High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Fractions Integers Math equations Algebraic expressionsOne step equations
Here you will learn about one step equations, including how to solve them and how to solve problems using them.
Students first learn about algebraic expressions and equations in the 6 th grade with their work with expressions and equations. They expand their knowledge of equations as they move through middle school math, Pre-algebra and Algebra 1.
What is one step equations?
One step equations are algebraic equations made up of variables and numbers. An equation is a mathematical sentence that shows two expressions are equal. One step equations can be solved in one step using either addition, subtraction, multiplication, or division.
For example,
x+5=8In order to solve an algebraic equation, you will need to isolate the variable (get it alone) on one side of the equation by doing the inverse operation.
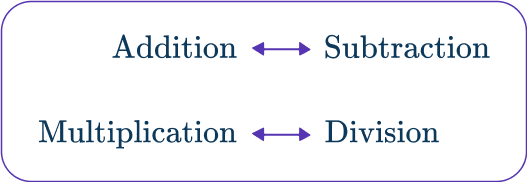
Let’s look at examples of solving one-step equations.
What is one step equations?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6 th grade math, 7 th grade math, and 8 th grade math?
- Grade 6 Number System (6.NS.C.6.c)
Find and position integers and other rational numbers on a horizontal or vertical number line diagram; find and position pairs of integers and other rational numbers on a coordinate plane.
- Grade 7 – Ratios and Proportional Relationships (7.RP.A.2.b)
Identify the constant of proportionality (unit rate) in tables, graphs, equations, diagrams, and verbal descriptions of proportional relationships.
- Grade 8 – Expressions and Equations (8.EE.B.5)
Graph proportional relationships, interpreting the unit rate as the slope of the graph.
![[FREE] One Step Equations Worksheet (Grade 6 to High School)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/One-step-equations-worksheet-listing-image-1.png)
[FREE] One Step Equations Worksheet (Grade 6 to High School)
![[FREE] One Step Equations Worksheet (Grade 6 to High School)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/One-step-equations-worksheet-listing-image-1.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 6 to high school students’ understanding of one step equations. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] One Step Equations Worksheet (Grade 6 to High School)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/One-step-equations-worksheet-listing-image-1.png)
[FREE] One Step Equations Worksheet (Grade 6 to High School)
![[FREE] One Step Equations Worksheet (Grade 6 to High School)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/One-step-equations-worksheet-listing-image-1.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 6 to high school students’ understanding of one step equations. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEHow to solve one step equations
In order to solve one step equations using inverse operations:
- Identify the inverse operation to use.
- Do the inverse operation on both sides of the equation.
- Solve for the unknown variable.
- Check the answer.
One step equation examples
Example 1: solve the equation using addition/subtraction
Solve the equation for x.
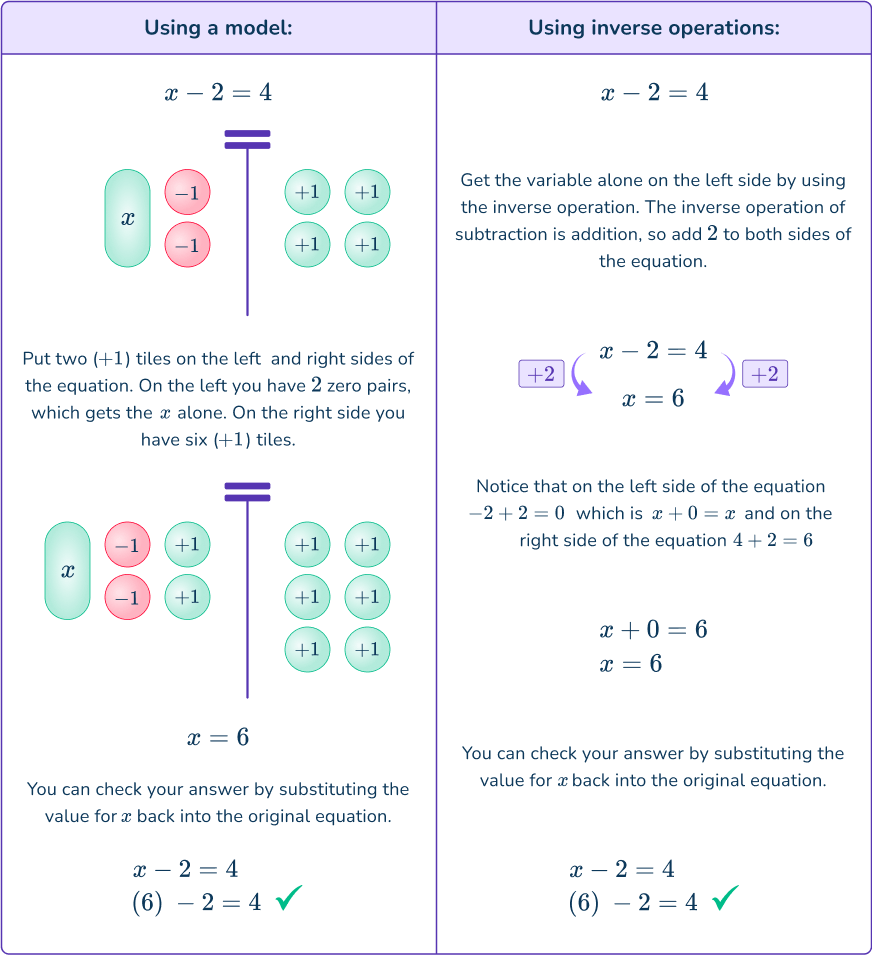
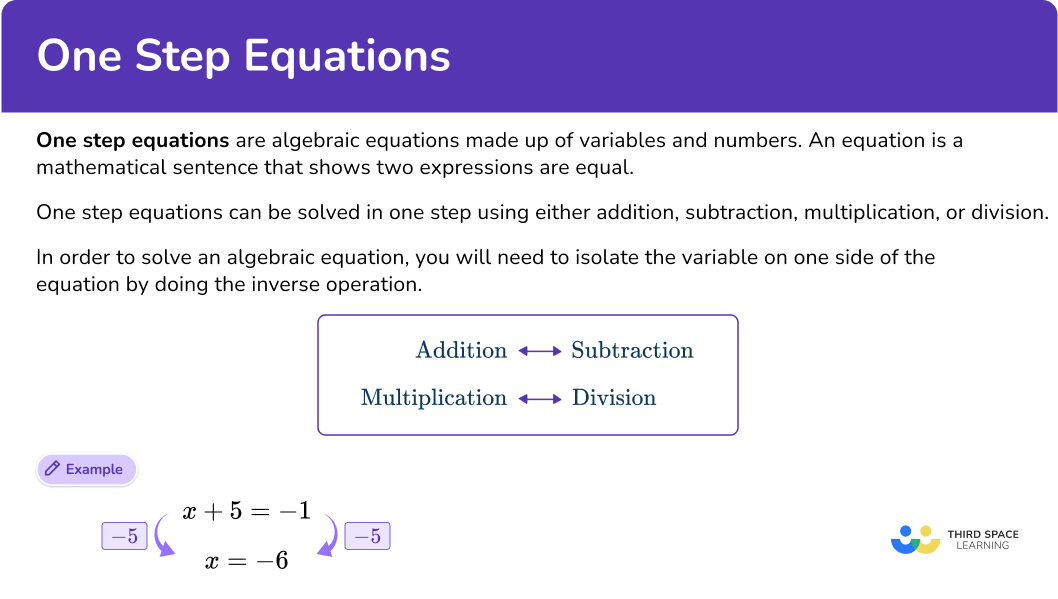
x-8=2- Identify the inverse operation to use.
x-8=2 → inverse operation is addition because addition undoes subtraction
2Do the inverse operation on both sides of the equation.
\begin{aligned} & x-8=2 \\\\ & +8=+8 \end{aligned}3Solve for the unknown variable.
On the left side of the equation -8+8=0
On the right side of the equation 2+8=10
\begin{aligned} x-8&=2 \\\\ +8&=+8 \\\\ x+0&=10 \\\\ x&=10 \end{aligned}4Check the answer.
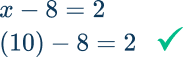
Example 2: solve for the variable using addition/subtraction
Solve the equation for x.
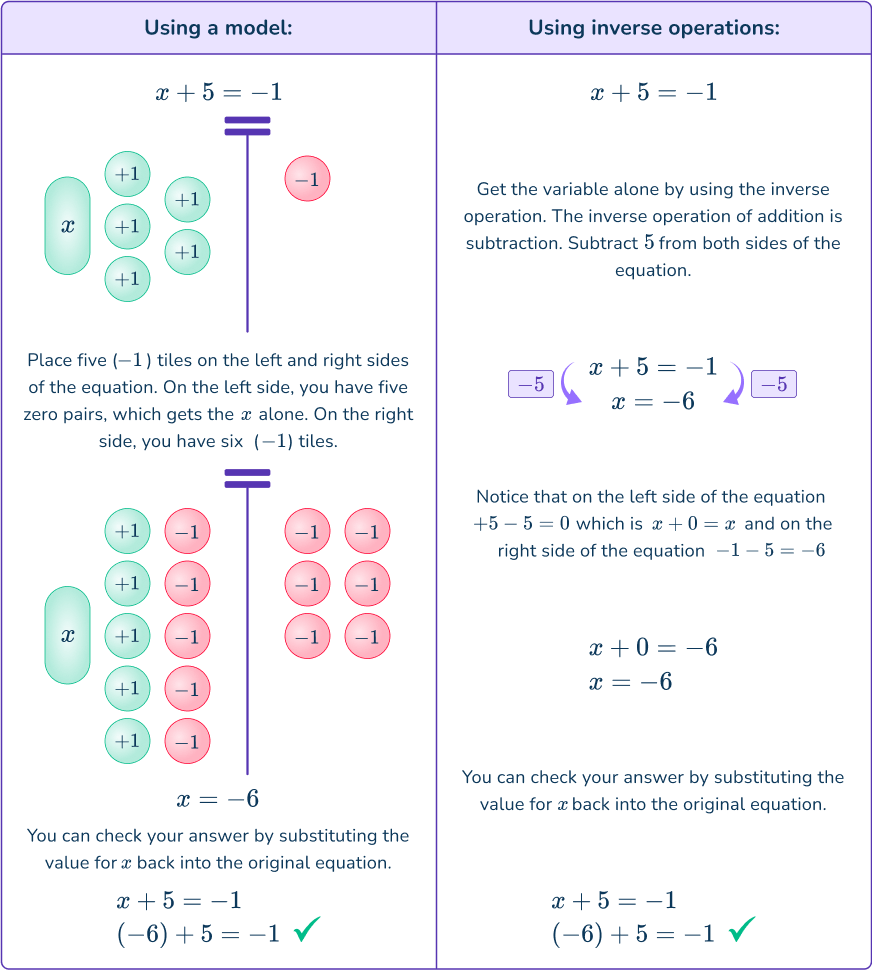
x+6=-7Identify the inverse operation to use.
x+6=-7 → inverse operation is subtraction because subtraction undoes addition.
Do the inverse operation on both sides of the equation.
Solve for the unknown variable.
On the left side of the equation +6-6=0
On the right side of the equation -7-6=-13
\begin{aligned} x+6&=-7 \\\\ -6&=-6 \\\\ x+0&=-13 \\\\ x&=-13 \end{aligned}
Check the answer.
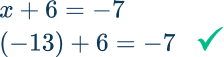
Example 3: solve the equation using multiplication/division
Solve the equation, \cfrac{1}{2} x=20, for x.
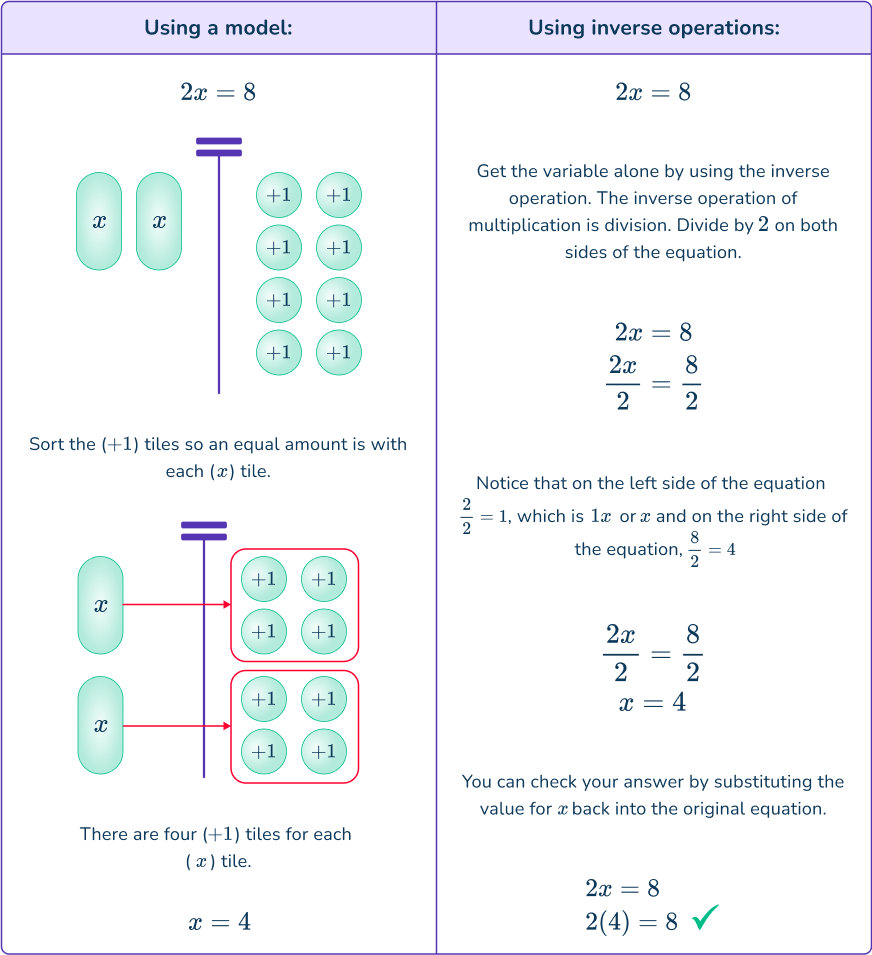
Identify the inverse operation to use.
\cfrac{1}{2} x=20 → inverse operation of multiplication is division
Do the inverse operation on both sides of the equation.
Solve for the unknown variable.
One the left side of the equation \cfrac{1}{2} \div \cfrac{1}{2}=\cfrac{1}{2} \times \cfrac{2}{1}=\cfrac{2}{2}=1
On the right side of the equation 20 \div \cfrac{1}{2}=20 \times \cfrac{2}{1}=\cfrac{40}{1}=40
\begin{aligned} \cfrac{1}{2} x&=20 \\\\ \cfrac{1}{2} \div \cfrac{1}{2} x&=20 \div \cfrac{1}{2} \\\\ 1 x&=40 \\\\ x&=40 \end{aligned}
Check the answer.
Example 4: solve the equation using multiplication/division
Solve the equation, \cfrac{x}{-3}=-4 for x.
Identify the inverse operation to use.
\cfrac{x}{-3}=-4 → inverse operation of division is multiplication
Do the inverse operation on both sides of the equation.
Solve for the unknown variable.
On the left side of the equation \cfrac{x}{-3} \bullet-3=\cfrac{-3 x}{-3}=1 x
On the right side of the equation -4 \cdot-3=12
\begin{aligned} \cfrac{x}{-3} \cdot-3 & =-4 \cdot-3 \\\\1 x & =12 \\\\x & =12 \end{aligned}
Check the answer.
Example 5: solve the equation using multiplication/division
Solve the equation for x.
-x=9Identify the inverse operation to use.
-x means -1x
-x=9 → The inverse operation of multiplication is division
Do the inverse operation on both sides of the equation.
Solve for the unknown variable.
On the left side of the equation \cfrac{-x}{-1}=1 x
On the right side of the equation \cfrac{9}{-1}=-9
\begin{aligned} \cfrac{-x}{-1}&=\cfrac{9}{-1} \\\\ x&=-9 \end{aligned}
Check the answer.
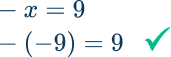
How to solve one step equations word problems
In order to solve one step equation word problems:
- Identify the variable and write the equation.
- Identify the inverse operation to use.
- Do the inverse operation on both sides of the equation.
- Solve for the unknown variable.
- Check the answer.
Example 6: problem solving
The product of a number and -5 is 100. Find the number.
Identify the variable and write the equation.
“A number” is represented by x.
Product means multiplication. So the equation is: -5x=100
Identify the inverse operation to use.
-5 x=100 → The inverse operation of multiplication is division.
Do the inverse operation on both sides of the equation.
Solve for the unknown variable.
On the left side of the equation \cfrac{-5 x}{-5}=1 x
On the right side of the equation \cfrac{100}{-5}=-20
\begin{aligned} \cfrac{-5 x}{-5}&=\cfrac{100}{-5} \\\\ 1 x&=-20 \\\\ x&=-20 \end{aligned}
The number is -20.
Check the answer.
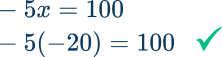
Example 7: problem solving
The sum of a number and -7 is 18. Find the number.
Identify the variable and write the equation.
“A number” is represented by x.
Sum means to add. So the equation is: x+(-7)=18
Identify the inverse operation to use.
The inverse operation of addition is subtraction.
Do the inverse operation on both sides of the equation.
Solve for the unknown variable.
Check the answer.
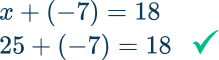
Teaching tips for one step equations
- Use manipulatives such as algebra tiles to help students build conceptual understanding of the abstract concept.
- Reinforce additive inverse and multiplicative inverse, along with the concept that 0+x = x and 1x=x.
- Although practice math worksheets and equation worksheets help students to review skills and procedures, visual models provide an opportunity for students to formulate an understanding of abstract algebraic concepts.
- Use digital platforms that incorporate game playing for students to review skills and procedures.
- Have students always check the value they get for the variable to make sure their answer makes sense and is correct.
Easy mistakes to make
- Using the incorrect inverse operation
For example, x+6=9 using addition to solve instead of subtraction.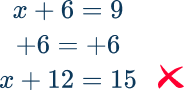
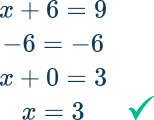
- Confusing integer rules
For example,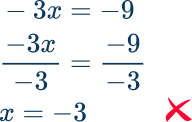
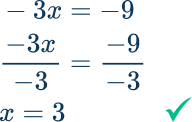
Related math equations lessons
Practice one step equations
1. Solve the equation for x.
x-8=-10




x-8=-10 → The inverse operation is addition, so add 8 to both sides of the equation.
\begin{aligned} x-8&=-10 \\\\ +8&=+8 \end{aligned}
On the left side of the equation -8+8=0. So it is, 0+x = x
On the right side of the equation -10+8=-2
\begin{aligned} x-8&=-10 \\\\ 8&=+8 \\\\ x+0&=-2 \\\\ x&=-2 \end{aligned}
Check:
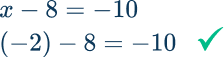
2. Solve the equation for x.
x+10=-4




x+10=-4 → The inverse operation is subtraction, so subtract 10 to both sides of the equation.
\begin{aligned} x+10 & =-4 \\\\ -10 & =-10 \end{aligned}
On the left side of the equation 10-10=0. So it is, 0+x = x
On the right side of the equation -4-10 =-14
\begin{aligned} x+10&=-4 \\\\ -10&=-10 \\\\ x+0&=-14 \\\\ x&=-14 \end{aligned}
Check:
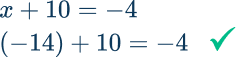
3. Solve the equation for x.
-3 x=18




-3x=18 → The inverse operation is division, so divide both sides of the equation by -3.
\cfrac{-3 x}{-3}=\cfrac{18}{-3}
On the left side of the equation \cfrac{-3 x}{-3}=1 x and 1 x=x
On the right side of the equation \cfrac{18}{-3}=-6
\begin{aligned} \cfrac{-3 x}{-3}&=\cfrac{18}{-3} \\\\ x&=-6 \end{aligned}
Check:
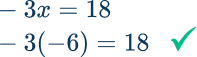
4. Solve the equation for x.
\cfrac{1}{3}+x=\cfrac{2}{3}




\cfrac{1}{3}+x=\cfrac{2}{3} → The inverse operation is subtraction, so subtract both sides of the equation by \cfrac{1}{3}.
\cfrac{1}{3}-\cfrac{1}{3}+x=\cfrac{2}{3}-\cfrac{1}{3}
On the left side of the equation \cfrac{1}{3}-\cfrac{1}{3}+x=0+x and 0+x=x
On the right side of the equation \cfrac{2}{3}-\cfrac{1}{3}=\cfrac{1}{3}
\begin{aligned} \cfrac{1}{3}-\cfrac{1}{3}+x&=\cfrac{2}{3}-\cfrac{1}{3} \\\\ 0+x&=\frac{1}{3} \\\\ x&=\cfrac{1}{3} \end{aligned}
Check:
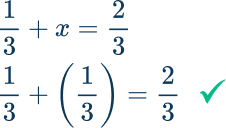
5. The sum of a number and 7 is 19. Find the number.




“A number” is represented by x. Sum means to use the operation of addition.
The equation is: x+7=19
x+7=19 → The inverse operation of addition is subtraction, so subtract 7 from both sides of the equation.
x+7-7=19-7
On the left side of the equation, x+7-7 = x+0 and x+0 is x
On the right side of the equation, 19-7=12
\begin{aligned} x+7-7&=19-7 \\\\ x+0&=12 \\\\ x&=12 \end{aligned}
The number is 12.
Check:
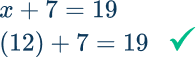
6. The quotient of a number and 3 is 8 . Find the number.




“A number” is represented by x. Quotient means to use the operation of division.
The equation is: \cfrac{x}{3}=8
\cfrac{x}{3}=8 → The inverse operation of division is multiplication, so multiply both sides of the equation by 3.
\begin{aligned} \cfrac{x}{3}&=8 \\\\ \cfrac{x}{3} \cdot 3&=8 \cdot 3 \\\\ \cfrac{x}{3} \cdot \cfrac{3}{1}&=8 \cdot 3 \end{aligned}
On the left side of the equation \cfrac{3 x}{3}=1 x, 1 x=x
On the right side of the equation, 8 \cdot 3=24
\begin{aligned} \cfrac{x}{3} \cdot \cfrac{3}{1}&=8 \cdot 3 \\\\ 1 x&=24 \\\\ x&=24 \end{aligned}
The number is 24.
Check:

7. The difference between a number and -19 is 24 . Find the number.




“A number” is represented by x. Difference means to use the operation of subtraction.
The equation is: x-(-19)=24
x-(-19)=24 → The inverse operation to subtraction is addition
x-(-19)=24
\begin{aligned} x-(-19)+(-19)&=24+(-19) \\\\ x&=24+(-19) \\\\ x&=5 \end{aligned}
Check:
\begin{aligned} x-(-19)&=24 \\\\ 5-(-19)&=24 \\\\ 5+19&=24 \end{aligned}
One step equations FAQs
No, the variable can be any letter (typically lowercase). The most common variable as you get into higher levels of mathematics is x.
No, as you progress through middle and high school, you will use more than one operation and can also use square root or cube root to solve for the equation.
The strategies used to solve two-step equations and multi-step equations build upon the strategies used to solve one-step equations. You will use inverse operations (opposite operations) and order of operations in the reverse order.
For example, to find the value of the variable, x, in the equation 2x-1=11, you first must move the -1 to the opposite side of the equation. Then to get the variable to have a coefficient of 1, divide by 2.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!