High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Congruent triangles Hypotenuse Circumference of a circleScale factor
Here you will learn about scale factor, including enlarging a shape by a scale factor on a grid. You will extend this to learn about fractional scale factors and how to calculate scale factors.
Students will first learn about scale factor as part of geometry in 7 th grade and continue to work with scale factor in high school.
What is a scale factor?
A scale factor is a ratio between two corresponding sides of similar shapes. A scale factor describes how much a shape has been scaled up or down.
To scale a shape up or down, you multiply every side length of a shape by the scale factor to increase or decrease the size. The sizes of the angles do not change. Changing a shape by a scale factor greater than \bf{1} will make the shape a larger figure. Scaled shapes can be referred to as images, while original shapes are referred to as preimages.
For example, shape A that has been enlarged by scale factor 2 to give shape B.
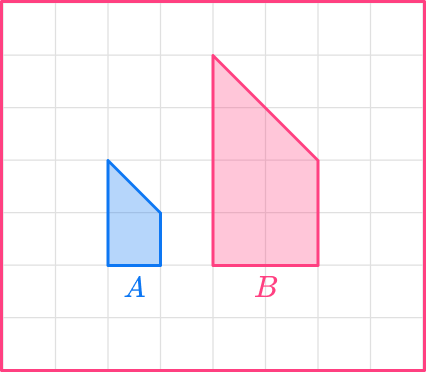
The corresponding angles are identical but each side in shape B is double the size of the original figure.
The two shapes are similar figures. Enlarging a shape by a scale factor between \bf{0} and \bf{1} will make the shape smaller. This is often written as a fraction or a decimal and is known as a fractional scale factor.
Here, shape A has been enlarged by scale factor \cfrac{1}{2} to get shape B.
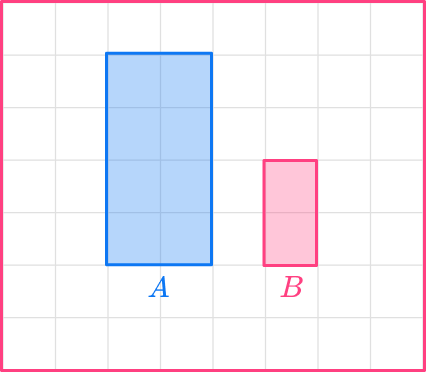
If you look at the corresponding sides in the scale drawing, each side in shape B is half the size of the original shape. The corresponding angles are identical. The two shapes are similar figures.
What is a scale factor?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 7 th grade and high school math?
- Grade 7 – Geometry (7.G.A.1)
Solve problems involving scale drawings of geometric figures, including computing actual lengths and areas from a scale drawing and reproducing a scale drawing at a different scale.
- High school: Geometry – Similarity, Right Triangles, and Trigonometry (HSG.SRT.A.1)
Verify experimentally the properties of dilations given by a center and a scale factor:
![[FREE] Scale Factor Worksheet (Grade 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Scale-Factor-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Scale Factor Worksheet (Grade 7)
![[FREE] Scale Factor Worksheet (Grade 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Scale-Factor-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your 7th grade students’ understanding of scale factor. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Scale Factor Worksheet (Grade 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Scale-Factor-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Scale Factor Worksheet (Grade 7)
![[FREE] Scale Factor Worksheet (Grade 7)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/Scale-Factor-Worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your 7th grade students’ understanding of scale factor. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEHow to use a scale factor
In order to use a scale factor to increase the size of a shape:
- Draw a scaled drawing of the first side.
- Scale another side.
- Complete the scaled shape.
How to use scale factor examples
Example 1: using a scale factor to enlarge a shape
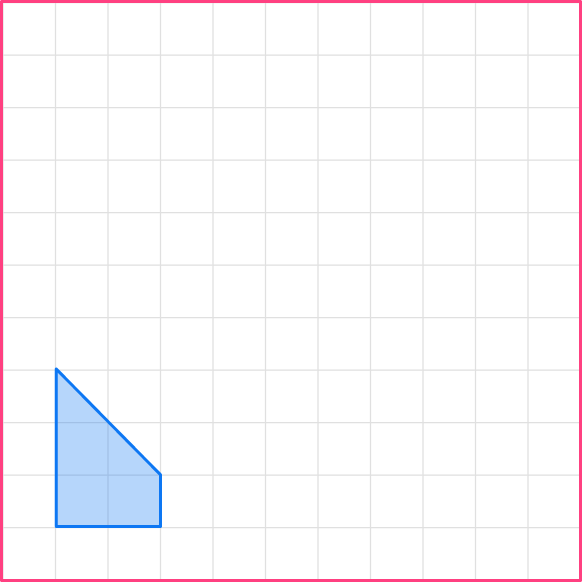
Enlarge this shape by scale factor 2 :
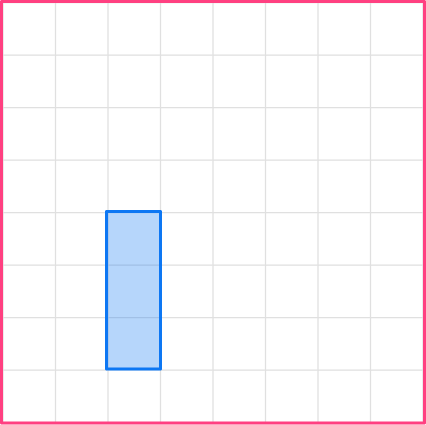
- Scale the first side.
Let’s start with the base. The base in the original shape is 1, so the base of the image will be 2.
1\times2=2
You can draw it anywhere on the grid.
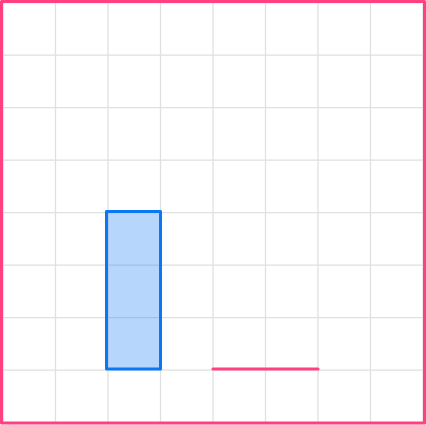
2Scale another side.
Let’s choose a side that is attached to the first side. The height of the first shape is 3, so the height of the enlarged shape will be 6.
3\times2=6
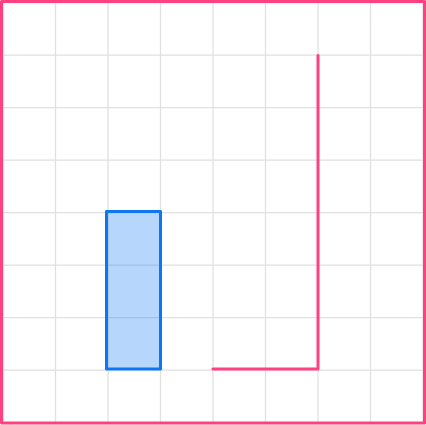
3Complete the scaled shape.
Now continue to draw the new shape.
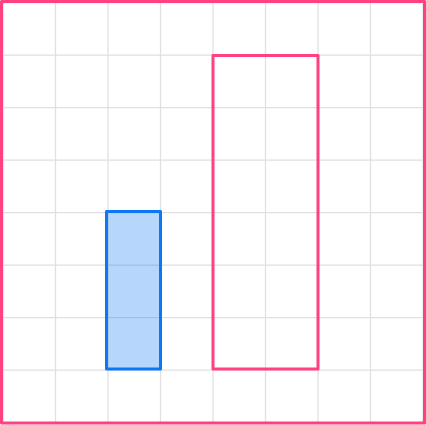
The lengths of the sides of the image are double the lengths of the preimage. You can see the different sizes of the shapes above.
Example 2: using a scale factor to enlarge a shape
Enlarge this shape by scale factor 3 :
The base in the original shape is 2, so the base in the bigger shape will be 6.
2\times3=6
You can draw it anywhere on the grid.
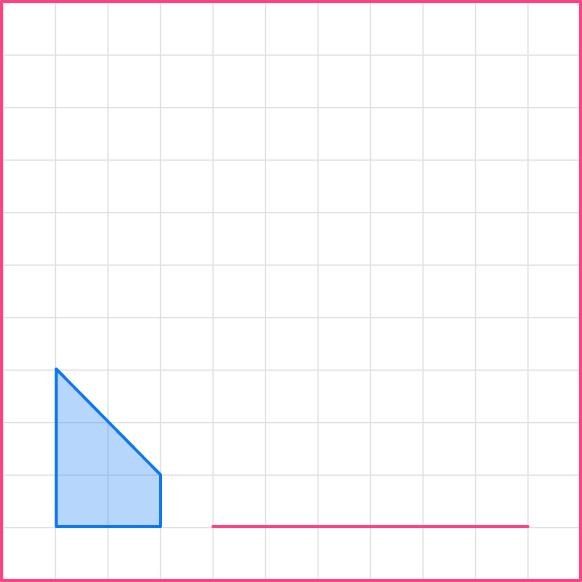
The left vertical side of the first shape is 3, so the corresponding side of the bigger shape will be 9.
3\times3=9
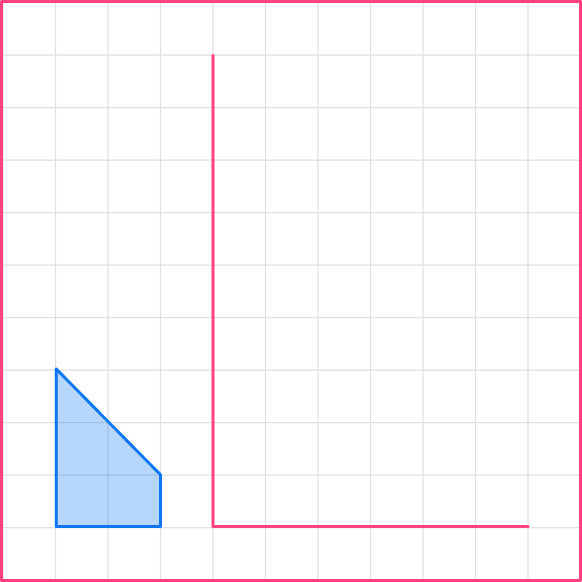
Now continue to draw the new shape. It is easier to do the horizontal and vertical sides first.
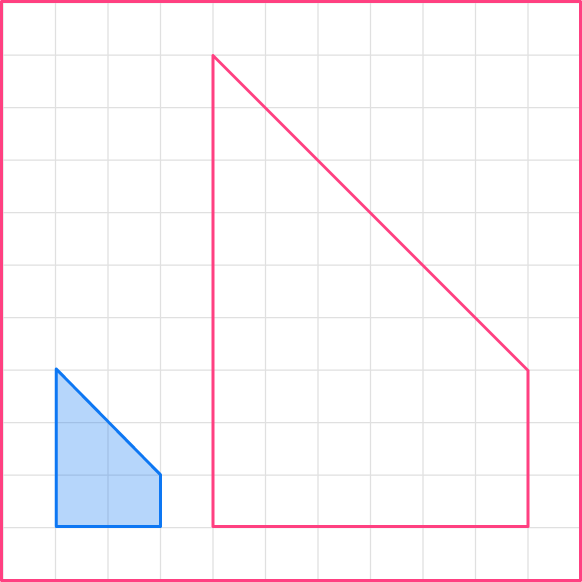
The lengths of the sides of the second shape are three-times the lengths of the original shape.
Example 3: using a scale factor to enlarge a shape
Draw this shape with a scale factor of \cfrac{1}{2} :
The base in the original shape is 4, so the base of the new shape will be 2.
4\times \cfrac{1}{2}=2
You can draw it anywhere on the grid.
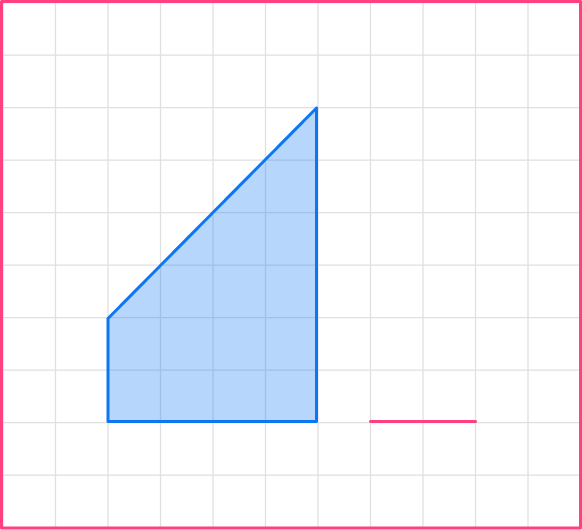
The left vertical side of the first shape is 2, so the length of the corresponding side of the new shape will be 1.
2\times \cfrac{1}{2}=1
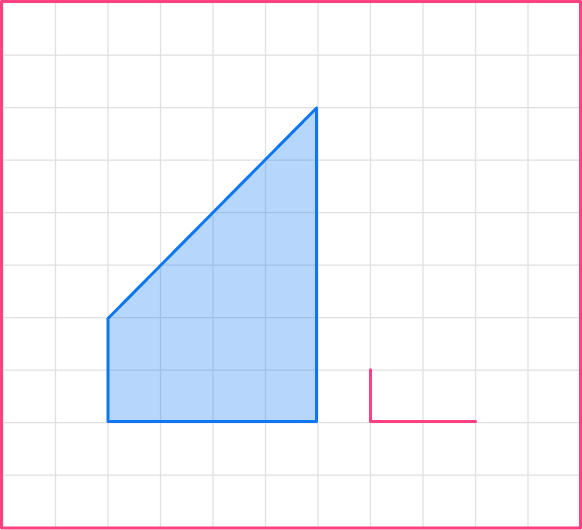
Now continue to draw the image. It is easier to do the horizontal and vertical sides first.
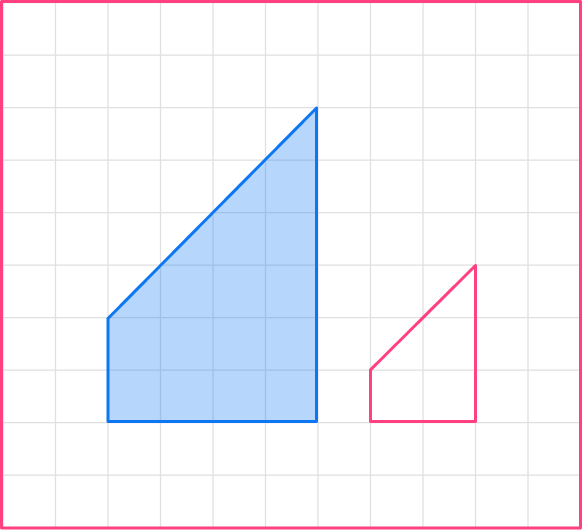
The length of the corresponding side of the second smaller figure are half the lengths of the original shape.
How to calculate a scale factor
In order to calculate a scale factor:
- Choose a pair of corresponding sides.
- Divide the length of the enlarged shape by the length of the original shape.
- Write down the scale factor.
Calculating scale factor examples
Example 4: calculating a scale factor
Calculate the scale factor for the image of Triangle A to Triangle B :
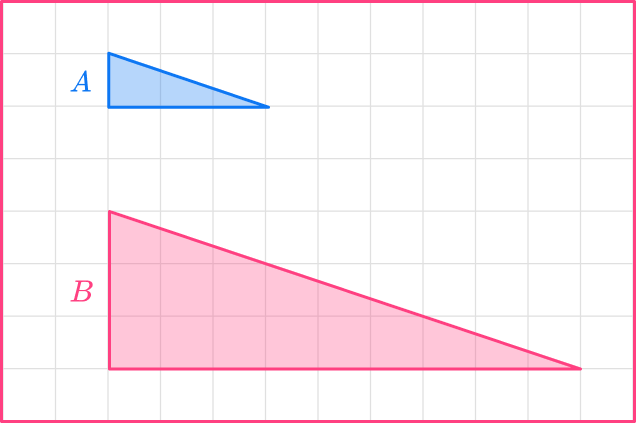
The two triangles are similar triangles.
Choose a pair of sides, either horizontal or vertical. Here I am choosing the bases.
The base of shape A is 3.
The base of shape B is 9.
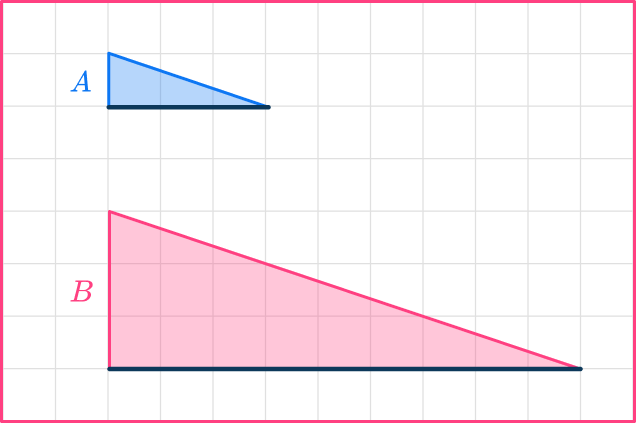
You need to divide the enlarged length by the original length.
scale \ factor = \cfrac{enlarged \ length}{ original \ length}=\cfrac{9}{3}=3
The scale factor for Triangle A to Triangle B is \bf{3}.
Example 5: calculating a scale factor
Calculate the scale factor for the preimage to the image of Shape A to Shape B :
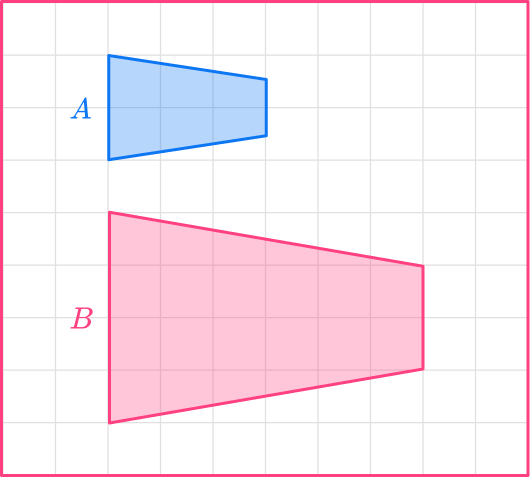
Let’s choose the vertical sides on the left.
The length of shape A is 2.
The length of shape B is 4.
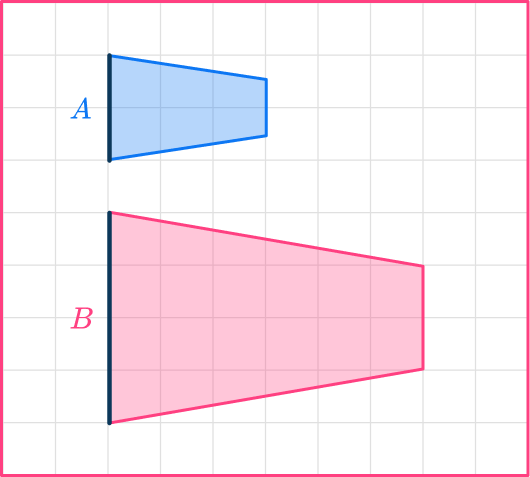
You need to divide the enlarged length by the original length.
scale \ factor = \cfrac{enlarged \ length}{ original \ length}=\cfrac{4}{2}=2
The scale factor for shape A to shape B is \bf{2}.
Example 6: calculating a scale factor
Calculate the scale factor for the preimage to image of Shape A to Shape B :
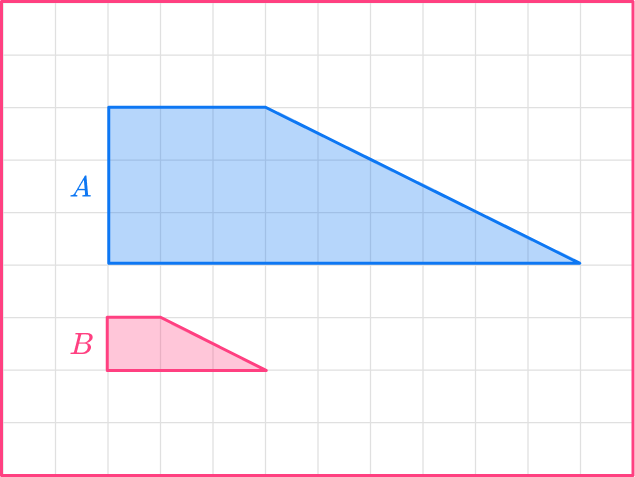
Let’s choose the bases.
The length of shape A is 9.
The base of shape B is 3.
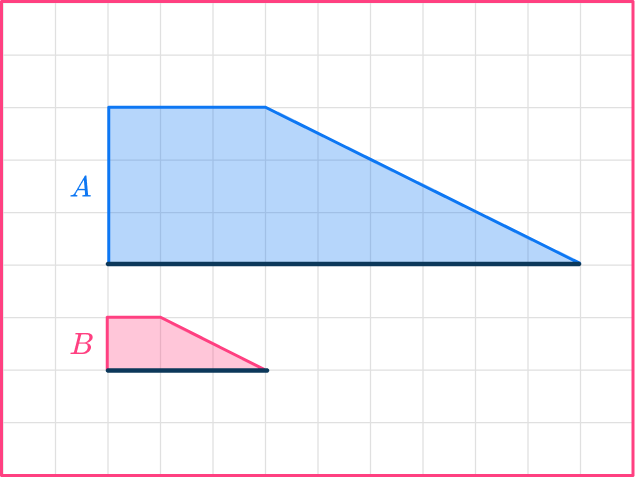
You need to divide the enlarged length by the original length.
scale \ factor = \cfrac{enlarged \ length}{ original \ length}=\cfrac{3}{9}=\cfrac{1}{3}
The scale factor for shape A to shape B is \cfrac{1}{3}.
Teaching tips for how to find the scale factor
- Allow students to explore scale factor using physical manipulatives, with a strong focus on fractional scales, before moving on to written examples. This will prepare students for the idea that multiplying side lengths by a fraction will result in a new shape that is smaller than the original figure.
- Bridge the gap between fractions and decimals for students when thinking about scale factor resulting in smaller figures. Posing the idea that 0.5 of the original figure is the same as \cfrac{1}{2} of the original figure will establish a connection that may be rooted in students’ understanding of number sense.
- Use real-world examples to help students understand where and when scale factor may be used in real life. Examples could include creating a scaled model of something, construction blueprint examples, or examples with scales on maps. Providing real-world problems could be accomplished using worksheets or other modalities.
Easy mistakes to make
- Not multiplying all sides of a polygon by the same number
An easy mistake to make when finding scale factor is not multiplying all sides of a polygon by the same number to enlarge the figure. In order to get scaled copies, all side lengths must be multiplied. The new shape will be a scale model of the original figure.
- Dividing instead of multiplying when the scale factor is less than \bf{1}
If the scale factor is less than one, students may divide instead of multiplying. This mistake would result in an incorrect answer because dividing by a decimal actually results in a larger number. For this reason, when using scale factor, you must always multiply. When you multiply by a decimal, you get a smaller figure than the original figure.
- Setting up the wrong ratio when finding the scale factor
When creating the ratio for the corresponding sides of similar geometric figures, the measurement for the original shape is always the denominator and the measurement of the scaled figure is always the numerator. Confusing the two will create an incorrect scale factor.
For example,
Below are two similar shapes.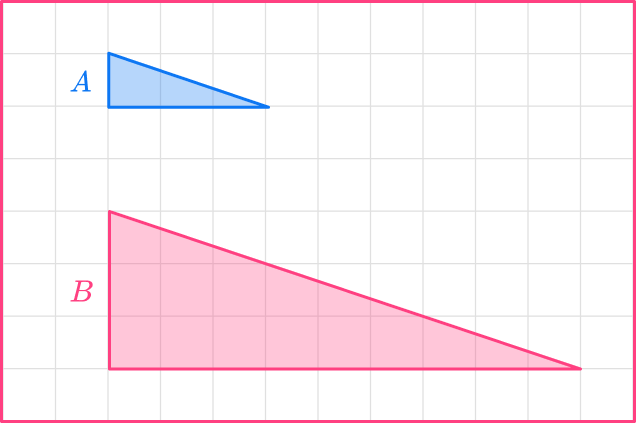
The base of shape A is 3 . The base of shape B is 9.
scale \ factor = \cfrac{scaled \ length}{ original \ length}=\cfrac{9}{3}=3 ✔
scale \ factor = \cfrac{scaled \ length}{ original \ length}=\cfrac{3}{9}=\cfrac{1}{3} ✖
^This is NOT the scale factor, but the inverse of the scale factor of the shapes above
Related transformations lessons
Practice how to find scale factor questions
1. Enlarge this shape by scale factor 2
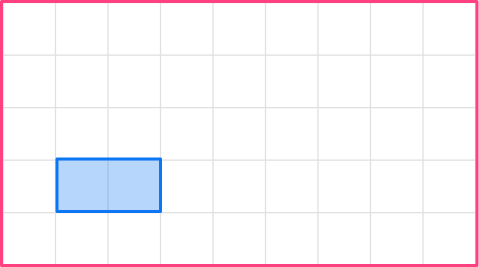
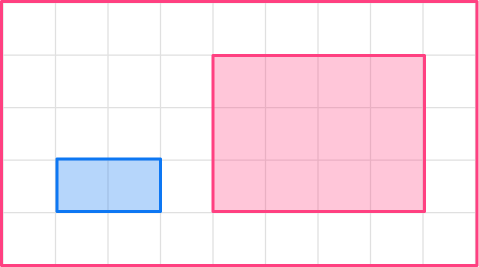

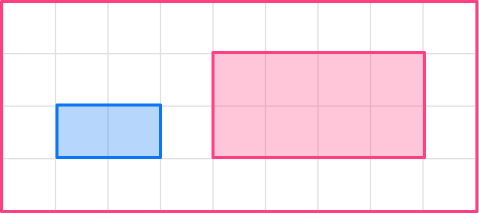

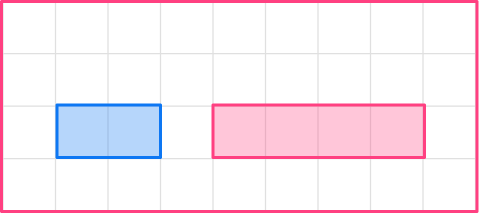

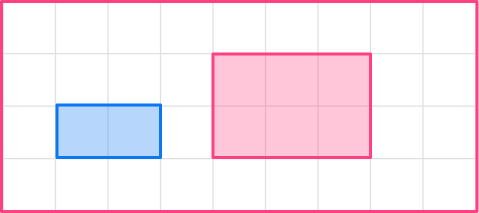

The original shape is a rectangle. The base of the original shape is 2, so the base of the enlarged shape will be 4.
2 \times 2=4
The height of the original shape is 1, so the height of the enlarged shape will be 2.
1 \times 2=2
The image will be a rectangle with base 4 and height 2.
2. Enlarge this shape by scale factor 4
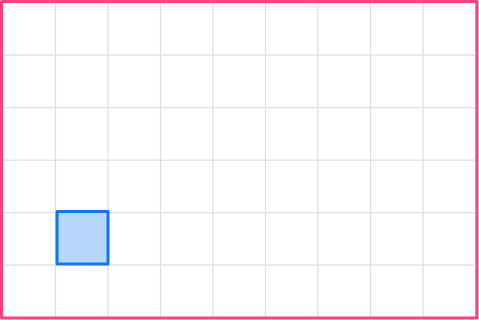
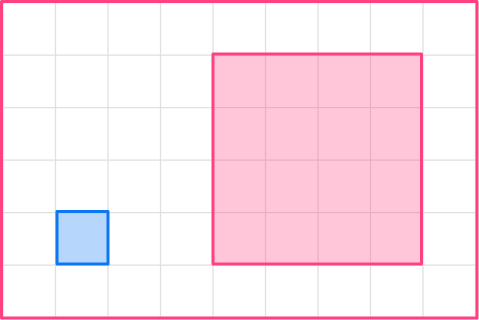




The original shape is a square, so will the enlarged shape. The side of the original square is 1, so the side of the enlarged square will be 4.
1 \times 4=4
The enlargement will be a square with side length 4.
3. Enlarge this shape by scale factor \cfrac{1}{2}
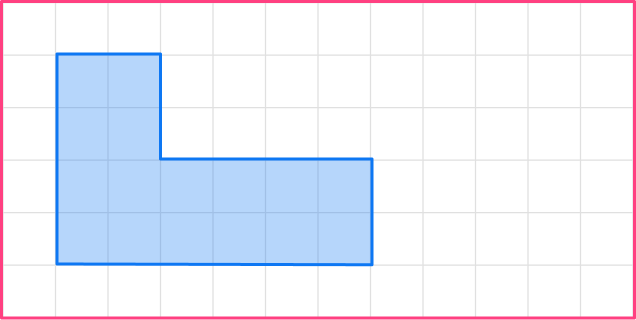
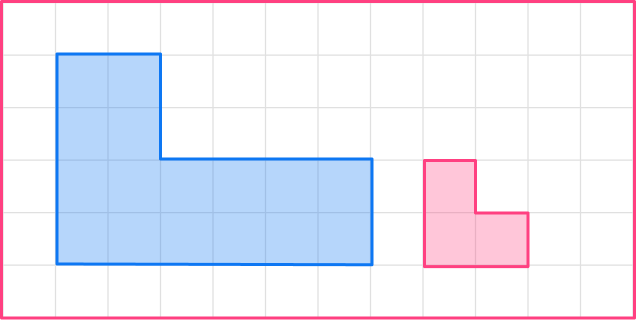

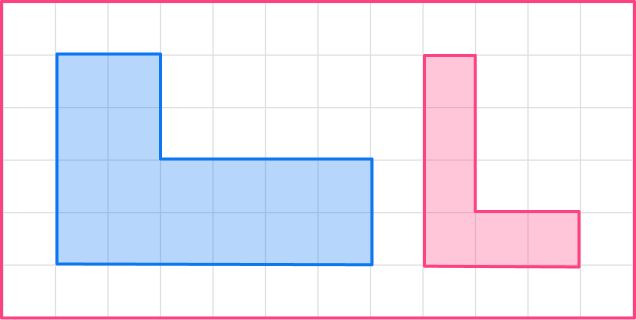

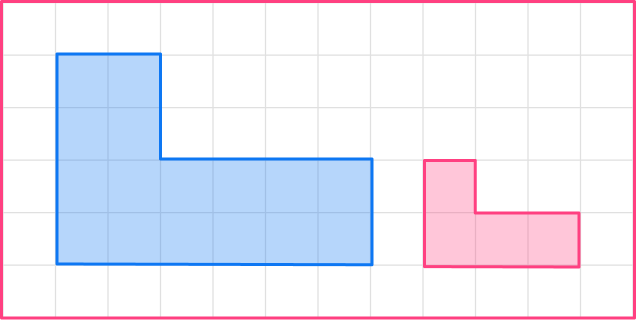

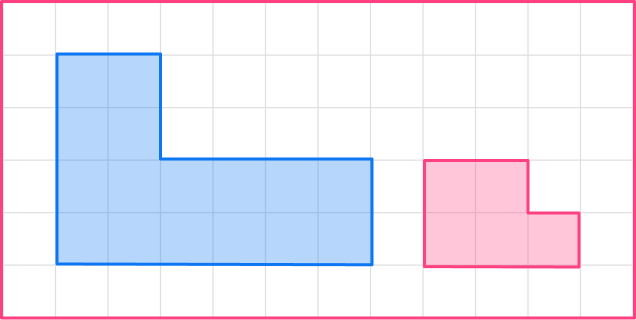

The original shape has a base of 6, so the base of the enlarged shape will be 3.
6 \times \cfrac{1}{2}=3
The other sides need to be halved too.
4. Calculate the scale factor from shape A to shape B.
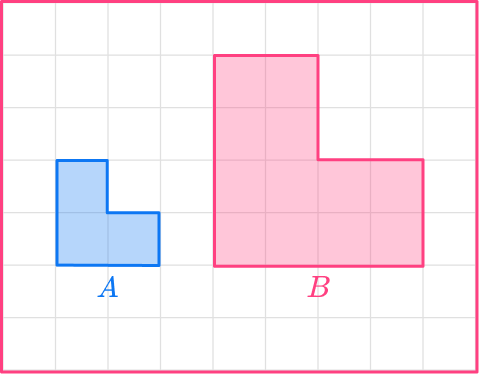
Scale factor \cfrac{1}{2}

Scale factor 4

Scale factor 2

Scale factor \cfrac{1}{4}

The original shape has a base of 2.
The base of the enlarged shape is 4.
scale \ factor = \cfrac{enlarged \ length}{ original \ length}=\cfrac{4}{2}=2
5. Calculate the scale factor from shape A to shape B.
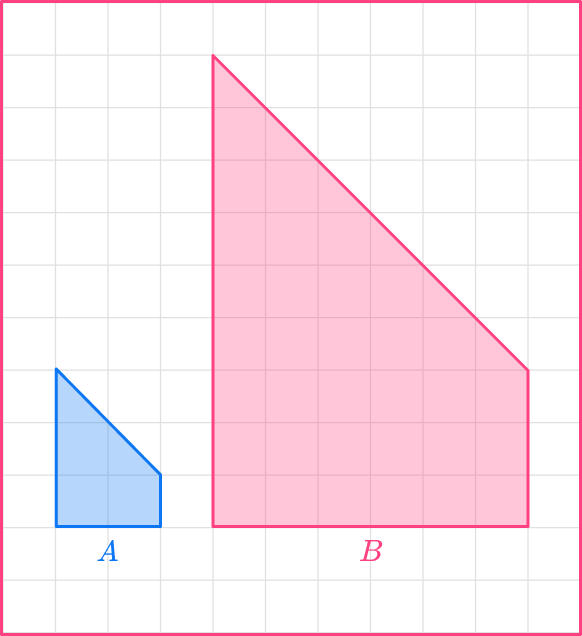
Scale factor 3

Scale factor \cfrac{1}{3}

Scale factor 2

Scale factor \cfrac{1}{2}

The original shape has a base of 6.
The base of the new shape is 2.
scale \ factor = \cfrac{enlarged \ length}{ original \ length}=\cfrac{6}{2}=3
6. Calculate the scale factor from shape A to shape B.
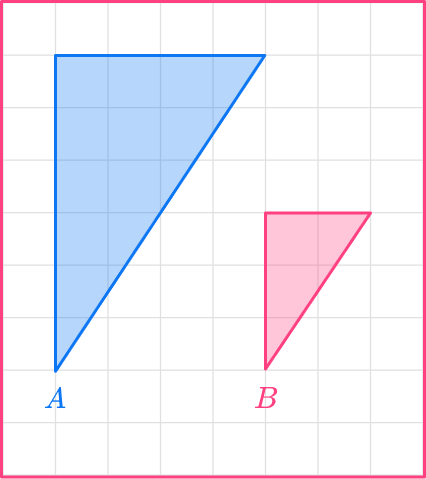
Scale factor \cfrac{1}{3}

Scale factor \cfrac{1}{2}

Scale factor 2

Scale factor 3

The two triangles need to be similar triangles.
The original shape has a vertical height of 6.
The vertical height of the new shape is 3.
scale \ factor = \cfrac{enlarged \ length}{ original \ length}=\cfrac{3}{6}=\cfrac{1}{2}
Scale factor FAQs
Scale factor is a number that is used to draw the enlarged or reduced shape of any given figure. It is a number by which the size of any geometrical figure or shape can be changed with respect to its original size. It helps in changing the size of the figure but not its shape.
Scale factor is a number by which the size of any geometrical figure or shape can be changed with respect to its original size. When things are too large, you use scale factors to calculate smaller, proportional measurements.
It is used to compare two similar geometric shapes and also in other fields like cooking, where the ingredients can be reduced or increased according to the given situation. Scale factor can also be used to find any missing dimensions in similar figures.
Scale is a ratio that is used to define the relation of the actual figure or object with its model. It is commonly used in maps to represent the actual figures in smaller units. For example, a scale of 1\text{:}3 means 1 on the map represents the size of 3 in the real world.
No, scale factor can also be used on 1D (flat) and 3D figures (solid). Students will also learn things like how to use area and volume scale factors.
The next lessons are
- Geometric proofs
- Area
- 3D shapes
- Area of a quadrilateral
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (3rd to 8th Grade)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these 3rd Grade to 8th Grade practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
Get your 6 multiple choice practice tests with detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math teachers for US math teachers!