High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Multiplication Division Converting units of time Converting metric units Rearranging equations SubstitutionSpeed distance time
Here you will learn about the speed distance time triangle including how they relate to each other, how to calculate each one and how to solve problems involving them.
Students will first learn about speed distance time as part of algebra in high school.
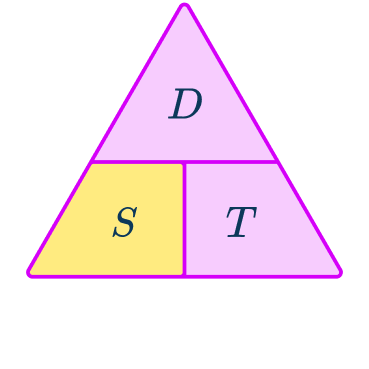
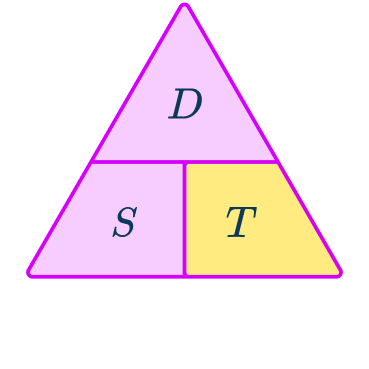
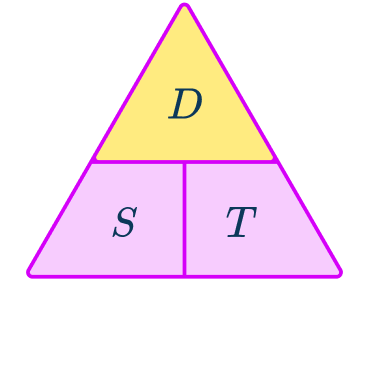
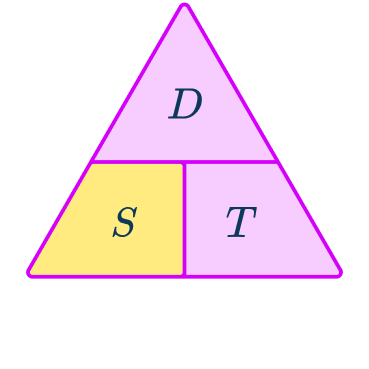
What is the speed distance time triangle?
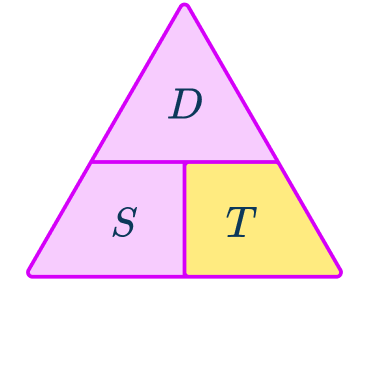
The speed distance time triangle is a way to describe the relationship between these three measures as shown by the formula:
\text{Speed}=\text{Distance}\div\text{Time}
“Speed equals distance divided by time”
Let’s look at an example to calculate speed.
If a car travels D=66\mathrm{~km} in T=1.5\mathrm{~hours} , then you can use this formula to calculate the speed, S.
S=D\div{T}=66\div{1.5}=44\mathrm{~km/h}This formula can also be rearranged to calculate distance D or calculate time T given the other two measures. An easy way to remember the formula and the different rearrangements is to use this speed distance time triangle.
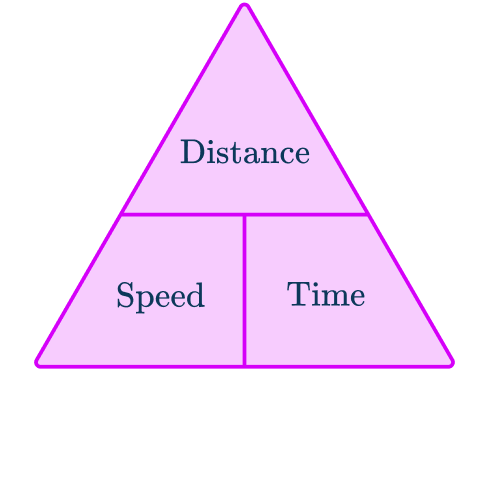
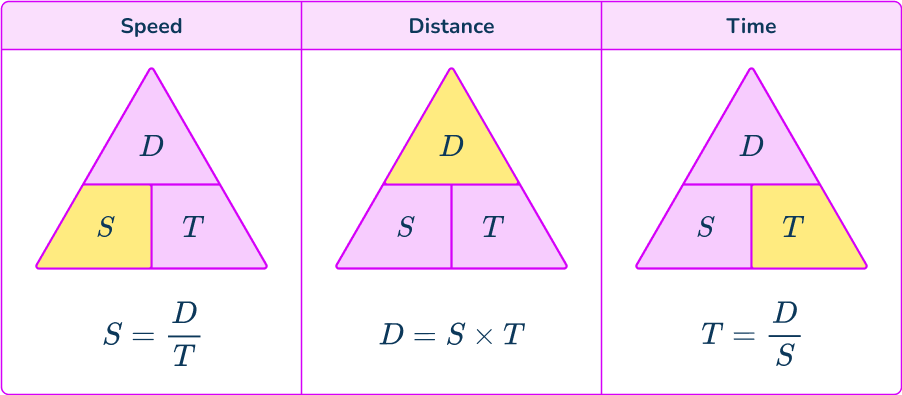
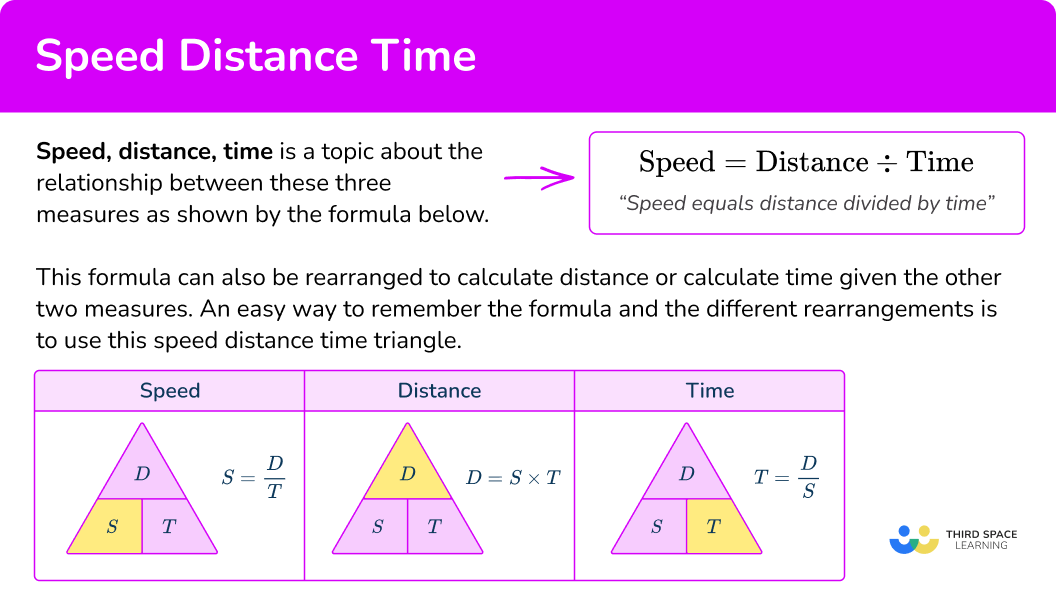
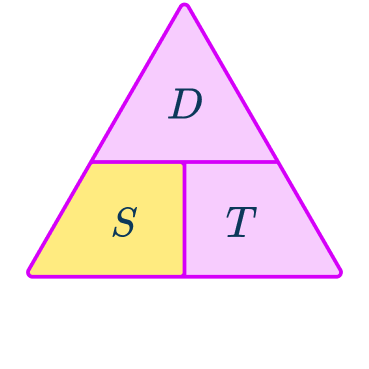
From this triangle, you can figure out how to calculate each measure. You can ‘cover up’ what you are trying to find and the formula triangle tells us what calculation to do.
![[FREE] Ratio Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Ratio-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
[FREE] Ratio Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)
![[FREE] Ratio Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Ratio-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 to 7 students’ understanding of ratios. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th and 7th grade ratio topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Ratio Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Ratio-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
[FREE] Ratio Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)
![[FREE] Ratio Worksheet (Grade 6 to 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Ratio-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 to 7 students’ understanding of ratios. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th and 7th grade ratio topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEUnits of speed, distance and time
Speed
- The speed of an object is the magnitude of its velocity.
Speed is most commonly measured in meters per second (m/s), miles per hour (mph) or kilometers per hour (km/hr). - For example, the average speed of a small plane is 124\mathrm{~mph}; the average walking speed of a person is 1.4\mathrm{~m/s}.
Distance
- The distance an object has traveled is most commonly in millimeters (mm), centimeters (cm), meters (m) and kilometers (km).
- For example, the distance from New York City to Austin is 1,743.5\mathrm{~miles} or 2,805.9\mathrm{~km}.
Time
- Time is measured in milliseconds (ms), seconds (s), minutes (mins), hours (hrs), days, weeks, months and years.
Speed is a compound measure and therefore involves two units; the division of a distance, by a time.
When you use the speed distance time formula, check that each measure is in the appropriate unit before you carry out the calculation. Sometimes you will need to convert a measure into different units. Here are some useful conversions to remember.
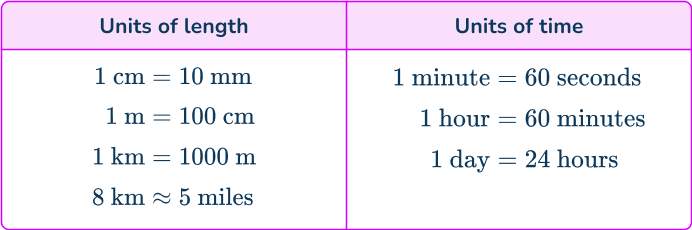
Sometimes you may need to convert an answer into different units.
What is the speed distance time triangle?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to high school math?
- Algebra – Creating Equations (HS-A.CED.A.4)
Rearrange formulas to highlight a quantity of interest, using the same reasoning as in solving equations. For example, rearrange Ohm’s law V=IR to highlight resistance R.
- Number and Quantity – Quantities (HS-N.Q.A.1)
Use units as a way to understand problems and to guide the solution of multi-step problems; choose and interpret units consistently in formulas; choose and interpret the scale and the origin in graphs and data displays.
How to calculate speed distance time
In order to calculate speed, distance or time:
- Write down the known measures including their units.
- Write down the formula you need to use from the speed, distance, time triangle.
- Check that the units are compatible with each other, converting them if necessary.
- Substitute the values into the selected formula and carry out the resulting calculation.
- Write your final answer with the required units.
Speed distance time triangle examples
Example 1: calculating average speed
Calculate the average speed of a car which travels 68\mathrm{~miles} in 2\mathrm{~hours}.
- Write down the known measures including their units.
Speed: unknown
Distance: 68\mathrm{~miles}
Time: 2\mathrm{~hours}
2Write down the formula you need to use from the speed, distance, time triangle.
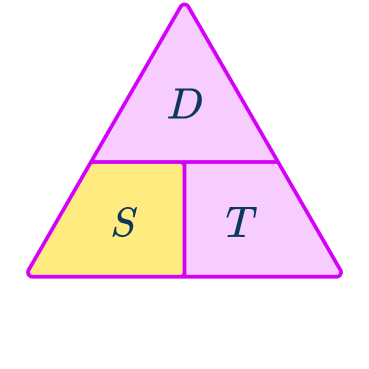
3Check that the units are compatible with each other, converting them if necessary.
The distance is in miles and the time is in hours. These units are compatible to give the speed in miles per hour.
4Substitute the values into the formula and carry out the resulting calculation.
\begin{aligned}S&=D\div{T} \\\\ &=68\div{2} \\\\ &=34 \end{aligned}5Write your final answer with the required units.
The units for the speed here are miles per hour.
S=34\mathrm{~mph}Example 2: calculating time
A golden eagle can fly at a speed of 55\mathrm{~km/h}. Calculate the time taken for a golden eagle to fly 66\mathrm{ ~km}, giving your answer in hours.
Speed: 55\mathrm{~km/h}
Distance: 66\mathrm{ ~km}
Time: unknown
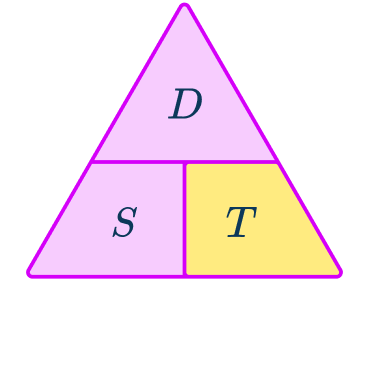
Speed is in kilometers per hour and the distance is in kilometers, so these are compatible to give an answer for time in hours.
\begin{aligned}T&=D\div{S} \\\\ &=66\div{55} \\\\ &=1.2 \end{aligned}The units for the time here are hours as \mathrm{miles}\div\cfrac{\mathrm{miles}}{\mathrm{hour}}=\mathrm{miles}\times\cfrac{\mathrm{hour}}{\mathrm{miles}}=\mathrm{hours}.
T=1.2\mathrm{~hours}
Example 3: calculating distance
Calculate the distance covered by a train traveling at a constant speed of 112\mathrm{~mph} for 4\mathrm{~hours}.
Speed: 112\mathrm{~mph}
Distance: unknown
Time: 4\mathrm{~hours}
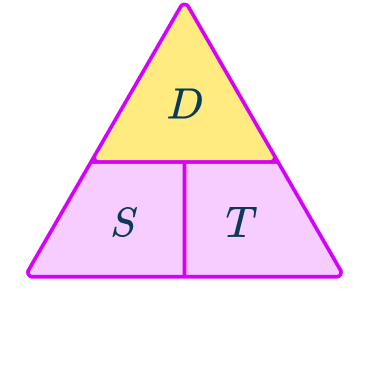
Speed is in miles per hour. The time is in hours. These units are compatible to find the distance in miles.
\begin{aligned}D&=S\times{T} \\\\ &=112\times{4} \\\\ &=448 \end{aligned}The units for the distance here are miles.
D=448\mathrm{~miles}
Example 4: calculating speed with unit conversion
A car travels for 1\mathrm{~hour} and 45\mathrm{~minutes}, covering a distance of 63\mathrm{~miles}. Calculate the average speed of the car giving your answer in miles per hour (mph).
Speed: unknown
Distance: 63\mathrm{~miles}
Time: 1\mathrm{~hour} and 45\mathrm{~minutes}
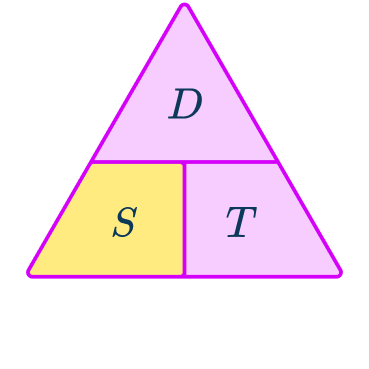
The distance is in miles. The time is in hours and minutes. To calculate the speed in miles per hour, the time needs to be converted into hours only.
1\mathrm{~hour} \; 45\mathrm{~minutes}=1\cfrac{3}{4}\mathrm{~hours}=1.75\mathrm{~hours}
The units for the speed here are miles per hour.
S=36\mathrm{~mph}
Example 5: calculating time with unit conversion
A small plane can travel at an average speed of 120 miles per hour. Calculate the time taken for this plane to fly 80\mathrm{~kilometers} giving your answer in minutes.
Speed: 120\mathrm{~mph}
Distance: 80\mathrm{~miles}
Time: unknown
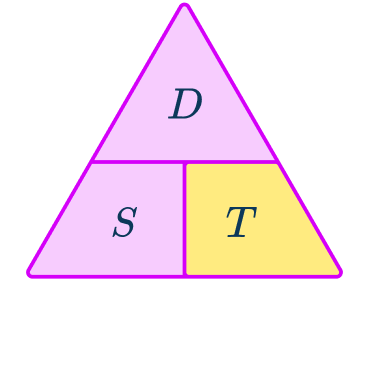
Speed is miles per hour and the distance is in kilometers. The distance must be converted to miles so that the units are compatible.
As 5\mathrm{~miles}\approx{8}\mathrm{~km},
80\mathrm{~km}=5\times{10}=50\mathrm{~miles}
Updating the known values:
Speed: 120\mathrm{~mph}
Distance: 50\mathrm{~miles}
Time: unknown
The units for the time here are minutes. As the time is currently in hours, multiply the time by 60 to convert to minutes.
T=0.41\dot{6}\times{60}=25\mathrm{~minutes}
Example 6: calculating distance with unit conversion
A train travels at a constant speed of 96 miles per hour for 135\mathrm{~minutes}. Calculate the distance covered giving your answer in miles.
Speed: 96\mathrm{~mph}
Distance: unknown
Time: 135\mathrm{~minutes}
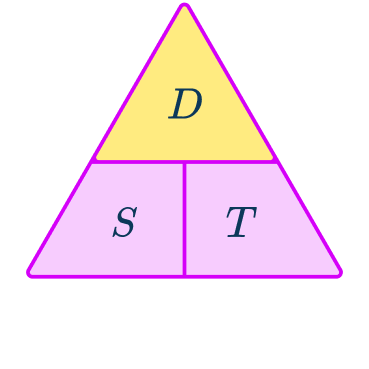
The speed is in miles per hour, but the time is in minutes. To make these compatible, the time needs to be changed into hours, then the calculation will give the distance in miles.
135\mathrm{~minutes}=135\div{60}=\cfrac{9}{4}=2\cfrac{1}{4}=2.25\mathrm{~hours}
The units for the distance here are miles.
D=216\mathrm{~miles}
Teaching tips for speed distance time
- Let students work with hands-on examples of this skill. For example, have them measure how far an object moves as they measure the amount of time. Let them use that to calculate the speed. Challenge them to repeat this process to create different speeds.
- Choose worksheets that have a variety of problem times, including word problems where the speed, distance or time is missing.
- Give struggling students access to specific conversions or calculators, like a time calculator that shows conversions between seconds, minutes and hours. This way students can focus on understanding the relationship between speed distance time, instead of getting lost in the calculations.
Easy mistakes to make
- Incorrectly rearranging the formula for a speed calculation
Make sure you rearrange the formula correctly to find the formula of speed, \text{Speed}=\text{Distance}\div\text{Time}. One of the simplest ways of doing this is to use the formula triangle.
In the triangle, you cover up the measure you want to find out and then the triangle shows you what calculation to do with the other two measures.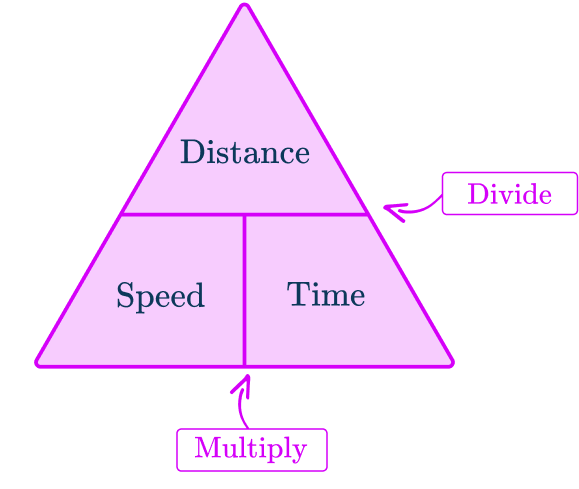
- Using incompatible units in a calculation
When using the speed distance time formula, you must ensure that the units of the measures are compatible.
For example, if a car travels at 80\mathrm{~km/h} for 30\mathrm{~minutes} and you are asked to calculate the distance, a common error is to substitute the values straight into the formula and do the following calculation.
D=S\times{T}=80\times{30}={2,400}\mathrm{~km}
The correct way is to notice that the speed uses hours but the time given is in minutes.
Therefore you must change 30\mathrm{~minutes} into 0.5\mathrm{~hours} and substitute these compatible values into the formula and do the following calculation.
D=S\times{T}=80\times{0.5}=40\mathrm{~km}
Practice speed distance time triangle questions
1. A car drives 120\mathrm{~miles} in 3\mathrm{~hours}. Calculate its average speed.




Speed: unknown
Distance: 120\mathrm{~miles}
Time: 3\mathrm{~hours}
\begin{aligned}S&=D\div{T} \\\\ &=120\div{3} \\\\ &=40\mathrm{~mph} \end{aligned}
2. A cyclist travels 100\mathrm{~miles} at an average speed of 20\mathrm{~mph}. Calculate how long the journey takes.




Speed: 20\mathrm{~mph}
Distance: 100\mathrm{~miles}
Time: unknown
\begin{aligned}T&=D\div{S} \\\\ &=100\div{20} \\\\ &=5\mathrm{~hours} \end{aligned}
3. An eagle flies for 30\mathrm{~minutes} at a speed of 66\mathrm{~km/h}. Calculate the total distance the bird has flown.




The time in the speed does not have the same units as the time given. Convert the minutes to hours.
30\mathrm{~minutes}=0.5\mathrm{~hours}
Speed: 66\mathrm{~km/h}
Distance: unknown
Time: 0.5\mathrm{~hours}
\begin{aligned}D&=S\times{T} \\\\ &=66\times{0.5} \\\\ &=33\mathrm{~km} \end{aligned}
4. Calculate the average speed of a truck traveling 54\mathrm{~miles} in 90\mathrm{~minutes}. Give your answer in miles per hour (mph).




First, convert 90\mathrm{~minutes} to hours\text{:}
90\mathrm{~minutes}=90\div{60}=1.5\mathrm{~hours}
\begin{aligned}S&=D\div{T} \\\\ &=54\div{1.5} \\\\ &=36\mathrm{~mph} \end{aligned}
5. Calculate the time taken for a plane to fly 90\mathrm{~miles} at an average speed of 120\mathrm{~mph}. Give your answer in minutes.




\begin{aligned}T&=D\div{S} \\\\ &=90\div{120} \\\\ &=0.75\mathrm{~hours} \end{aligned}
Convert 0.75\mathrm{~hours} to minutes\text{:}
0.75\times{60}=45\mathrm{~minutes}
6. A helicopter flies 18\mathrm{~km} in 20\mathrm{~minutes}. Calculate its average speed in km/h.




First, convert 20\mathrm{~minutes} to hours\text{:}
20\div{60}=\cfrac{1}{3}\mathrm{~hours}
Use the formula S=D\div{T}\text{:}
\begin{aligned}S&=18\div\cfrac{1}{3} \\\\ &=18\times{3} \\\\ &=54\mathrm{~km/h} \end{aligned}
Speed distance time FAQs
The three formulas are s=\cfrac{d}{t} \; (distance \div time), \; d=s \times t (speed \times time), \; t=d \div s \; (distance \div speed).
It is a distance calculation that is based on the Pythagorean theorem.
The formula is d=\sqrt{\left(x_{2}-x_{1}\right)^2-\left(y_{2}-y_{1}\right)^2} where the coordinates \left(x_{1}, y_{1}\right) and \left(x_{2}, y_{2}\right) are the two points in which the distance is being measured.
No, average velocity considers displacement, whereas average speed does not.
They are the same unit of measurement as centimeters, but are spelled in this way in the United Kingdom.
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!