Multiplication Worksheets For Grades 3-8: Free And Printable Worksheets
Multiplication worksheets are an essential resource for both students and teachers from grades 3 through 8. They help reinforce fundamental multiplication skills and provide ample opportunities for practicing multiplication facts. For learners, these worksheets provide ample opportunities to practice and master basic multiplication concepts, such as multiplication equations and multiplication tables, which are foundational for tackling more complex math problems, such as division and algebra.
Engaging in multiplication practice helps learners enhance their critical thinking and problem-solving skills, setting the stage for future success in mathematics.
This guide to multiplication worksheets provides teachers with worksheets for 3rd-8th grade students to help build a conceptual understanding of the multiplication skills necessary in elementary and middle school.
How children learn multiplication strategies
Children learn the multiplication operation in the elementary and middle school grades. Learning to multiply is a critical real-world math skill used in and out of the classroom.
Beginning in second grade, children learn pre-multiplication skills such as skip counting and basic arrays. In third grade math, they build on this conceptual understanding and fluency of single-digit multiplication facts within 100.
In upper elementary, children learn multi-digit multiplication with larger numbers, as well as with non-whole numbers such as decimals and fractions.
Middle school progresses children’s fluency in multiplying multi-digit decimals, apply multiplication skills to solve ratio and rate problems and apply their understanding of multiplication to solve simple algebraic equations using multiplication.
By 7th and 8th grade, children learn to apply multiplication skills to real world problems including positive and negative integers, as well as using multiplication to understand scientific notation and linear equations.
Multiplication is taught concurrently with division as they are inverse operations.
Why we’ve brought together these multiplication worksheets
We’ve spoken with hundreds of educators who tell us they want a bank of ready-to-go worksheets to use with their elementary and middle schoolers in class and to set as homework.
Third Space Learning is passionate about making math accessible to all learners and closing the math achievement gap while saving teachers time!
This guide brings together our collection of multiplication worksheets for teachers to use to help students when practicing multiplication facts and boost learners’ multiplication understanding and application.

Meet Skye, the voice-based AI tutor making math success possible for every student.
Built by teachers and math experts, Skye uses the same pedagogy, curriculum and lesson structure as our traditional tutoring.
But, with more flexibility and a low cost, schools can scale online math tutoring to support every student who needs it.
Find out moreWhat to expect from these multiplication worksheets
Math experts have designed every worksheet in this collection so they align with the Common Core State Standards. And, each worksheet can be adapted to state-specific standards.
Every printable worksheet, complete with an answer key, is designed to provide learners with the necessary multiplication practice to help master the skills required to reach proficiency at each grade-level, including practicing multiplication facts.
How to use these multiplication worksheets
There are many ways to use these printable worksheets, both in and out of the classroom. To download, the appropriate worksheet, click the link in this guide, enter your email address and the worksheet will be sent to your inbox.
Some of the ways you can use these worksheets to solidify learners understanding and fluency of multiplication facts include:
Independent practice in class or math centers;
Math warm ups;
As part of the school’s math curriculum;
At home math practice.
Multiplication worksheets to develop reasoning and problem solving skills for grades 3, 4 and 5.
Download Free Now!Multiplication worksheets by grade
This guide includes explanations of the multiplication facts learners will need to know at each stage of elementary and middle school.
You’ll find multiplication strategies, worked examples and a practice problem for learners to complete in addition to the relevant Third Space Learning multiplication worksheet for each grade.
3rd Grade multiplication worksheets
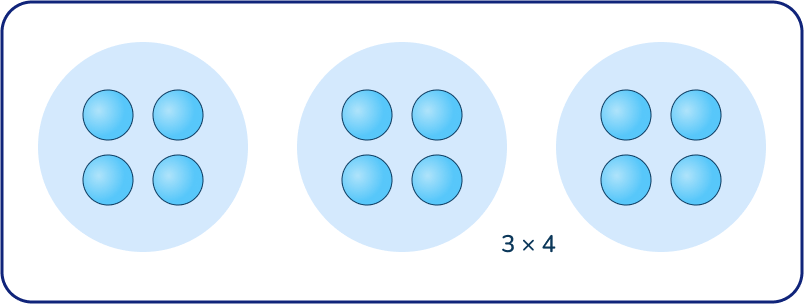
Third grade math lays the foundation for multiplication in elementary school. Children learn to apply the principle of repeated addition to understand multiplication of equal groups.
Often, it helps to use visual models such as the one shown below to draw pictures of equal groups, or use physical objects to model multiplication.
3rd graders also use the array model for multiplication. They begin by modelling it using a concrete model and representing the number of rows and a specific number of objects in each row.
Then they transition to more abstract strategies such as an open area model. This connects physical and concrete strategies to more abstract and efficient strategies.
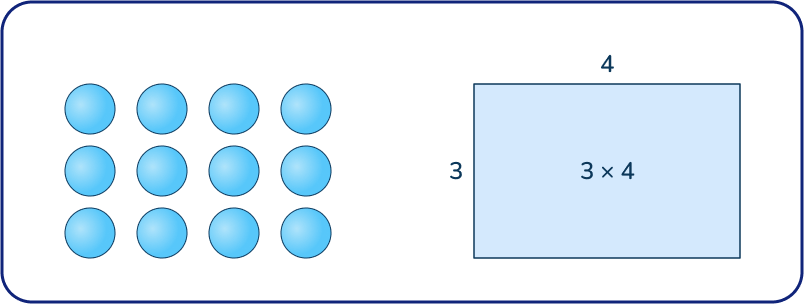
Third graders learn to multiply using the properties of multiplication, such as the commutative, associative and distributive properties. This helps develop more efficiency in problem solving and ultimately develop multiplication fact fluency with single-digit multiplication within 100.
Fluency in multiplication facts or ‘times tables’ requires learners to find the product of a multiplication equation. There are many ways to teach multiplication facts and learn times tables, but often, multiplication charts and playing multiplication games helps build fluency with multiplication facts.
Worked examples
Example 1
6 x 7
Answer: 42
First, model 6 groups with 7 objects in each group or an array with 6 rows with 7 objects in each row.
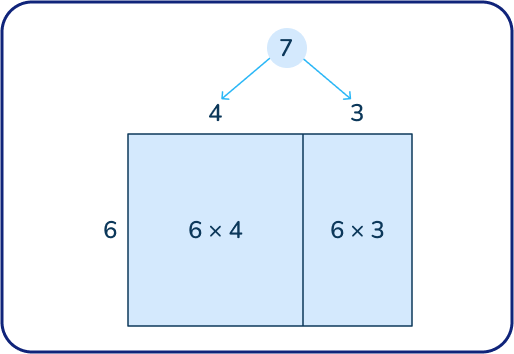
Next, model this using an open area model showing 6 on one side and 7 on the other side. This model helps children see that they can use the distributive property to use a smaller problem to help them solve the larger problem.
For example, if they don’t know 6 x 7 but they do know 6 x 4, they can decompose the number 7 into 4 and 3 and solve (6 x 4) + (6 x 3) to get a product of 42.
Example 2
4 x 12
Answer: 48
For this problem, students might use the commutative property to change around the order of the factors, making the problem 12 x 4 which will have the same product as 4 x 12.
Then, use the distributive property to break 12 apart by place value into 10 + 2.
They can then multiply 10 x 4 = 40 and 2 x 4 = 8 to get a total product of 48.
4 x 12 = 12 x 4
12 = 10 + 2
12 x 4 = (10 x 4) + (2 x 4)
Practice problem
I went apple picking with my family. I filled four baskets with 8 apples in each basket. How many apples in total did I pick?
Answer: 32 total apples because 4 x 8 = 32
4th grade multiplication worksheets
Fourth graders learn to interpret multiplication as a comparison. Multiplicative comparison is a new context for multiplication and children.
Multiplication includes more complex word problems because this new multiplication is all about the context. Teachers can support students through bar models or number lines to make sense of this multiplication context.
As fourth graders should already be fluent in their multiplication facts within 100, they now learn to find factor pairs for each number within 100.
4th Graders also learn to apply their multiplication fact fluency to larger problems with two-digit factors, and learn to multiply 4-digit factors by 1-digit factors using long multiplication, which includes two digit multiplication.
At this level, children learn to use the ‘standard algorithm’ for multiplying numbers efficiently.
Worked examples
Example 1
32 x 47
Answer: 1,504
Students could solve this problem using the area model and breaking apart one or both numbers. This is often known as the ‘partial products’ or box method multiplication.
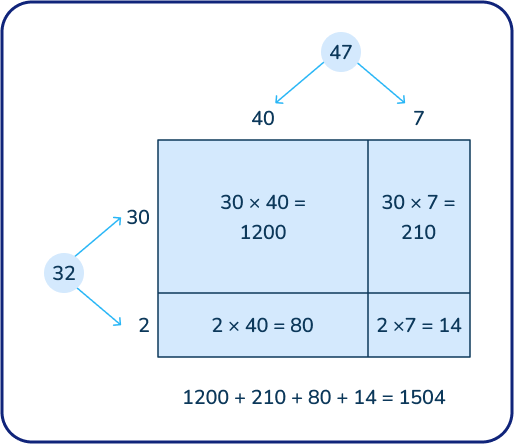
At this level, children might also use the standard algorithm:
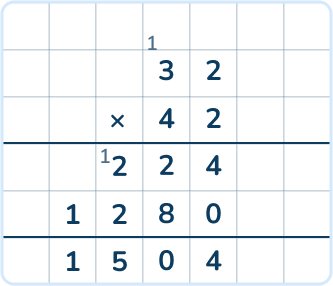
Example 2
Last year 1,452 people attended the summer festival. This year, 4 times as many people attended the festival. How many people attended the festival this year?
Answer: 5,808
First, make a bar model or tape diagram to help children understand where the unknown information is and determine a strategy to solve to find the unknown.
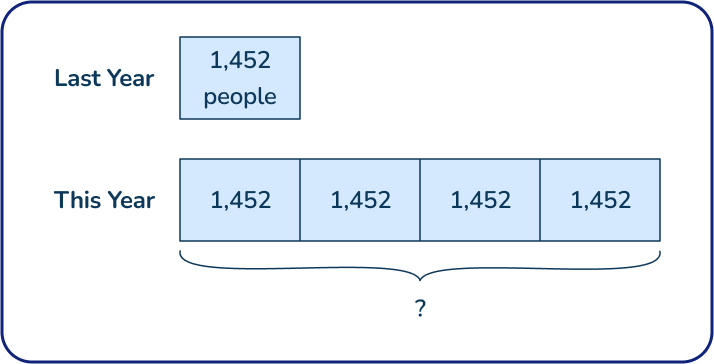
Next, solve the problem by choosing an efficient problem solving strategy. For multiplication of large numbers, fourth graders often use the partial products strategy that they learned previously or the standard algorithm.
Practice problem
On Saturday, Fresh Food Market made 8 times as much money as Guy’s Good Grocery Store. If Guy’s Good Grocery Store made $2,417 on Saturday, how much money did Fresh Food Market Make?
Answer: Fresh Food Market made $19,336 because $2,417 x 8 = $19,336.
5th grade multiplication worksheets
Fifth graders are expected to multiply multi-digit numbers using the standard algorithm, fluently. At this level, children should have a foundation of conceptual understanding of multiplication and solve problems efficiently.
5th graders learn to apply their understanding of multiplying whole numbers to measurement, multiplying decimals to the hundredths and multiplying fractions using visual models, including:
Hundred grids;
Place value charts;
Number lines;
Fraction tiles.
Worked examples
Example 1
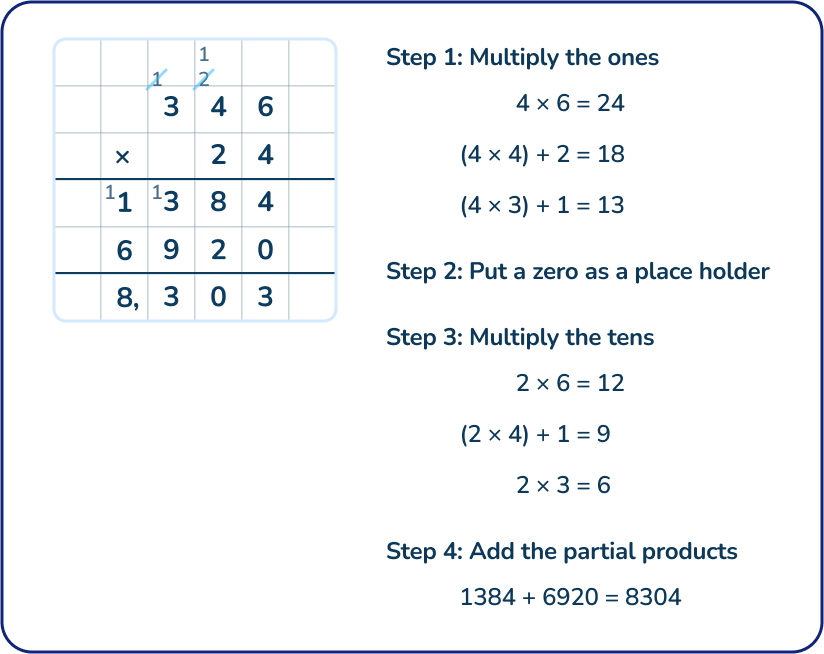
346 x 24
Answer: 8,304
Fifth graders should be able to efficiently and accurately solve this problem using the standard algorithm. Students will realize that using the partial products method is a possible but inefficient strategy to solve this problem.
Teachers should encourage students to use the standard algorithm for multiplication when solving whole number multi-digit multiplication problems.
Example 2
0.6 x 0.8
Answer: 0.48
Since fifth grade is the first time children learn to multiply decimals, using a visual model is a helpful problem solving tool. One of the best ways to help children understand multiplying decimals is to use hundreds grids.
Children can think about this problem as six tenths of eight tenths. They start by modelling 8 tenths, and then they can shade in 6 tenths of that 8 tenths. The double shaded part represents 6 tenths of 8 tenths.
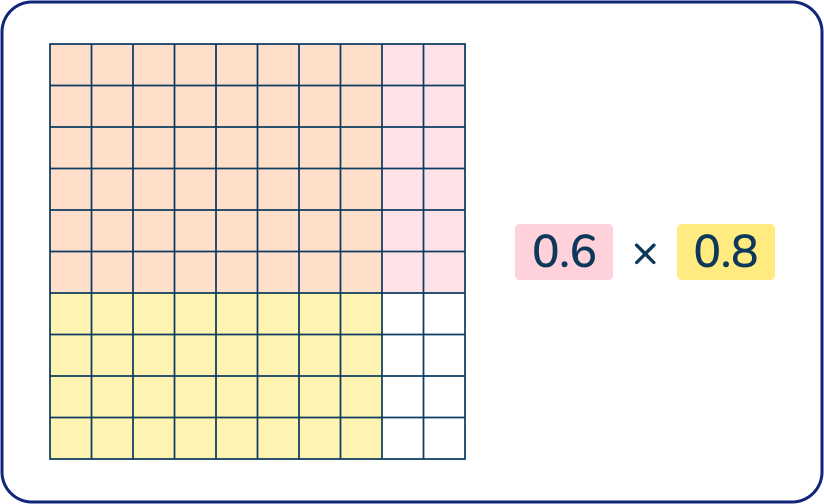
As fifth graders get more advanced in their problem solving they learn to recognize their basic multiplication facts within these decimal problems (in this case, 6 x 8 = 48) and learn what it means when the decimal is in different places in the factors.
Example 3
8 x \frac{1}{2} or \frac{1}{2} x 8
Answer: 4
When multiplying fractions, context helps build conceptual understanding. Based on the context, the problem can be modelled differently. In this problem, it can be thought of as 8 times as much as \frac{1}{2} or as \frac{1}{2} of 8.
5th graders build on their conceptual understanding of the meaning of multiplication from previous grades to understand fraction multiplication. This context and visual model helps children understand what the product means and helps them sense check their answers.
As fifth graders get more advanced in their multiplication skills, they learn to calculate the product by multiplying the numerators and multiplying the denominators,
Practice problem
Some fifth graders had a bake sale to raise money for a field trip. They sold brownies for $0.75 and cupcakes for $0.60. If they sold 34 brownies and 48 cupcakes, did they make more money selling brownies or selling cupcakes? Explain.
Answer: They made $25.50 selling brownies and $28.80 selling cupcakes, so they made $3.30 more selling cupcakes than selling brownies.
6th grade multiplication worksheets
Sixth grade multiplication focuses heavily on applying multiplication to other contexts such as algebraic expression and ratio and proportional relationships. Sixth graders are also expected to be fluent, efficient and accurate in solving multiplication problems including multi-digit decimals.
Children should be able to fluently and flexibly solve multi-digit multiplication problems with whole numbers and decimals. They also learn to find the greatest common factor for a number or set of numbers.
They use these problem-solving abilities to solve rate problems in real world contexts as well as to calculate percentages. 6th graders also use multiplication to understand inequalities as well as solve problems involving a variable that represents an unknown value.
Worked examples
Example 1
It takes 9 hours to mow 5 lawns. At this rate, how many lawns could be mowed in 54 hours?
Answer: 30 lawns
First, set up a rate equation. 9 hours/5 lawns is equivalent to 54 hours/ ____ lawns.

Next, students use their knowledge of multiplication facts to figure out how many times 9 goes into 54, which is 6.
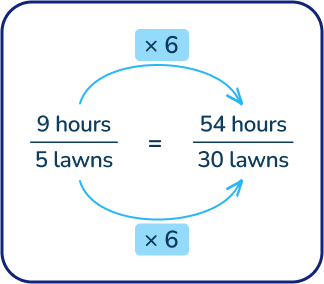
Then, multiply the 5 lawns by 6 to get to 30 lawns that could be mowed in 54 hours.
Students use their knowledge of multiplicative from fourth grade to make sense of this problem.
Students could calculate the rate by dividing 9 by 5 to get a unit rate of 1.8 hours to mow every lawn. Then they could divide 54 by 1.8 to get to the 30 lawns mowed in 54 hours. However, this solution strategy is more aligned with 7th grade math standards.
Example 2
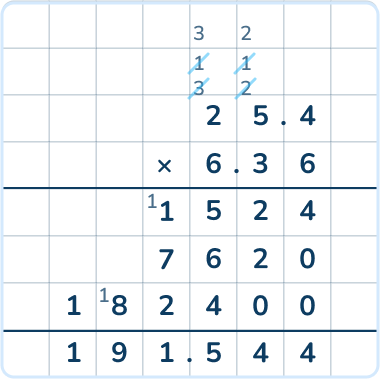
25.4 x 6.36
Answer: 191.544
Students should solve this problem using the standard algorithm. They need to account for the decimals at the end of the multiplication strategy to determine how many numbers are to the right and the left of the decimal.
They can also solve the problem using place value: 254 x 636 and divide the product by 10.
Practice problem
A band was selling t-shirts. They sold 48 t-shirts for $8.75 each. How much money did they make from selling the t-shirts?
Answer: 48 x 8.75 = $420
7th grade multiplication worksheets
Multiplication for seventh graders is centered around the extension and application of multiplication at the previous levels. 7th graders must have deep knowledge and understanding of multiplication to apply this operation to rational numbers.
7th grade math in the number system domain of the Common Core State Standards focuses on all four operations with rational numbers. This includes both positive and negative integers. Students also learn to solve real-world mathematical problems involving unit rate (proportional relationships) with fraction and decimal numbers.
7th graders also learn to apply properties of operations to factor and expand linear expressions with rational coefficients.
Worked examples
For practice multiplying positive and negative integers, 7th graders might solve this set of problems:
Example 1:
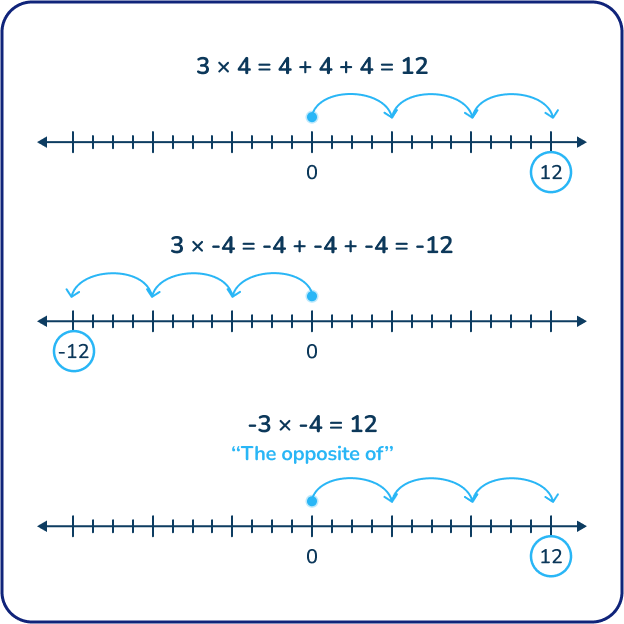
3 x 4 =
3 x -4 =
-3 x -4 =
Answer:
3 x 4 = 12
3 x -4 = -12
-3 x -4 = 12
7th graders learn the rules and practice multiplying positive and negative integers. Primarily that:
Multiplying two positive numbers results in a positive produce;
Multiplying one negative and one positive number results in a negative product;
Multiplying two negative numbers results in a positive product.
Students can use repeated addition from 3rd grade and number lines with positive and negative integers to understand whether the product is positive or negative.
Example 2
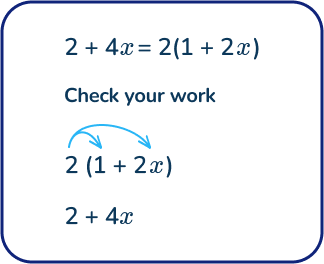
Factor out the greatest common factor in the expression 2 + 4x
Answer:
Step 1: Determine the greatest common factor of both 2 and 4. In this case it is 2.
Step 2: Use knowledge of the distributive property to divide both numbers by the greatest common factor and rewrite the expression.
Step 3: Check your work by using the distributive property to distribute the greatest common factor across the expression to ensure it is equivalent to the original expression.
Practice problem
The store sells AAA batteries in two different sized packs. Calculate the unit rate and determine which has a lower price per battery.
12 batteries for $8.40 or 16 batteries for $9.60
Extension
Use the cost per battery of the better buy option. At this rate, what would the cost of 20 batteries be?
Answer:
Determine the unit cost (cost per battery) for each option:
$8.40 12 = $0.70 per battery
$9.60 16 = $0.60 per battery so this is the better buy
At this rate, for 60 cents per battery, it would cost $12 for 20 batteries.
8th grade multiplication worksheets
Multiplication at this level is embedded into the other math concepts that 8th graders learn. This includes:
Solving linear equations;
Performing operations with numbers expressed using scientific notation;
Constructing functions to model linear relationships.
These are new and often complex ideas for 8th graders. While students are exposed to scientific notation in previous grades, this is the first time they are expected to use multiplication with different exponents.
Additionally, the focus on linear equations which show the relationship between two variables is an important foundational concept that children will build on beyond 8th grade. Teachers can support eighth graders in understanding these complex multiplication concepts through visual models when possible and spending a lot of time in the conceptual understanding phase to help students understand how and why these equations, functions and exponents work.
Worked examples
Example 1
4⁶ x 8³
Answer: 2,097,152
Students first need to understand the concept of an exponent.
In the example of 4⁶, 4 is multiplied by itself 6 times or 4 x 4 x 4 x 4 x 4 x 4. Using a base understanding of exponents with base numbers of 10 from previous grade levels (such as 10³ = 1,000) will help children understand this concept.
Example 2
7x + 9 = 23
Answer: x = 2
- First, students must understand the meaning of the equal sign, which is that both sides of the equal sign must have the same value.
- Subtract 9 from the right side of the equation to make the equation 7x = 14.
- Then, divide 14 by 7 to find the value of x which is 2. x = 2.
- Finally, the value of x is put back into the original equation to check and make sure both sides of the equal sign have the same value. 7(2) + 9 = 23.
Practice problem
Write a linear equation to represent the following word problem then solve it.
Rachel bought a lemonade for $3.75 and 8 cookies from the school fundraiser and spent a total of $34.15. How much did she spend on each cookie?
Answer: 8c + $3.75 = 34.15
$34.15 –$ 3.75 = $30.40
$30.40 ÷ 8 = $3.80
So each cookie cost $3.80
Where to find more multiplication worksheets and resources
Browse the Third Space Learning resource library for more free resources. You’ll find a selection of free printable worksheets, topic guides and additional resources on Numbers and Quantity
For quick download, here’s a list of ready-to-go, easy-to-use multiplication worksheets for 3rd through 8th graders:
Multiplication key takeaways
Multiplication is taught using a spiral curriculum from 3rd grade through grade 8. In this progression students:
Learn multiplication and division concurrently because they are inverse operations.
Build a conceptual understanding of the meaning of multiplication, starting with equal groups multiplication and hands-on multiplication models such as drawings and other concrete models.
Transition from visual models such as arrays and open area models to building fluency with symbolic strategies like the standard algorithm.
Apply multiplication to multiplying multi-digit numbers, decimals and fractions.
Use multiplication skills for real-world problems including but not limited to, multiplicative compare, ratios and rates, among other contexts.
Teachers can support students by providing opportunities for hands-on learning and contextual examples of multiplication to help students build deeper understanding.
In addition to a wide range of free worksheets, topic guides and resources, Third Space Learning provides one-on-one AI math tutoring for struggling students.
Math curriculum experts carefully design each lesson to align with Common Core and state-specific standards. Students across the U.S. signed up for our math programs follow personalized pathways aligned to their state.
Because lessons take place online, schools can organize lessons to suit their schedule, before, during or after school. The one-on-one nature allows targeted support for each individual student to help them close their individual learning gaps.
Multiplication worksheets FAQs
What is the easiest way to teach multiplication?
There isn’t one specific strategy for multiplication that works better than another. However, typically students learn the concept of multiplication best when first introduced through physical and visual models, progressing to more abstract models such as the standard algorithm.
What is the fastest way to memorize multiplication tables?
Children should use smaller multiplication facts and fact families in their times tables to help them become fluent in new multiplication facts. For example, if a student doesn’t know 4 x 8 but they know 4 x 6, they can start with 4 x 6 and then add two more groups of 4. Beginning with smaller multiplication facts as well as doubles facts is helpful when learning times tables. Playing multiplication games and using multiplication worksheets helps support fluency and memorization of multiplication tables.
What is the easiest multiplication method?
The standard algorithm for multiplication is the most efficient method for multiplication. It can be challenging to learn this strategy at first. However, once a child understands how and why this strategy works, it is the most efficient and accurate multiplication strategy. With any multiplication strategy, children should always check their work for accuracy and make sure their answer is reasonable by using estimation.
Do you have students who need extra support in math?
Skye – our AI math tutor built by experienced teachers – provides students with personalized one-on-one, spoken instruction that helps them master concepts, close skill gaps, and gain confidence.
Since 2013, we’ve delivered over 2 million hours of math lessons to more than 170,000 students, guiding them toward higher math achievement.
Discover how our AI math tutoring can boost student success, or see how our math programs can support your school’s goals:
– 3rd grade tutoring
– 4th grade tutoring
– 5th grade tutoring
– 6th grade tutoring
– 7th grade tutoring
– 8th grade tutoring