FREE DOWNLOAD
Compound Measures Worksheet
Help your students prepare for their Maths GCSE with this free compound measures worksheet of 34 questions and answers
- Section 1 of the compound measures worksheet contains 27 skills-based compound measures questions, in 3 groups to support differentiation
- Section 2 contains 3 applied compound measures questions with a mix of worded problems and deeper problem solving questions
- Section 3 contains 4 foundation and higher level GCSE exam style compound measures questions
- Answers and a mark scheme for all compound measures questions are provided
- Questions follow variation theory with plenty of opportunities for students to work independently at their own level
- All questions created by fully qualified expert secondary maths teachers
- Suitable for GCSE maths revision for AQA, OCR, and Edexcel and WJEC exam boards
Compound measures at a glance
Compound measures are measures that use more than one unit.
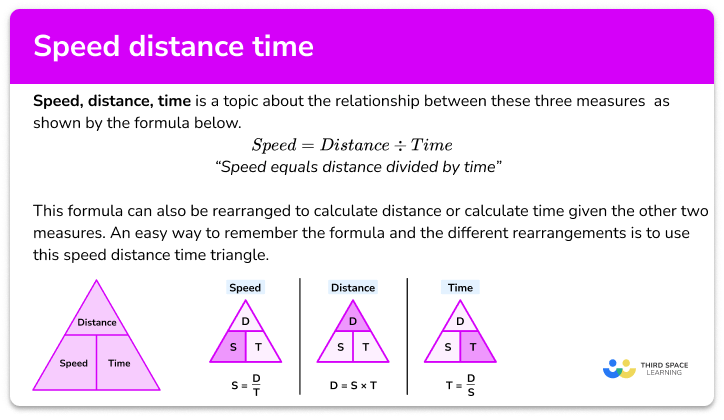
Speed (Distance, Time)
Speed is found using the formula Speed = Distance divided by Time. The units for speed are therefore distance per unit of time. Examples include miles per hour or metres per second.
To find the average speed for a whole journey we would calculate the total distance divided by the total time.
Density (Mass, Volume)
Density is calculated using the formula Density – Mass divided by Volume. The units for density are therefore mass per unit of volume. Examples include g/cm3 and kg/m3, since the volume of cuboids, prisms and all 3D objects is measured in cubic units.
Pressure (Force, Area)
Pressure is calculated using the formula Pressure = Force divided by Area. The units are therefore force per unit of area. Examples include N/m2 and Pa (Pascals).
Other compound measures
Other measures that use compound units include rates of pay, for example £15/hour and rates of flow, for example 10 litres/min.
Looking forward, students can then progress to additional ratio and proportion worksheets, for example a ratio worksheet or a simplifying and equivalent ratios worksheet.
For more teaching and learning support on Ratio and Proportion our GCSE maths lessons provide step by step support for all GCSE maths concepts.
Do you have students who need additional support?
With Third Space Learning's secondary maths tutoring programmes, students in Year 7-11 receive regular one to one maths tutoring to address gaps, build confidence and boost progress.
"My confidence in the tutoring is high. We've had some phenomenal results. I even had one girl get a Grade 8 this year; she came to every tutoring session."
Stacey Atkins, Maths Director, Outwood Grange Academies Trust