High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Place value Ratio How to write a ratio Dilations Metric units of measurementScale math
Here you will learn about scale math, including scale diagrams, scale drawing, scale factors and real life applications.
Students will first learn about scale math as part of geometry in th grade.
What is scale math?
Scale math involves enlarging or reducing objects. It refers to the process of resizing an object or drawing by a certain ratio, known as the scale factor, while maintaining its proportions.
If you have two similar geometric figures, one will be a scale diagram of the other.
You can calculate the scale factors for length, area and volume.
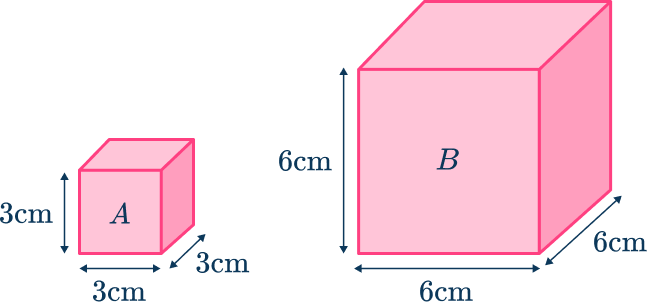
Let’s look at this example,
![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)
![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
Prepare for your math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 8 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents. 40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)
![[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/10/common-core-practice-tests.png)
Prepare for your math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 8 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents. 40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!
DOWNLOAD FREELength scale factor
The length scale factor can be calculated by comparing two lengths.
You can compare the length of (the smaller figure) with the length of (the larger figure).

This gives the ratio which simplifies to
The length scale factor from to is
Area scale factor
The area scale factor can be calculated by comparing two areas.
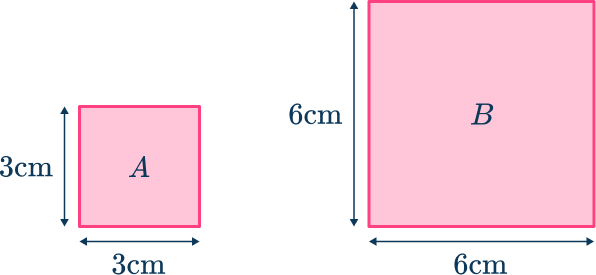
You can compare the area of with the area of
Area
Area
This gives the ratio which simplifies to
The area scale factor from to is
Volume scale factor
The volume scale factor can be calculated by comparing two volumes.
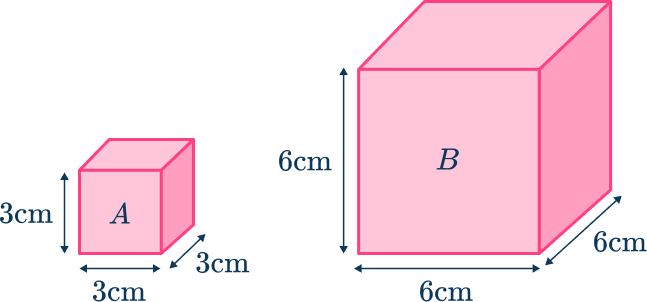
Volume
Volume
This gives the ratio which simplifies to
The volume scale factor from to is
Alternatively you can calculate the area and volume scale factors by starting with the scale factor for length.
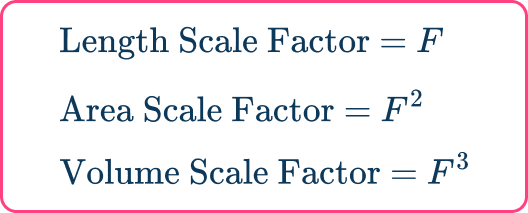
You can square the length scale factor to calculate the area scale factor.
You can cube the length scale factor to calculate the volume scale factor.
In the above example,
Scale factor for length
Scale factor for area
Scale factor for volume
Scale math is used for real world scale drawings as it is much easier to create a scale drawing of an object, than to draw the object using actual distances. The ratio usually takes the form of the model/plan to the actual distance.
Step-by-step guide: Scale drawing
For example, below is a scale diagram of a floor plan of a house where square is equal to meters.
Writing this as a ratio you get square
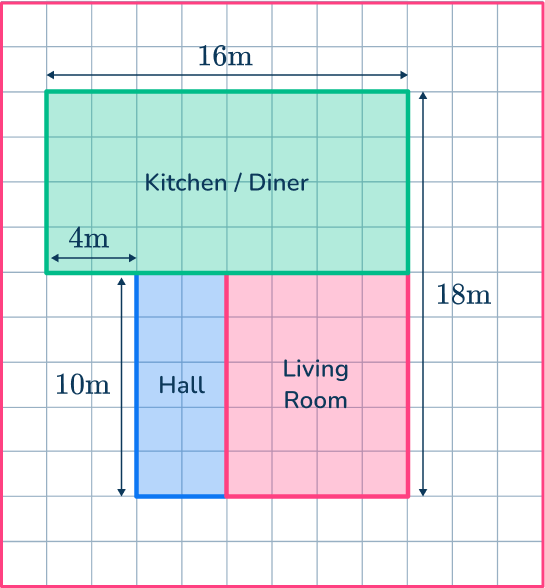
From this diagram, you can calculate the width of the living room by counting squares:
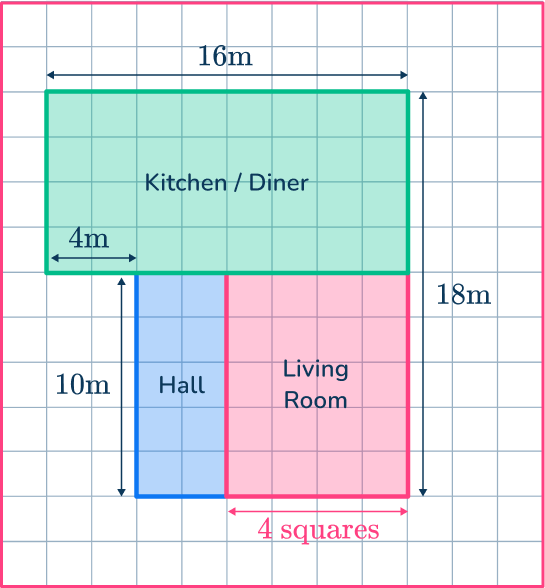
As the living room is squares wide and you have the ratio square: multiplying the number of squares by you get the actual width of the living room.
, so the living room is wide.
What is scale math?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to th grade math?
- Grade 7 – Geometry (7.G.A.1)
Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including computing actual lengths and areas from a scale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale.
How to use scale math
In order to calculate the actual / real life distance from a scale:
- State the scale factor as a ratio in the form
- Multiply by the length given from the model.
- Write the units.
In order to calculate the model length from a scale:
- Divide the real life distance by the map scale ratio.
- Write the units.
In order to calculate a ratio from a scale diagram:
- Identify two lines that are mathematically similar.
- Express the lengths as a ratio
- Simplify the ratio.
Scale math examples
Example 1: map (find the actual distance)
A map has a scale of Find the actual distance represented by on the map.
- State the scale factor as a ratio in the form
2Multiply by the length given from the model.
3Write the units.
Example 2: plan of a structure (find the actual distance)
The construction plans for a structure has the scale What is the actual distance of on the plan?
State the scale factor as a ratio in the form
You have the ratio which you can express as the ratio or in centimeters,
Multiply by the length given from the model.
Write the units.
or
Example 3: map of the UK (find the model length)
A map of the UK is drawn using the scale Calculate how far would be on the map.
Divide the real life distance by the map scale ratio.
Before you do this, convert the ratio to the form by dividing both sides of the ratio by
Now you can calculate the length on the map.
Write the units.
Example 4: floor plan (find the model length)
A plan of a kitchen uses the scale Calculate the distance on the plan for the actual distance of
Divide the real life distance by the map scale ratio.
Before you do this, convert the ratio to the form by dividing both sides of the ratio by
You also can convert to centimeters by multiplying it by
Write the units.
Example 5: 2D polygon (calculate the ratio)
A kite has a vertical height of and a width of The scale diagram of the same kite has a width of What is the ratio of the real kite to the scale diagram? Write your answer in its simplest form.
Identify two lines that are mathematically similar.
Here you have the two widths of the kite with the lengths and
Express the lengths as a ratio
The ratio is of the form actual : scale diagram so you have the ratio
Simplify the ratio.
Writing the ratio in the simplest form (divide throughout by ) you have:
or
Example 6: scale model
The circumference of Jupiter is A scale model of the planet has a diameter of Calculate the ratio of the scale diagram to the real planet Jupiter. Give your answer if the form Write and correct to significant figures.
Identify two lines that are mathematically similar.
The circumference of a circle and so the circumference of the scale diagram of Jupiter is
You can now use the two circumferences and
Express the lengths as a ratio
The ratio is of the form scale diagram : actual so you have the ratio
Simplify the ratio.
Rounding the ratio, you get
Teaching tips for scale math
- Use real-world objects, like maps, blueprints, or model cars, to introduce the concept of scale. Discuss how scale represents a ratio between the measurements on the model and the actual size of the object.
- Engage students in activities where they create their own scaled drawings or models on a piece of paper. For example, have them draw a simple object at a different scale or create a scale model of a room using graph paper.
- Clearly explain the scale factor as the ratio of any two corresponding side lengths in the original figure and the scaled figure. Provide worksheets to practice calculating the scale factor with different examples.
- Discuss how scaling can involve both enlarging and reducing objects. Use examples to illustrate how the scale factor greater than indicates enlargement (scale up), while a scale factor less than indicates reduction (scale down).
Easy mistakes to make
- Multiplying the real life distance by the ratio scale
Multiplying the actual real-life distance by the ratio scale to find the distance on a plan will lead to an incorrect result.
- Dividing the model / plan / map distance by the ratio scale
A common misconception is to divide the distance on the model / plan / map by the ratio scale resulting in an incorrect real life distance.
- The order of the ratio is incorrect
Stating the ratio in the incorrect order will mean that the scale diagram is much larger / smaller than expected.
For example, a ratio represents the scale diagram to the real life distance. The ratio means that the real life distance is twice the length of the scale diagram. The ratio on the other hand, means that the real life distance is half of the scale diagram.
- Ratio scale not simplified
If given the ratio it is easier to calculate when the ratio is in the form and so you must find an equivalent ratio before using the scale. Here the ratio would be so on the map would be equal to in real life.
- Incorrect units in the solution
A common misconception is to mix up the units for the model with the units for the real life distance.
For example, if you were calculating the distance of on a map with the scale ratio of could be incorrectly stated. Whereas the correct solution would be
- Converting units
Sometimes the units need to be converted, so it is important to be able to confidently convert between different metric units.
For example, the map scale is given as which means that on the map is equivalent to in real life. If the answer needs to be written in kilometers, the real life value in centimeters must be divided by to get the same measurement in kilometers.
Related congruence and similarity lessons
Practice scale math questions
1. A map has a scale The distance between two points on the map is What is the real distance in kilometers?




2. The plan of a window seat is drawn using the scale of What is the actual length of the window seat if it measures on the scale drawing?




3. A map has a scale of The length of a walk is measured as What would the distance on the map be for the same walk? Give your answer to the nearest tenth ( decimal place).




This rounds to
4. A plan of a cruise ship uses the scale The deck of the ship is in length. Calculate the length of the model cruise ship in meters.




5. Below is a diagram showing two triangular prisms. Prism is a model of Prism
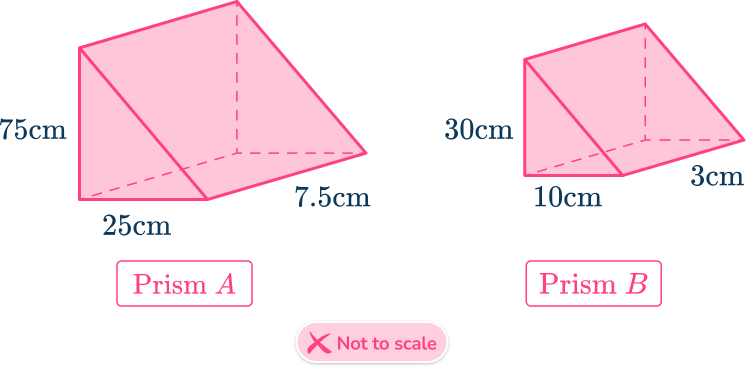
Calculate the ratio of lengths of Prism to lengths of Prism in its simplest form.




Taking one similar length (the height for example) from each prism
6. The length of a table is the length of the table is times its width. The width of the table on the diagram is Calculate the ratio of the length of real table to the length of the diagram table. Give your answer in the form where and are integers.




Scale math FAQs
A scale is a ratio that compares the dimensions of a model, drawing, or map to the actual dimensions of the original object it represents. For example, a scale of means that unit on the drawing corresponds to units in real life.
The scale factor is the number by which all dimensions of an object are multiplied to achieve a scaled version. If a shape is enlarged or reduced by a scale factor, the corresponding sides of the original shape and the scaled shape maintain the same ratio.
To find the scale factor, divide a length on the scaled drawing by the corresponding length on the original object. If the drawing is smaller than the original, the scale factor will be less than If it’s larger, the scale factor will be greater than
To use scale factors, multiply the original dimensions of a shape by the scale factor to find the dimensions of the new shape.
The next lessons are
- Transformations
- Mathematical proof
- Area
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!