[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Decimals Fractions Addition and subtraction Multiplication and division Exponents Order of operations (PEMDAS)Evaluate the expression
Here you will learn how to evaluate the expression given a value for the variable.
Students will first learn how to evaluate the expression as part of expressions and equations in 6th grade.
What does it mean to evaluate the expression?
To evaluate the expression means to substitute the variable(s) of a polynomial with given value(s).
For example,
If x=6, what is the value of 6x+1?
Substitute 6 for x and follow the order of operations:
\begin{aligned} & 6(6)+1 \\\\ & =36+1 \\\\ & =37 \end{aligned}
The same process can be used when there is more than one variable.
For example,
If c=2 and t=4, what is the value of 3 \, (c-1)+t^2?
Substitute 2 for c and 4 for t , and follow the order of operations:
\begin{aligned} & 3(2-1)+4^2 \\\\ & =3(1)+4^2 \\\\ & =3(1)+16 \\\\ & =3+16 \\\\ & =19 \end{aligned}
What does it mean to evaluate the expression?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to 6th grade math?
- Grade 6 – Expressions and Equations (6.EE.B.5)
Understand solving an equation or inequality as a process of answering a question: which values from a specified set, if any, make the equation or inequality true? Use substitution to determine whether a given number in a specified set makes an equation or inequality true.
How to evaluate the expression
In order to evaluate the expression:
- Substitute each variable with its given value.
- Evaluate using the order of operations.
![[FREE] Evaluate the Expression Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Evaluate-the-expression-worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Evaluate the Expression Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)
![[FREE] Evaluate the Expression Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Evaluate-the-expression-worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 6 – 8 students’ understanding of evaluating expressions. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Evaluate the Expression Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Evaluate-the-expression-worksheet-listing-image.png)
[FREE] Evaluate the Expression Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)
![[FREE] Evaluate the Expression Worksheet (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/Evaluate-the-expression-worksheet-listing-image.png)
Use this worksheet to check your grade 6 – 8 students’ understanding of evaluating expressions. 15 questions with answers to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEEvaluate the expression examples
Example 1: one step, one variable
Evaluate 4m when m=35.
- Substitute each variable with its given value.
Remember, numbers and letters written next to each other are being multiplied:
4 \times 35
2Evaluate using the order of operations.
There is only one step, multiply.
4 \times 35=140
Example 2: two steps, one variable
Evaluate 3 \, (h+22) when h=9.
Substitute each variable with its given value.
3 \, (9+22)
Evaluate using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 3(9+22) \\\\ & =3(31) \quad \quad \text{ *Remember, } 3 \, (31) \text{ is the same as } 3 \times 31 \\\\ & =93 \end{aligned}
Example 3: two steps, one variable, and a fraction
Evaluate 50-\cfrac{m}{2} when m=20.
Substitute each variable with its given value.
50-\cfrac{20}{2}
Evaluate using the order of operations.
Because the numerator is larger than the denominator, the fraction can be simplified with division: \, \cfrac{20}{2}=20 \div 2.
\begin{aligned}
& 50-\frac{20}{2} \\\\
& =50-10 \\\\
& =40
\end{aligned}
Example 4: two steps, two variables
Evaluate 11x-2y , when x=5 and y=6.
Substitute each variable with its given value.
11 \times 5-2 \times 6
Evaluate using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 11 \times 5-2 \times 6 \\\\ & =55-2 \times 6 \\\\ & =55-12 \\\\ & =43 \end{aligned}
Example 5: three steps, two variables, and a mixed number
Evaluate 5(3+p)-r , when p=11 and r=22 \, \cfrac{1}{3} \, .
Substitute each variable with its given value.
5(3+11)-22 \, \cfrac{1}{3}
Evaluate using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 5(3+11)-22 \cfrac{1}{3} \\\\ & =5(14)-22 \cfrac{1}{3} \quad \quad \text{ **Remember } 5(14) \text{ is the same as } 5 \times 14 \\\\ & =70-22 \cfrac{1}{3} \\\\ & =47 \cfrac{2}{3} \end{aligned}
Example 6: three steps, two variables, and an exponent
Evaluate a^3(n-7) , when a=3 and n=9.
Substitute each variable with its given value.
3^3(9-7)
Evaluate using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 3^3(9-7) \\\\ & =3^3(2) \quad \quad \text{ **Remember } 3^3 \text{ is the same as } 3 \times 3 \times 3 \\\\ & =27(2) \quad \quad \text{ **Remember } 27(2) \text{ is the same as } 27 \times 2\\\\ & =54 \end{aligned}
Teaching tips for evaluating the expression
- A great way to build the conceptual knowledge needed for evaluating algebraic expressions is with hands-on representations, like algebra tiles or other manipulatives. It is also a good idea to start with whole number coefficients and constants, as they are easier for students to make sense of and typically work better with manipulatives.
- While “finding the answer” is an important part of this skill, it should not be the only focus. At this stage in their development, students are still building foundational ideas about algebraic expressions, so it is important to draw attention to all parts of the process and help them make mathematical connections. Give students time to find and explore different numbers in the solution set, and encourage them to look for patterns between an expression and its solution set.
- Use expressions that come from real life scenarios when possible. This can help students think more deeply about how and why a solution set fits a given algebraic expression. For example, if the expression 8h is created to represent how many hotdogs there are based on h, the number of packets, students use the scenario to make connections between the expression and its solution set.
Easy mistakes to make
- Not following order of operations (pemdas)
The order of operations should always be used to evaluate the expression. For any given expression, this means solving within the parentheses, then the exponents, then multiplying or dividing from left to right, and finally adding or subtracting left to right. Not following this order will give the incorrect answer.
For example,
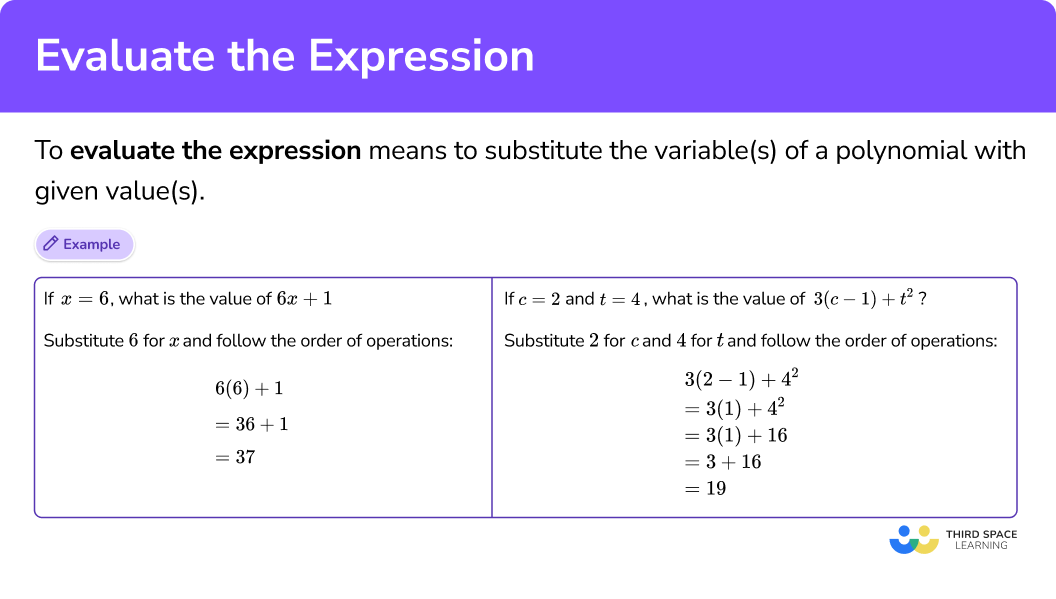
Evaluate x -3y when x=10 and y=2.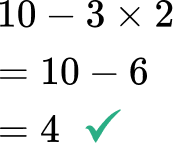
- Confusing the values of the variables when there is more than one
Always pay attention to which value is assigned to each variable. Mixing them up will result in a different answer.
For example,
Evaluate 5x+y when x=3 and y=4.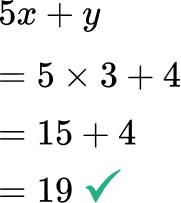
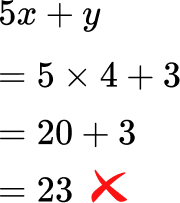
- Confusing the meaning of a number next to a parenthesis
Remember in an expression when there is a number next to parenthesis, the operation is multiplication.
For example,
If 4 \, (k+10), evaluate the expression when k=1.
\begin{aligned} & 4(1+10) \\ & =4(11) \\ & =44 \end{aligned}
Related algebraic expressions lessons
Practice evaluating the expression questions
1. Evaluate 8x-10 when x=3.




Substitute the variable with its given value.
8 \times 3-10
Evaluate using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 8 \times 3-10 \\\\ & =24-10 \\\\ & =14 \end{aligned}
2. Evaluate \, \cfrac{x}{5} \, when x=23.




Substitute the variable with its given value.
\cfrac{23}{5}
To simplify, \, \cfrac{23}{5} \, can be converted into a mixed number or written as decimal by working out 23 \div 5.
23 \div 5=4 \, \cfrac{3}{5}
3. Evaluate 9(12-f) when f=2 \, \cfrac{1}{2} \, .




Substitute the variable with its given value.
9\left(12-2 \, \cfrac{1}{2}\right)
Evaluate using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 9\left(12-2 \, \cfrac{1}{2}\right) \\\\ & =9\left(9 \, \cfrac{1}{2}\right) \quad \quad \text{ **Remember } 9\left(9 \, \cfrac{1}{2}\right) \text{ is the same as } 9 \times 9 \, \cfrac{1}{2}\\\\ & =85 \, \cfrac{1}{2} \end{aligned}
4. Evaluate 6 z+7 r when r=8 and z=1.3.




Substitute each variable with its given value.
6 \times 1.3+7 \times 8
Evaluate using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 6 \times 1.3+7 \times 8 \\\\ & =7.8+7 \times 8 \\\\ & =7.8+56 \\\\ & =63.8 \end{aligned}
5. Evaluate w-2(b+3) when w=44 and b=4.




Substitute each variable with its given value.
44-2(4+3)
Evaluate using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 44-2(4+3) \\\\ & =44-2(7) \quad \quad \text{ **Remember } 2(7) \text{ is the same as } 2 \times 7\\\\ & =44-14 \\\\ & =30 \end{aligned}
6. Evaluate 5 t^4+t when t=3 .




Substitute each variable with its given value.
5(3)^4+3
Evaluate using the order of operations.
\begin{aligned} & 5 \times 3^4+3 \quad \quad \text{ **Remember } 3^4=3 \times 3 \times 3 \times 3 \\\\ & =5 \times 81+3 \\\\ & =405+3 \\\\ & =408 \end{aligned}
Evaluate the expression FAQs
When evaluating for a specific value, you use only numbers, so the variables in an algebraic expression need to be substituted. Then you evaluate both types of expressions by following the order of operations.
You can evaluate them in the same way that you do expressions, by substituting a value for the variable(s).
The next lessons are
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!