[FREE] Fun Math Games & Activities Packs
Always on the lookout for fun math games and activities in the classroom? Try our ready-to-go printable packs for students to complete independently or with a partner!
In order to access this I need to be confident with:
Coordinate grid
Substitution Exponents Geometric sequencesExponential graph
Exponential function
Here you will learn about the exponential function, how to graph exponential functions, and how to find exponential equations.
Students will first learn about exponential functions as part of algebra and functions in high school.
What is an exponential function?
An exponential function is a mathematical function in the form y=ab^x, where x and y are variables, and a and b are constants, b>0.
For example,
The diagram shows the graphs of y=2^x, y=0.4^x, and y=0.5(3^x).
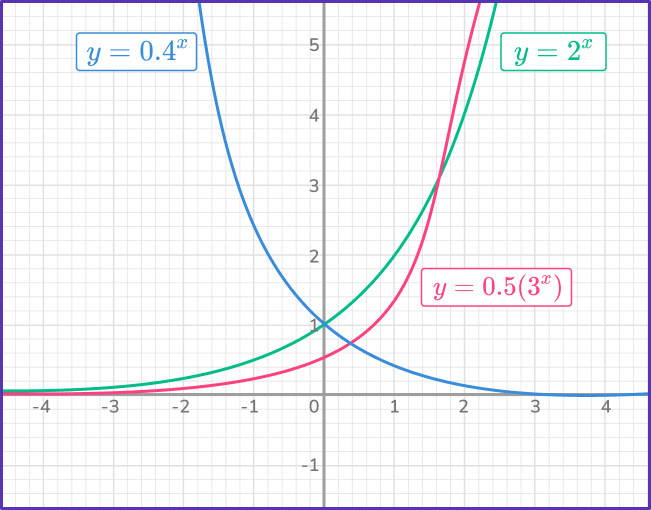
The graph of an exponential function has a horizontal asymptote. The functions graphed above all have a horizontal asymptote at y=0 (the x -axis) because a b^x can never equal zero. Though it may appear that the functions reach the y -axis, they are actually continually getting closer and closer, but will never intersect.
Exponential functions are a very important part of mathematics and can be applied to many real-life situations such as finance, population growth, radioactive decay, and the spread of viruses.
If something is said to have exponential growth or exponential decay, then it can be modeled using an exponential function.
An equation in the form y=ab^x is called an exponential equation because the independent variable x is the exponent in the equation.
An exponential function can also have a negative exponent y=ab^{-x}.
These can be rewritten with a positive exponent using the laws of exponents.
For example,
\begin{aligned} y&=4^{-x} \\\\ y&=(4^{-1})^x \\\\ y&=(\cfrac{1}{4})^x \end{aligned}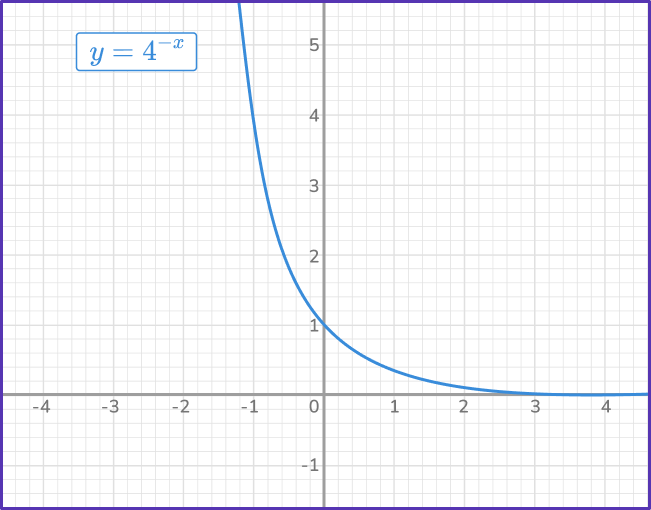
Notice the output values go down as the function moves from left to right. When 0<b<1, the exponential function will decrease. When b>1, the exponential function will increase.
In general, y=ab^{-x} is the same as y=a(\cfrac{1}{b})^x.
Note that \textbf{b} will always be a positive real number.
This page will only explore general exponential functions. However, there is a special exponential function that is worth mentioning. It involves a special number e.
e is a very important mathematical constant just like \pi. \; e=2.7182818 \ldots and is an irrational number whose decimals never repeat or terminate.
e is also known as Euler’s number after the Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler, but it was actually another Swiss mathematician called Jacob Bernoulli who discovered it while studying compound interest.
y=e^x is known as “natural exponential function”. e has some very special properties. The value of the derivative of y=e^x is e^x. This means the slope of the graph of y=e^x at any value x is the same as the value of e^x.
It can also be approximated using the formula (1+\cfrac{1}{n})^n. If you use increasing large values for n, the approximation will get closer and closer to e.
The inverse function of exponential functions are called logarithms. Logarithmic functions have different bases depending on the base of the original exponential function.
- The inverse of an exponential function y=2^x would be y=\log_2 x.
- The inverse of the exponential function y=e^x isn’t written as y=\log_e x but y=\ln x.
This is known as the natural logarithm instead of saying “log base e ”.
Logarithms are used to solve exponential equations.
What is an exponential function?
Common Core State Standards
How does this relate to high school math?
- Algebra – Creating Equations (HSA.CED.A.1)
Create equations and inequalities in one variable and use them to solve problems. Include equations arising from linear and quadratic functions, and simple rational and exponential functions.
- Functions – Interpreting Functions (HSF.IF.C.7e)
Graph exponential and logarithmic functions, showing intercepts and end behavior, and trigonometric functions, showing period, midline, and amplitude.
- Functions – Linear, Quadratic and Exponential Models (HSF.LE.A.2)
Construct linear and exponential functions, including arithmetic and geometric sequences, given a graph, a description of a relationship, or two input-output pairs (including reading these from a table).
![[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Algebra-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)
![[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Algebra-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 – grade 8 students’ understanding of algebra. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th to 8th grade algebra topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREE![[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Algebra-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)
![[FREE] Algebra Check for Understanding Quiz (Grade 6 to 8)](https://thirdspacelearning.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/07/Algebra-check-for-understanding-quiz-listing-image-.png)
Use this quiz to check your grade 6 – grade 8 students’ understanding of algebra. 10+ questions with answers covering a range of 6th to 8th grade algebra topics to identify areas of strength and support!
DOWNLOAD FREEHow to draw exponential graphs
In order to draw exponential graphs:
- Make a table of values for \textbf{x} and calculate the \textbf{y} values.
- Plot the points on a coordinate grid.
- Join the points with a smooth curve.
Drawing exponential graph examples
Example 1: drawing an exponential graph in the form y = bx, b > 1
Draw the graph of y=3^x on the axes provided.
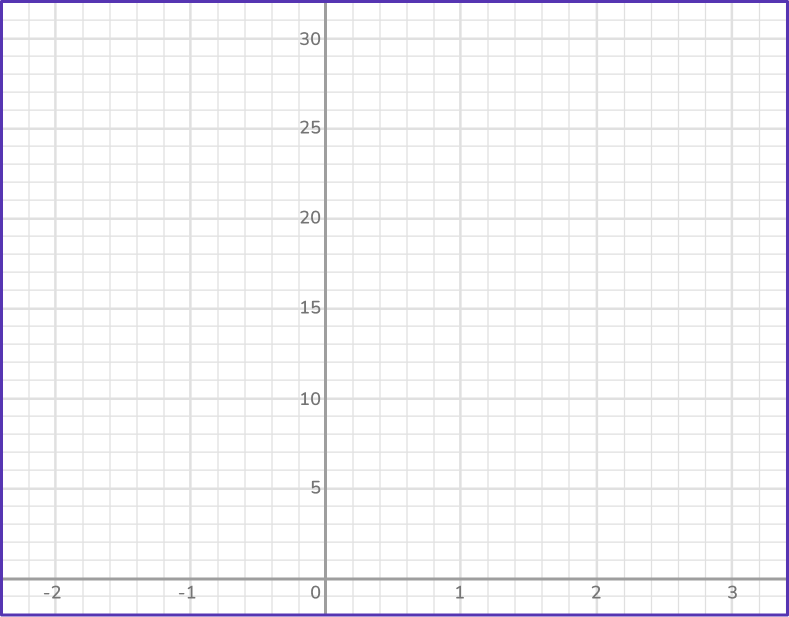
- Make a table of values for \textbf{x} and calculate the \textbf{y} values.
The given equation allows us to find the value of the function at any point.
Calculate the value of y for the x values from -2 to 3.
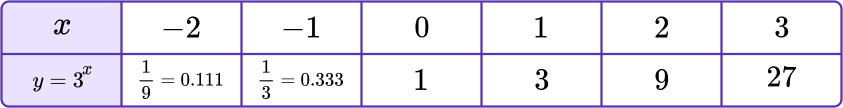
2Plot the points on a coordinate grid.
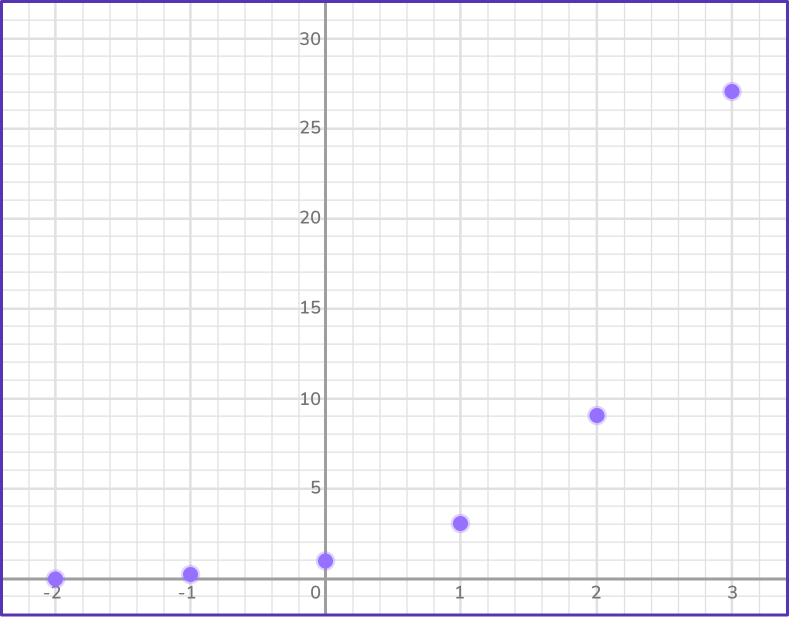
3Join the points with a smooth curve.
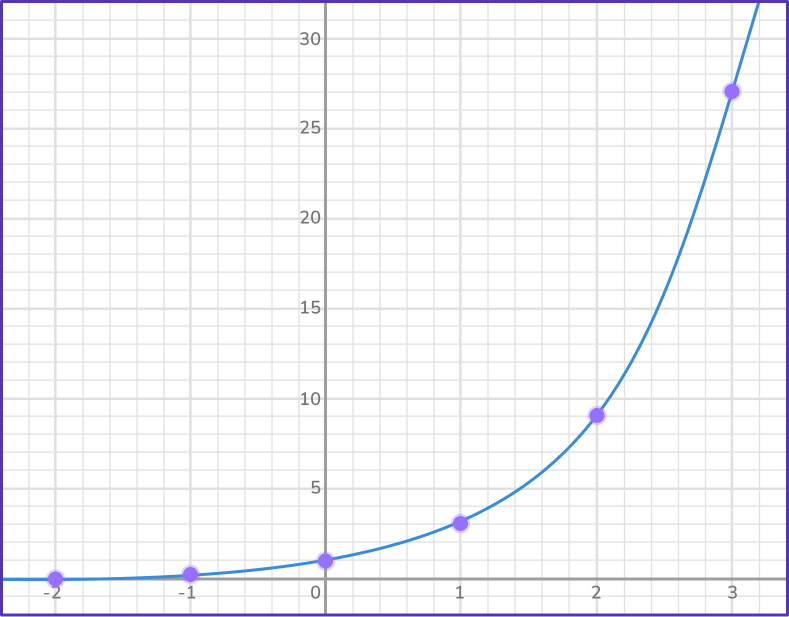
Example 2: drawing an exponential graph in the form y = bx, 0 < b < 1
Draw the graph of y=0.5^x on the axes provided.
Make a table of values for \textbf{x} and calculate the \textbf{y} values.
The given equation allows us to find the value of the function at any point.
Calculate the value of y for the x values from -3 to 2.

Plot the points on a coordinate grid.
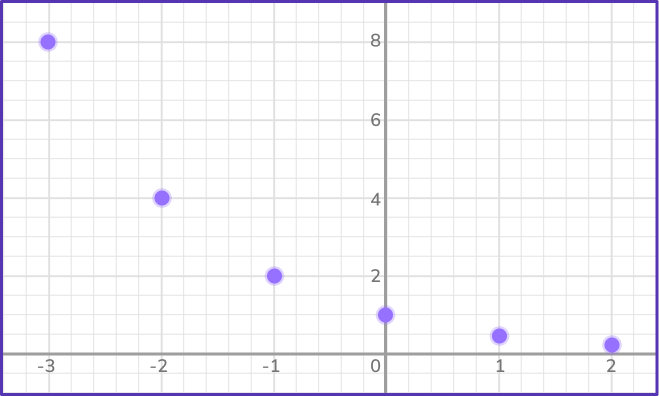
Join the points with a smooth curve.
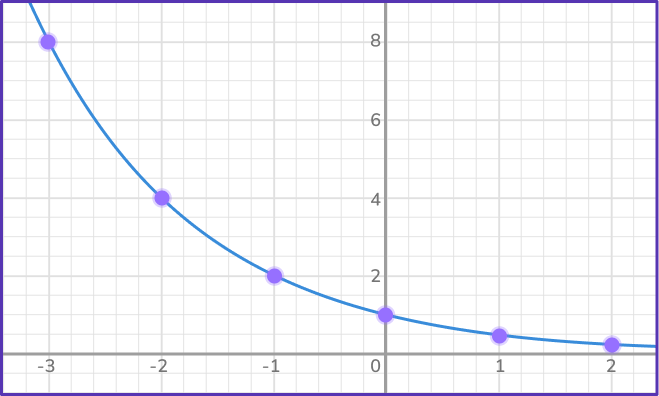
Example 3: drawing an exponential graph in the form y = abx
Draw the graph of y=0.2(4^x) on the axes provided.
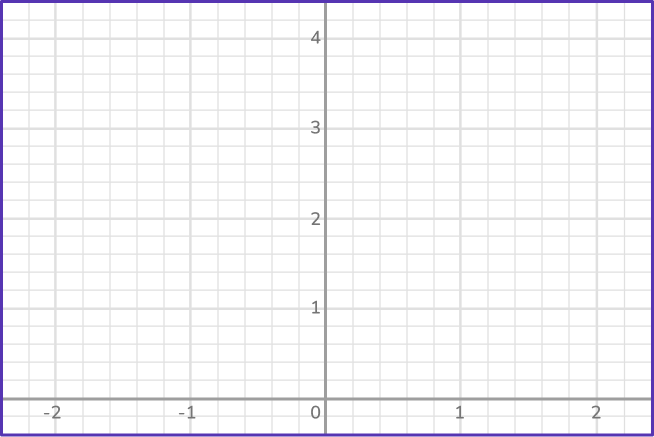
Make a table of values for \textbf{x} and calculate the \textbf{y} values.
The given equation allows us to find the value of the function at any point.
Calculate the value of y for the x values from -2 to 2.
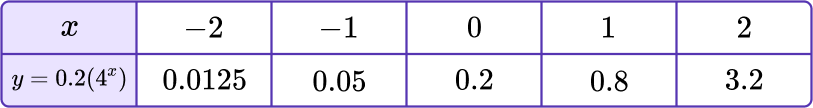
Plot the points on a coordinate grid.
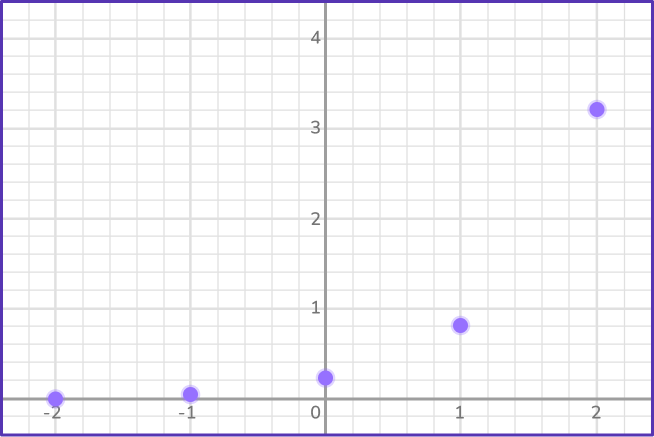
Join the points with a smooth curve.
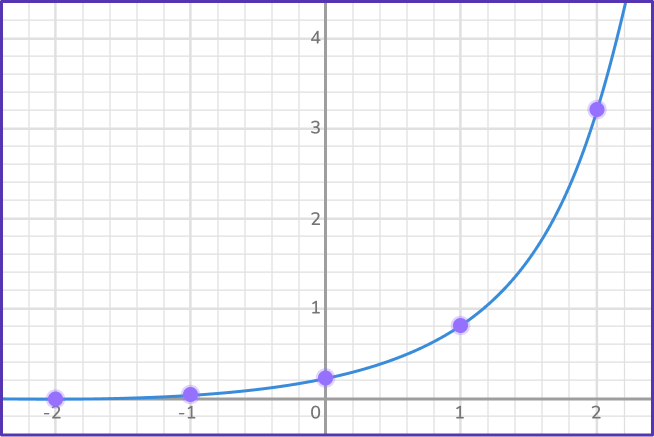
How to find the equation of exponential functions
In order to find the equation of exponential functions:
- Find two points that lie on the graph.
- Form two equations in the form \bf{\textbf{y}=\textbf{ab}^\textbf{x}}.
- Solve the equations simultaneously.
Example 4: finding exponential functions given the y -intercept
Find the equation of the exponential function in the form y=ab^x.
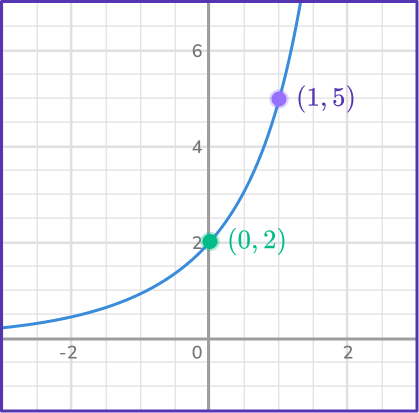
Find two points that lie on the graph.
You have the points (0, 2) and (1, 5).
Form two equations in the form \bf{\textbf{y}=\textbf{ab}^\textbf{x}} .
(0, 2) gives us 2=ab^0.
(1, 5) gives us 5=ab^1.
Solve the equations simultaneously.
You can simplify the two equations before solving.
b^0=1, therefore
2=ab^0 gives us a=2.
b^1=b, therefore
5=ab^1 gives us 5=ab.
You know a=2, therefore,
5=2b
b=2.5
The exponential equation is y=2(2.5^x).
Example 5: finding exponential functions by dividing the equations
Find the equation of the exponential function in the form y=ab^x.
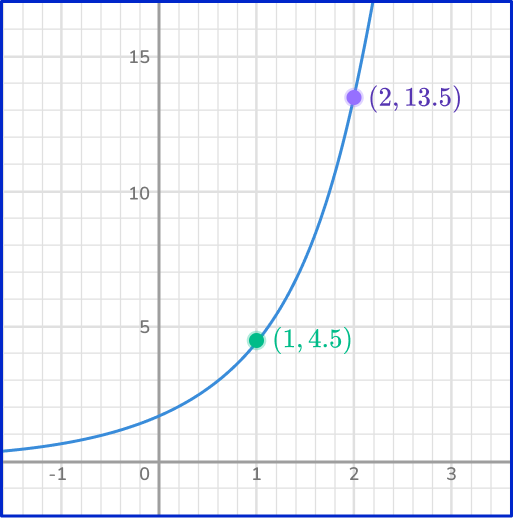
Find two points that lie on the graph.
You have the points (1, 4.5) and (2, 13.5).
Form two equations in the form \bf{\textbf{y}=\textbf{ab}^\textbf{x}} .
(1, 4.5) gives us 4.5=ab.
(2, 13.5) gives us 13.5=ab^2.
Solve the equations simultaneously.
You can solve the equations simultaneously by dividing one equation by the other.
\cfrac{13.5}{4.5}=\cfrac{ab^2}{ab}
This gives 3=b.
Substituting this into 4.5=ab gives
4.5=3a
a=1.5
The exponential equation is y=1.5(3^x).
Example 6: finding exponential functions by dividing the equations
Find the equation of the exponential function in the form y=ab^x.
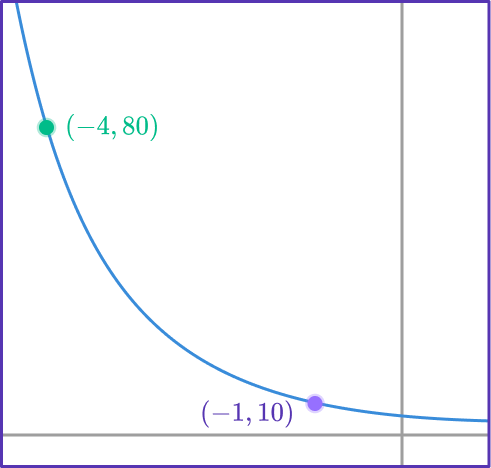
Find two points that lie on the graph.
You have the points (-4, 80) and (-1, 10).
Form two equations in the form \bf{\textbf{y}=\textbf{ab}^\textbf{x}}.
(-4, 80) gives us 80=ab^{-4}.
(-1, 10) gives us 10=ab^{-1}.
Solve the equations simultaneously.
You can solve the equations simultaneously by dividing one equation by the other.
\cfrac{10}{80}=\cfrac{ab^{-1}}{ab^{-4}}
This gives
\begin{aligned} & \cfrac{1}{8}=b^3 \\\\ & \cfrac{1}{2}=b \end{aligned}
Substituting this into 10=ab^{-1} gives
10=2a
a=5
The exponential equation is y=5(0.5^x).
Teaching tips for exponential function
- Introduce exponential functions through real world examples like compound interest or radioactive decay. This allows students to make sense of these functions and also see how they are relevant in the real world.
- Encourage students to have conversations about exponential functions as they are solving. This will also give them opportunities to practice reading the equations and functions using the correct mathematical vocabulary.
Easy mistakes to make
- Incorrectly applying the exponent to both variables
A common error is to confuse y=ab^x with y=(ab)^x. This is especially important when substituting values into a calculator or finding values to plot a graph. y=ab^x means y=a\times (b^x) and treating it like y=(ab)^x will result in a different function.
- Incorrectly applying laws of exponent
Confusion can also happen when substituting values for the exponent that are not positive integers.
For example,
Substituting \cfrac{1}{2} for x in the function y=2\left(9^x\right), is equal to y=2 \cdot \sqrt{9}=2(3)=6.
The \cfrac{1}{2} fraction as an exponent operates like a square root and the square root of 9 is 3.
- Confusing exponentials with polynomials
Some students can make the mistake of thinking 2^x is the same as x^2 and calculate 2^3 as 9.
Related functions in algebra lessons
- Function machines
- Function notation (basic)
- Compound functions
Practice exponential function questions
1. If g(x)=2^x, which graph shows function g?
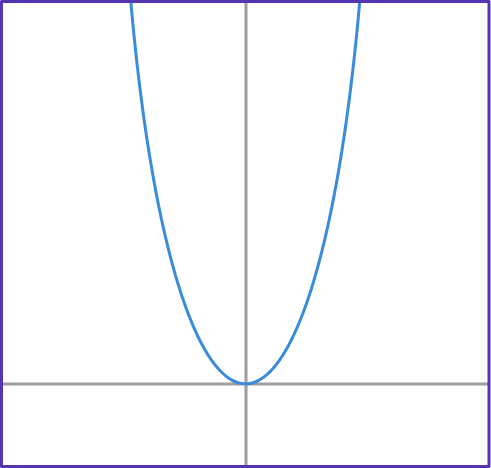

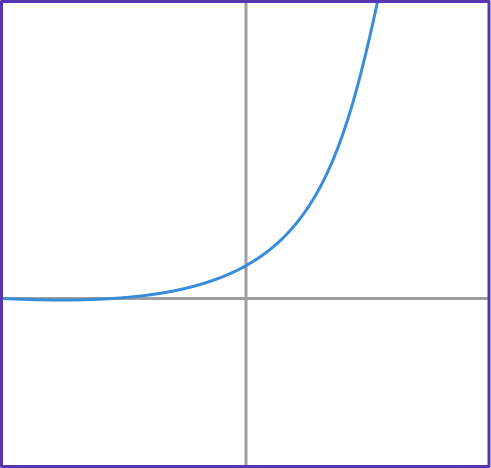


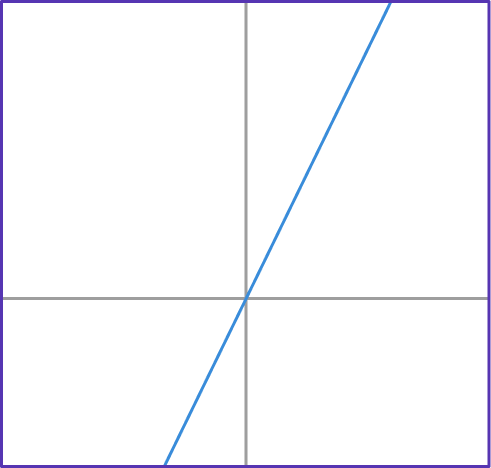

g(x)=2^x has the table of values shown below.

Notice that the g(x) values are increasing exponentially. This table of values matches the form of the graph…
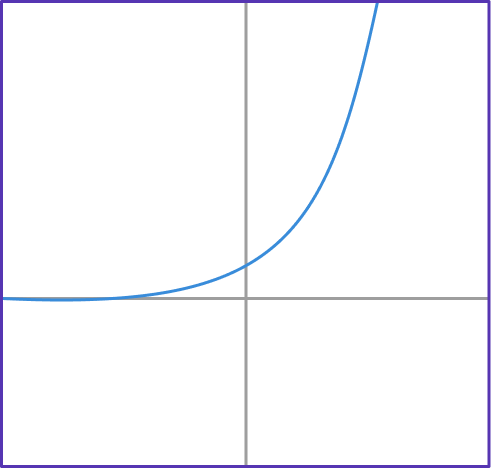
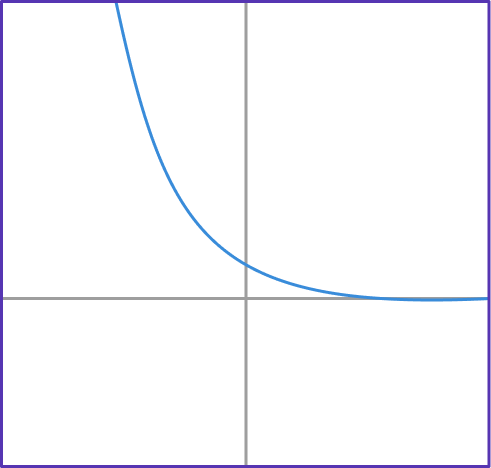
2. If f(x)=(\cfrac{1}{2})^x, which graph shows the exponential function f(x)?




y=(\cfrac{1}{2})^x has the table of values shown below.
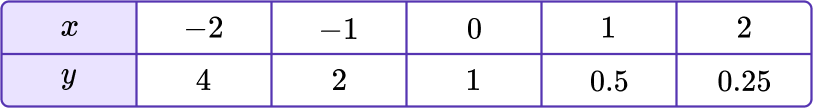
Notice that the y values are decreasing exponentially; getting closer to 0, but never reaching it. This table of values matches the form of graph D.
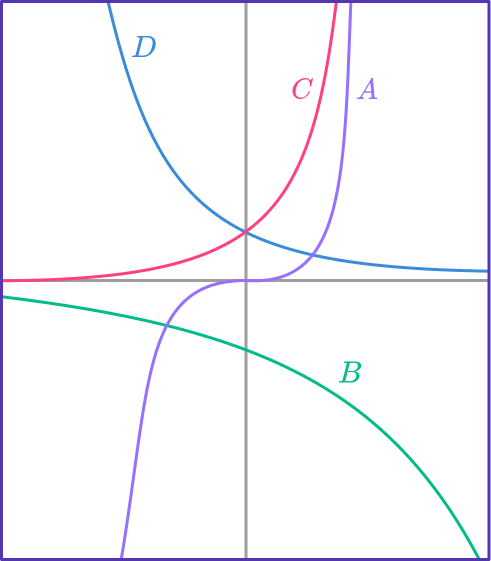
3. Which of the graphs is y=2\left(3^{-x}\right)?
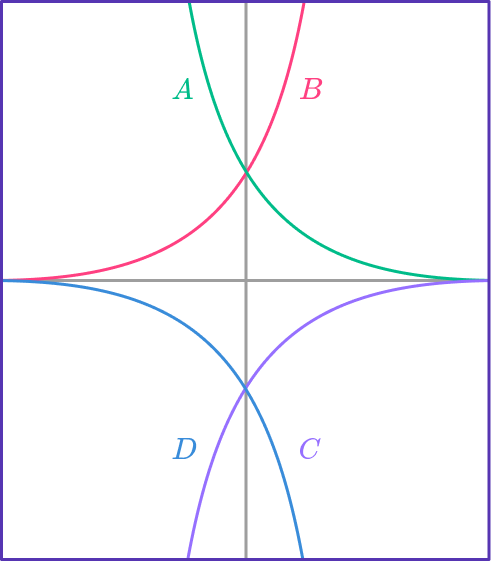




y=2\left(3^{-x}\right) has the table of values shown below.
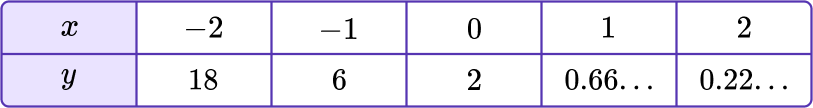
Notice that the y values are decreasing exponentially; getting closer to 0, but never reaching. This table of values matches the form of graph A.
4. An exponential function goes through the points (0, 1) and (2, 25). What is the function?




Using the points and y=ab^x, b>0.
(0, 1) gives 1=a.
(2, 25) gives 25=ab^2.
Substitute 1=a to solve 25=ab^2.
b^2=25
b=5, because b is always positive.
5. An exponential function goes through the points (0, 3) and (2, 48). What is the function?




Using the points and y=ab^x, b>0.
(0, 3) gives 3=a.
(2, 48) gives 48=ab^2.
Substitute 3=a to solve 48=ab^2.
48=3b^2
b^2=16
b=4, because b is always positive.
6. An exponential function goes through the points (1, 9) and (4, 30.375). What is the function?




Using the points and y=ab^x, b>0.
(1, 9) gives 9=ab.
(4, 30.375) gives 30.375=ab^4.
Dividing gives
\begin{aligned}\cfrac{30.375}{9}&= \cfrac{ab^4}{ab} \\\\ 3.375 &= b^3 \\\\ b&=1.5\end{aligned}
Substituting into 9=ab gives a=6.
Exponential function FAQs
The rate of change in a linear function is multiplied by the input each time, which causes the graph of the function to be a line. In an exponential function, the rate of change is multiplied by itself over and over again, causing the graph of the function to be a curve.
Differential equations include a function and its derivative. To go from a derivative to a function (the opposite way) use integration.
The next lessons are
- Laws of exponents
- Standard form
- Factoring
- Trigonometric functions
Still stuck?
At Third Space Learning, we specialize in helping teachers and school leaders to provide personalized math support for more of their students through high-quality, online one-on-one math tutoring delivered by subject experts.
Each week, our tutors support thousands of students who are at risk of not meeting their grade-level expectations, and help accelerate their progress and boost their confidence.

Find out how we can help your students achieve success with our math tutoring programs.
[FREE] Common Core Practice Tests (Grades 3 to 6)
Prepare for math tests in your state with these Grade 3 to Grade 6 practice assessments for Common Core and state equivalents.
40 multiple choice questions and detailed answers to support test prep, created by US math experts covering a range of topics!