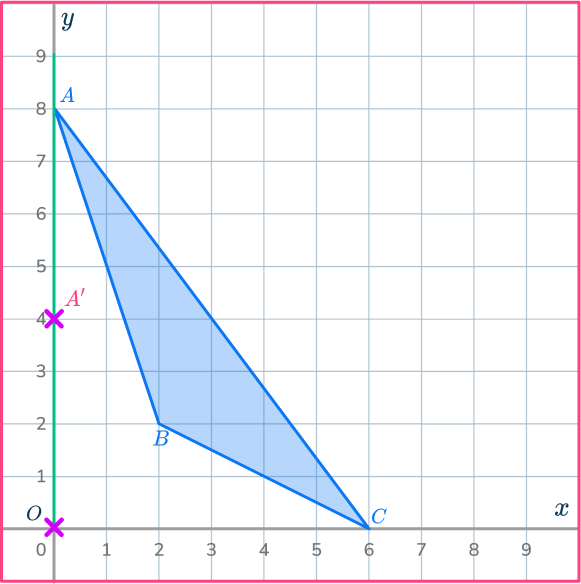
Mark the other new points.
Draw ray lines going through point B and point C.
Measure the distances of these points from the center of dilation, point O.
Multiply the distances by the scale factor \cfrac{1}{2}.
Measure these new distances from point O and put marks for the new points.
OB’=\cfrac{1}{2}\times OB
OC’=\cfrac{1}{2}\times OC
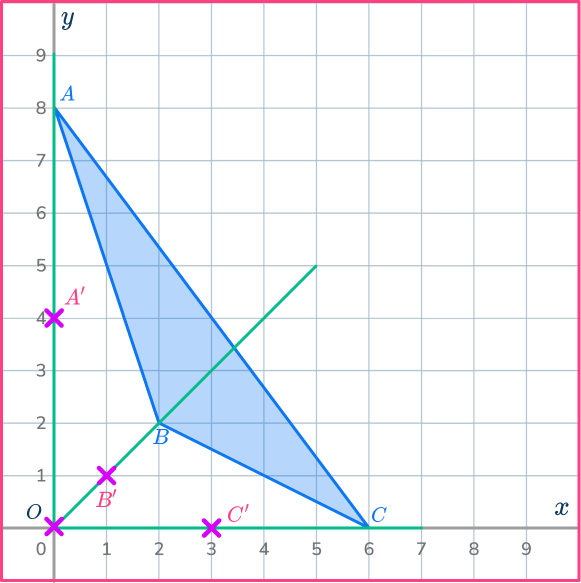
Complete the shape.
Join up the points to make the new triangle A’B’C’.
How to find a center of dilation
In order to find a center of dilation:
- Draw a ray line through a pair of points.
- Draw more ray lines.
- Write down the coordinates of the center of dilation.
Example 5: find a center of dilation
Triangle A has been enlarged to make triangle B.
Find the center of dilation.
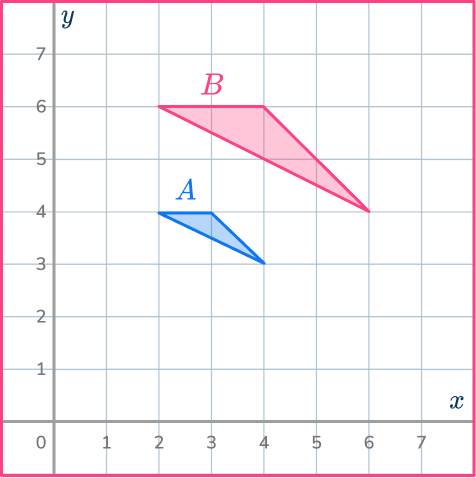
Draw a ray line through a pair of points.
Find a pair of corresponding vertices and draw a ray line going through the points.
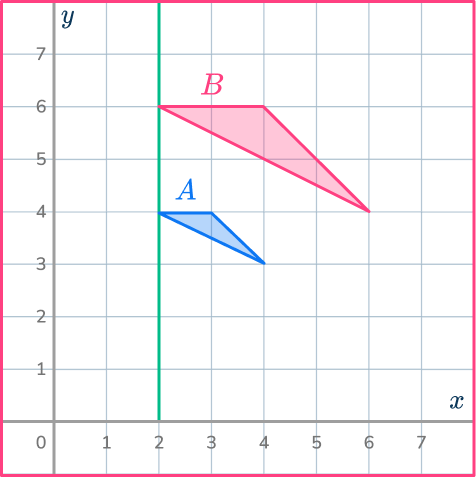
Draw more ray lines.
Find more pairs of corresponding vertices. Draw ray lines through the pairs of points.
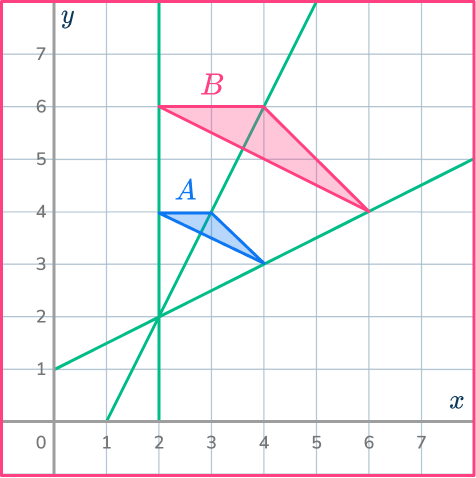
Write down the coordinates of the center of dilation.
The point at which your ray lines meet will be the center of dilation.
The center of dilation is (2,2).
You may also be asked to find the scale factor of dilation. For this example, the scale factor of dilation is 2. You can calculate the scale factor by choosing a pair of corresponding sides and dividing the enlarged length by the original length.
scale \, factor = \cfrac{enlarged \, length}{ original \, length}=\cfrac{2}{1}=2
Example 6: find a center of dilation
Triangle A has been reduced to make triangle B.
Find the center of dilation.
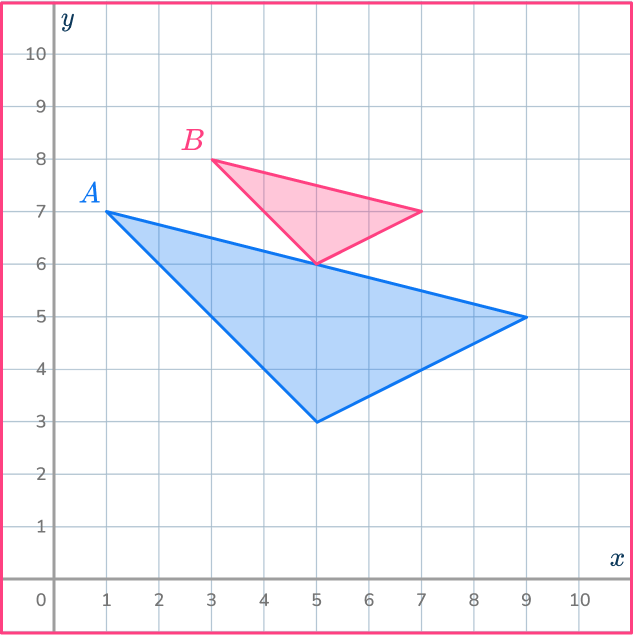
Draw a ray line through a pair of points.
Find a pair of corresponding vertices and draw a ray line going through the points.
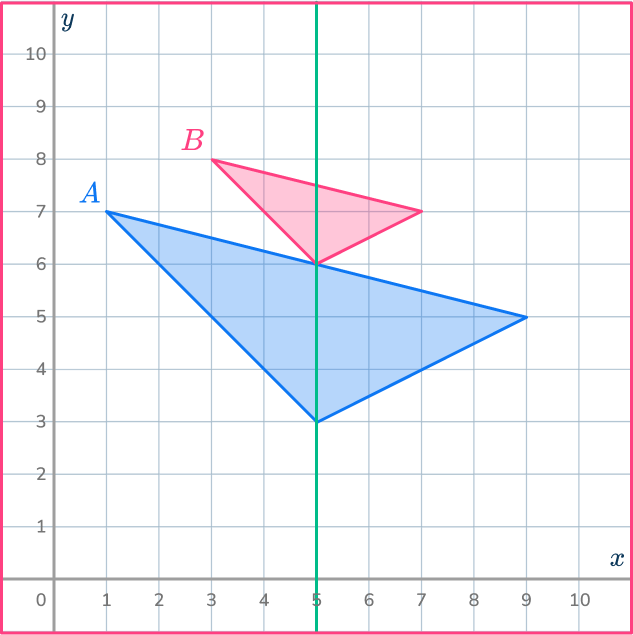
Draw more ray lines.
Find more pairs of corresponding vertices. Draw ray lines through the pairs of points.
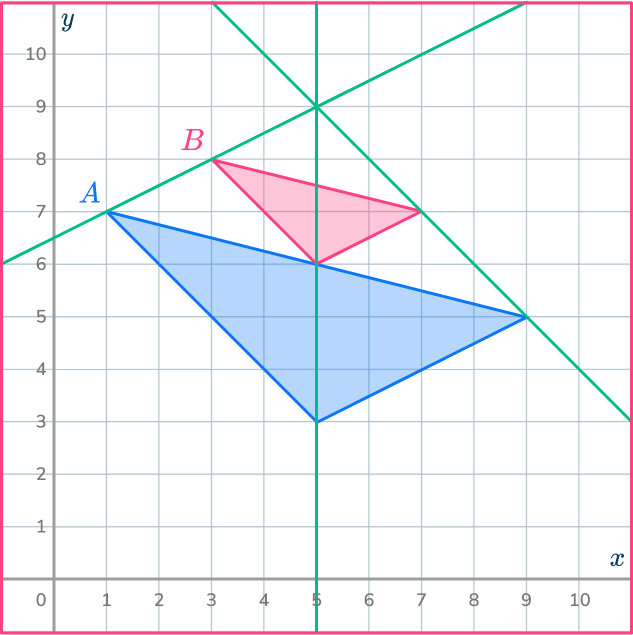
Write down the coordinates of the center of dilation.
The point at which your ray lines meet will be the center of dilation.
The center of dilation is (5,9).
How to enlarge or reduce a shape using a negative scale factor (ADVANCED)
In order to enlarge or reduce a shape using a center of dilation on a coordinate plane:
- Draw a ray line.
- Mark the new point.
- Mark the other new points.
- Complete the shape.
Example 7: negative scale factor
Enlarge the triangle ABC by scale factor - \, 2 about the point O.
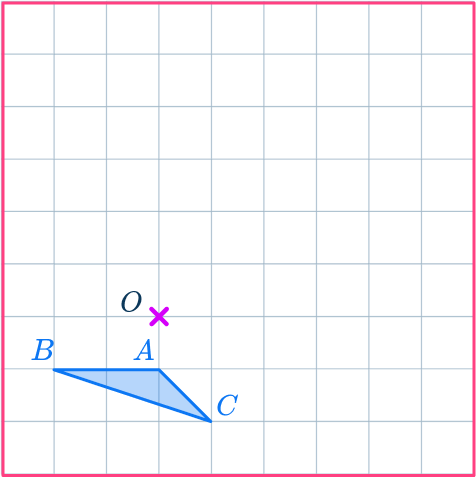
Draw a ray line.
Choose a point to start with.
Point A is a good place to start as it is straight down from the center of dilation, point O.
Draw a ray line from point A through point O and extend the line back through the center of dilation.
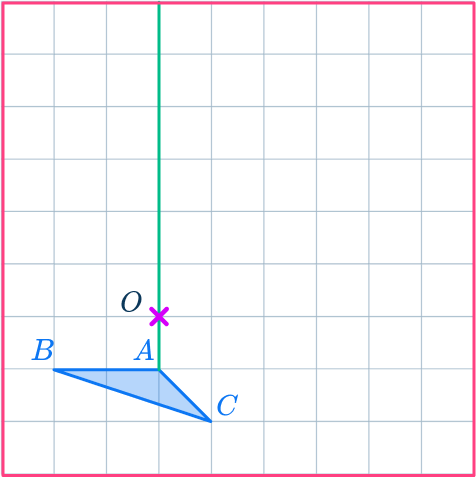
Mark the new point.
Measure the distance from point O to point A.
Multiply the distance by 2, but since the scale factor is negative 2 you mark the point A’ measuring backwards along the ray line from point O.
The ray line is like a number line where you have positive and negative numbers with 0 in between.
OA’=- \, 2\times OA
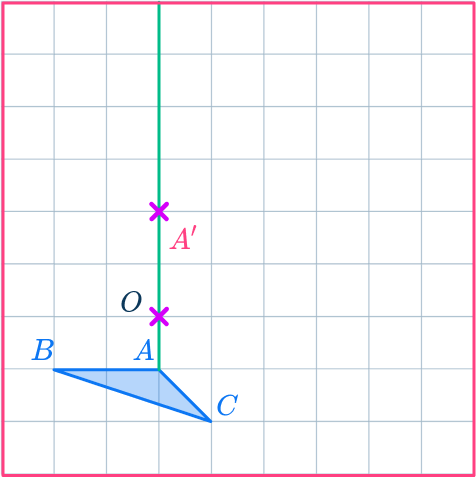
Mark the other new points.
Draw ray lines going through point B and point C.
Measure the distances of these points from the center of dilation, point O.
Multiply the distance by 2, but since the scale factor is negative 2 you mark the new points’ measuring backwards along the ray line from point O.
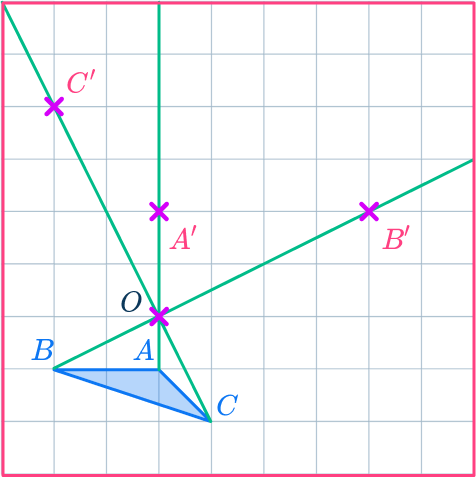
Complete the shape.
Join up the points to make the new triangle A’B’C’.
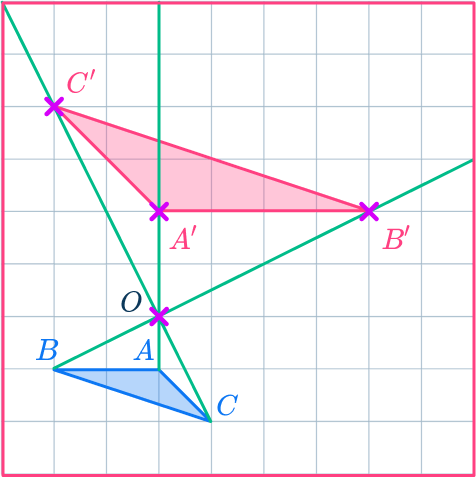
Example 8: negative scale factor
Enlarge the triangle ABC by scale factor - \, 2 about the origin.
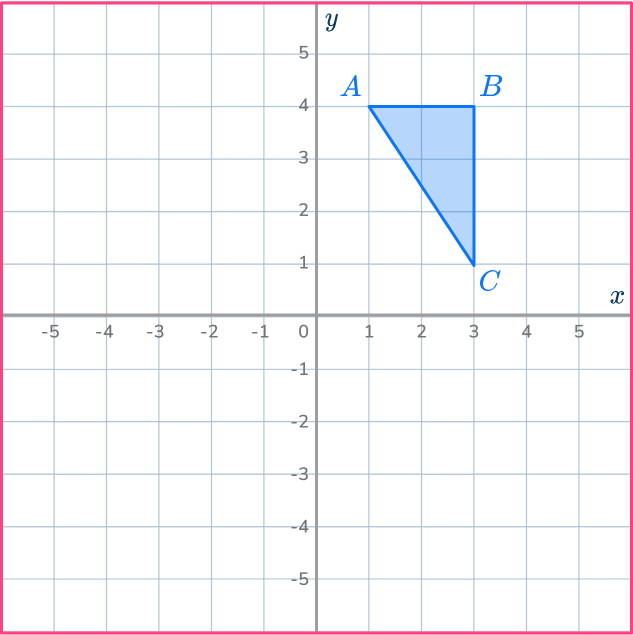
Draw a ray line.
The center of dilation is O, the origin.
Choose a point to start with. Let’s choose point A.
Draw a ray line from point A through O and extend the line back through the center of dilation.
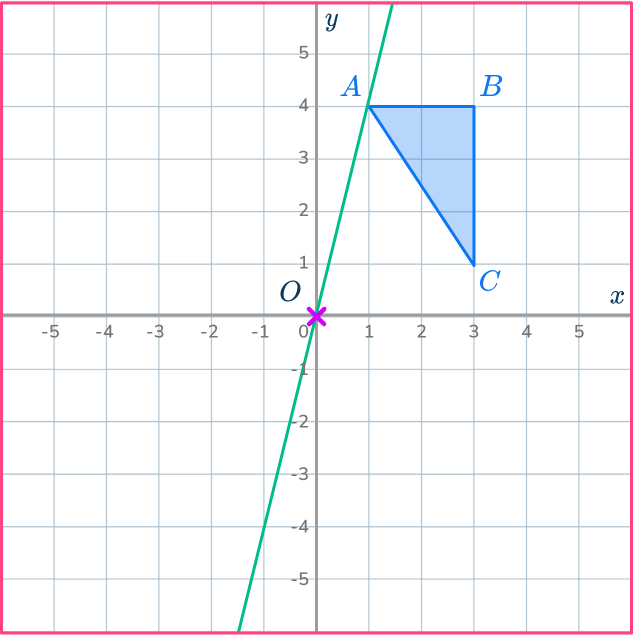
Mark the new point.
Measure the distance from point O to point A. Since the scale factor is negative 1 you mark the point A’ measuring backwards along the ray line from point O. The ray line is like a number line where you have positive and negative numbers with 0 in between.
OA’=- \, 1\times OA
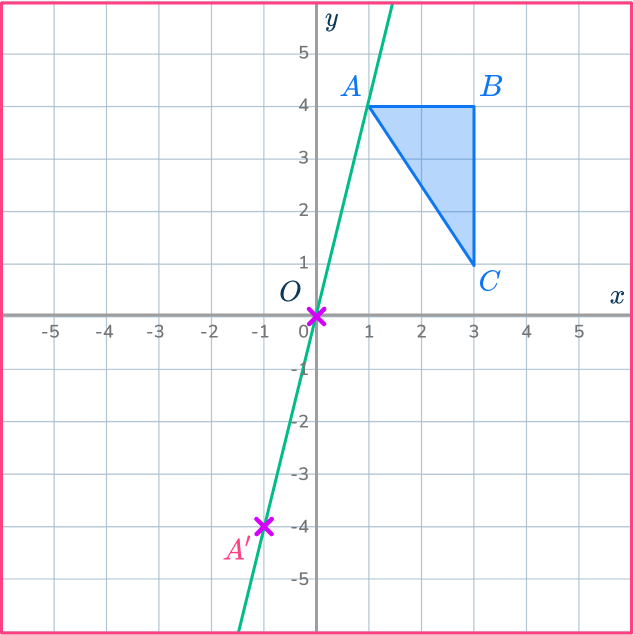
Mark the other new points.
Draw ray lines going through point B and point C.
Measure the distances of these points from the center of dilation, point O.
Since the scale factor is negative 1 you mark the new points measuring backwards along the ray line from point O.
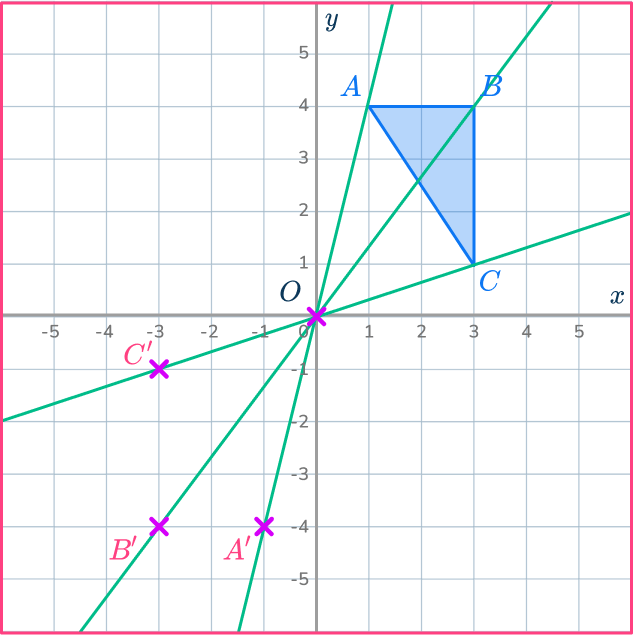
Complete the shape.
Join up the points to make the new triangle A’B’C’.
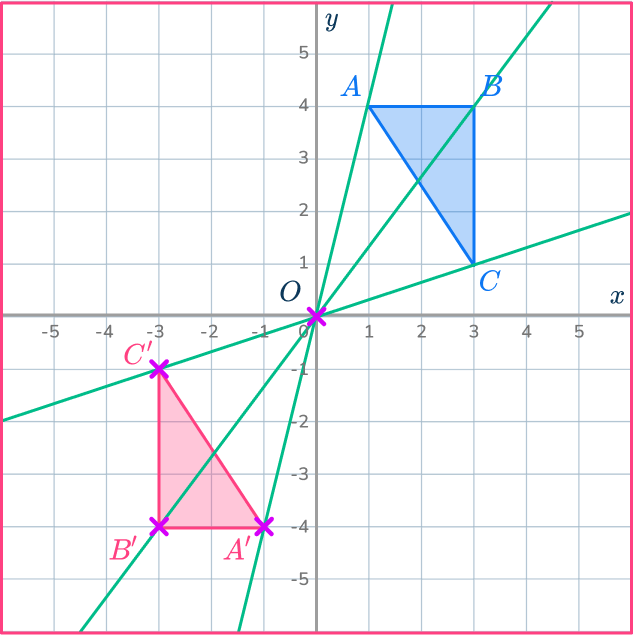
You may notice that this is the same result as a rotation of 180^{\circ} about the same point.
Teaching tips for center of dilation
- Guide students through practice questions where they manually apply dilations from different centers, helping them understand how the distance from the center changes with different scale factors.
- Start with simpler polygons and gradually introduce more complex ones, reinforcing how the center of dilation dictates the direction and placement of the new figure.
- Use digital learning resources such as geometry software or visual aids to show how changing the center of dilation affects the figure’s position. Let students experiment with placing the center inside, on, and outside the figure.
- Create a worksheet that asks students to plot dilations with different centers, including one inside the figure, one on the figure, and one outside the figure. Include guided questions that prompt them to compare how the figure’s position changes depending on the center of dilation.
Easy mistakes to make
- Inaccurate drawings
Use a sharp pencil and make use of the grid lines to help draw accurate straight lines.
- Not extending ray lines
Remember that the ray lines can be extended as far as needed.
- Not drawing multiple ray lines
It is a good idea to draw at least 3 ray lines to make sure you find the correct center of dilation.
- Misunderstanding the positioning of the center of dilation
Remember, the center of dilation can be within the shape.
For example,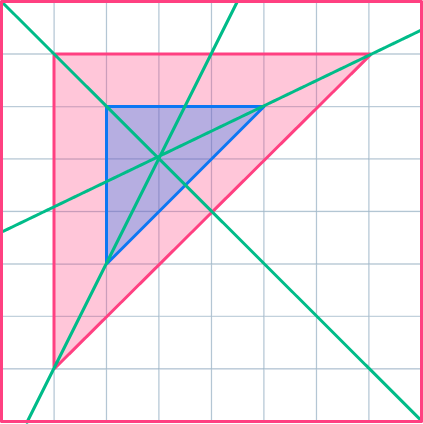
- Not knowing the origin on a coordinate plane
The origin of a coordinate plane has the coordinates (0,0), where the x – and y -coordinates are both zero. It is commonly denoted as O. It is used often as the center of dilation.
- Confusing objects and images
The original shape or original figure is known as an object or pre-image. The enlarged or reduced shape is known as an image, dilated image, or dilated figure. They can overlap.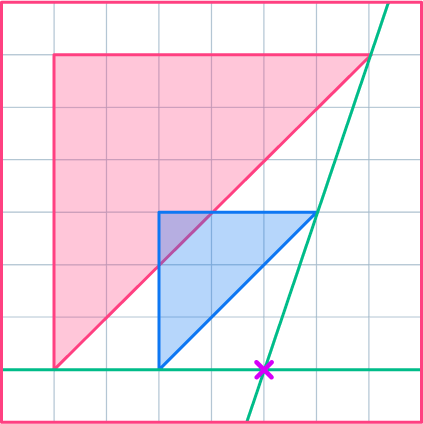
Related transformations lessons
Practice center of dilation questions
1. Enlarge this shape by scale factor 3 about the point O.
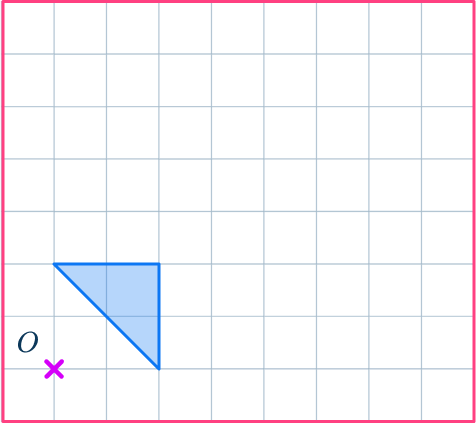
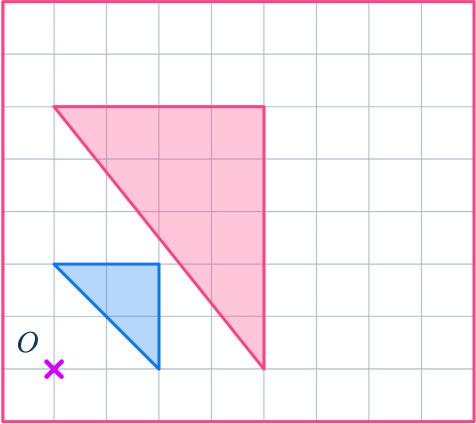

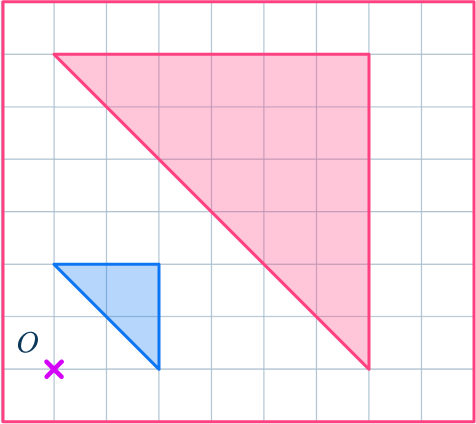

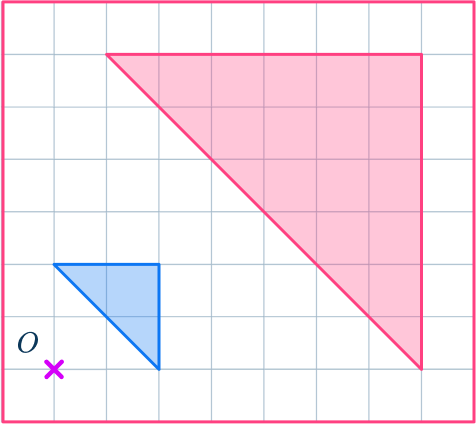

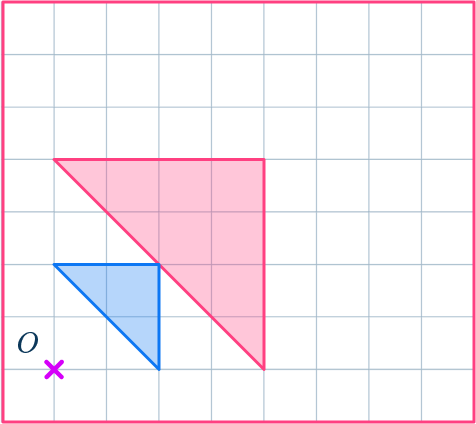

Draw ray lines to make sure you get the enlarged triangle in the correct position. The sides of the enlarged triangle should be 3 times bigger than the original shape.
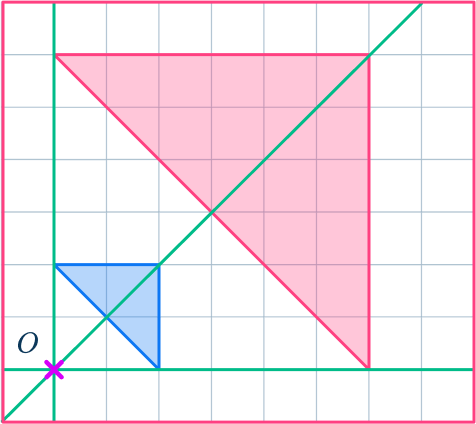
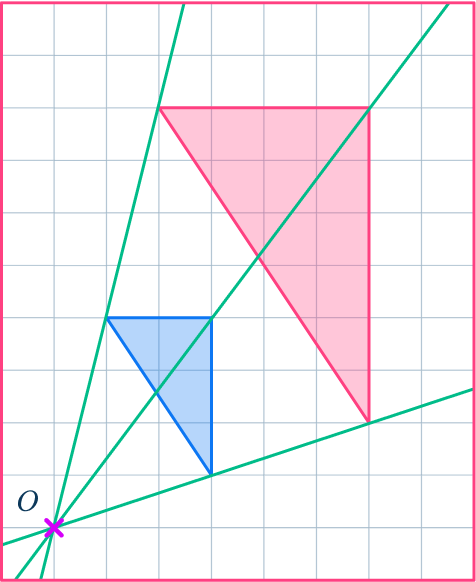
2. Enlarge this shape by scale factor 2 about the point O.
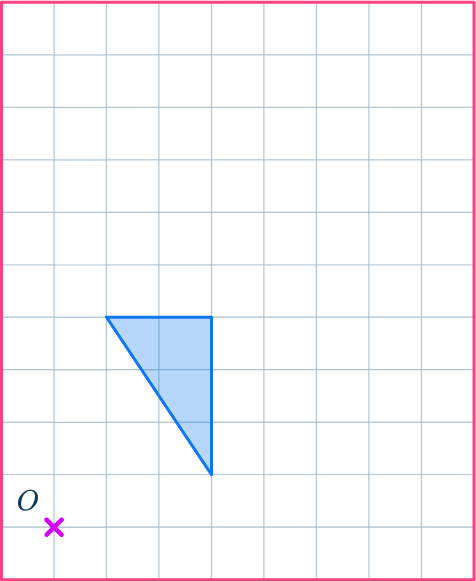
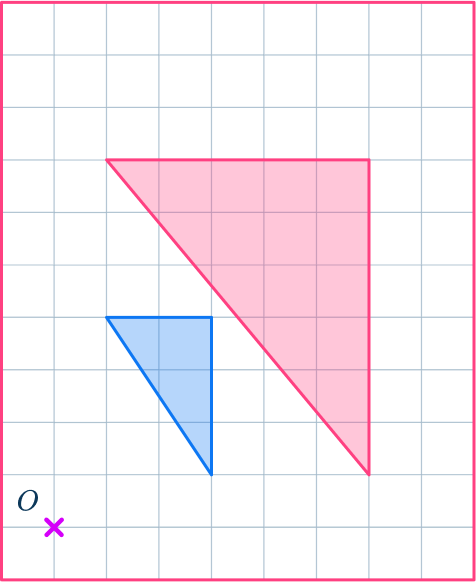

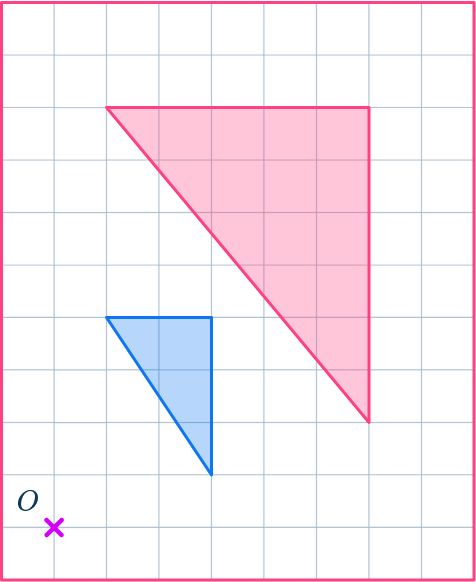



Draw ray lines to make sure you get the enlarged triangle in the correct position. The scale factor is 2, so each of the sides of the enlarged triangle should be double the sides of the original triangle.
3. Enlarge this shape by scale factor 2 about the point (5,1).
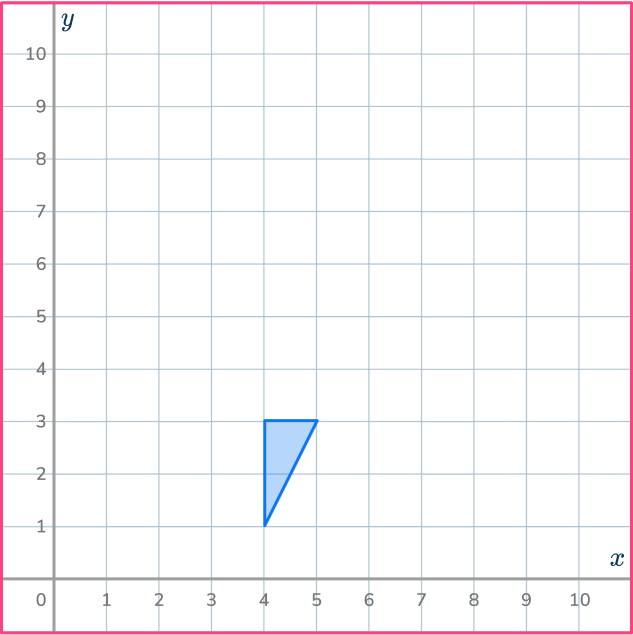
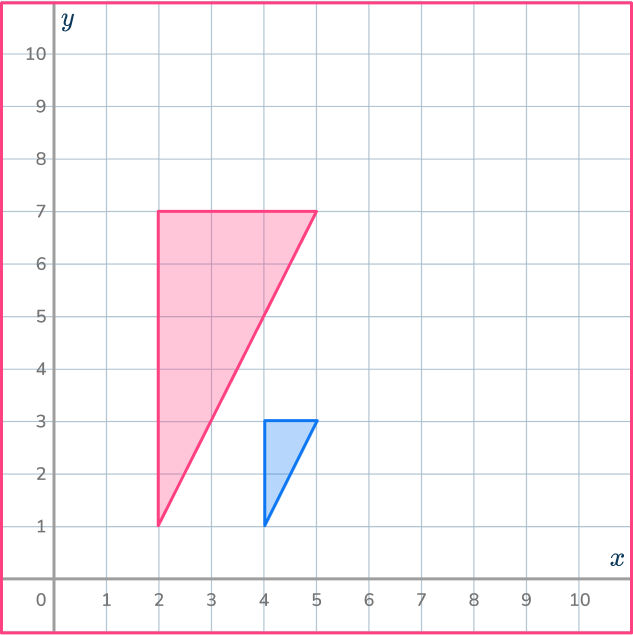

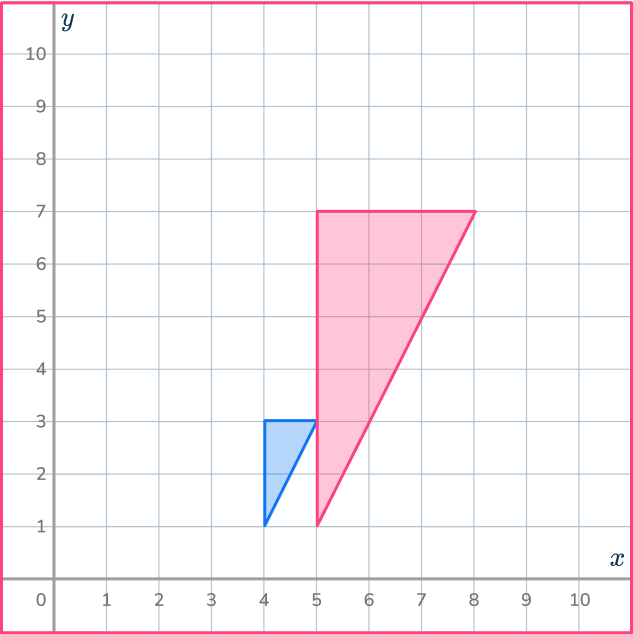

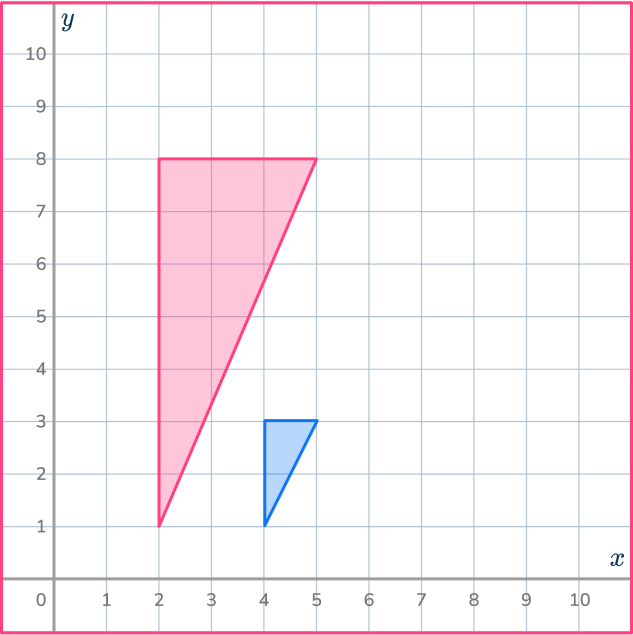

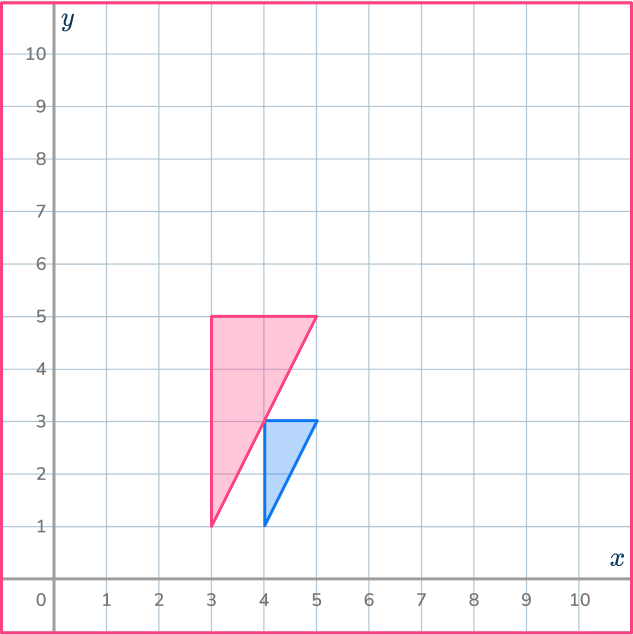

Draw ray lines to make sure you get the enlarged triangle in the correct position. The scale factor is 3, so each of the sides of the enlarged triangle should be 3 times bigger than the sides of the original triangle.
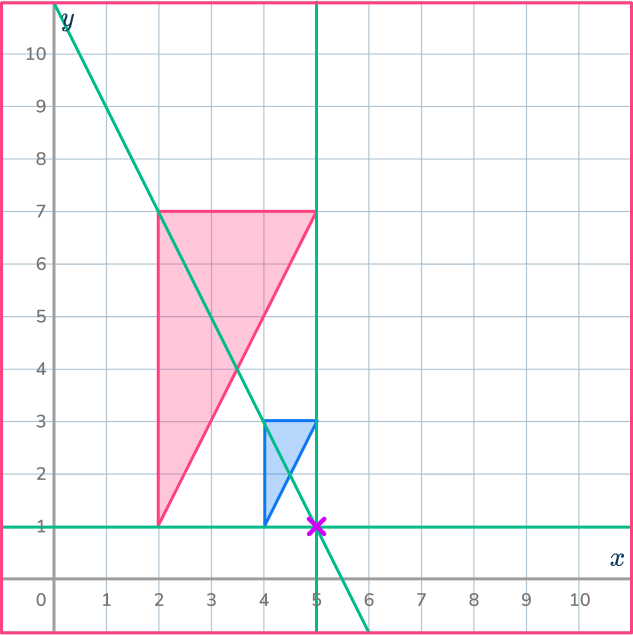
4. Reduce this shape by scale factor \cfrac{1}{2} about the point O.
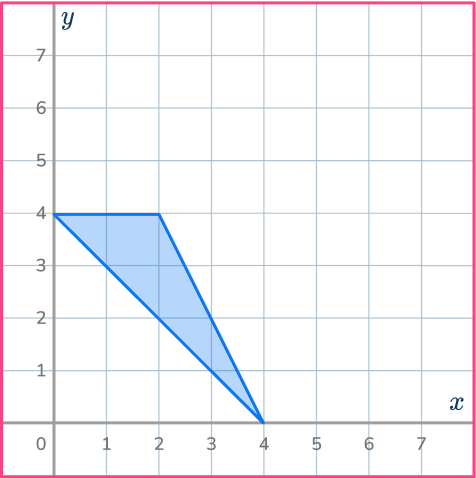
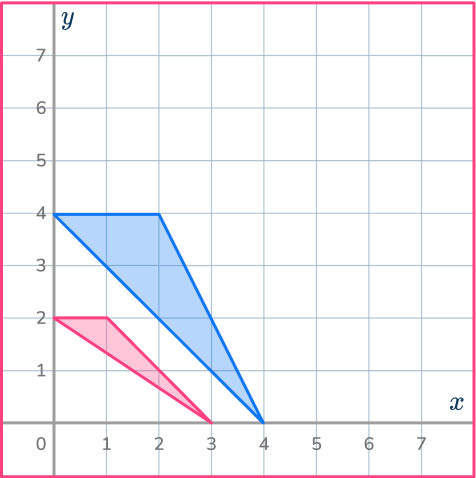

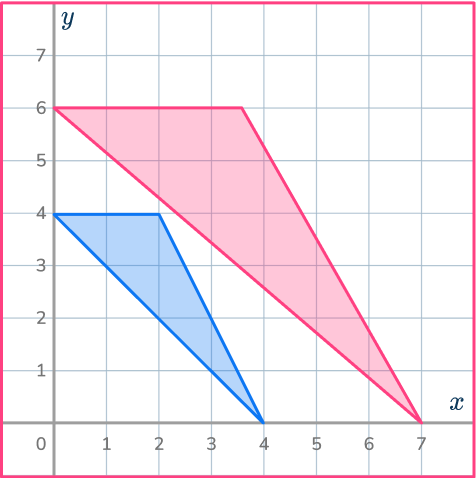

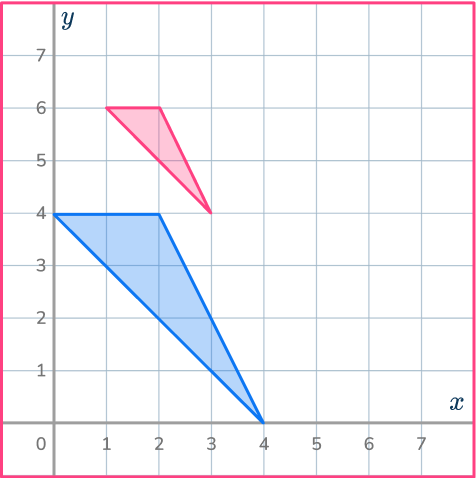

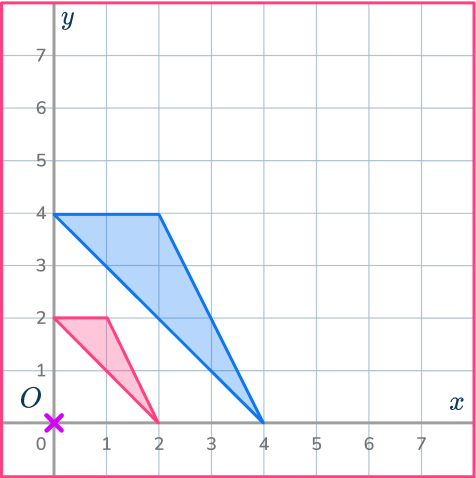

The point O is the origin. Draw ray lines to make sure you get the enlarged triangle in the correct position. The scale factor is \cfrac{1}{2} , so the triangle gets smaller.
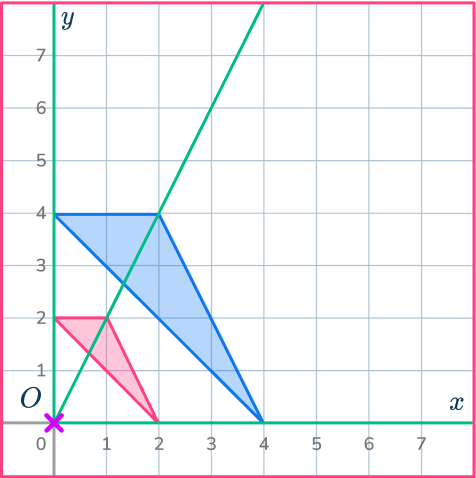
5. Find the center of dilation.
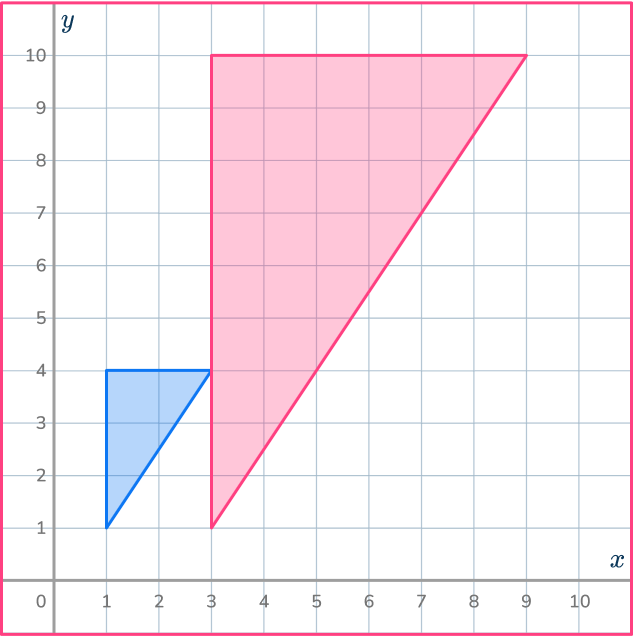




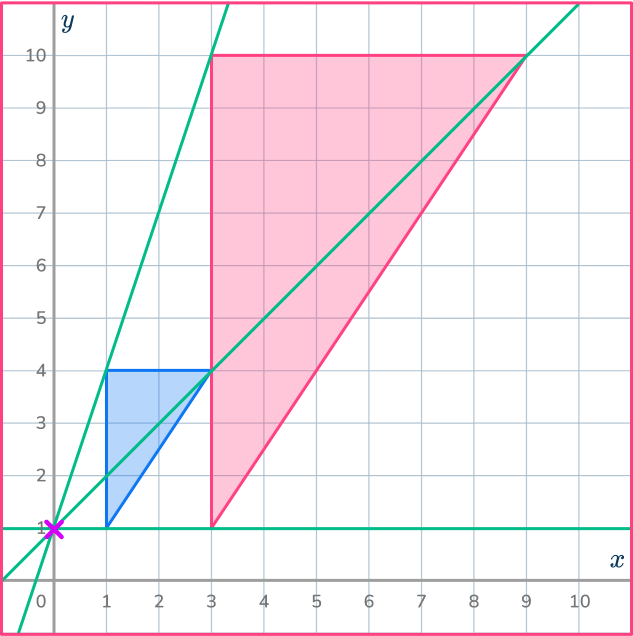
Draw ray lines through pairs of corresponding points. Draw all 3 of them to make sure you get the correct point.
6. Find the center of dilation.
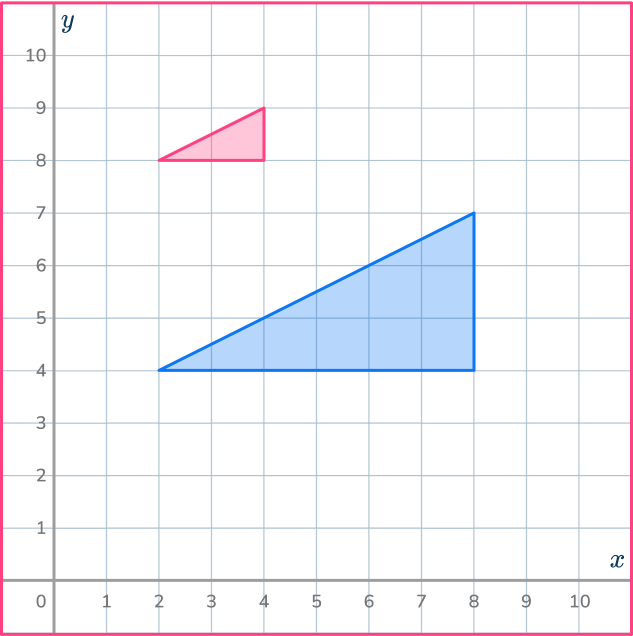




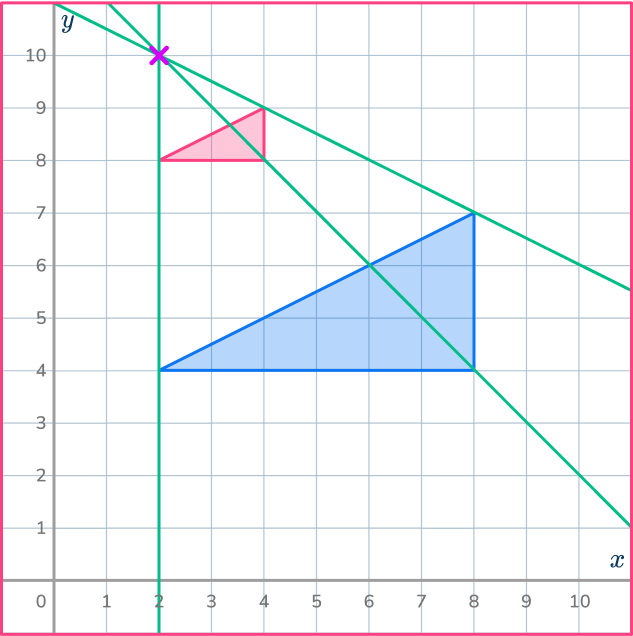
Draw ray lines through pairs of corresponding points. Draw all 3 of them to make sure you get the correct point.
Center of dilation FAQs
The center of dilation is the fixed point from which all points of a figure are resized in a dilation transformation. Every point on the figure moves along a line that passes through this center.
No, the center of dilation can be inside, on, or outside the figure. The location of the center affects where the dilated figure will be placed.
The center of dilation determines the direction and distance that the points of the figure will move. If the center is outside the figure, the figure moves toward or away from it. If the center is inside, the figure expands or contracts around that point.
The absolute value represents the distance from a point to the center of dilation. This distance is multiplied by the scale factor to determine the new position of the point after dilation, ensuring proportional resizing.
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!