GCSE Tutoring Programme
Our chosen students improved 1.19 of a grade on average - 0.45 more than those who didn't have the tutoring.
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
3D shapes Area of triangles and quadrilaterals Substituting into formulaeThis topic is relevant for:

Prism Shape
Here we will learn about prisms, including what prisms are, types of prisms, nets of prisms and how to find the volume and surface area of prisms.
There are also volume and surface area of prisms worksheets based on Edexcel, AQA and OCR exam questions, along with further guidance on where to go next if you’re still stuck.
What is a prism shape?
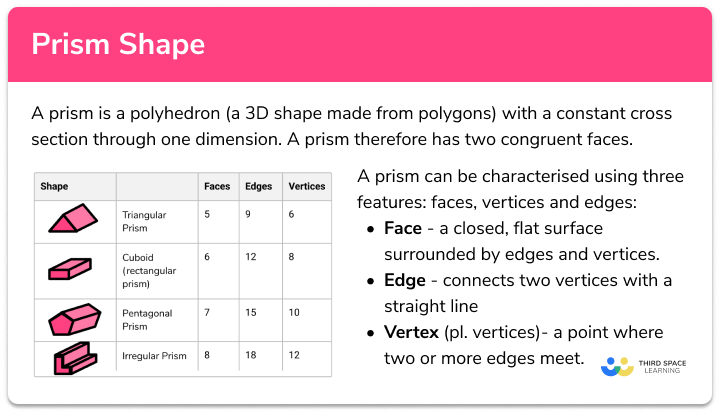
A prism shape is a polyhedron (a 3D shape made from polygons) with a constant cross section through one dimension. A prism shape has two congruent faces (identical ends).
For example, below are three different types of prisms:
The name of the prism is represented by the shape of its cross section.
Faces, edges and vertices
A prism can be characterised using three features: faces, vertices and edges:
- Face: a closed, flat surface surrounded by edges and vertices.
- Edge: connects two vertices with a straight line
- Vertex (pl. vertices): a point where two or more edges meet.
We can label the vertices (corners) of a prism to help us identify certain edges or faces. Below is an example of a triangular prism where the letters A – F represent the 6 vertices of the prism:
Using this labelling we can identify lengths such as the length AB :
We can also identify faces such as the face ABC :
The number of faces, edges and vertices can vary depending on the prism. Let’s look at some examples:
| Shape | Faces | Edges | Vertices |
Triangular prism | 5 | 9 | 6 |
Cuboid (rectangular prism) | 6 | 12 | 8 |
Pentagonal prism | 7 | 15 | 10 |
L-shaped prism | 8 | 18 | 12 |
A prism is irregular if the cross section is not a regular polygon. For example, the L-shaped prism above is an irregular prism because the cross section is not a regular polygon.
What is a prism?
Nets
If you unfold a three-dimensional shape and lay it down so that it is flat, the result would be the net of the shape. We can draw a net for any prism.
E.g.
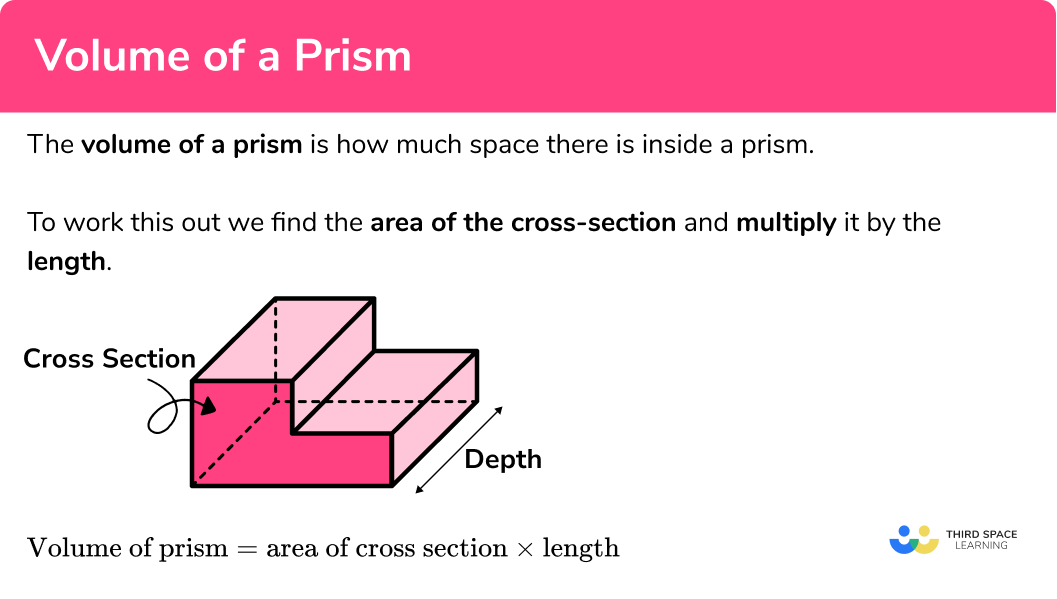
Volume of a prism
The volume of a prism is how much space there is inside a prism.
To calculate the volume of a prism, we find the area of the cross section and multiply it by the depth.
Volume of prism = Area of cross section × Depth
Volume is measured in cubic units (e.g. mm^3, cm^3, m^3 etc).
Step-by-step guide: Volume of a prism
Volume of a prism
How to calculate the volume of a prism
In order to do this I need to follow the steps:
- Write down the formula.
- Calculate the area of the cross section.
- Calculate the volume of the prism.
- Write the answer, including the units.
How to calculate the volume of a prism

Prism shape worksheet

Get your free prism shape worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREE
Prism shape worksheet

Get your free prism shape worksheet of 20+ questions and answers. Includes reasoning and applied questions.
DOWNLOAD FREEVolume of a prism examples
Example 1: triangular prism, given the area of the cross-section
Below is a triangular prism:
The cross-sectional area of the prism is 43cm^2 . Calculate the volume of the prism.
- Write down the formula.
Volume of prism = Area of cross section × Depth
2Calculate the area of the cross section.
The area of the cross section is already stated as 43cm^2 so we can move on to the next step.
3Calculate the volume of the prism.
4Write the answer, including the units.
The measurements on this prism are in cm so the volume will be measured in cm^3 .
Volume = 387cm^3 .
Example 2: parallelogram prism
Work out the volume of the prism
- Write down the formula.
Volume of prism = Area of cross section × Depth
2Calculate the area of the cross section.
3Calculate the volume of the prism.
4Write the answer, including the units.
The measurements on this prism are in m so the volume will be measured in m^3 .
Volume = 480m^3 .
Example 3: trapezoidal prism
Calculate the volume of the prism below.
- Write down the formula.
Volume of prism = Area of cross section × Depth
2Calculate the area of the cross section.
3Calculate the volume of the prism.
4Write the answer, including the units.
Volume = 280cm^3
Surface area of a prism
The surface area of a prism is the total area of all of the faces.
The surface area of a prism is special because all of the lateral faces are rectangles. To calculate the surface area of a prism, we calculate twice the area of the cross section and add the perimeter of the cross section multiplied by the depth of the prism.
In general, the surface area of any prism is:
Surface Area of a Prism = 2A+PD
where:
- A = Area of the cross section
- P = Perimeter of the cross section
- D = Depth of the prism
Step-by-step guide: Surface area of a prism
Surface area of a prism

How to calculate the surface area of a prism
In order to work out the surface area of a prism:
- Calculate the area of the cross section.
- Calculate the perimeter of the cross section.
- Substitute all known values into the formula and solve.
- Write the answer, including the units.
How to calculate the surface area of a prism

Surface area of a prism examples
Example 4: surface area using a formula
Calculate the surface area of the following triangular prism.
- Calculate the area of the cross section.
The cross section is a right angle triangle.
2Calculate the perimeter of the cross section.
The perimeter is the sum of the edges of the cross section:
P=5+12+13=30\text{cm}3Substitute all known values into the formula and solve.
Using the formula Surface Area of a Prism = 2A+PD , when A=30, P=30, and D=10 , we have
4Write the answer, including the units.
The surface area of the triangular prism is 360cm^2 .
Example 5: surface area of a cylinder
A cylinder has a height of 5m and a radius of 2m . Calculate the surface area of the cylinder. Write your answer in terms of \pi .
- Calculate the area of the cross section.
The cross section is a circle.
2Calculate the perimeter of the cross section.
The perimeter of a circle is the circumference:
P=\pi\times{2r}=\pi\times{2}\times{2}=4\pi\text{ m}3Substitute all known values into the formula and solve.
Using the formula Surface Area of a Prism = 2A+PD , when A=4, P=4, and D=5 , we have
4Write the answer, including the units.
The surface area of the triangular prism is 28\pi\text{ m}^{2}
Example 6: surface area of a compound prism
Calculate the surface area of the compound prism below.
- Calculate the area of the cross section.
The cross section is a kite.
2Calculate the perimeter of the cross section.
The perimeter is the sum of the edges of the cross section:
P=10+17+17+10=54\text{cm}3Substitute all known values into the formula and solve.
Using the formula Surface Area of a Prism = 2A+PD , when A=168, P=54, and D=4, we have
4Write the answer, including the units.
The surface area of the compound prism is 552cm^2 .
Common misconceptions
- Calculating the volume instead of the surface area of the prism
Volume and surface area are different things – volume tells us the space within the shape whereas surface area is the total area of the faces. To find surface area, work out the area of each face and add them together.
- All of the rectangles have the same area
Usually all of the rectangles have different areas (unless the shape of the cross section is a regular polygon)
- Missing faces
This usually occurs on a compound prism where it can be difficult to visualise all of the face
- Missing/incorrect units
You should always include units in your answer. Remember, volume is measured in units cubed (e.g. mm^3, cm^3, m^3 etc) and surface area is measured in units squared (e.g. mm^2, cm^2, m^2 etc)
- Calculating with different units
You need to make sure all measurements are in the same units before calculating volume or surface area. (E.g. you can’t have some in cm and some in m )
- Using the wrong formula
Be careful to apply the correct prism related formula to the correct question type.
Practice prism shape questions
1. Work out the volume of the prism




\text{Volume of prism }=16\times{9}\\ =144\mathrm{cm}^{3}
2. Calculate the volume of the L-shaped prism.




Area of cross section:
6 \times 5=30\\
3\times 11=33\\
30+33=63
\text{Volume of prism }=63 \times 10\\ =630\mathrm{cm}^{3}
3. The volume of this regular octagonal prism is 360m^3 . The area of the cross section is 45m^2 . Work out the length, L, of the prism.




We know the area of the octagon is 45m^2 and the volume of the prism is 360m^3 .
\text{Volume of prism } = \text{Area of cross-section } \times \text{Depth}\\ 360=45 \times{D}\\ D=8
The depth of the prism is 8m .
4. Work out the surface area of this parallelogram prism




Work out the area of each face:
| Face | Area |
| Front | 12×4=48 |
| Back | 48 |
| Bottom | 12×20=240 |
| Top | 240 |
| Left side | 5×20=100 |
| Right side | 100 |
\text{Total surface area }=48+48+240+240+100+100=776\mathrm{m}^{2}
5. Work out the surface area of the prism. Write your answer in cm^2 .




| Face | Area |
| Front | 70×30=2100 |
| Back | 2100 |
| Bottom | 70×120=8400 |
| Top | 8400 |
| Left side | 30×120=3600 |
| Right side | 3600 |
\text{Total surface area }=2100+2100+8400+8400+3600+3600=28200\mathrm{cm}^{2}
6. Work out the surface area of the prism




Area of cross section:
Area A: \frac{1}{2} \times 8 \times 3=12
Area B: 4\times 8=32
Total area = 12+32=44
Work out the area of each face:
| Face | Area |
| Front | 44 |
| Back | 44 |
| Bottom | 8×11=88 |
| Left side | 4×11=44 |
| Top left | 5×11=55 |
| Top right | 55 |
| Right side | 44 |
\text{Total surface area }=44+44+88+44+55+55+44=374\mathrm{mm}^{2}
Prism shape GCSE questions
1. Work out the surface area of the prism
(3 marks)
\frac{1}{2}(7+17) \times 12=144
For calculating the area of the cross section (trapezium)
(1)
272, 208, 208 and 112
For calculating the area of each lateral face (rectangles)
(1)
144+144+272+208+208+112=1088\mathrm{cm}^{2}
For calculating the total surface area of the prism
(1)
2. (a) The volume of this prism is 132m^3 . Work out the height of the prism.
(b) Hence calculate the surface area of the prism.
(a)
5h
For calculating the area of the cross section
(1)
5h\times 12=60h
For calculating the volume of the prism
(1)
60h=132
For forming an equation to calculate the height of the prism
(1)
h=132\div{60}=2.2\text{m}
For the correct answer
(1)
(b)
5 \times 2.2=11
For calculating the area of the cross section
(1)
60(T), 60(B), 36(L), 36(R)
For calculating the area of the rectangular faces
(1)
\text{Total surface area: }11+11+60+60+36+36=214\mathrm{m}^{2}
For calculating the total surface area of the prism
(1)
3. Richard would like to fill the container below with apple juice.
Can Richard pour 5 litres of apple juice into the container without it overflowing?
(4 marks)
\frac{1}{2} (12+16) \times 12=168
For calculating the area of the cross section (trapezium)
(1)
168 \times 25 = 4200\mathrm{cm}^{3}
For calculating the volume of the container
(1)
4200\mathrm{cm}^{3}=4.2\text{ litres}
For converting the volume into litres
(1)
No, it will not fit
For correct conclusion
(1)
Learning checklist
You have now learned how to:
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
Prepare your KS4 students for maths GCSEs success with Third Space Learning. Weekly online one to one GCSE maths revision lessons delivered by expert maths tutors.

Find out more about our GCSE maths tuition programme.